What is Python GUI Programming – Python Tkinter Tutorial
Python course with 57 real-time projects - Learn Python
1. Python GUI Programming
In this Python tutorial, we will discuss different interfaces that we can use to develop a Python GUI (graphical user interface). Also, we will see many options for Python GUI Programming, of these, we will focus on Python Tkinter. Moreover, in this Python Tkinter tutorial for Python 3, we will discuss Tkinter with its 19 kinds of widgets. Along with this, we are going to learn the Tkinter download process.
So, let’s begin Python GUI Tkinter.
2. Alternatives For Python GUI Programming
Following are options for Python GUI Programming. We may use one of the following alternatives for programming a Python GUI:
Python Lambda Expressions with Syntax and Examples
a. Tkinter
Python ships with the Tk GUI toolkit. Tkinter is an interface to this.
b. PyQt
A Python binding of the cross-platform GUI toolkit Qt, PyQt is implemented as a plug-in for Python.
c. wxPython
wxWidgets is a cross-platform GUI API for Python; wxPython is a wrapper for this.
3. What is the Python Tkinter?
Tkinter in Python GUI Programming is standard Python GUI library. It gives us an object-oriented interface to the Tk GUI toolkit.
So, let’s start Python graphics, let’s create a simple GUI application:
- Import the module Tkinter.
- Create the main window for the application.
- Add a widget or more.
- Enter the main event loop to deal with an event when it is triggered.
7 Reasons Why Should You Learn Python in 2018
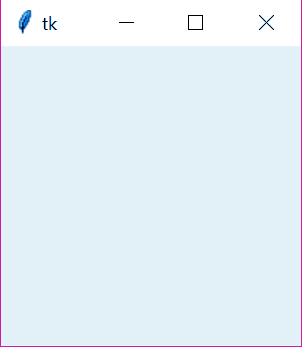
>>> import tkinter >>> top=tkinter.Tk() >>> top.mainloop()
Now, this creates the following window:
4. Python Tkinter Widgets
Tkinter in Python GUI Programming provides 19 kinds of widgets (controls)- buttons, labels, and more. Let’s discuss these Python Tkinter widgets in detail.
a. Button
You can add a button to your application.
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> top=Tk()
>>> top.geometry('600x200'
''
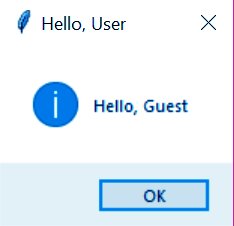
>>> def helloCallBack():
msg=messagebox.showinfo("Hello, User","Hello, Guest")
>>> B=Button(top,text="Initiate",command=helloCallBack)
>>> B.place(x=300,y=100)Now, Clicking on the Initiate button gives us this:
b. Canvas
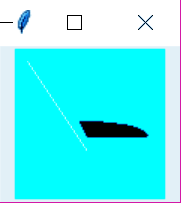
A Canvas in Tkinter Python GUI Programming will let you draw shapes- lines, polygons, ovals, and more.
Explore Python Functions with Syntax and Examples
>>> from tkinter import * >>> from tkinter import messagebox >>> top=Tk() >>> C=Canvas(top,bg="cyan",height=100,width=100) >>> coord=10,50,90,70 >>> arc=C.create_arc(coord,start=0,extent=97,fill='black') >>> line=C.create_line(10,10,50,70,fill='white') >>> C.pack()
c. Checkbutton
A Checkbutton is an option that a user can choose to select or leave. They can select as many checkboxes at once as they want to.
Explore 13 Unique Features of Python Programming Language
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> CheckVar1=IntVar() >>> CheckVar2=IntVar() >>> C1=Checkbutton >>> C1=Checkbutton(top,text="Pizza",variable=CheckVar1,onvalue=1,offvalue=0,height=5,width=20) >>> C2=Checkbutton(top,text="Fries",variable=CheckVar2,onvalue=1,offvalue=0,height=5,width=20) >>> C1.pack() >>> C2.pack()
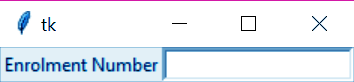
d. Entry
Next, this lets us add a single-line input tray for taking input from the user.
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> L1=Label(top,text="Enrolment Number") >>> L1.pack(side=LEFT) >>> E1=Entry(top,bd=3) >>> E1.pack(side=RIGHT)
e. Frame
Generally, a frame is a container widget to help hold other widgets.
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> frame=Frame(top) >>> frame.pack() >>> frametwo=Frame(top) >>> frametwo.pack(side=BOTTOM) >>> redbutton=Button(frame,text="One",fg="red") >>> redbutton.pack(side=LEFT) >>> bluebutton=Button(frame,text="Two",fg="blue") >>> bluebutton.pack(side=LEFT) >>> greenbutton=Button(frametwo,text="Three",fg="green") >>> greenbutton.pack(side=BOTTOM)
f. Label
Basically, this lets us add a single-line caption for other widgets. We saw this in section 4d.
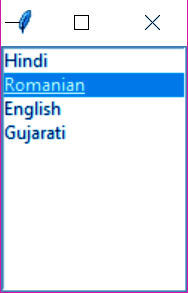
g. Listbox
This widget lets us add a list of options for the user to choose from.
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> LB1=Listbox(top) >>> LB1.insert(1,"Hindi") >>> LB1.insert(2,"Romanian") >>> LB1.insert(3,"English") >>> LB1.insert(4,"Gujarati") >>> LB1.pack()
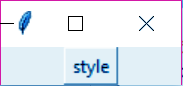
h. Menu button
This lets us add a menu button anywhere in our application.
Python Number Types and Their Conversion Functions
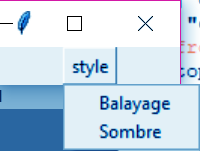
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> mb=Menubutton(top,text="style",relief=RAISED) >>> mb.grid() >>> mb.menu=Menu(mb,tearoff=0) >>> mb["menu"]=mb.menu >>> balayageVar=IntVar() >>> sombreVar=IntVar() >>> mb.menu.add_checkbutton(label='Balayage',variable=balayageVar) >>> mb.menu.add_checkbutton(label='Sombre',variable=sombreVar) >>> mb.pack()
Clicking on this button does this:
i. Menu
This lets us put all kinds of menus in our application.
>>> from tkinter import * >>> def donothing(): filewin=Toplevel(top) button=Button(filewin,text="This does nothing") button.pack() >>> top=Tk() >>> menubar=Menu(top) >>> filemenu=Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) >>> filemenu.add_command(label="New",command=donothing) >>> filemenu.add_command(label="Open",command=donothing) >>> filemenu.add_command(label="Save",command=donothing) >>> filemenu.add_command(label="Close",command=donothing) >>> filemenu.add_separator() >>> filemenu.add_command(label="Exit",command=top.quit) >>> menubar.add_cascade(label="File",menu=filemenu) >>> editmenu=Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) >>> editmenu.add_command(label="Undo",command=donothing) >>> editmenu.add_separator() >>> editmenu.add_command(label="Cut",command=donothing) >>> editmenu.add_command(label="Copy",command=donothing) >>> editmenu.add_command(label="Paste",command=donothing >>> editmenu.add_command(label="Delete",command=donothing) >>> menubar.add_cascade(label="Edit",menu=editmenu) >>> top.config(menu=menubar) >>> top.mainloop()
Read Loops in Python with Syntax and Examples
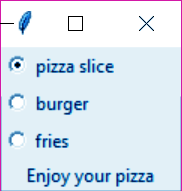
k. Radiobutton
When a user has a few choices of radio buttons, they may only choose one at once.
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> def sel():
selection=f"Enjoy your {var.get()}"
label.config(text=selection)
>>> top=Tk()
>>> var=StringVar()
>>> R1=Radiobutton(top,text="pizza slice",variable=var,value='pizza',command=sel
>>> R1.pack(anchor=W)
>>> R2=Radiobutton(top,text="burger",variable=var,value='burger',command=sel)
>>> R2.pack(anchor=W)
>>> R3=Radiobutton(top,text="fries",variable=var,value='fries',command=sel)
>>> R3.pack(anchor=W)
>>> label=Label(top)
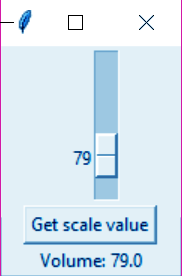
>>> label.pack()l. Scale
Scale widget provides a slider.
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> def sel():
selection=f"Volume: {str(var.get())}"
label.config(text=selection)
>>> top=Tk()
>>> var=DoubleVar()
>>> scale=Scale(top,variable=var)
>>> scale.pack(anchor=CENTER)
>>> button=Button(top,text="Get scale value",command=sel)
>>> button.pack(anchor=CENTER)
>>> label=Label(top)
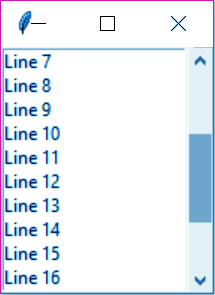
>>> label.pack()m. Scrollbar
This adds scrolling capability to other widgets like lists.
Have a Look At Python Decision Making Statements with Syntax
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> top=Tk()
>>> scrollbar=Scrollbar(top)
>>> scrollbar.pack(side=RIGHT,fill=X)
>>> scrollbar.pack(side=RIGHT,fill=Y)
>>> list=Listbox(top,yscrollcommand=scrollbar.set)
>>> for line in range(22):
list.insert(END,f"Line {str(line)}")
>>> list.pack(side=LEFT,fill=BOTH)
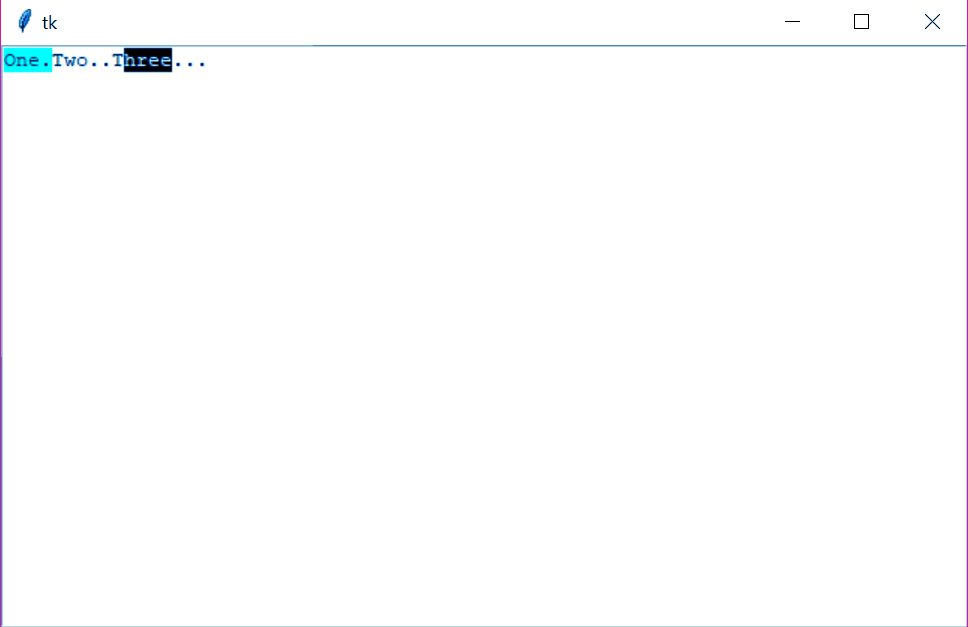
>>> scrollbar.config(command=list.yview)n. Text
This displays text in multiple lines.
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> top=Tk()
>>> text=Text(top)
>>> text.insert(INSERT,"One.")
>>> text.insert(END,"Two..Three...")
>>> text.pack()
>>> text.tag_add("first","1.0","1.4")
>>> text.tag_add("second","1.10","1.14")
>>> text.tag_config("first",background="cyan",foreground="black")
>>> text.tag_config("second",background="black",foreground="white")o. Toplevel
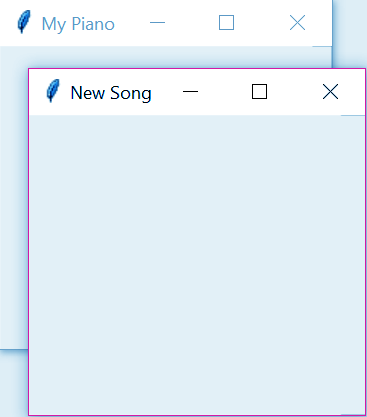
This provides a separate window container.
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> main=Tk()
>>> main.title("My Piano")
''
>>> new=Toplevel()
>>> new.title("New Song")
''p. Spinbox
Basically, Spinbox is like an entry field, except it lets us select from a fixed number of values.
Python Variables and Data Types with Syntax and Examples
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> s=Spinbox(top,from_=0,to=18) >>> s.pack()
q. PanedWindow
This is a container widget that can hold any number of panes horizontally or vertically.
>>> from tkinter import * >>> w1=PanedWindow() >>> w1.pack(fill=BOTH, expand=1) >>> left=Entry(w1,bd=5) >>> w1.add(left) >>> w2=PanedWindow(w1,orient=VERTICAL) >>> w1.add(w2) >>> top=Scale(w2,orient=HORIZONTAL) >>> w2.add(top) >>> bottom=Button(w2,text="OK") >>> w2.add(bottom)
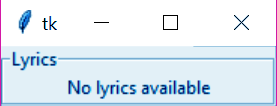
r. LabelFrame
So, this is a container widget holding complex window layouts.
>>> from tkinter import * >>> top=Tk() >>> labelframe=LabelFrame(top,text="Lyrics") >>> labelframe.pack(fill="both",expand="yes") >>> left=Label(labelframe,text="No lyrics available") >>> left.pack()
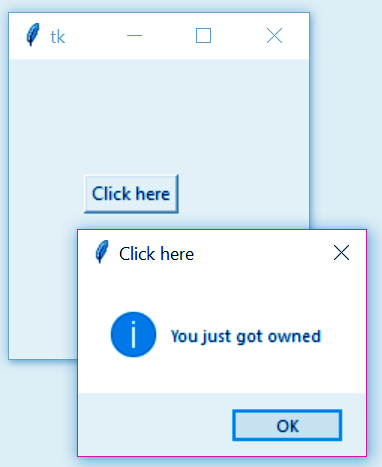
s. tkMessageBox
This widget displays a message box.
>>> from tkinter import *
>>> from tkinter import messagebox
>>> top=Tk()
>>> def clickhere():
messagebox.showinfo("Click here","You just got owned")
>>> button=Button(top,text="Click here",command=clickhere)
>>> button.place(x=50,y=77)So, this was all about Python GUI Programming. Hope you like our explanation of Tkinter Tutorial in Python 3.
Data Structures in Python – Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries
5. Conclusion
Hence, we completed the Python Tkinter tutorial. Now, it is time to get started with Python GUI programming. In addition, we saw Python GUI Programming and alternative for Python GUI Programming. Moreover, we discussed Tkinter and widgets. At last, we learned different kind of widgets that Tinker provides. Furthermore, for any query regarding Python GUI Programming with Tkinter, feel free to ask in the comment section.
For reference
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google












Is there any kind of tutorial for kivy (a python GUI framework on dataflair). If any, kindly send me the link on my email.
thank you
Hi Varchasa,
Currently, we don’t have a tutorial for kivy, soon we will publish it. Stay connected to DataFlair for more updates.
wonderfully explained. Good job in picking the most commonly used GUI controls and explained well.
This should be enough info to get started on the first project.
Thank you
Ashutosh
Very Well Explained…
Thank You