Python Array Module – How to Create and Import Array in Python
Python course with 57 real-time projects - Learn Python
Today in this Python Array Tutorial, we will learn about arrays in Python Programming. Here, we will discuss how Python array import module and how can we create Array.
Along with this, we will cover the Python Array Class Modules and Data Items.
What is a Python Array Module?
Python array module gives us an object type that we can use to denote an array. This is a collection of a type of values.
In a way, this is like a Python list, but we specify a type at the time of creation.
Here’s a list of such type codes-
Type Code | C Type | Python Type | Technology is evolving rapidly! Minimum size (bytes) |
b | signed char | int | 1 |
B | unsigned char | int | 1 |
u | Py_UNICODE | Unicode character; deprecated since Python 3.3 | 2 |
h | signed short | int | 2 |
H | unsigned short | int | 2 |
i | signed int | int | 2 |
I | unsigned int | int | 2 |
l | signed long | int | 4 |
L | unsigned long | int | 4 |
q | signed long long | int | 8 |
Q | unsigned long long | int | 8 |
f | float | float | 4 |
d | double | float | 8 |
How to Import Python Array Module?
If a Python array is installed on your machine, you can import it as:
>>> import array
How to Create a Python Array?
You can create an array using the following piece of code-
class array.array(typecode[,initializer])
This creates a new array with items of the type specified by the type code. You can optionally provide an initializer value- a list.
Let’s try creating an array in Python.
>>> arr=array.array('i',[1,3,4])
>>> arrOutput
>>> array.array('u', 'hello \u2641')Output
Python Array Class – Data Items
The class array has the following data items-
1. array.typecodes
This is a string with all available type codes- the ones in the table above.
>>> array.typecodes
Output
2. array.typecode
This gives us the type code character we used when creating the array in Python.
>>> arr.typecode
Output
3. array.itemsize
This returns the number of bytes one item from the Python array takes internally.
>>> arr.itemsize
Output
Python Array Class – Methods
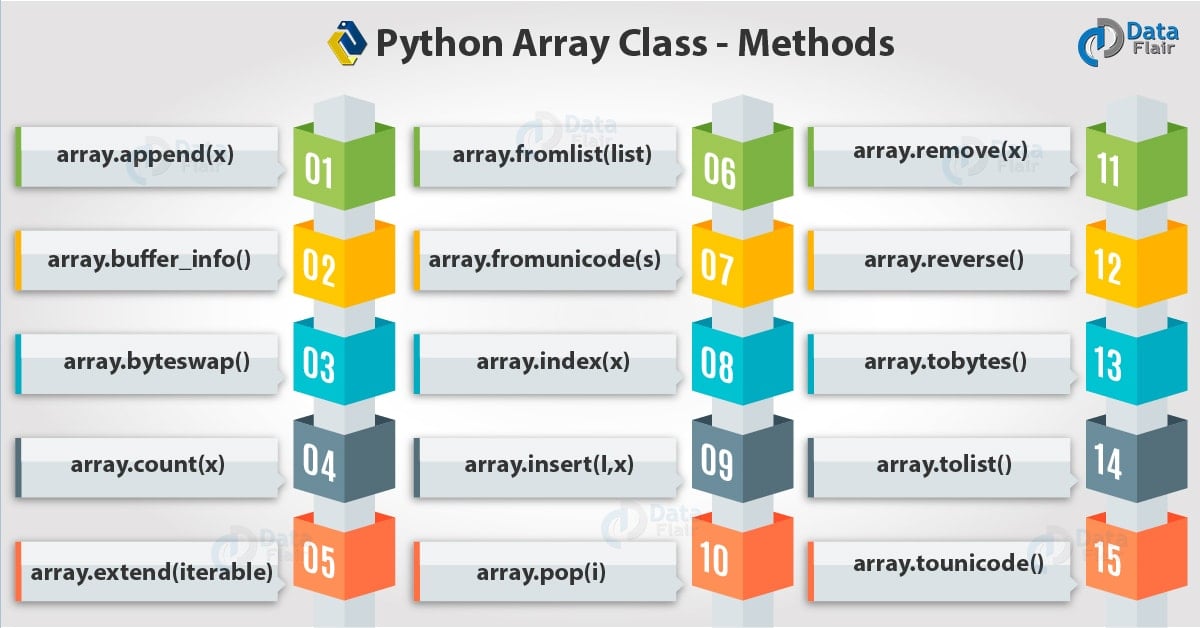
Now, which methods does Array Class support? Here you go:
1. array.append(x)
This appends the item x to the array.
>>> arr.append(2) >>> arr
Output
2. array.buffer_info()
This returns a tuple that holds the address in memory and the length of elements in the buffer that holds the contents of the array.
>>> arr.buffer_info()
Output
3. array.byteswap()
This performs an operation of bytes wap on an array.
>>> arr.byteswap() >>> arr
Output
4. array.count(x)
Let’s find out how many 3s there are in our Python array.
>>> arr=array.array('i',[1,3,2,4,3,5])
>>> arr.count(3)Output
5. array.extend(iterable)
This attaches the iterable to the end of the array in Python.
>>> arr.extend([7,9,8]) >>> arr
Output
But if you add another array, make sure it is the same type. The following code throws an error.
>>> arr.extend(array.array('u',['H','e','l','l','o']))Output
File “<pyshell#19>”, line 1, in <module>
arr.extend(array.array(‘u’,[‘H’,’e’,’l’,’l’,’o’]))
TypeError: can only extend with array of same kind
6. array.fromlist(list)
This appends item from a list to the Python arrays.
>>> arr.fromlist([9,0]) >>> arr
Output
7. array.fromunicode(s)
This appends the Unicode string to the one we call it on- this should be Unicode too.
>>> unicodearr=array.array('u','Hello')
>>> unicodearrOutput
>>> unicodearr.fromunicode(' world')
>>> unicodearrOutput
8. array.index(x)
This returns the index for the first occurrence of x in the Python array.
>>> arr=array.array('i',[1,3,2,4,3,5])
>>> arr.index(3)Output
9. array.insert(I,x)
>>> arr.insert(2,7) >>> arr
Output
This inserts the element 7 at index 2.
10. array.pop(i)
This lets us drop the element at the position i.
>>> arr.pop(2)
Output
11. array.remove(x)
This will let you remove the first occurrence of an element from the Python array.
>>> arr.remove(3) >>> arr
Output
12. array.reverse()
This reverses the Python array.
>>> arr.reverse() >>> arr
Output
13. array.tobytes()
This returns a representation in bytes of the values of the array in Python.
This is the same as array.tostring(), which is deprecated.
>>> arr.tobytes()
Output
14. array.tolist()
This converts the array into a list.
>>> arr.tolist()
Output
15. array.tounicode()
This converts an array to a Unicode string. You need a Unicode array for this.
>>> unicodearr.tounicode()
Output
Python Array – More Information
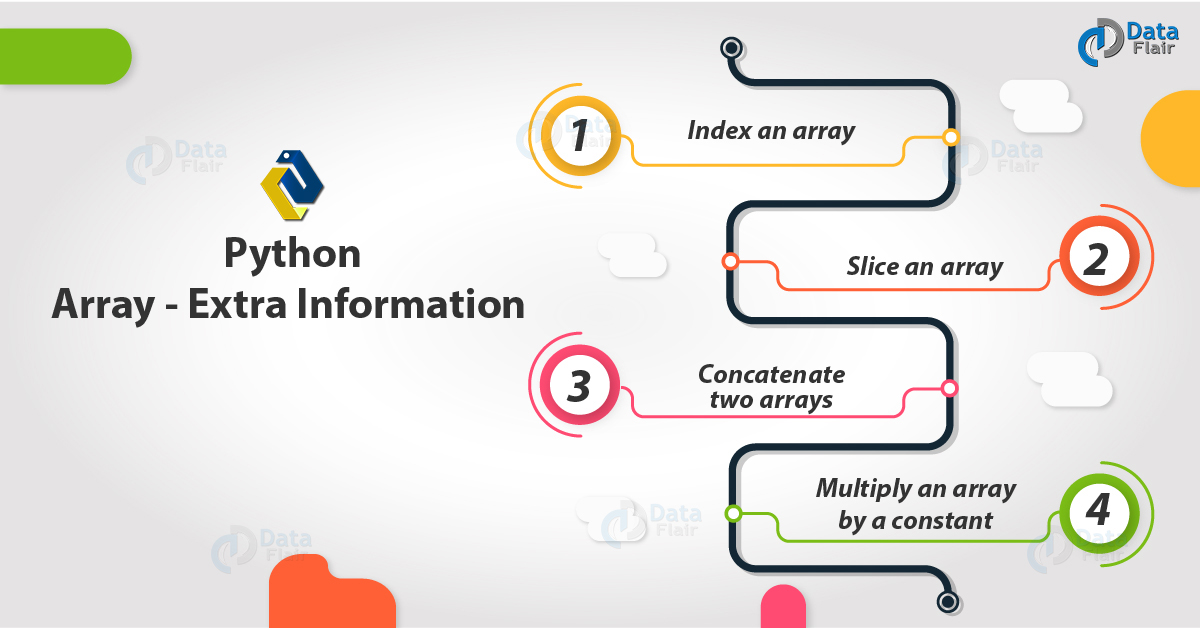
Python Arrays are space-efficient collections of numeric values that are uniformly-typed. You can:
1. How to Index an Array in Python?
>>> arr
Output
>>> arr[1]
Output
2. Slice an array
>>> arr[1:4]
Output
3. Concatenate two arrays in Python
>>> arr+arr
Output
4. Multiply an array by a constant
>>> arr*2
Output
So, this was all about Python Arrays Tutorial. Hope you like our explanation
Python Interview Questions on Array Module
- What is array module in Python?
- How do you display an array in Python?
- How to use an array module in Python?
- What is the difference between array and list in Python?
- How to read an array in Python?
Conclusion
Hence, while Python does not have arrays as a primary data structure, it does provide a module to let us work with arrays.
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google



this was so helpful to me understand about arrays also this can be done by myself so easily thank you for this tutorial <3 🙂
Hey Udayanga Rukshan,
I am glad that you liked our tutorial, you can also refer our sidebar for more such Python tutorials.
How to store characters using python array module ?
Here’s is a way:
import array
a = array.array(‘u’,)
a.append(‘i’)
a.append(‘e’)
print(a)
3. array.byteswap()
This performs an operation of bytes wap on an array.
>>> arr.byteswap()
>>> arr
Output
array(‘i’, [16777216, 50331648, 67108864, 33554432])
I think you meant to say “byteswap” and it’s a pretty advanced topic that seems out of place here…I’d take it out.
Yes, it should be byteswap. We included this function so that we can cover as many methods on the arrays as possible. This might be helpful for someone searching for this functionality. Thank you for correcting us and also for the suggestion.