Tableau Operators- Arithmetic, Relational & Logical Operators
FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
1. Objective
In this Tableau tutorial, we are going study about Tableau Operators, types of Operators in tableau: Arithmetic Operators, Relational Operators, Logical Operators with examples.
Let us start with Operators in Tableau.
2. What are Tableau Operators
An image which is utilized to impart the compiler to play out certain scientific or consistent controls is an Operator. Various administrators are offered by Tableau to make recipes and computed fields.
Learn about Tableau Design Flow & Tableau Data Types in detail.
3. Types of Tableau Operators
There are 3 basic operators in tableau:
- Arithmetic Tableau Operators
- Relational Tableau Operators
- Logical Tableau Operators
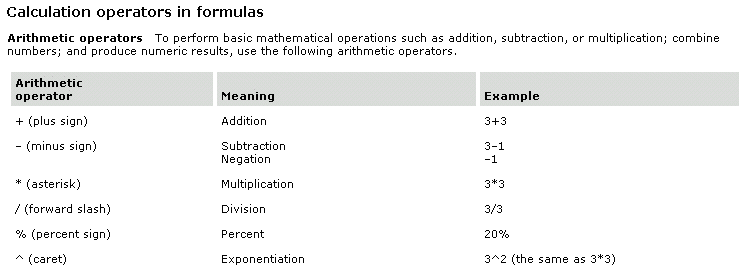
a. Arithmetic Operators
The Arithmetic administrators can be utilized to make articulations on numbers and date information compose segments.
- Addition – +
- Subtraction – –
- Multiply – *
- Divide – /
- Modulation – %
- Power – ^
Note: The Arithmetic Tableau Operators can be used in any clause of a SQL statement, except the from clause.
Let’s read about Tableau Show me How- I & Tableau Show me How- II in detail.
b. Relational Operators
A comparison operator is a binary operator that takes two operands whose values are being compared. Comparison operators are used in conditional statements, especially in loops, where the result of the comparison decides whether execution should proceed. They form the key to program flow control, known as conditional processing.
- Equality Operator – =
- Not Equality Operator – < >, !=, ^=
- Greater Than Operator – >
- Less Than Operator – <
- Greater Than Equal to Operator – >=
- Less Than Equal to Operator – <=
Example:
- Select Ename, Sal, Job From Emp Where Job = ’SALES MANAGER’;
- Select Ename, Hiredate, Deptno, Sal From Emp where Deptno < > 10;
- Select Empno, Ename, Sal From Emp where Sal >= 3000;
- Select Ename name, Sal basic, Sal * 12 Annual From Emp where sal * 12 > 60000;
Let’s revise Tableau Data Source & Tableau Data Extract in detail.
c. Logical Operators
Logical operators contain only three commands.
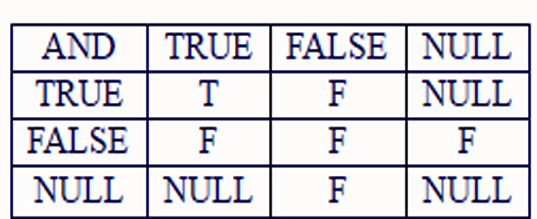
a. Logical conjunction operator “AND”
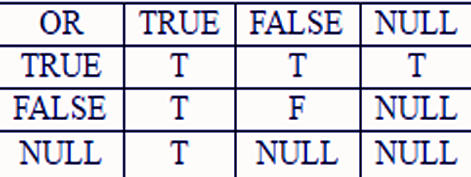
b. Logical disjunction operator “ OR”
c. Logical negation operator “NOT”
i. Conditions satisfy “AND” Operators
- It Returns TRUE if both or all component conditions are TRUE.
- It Returns FALSE if either is FALSE, else returns unknown.
ii. Conditions satisfy “OR” Operators
- It Returns TRUE if either of the component conditions is TRUE.
- It Returns FALSE if both are FALSE, else returns unknown.
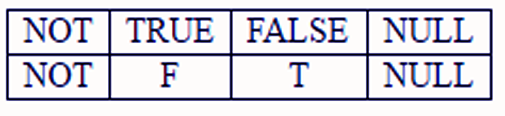
iii. Conditions satisfy “NOT” Operators
- It Returns TRUE if the following condition is FALSE.
- It Returns FALSE if the following condition is TRUE.
- If the condition is unknown, it returns unknown.
Related Topics – Tableau Field Operations & Tableau Data Blending
4. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned about different types of Tableau operators, its classification: Arithmetic Operators, Relational Operators, Logical Operators with examples. This will help us work with Tableau better and do our work more efficiently. If you have any query, feel free to ask in a comment section.
See This- Adding Worksheets And Renaming Worksheet In Tableau
For reference
Did you like our efforts? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google