Python XML Parser – XML Processing with Python 3
Python course with 57 real-time projects - Learn Python
In this Python XML Parser Tutorial, we will study what is Python XML Processing.
Moreover, we will study the Python XML Parser Architecture and API and Python XML FIle. Along with this, we will learn Python Parsing XML with DOM and SAX.
So, let’s start Python XML Parser Tutorial.
What is XML?
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language which encodes documents by defining a set of rules in both machine-readable and human-readable format.
Extended from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), it lets us describe the structure of the document. In XML, we can define custom tags.
We can also use XML as a standard format to exchange information.
Python XML Parser Architecture and API
Like we mentioned earlier, we will make use of two APIs to deal with Python XML Parser here- SAX and DOM.
1. SAX (Simple API for XML)
When we have large documents or memory limitations, we can register callbacks for certain events.
Then, we can let the parser to parse the file as reading it from the disk. Because of this, it never stores the entire file in the memory. It is read-only.
2. DOM (Document Object Model API)
A W3C recommendation, DOM can represent all features of an XML document by reading an entire file into memory and storing it hierarchically.
This is the faster choice when working with large files. For a large project, you can use both, as they complement each other. But using this on too many small files can suck your resources up.
Python XML File
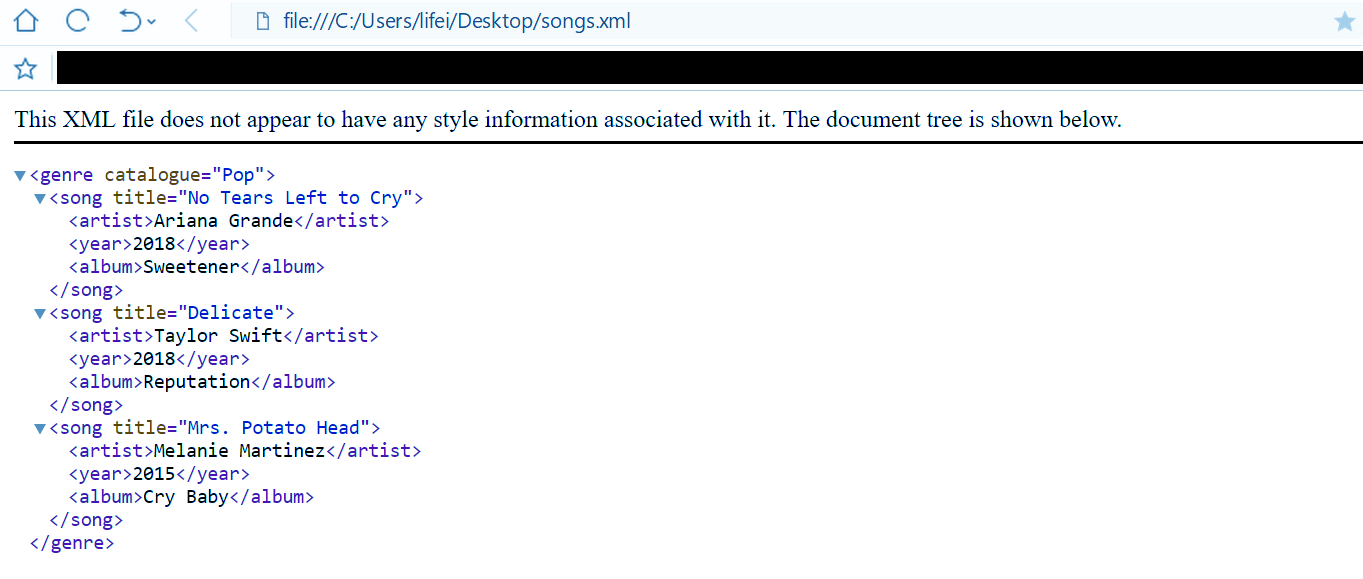
This is the Python XML file we’re going to use:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <genre catalogue="Pop"> <song title="No Tears Left to Cry"> <artist>Ariana Grande</artist> <year>2018</year> <album>Sweetener</album> </song> <song title="Delicate"> <artist>Taylor Swift</artist> <year>2018</year> <album>Reputation</album> </song> <song title="Mrs. Potato Head"> <artist>Melanie Martinez</artist> <year>2015</year> <album>Cry Baby</album> </song> </genre>
We have saved it as songs.xml on our Desktop
This stores a collection of songs in the genre Pop. The ones we have currently include the songs No Tears left To Cry, Delicate, and Mrs. Potato Head.
Python XML Parser with DOM
DOM stands for Document Object Model and is a cross-language API from the W3C that lets us access and modify XML documents.
We can use it for random-access applications. While with SAX, you can only ever access one SAX element at once.
Let’s use the xml.dom module to load an XML document and create a minidom object.
Then, using the parser() method, we can create a DOM tree from this document.
>>> from xml.dom.minidom import parse
>>> import xml.dom.minidom
>>> import os
>>> os.chdir('C:\\Users\\lifei\\Desktop')
>>> DOMTree = xml.dom.minidom.parse("songs.xml") #Opening the XML document
>>> genre=DOMTree.documentElement
>>> if genre.hasAttribute('catalogue'):
print(f'Root: {genre.getAttribute("catalogue")}')
Root: Pop
>>> songs=genre.getElementsByTagName('song') #Get all songs in the genre Pop
>>> for song in songs: #Print each song’s details
print('Song:')
if song.hasAttribute('title'):
print(f'Title: {song.getAttribute("title")}')
artist=song.getElementsByTagName('artist')[0]
print(f'Artist: {artist.firstChild.data}')
year=song.getElementsByTagName('year')[0]
print(f'Release Year: {year.firstChild.data}')
album=song.getElementsByTagName('album')[0]
print(f'Album: {album.firstChild.data}')Output
Title: No Tears Left to Cry
Artist: Ariana Grande
Release Year: 2018
Album: Sweetener
Song:
Title: Delicate
Artist: Taylor Swift
Release Year: 2018
Album: Reputation
Song:
Title: Mrs. Potato Head
Artist: Melanie Martinez
Release Year: 2015
Album: Cry Baby
Python XML Parser with SAX
SAX is a standard interface and will help you with event-driven XML parsing. You’ll need to subclass xml.sax.ContentHandler to create a ContentHandler for this purpose.
This will handle your tags and attributes and will also serve methods for handling parsing events. The Python XML parser that owns it calls these methods parsing the XML file.
Let’s look at some of these methods. When it begins parsing the file, it calls startDocument(), and calls endDocument() when ending the parsing at the end of the file.
Also, it passes the XML file’s character data as a parameter to the characters(text) method.
At the start and end of each element, it calls the ContentHandler. If the Python XML parser is in namespace mode, it calls methods startElementNS() and endElementNS().
Otherwise, it calls startElement(tag, attributes) and endElement(tag), where a tag is the element tag and attributes is an Attributes object.
Now, in Python XML Processing, let’s take a look at few methods first.
1. make_parser()
This method creates and returns a parser of the first type the system can find. This is the syntax:
xml.sax.make_parser([parser_list])
It takes a list of parsers to be used.
2. parse()
This uses the following syntax:
xml.sax.parse(xmlfile,contenthandler[,errorhandler])
This creates a SAX parser and then uses it in parsing the document specified by the parameter xmlfile. contenthandler is a ContentHandler object and errorhandler is a SAX ErrorHandler object.
3. parseString()
This method creates a SAX parser and parses an XML string. It has the following syntax:
xml.sax.parseString(xmlstring,contenthandler[,errorhandler])
The parameter xmlstring is the XML string to read from and the other two parameters are the same as above.
Example
Now, let’s take an example program to parse an XML document using SAX.
>>> import xml.sax
>>> class SongHandler(xml.sax.ContentHandler):
def __init__(self):
self.CurrentData=''
self.artist=''
self.year=''
self.album=''
def startElement(self,tag,attributes):
self.CurrentData=tag
if tag=='song':
print('Song:')
title=attributes['title']
print(f'Title: {title}')
def endElement(self,tag):
if self.CurrentData=='artist':
print(f'Artist: {self.artist}')
elif self.CurrentData=='year':
print(f'Year: {self.year}')
elif self.CurrentData=='album':
print(f'Album: {self.album}')
self.CurrentData=''
def Characters(self,content):
if self.CurrentData=='artist':
self.artist=content
elif self.CurrentData=='year':
self.year=content
elif self.CurrentData=='album':
self.album=content
>>> if __name__=='__main__':
parser=xml.sax.make_parser() #creating an XMLReader
parser.setFeature(xml.sax.handler.feature_namespaces,0) #turning off namespaces
Handler=SongHandler()
parser.setContentHandler(Handler) #overriding default ContextHandler
parser.parse('songs.xml')Output
Title: No Tears Left to Cry
Artist: Ariana Grande
Year: 2018
Album: Sweetener
Song:
Title: Delicate
Artist: Taylor Swift
Year: 2018
Album: Reputation
Song:
Title: Mrs. Potato Head
Artist: Melanie Martinez
Year: 2015
Album: Cry Baby
So, this was all about Python XML Parser tutorial. Hope you like our explanation.
Python Interview Questions on XML Processing
- How do you process XML in Python?
- How to open a XML file in Python?
- How to pass XML parameter in Python?
- How do you add sub elements in XML in Python?
- Which module can you use to parse an XML file using Python?
Conclusion
Hence, we have a complete understanding of XML processing in Python 3. In addition, we studied Python XML parser architecture and Python XML file.
In addition, we studied 2 API for Python XML Parser that is SAX and DOM. Also,. At last, we discussed methods of SAS XML Parser.
Furthermore, if you have any query, feel free to ask in the comment section.
Did you like this article? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google



That’s really informative post. I appreciate your skills. Thanks for sharing.
Thanks for the post. There is a typo in the code. “def Characters(self, content)” should have the function name lowercase: “def characters(self, content)”. Otherwise, the Characters function is never called.
DataFlair I am really disappointed for sending many emails without you even answering to a single one of them.