Numeric and Character Functions in R – Gain Proficiency in the concept!
FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
In this tutorial, we will learn about R built-in functions, in which we will focus on different types of numeric and character functions in R. Along with this, we will also understand different types of properties of character functions.
So, let’s start the R numeric and character functions tutorial.
R Built-in Functions
We use R built-in functions to perform almost everything in R. Here we are only referring to numeric and character functions that are generally used in creating or recording variables.
Wait! Have you checked – R Vector Functions
R Numeric Functions
Let us see R Numeric functions:
Function Description
- abs(x) absolute value
- ceiling(x) ceiling(3.475) is 4
- sqrt(x) square root
- floor(x) floor(3.475) is 3
- log(x) natural logarithm
- trunc(x) trunc(5.99) is 5
- round(x, digits=n) round(3.475, digit=2) is 3.48
- log10(x) common logarithm
- signif(x, digits=n) signif(3.475, digit=2) is 3.5
- exp(x) e^x
- cos(x), sin(x), tan(x) also acos(x), cosh(x), acosh(zx) etc
Character Functions in R
Let us see various R character functions:
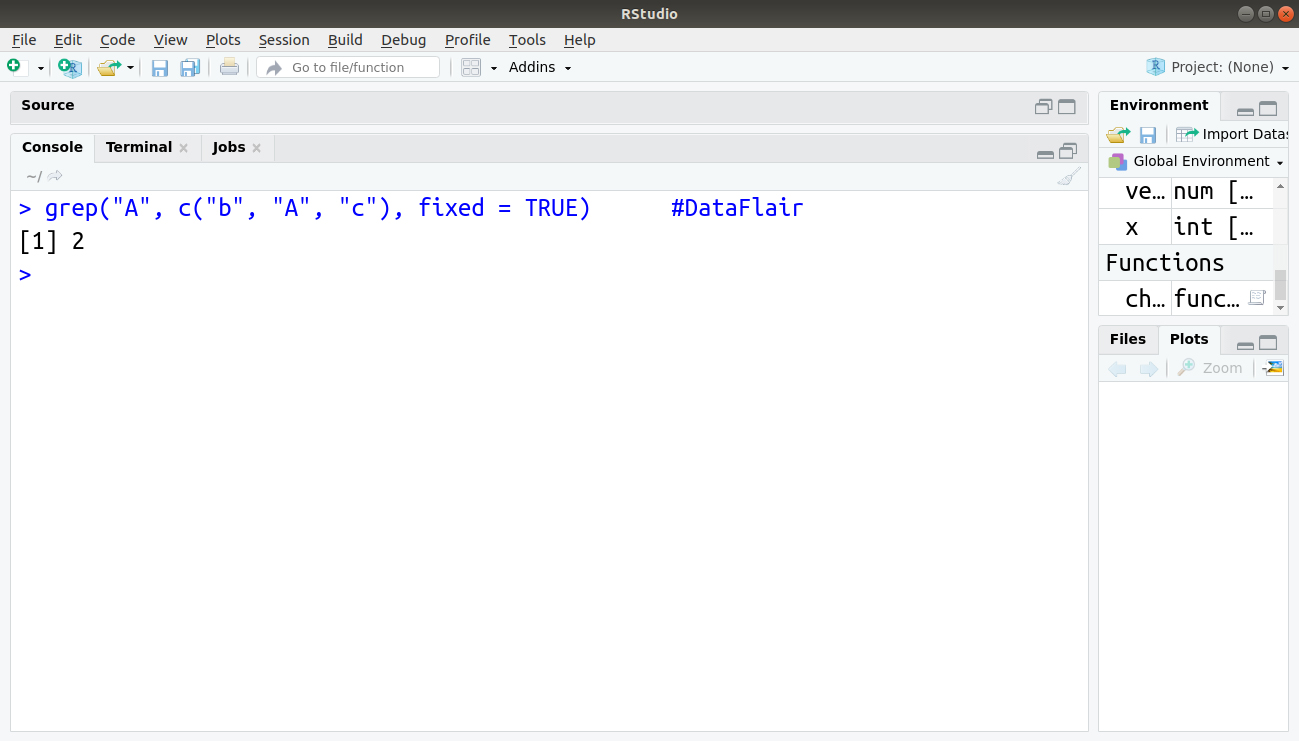
1. grep(pattern, x , ignore.case=FALSE, fixed=FALSE)
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
Description:
- Search for a pattern in x.
- If fixed =FALSE, then the pattern is a regular expression.
- If fixed=TRUE, then the pattern is a text string.
- Returns matching indices.
> grep("A", c("b", "A", "c"), fixed = TRUE)Output:
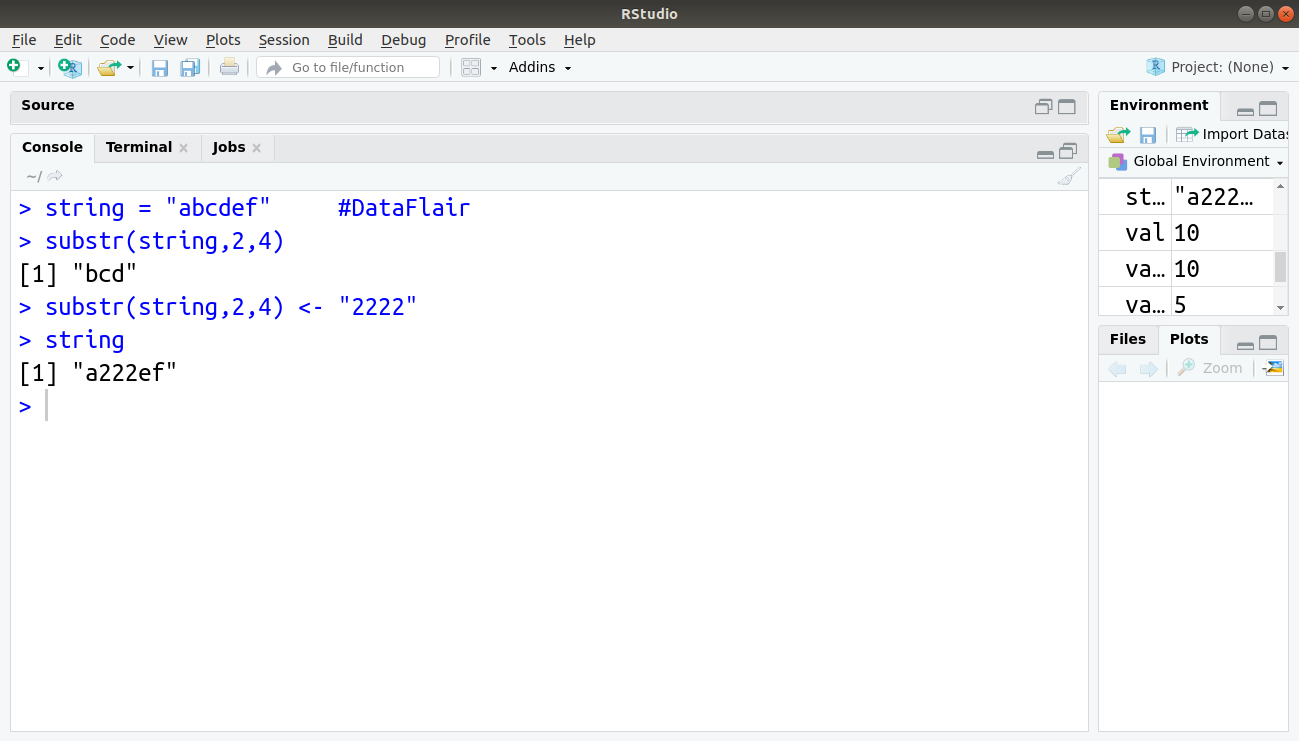
2. substr(x, start=n1, stop=n2)
Description:
- Extract or replace substrings in a character vector.
> string = "abcdef" > substr(string,2,4) > substr(string,2,4) <- "2222" > string
Output:
You must definitely explore the R Recursive Function Tutorial
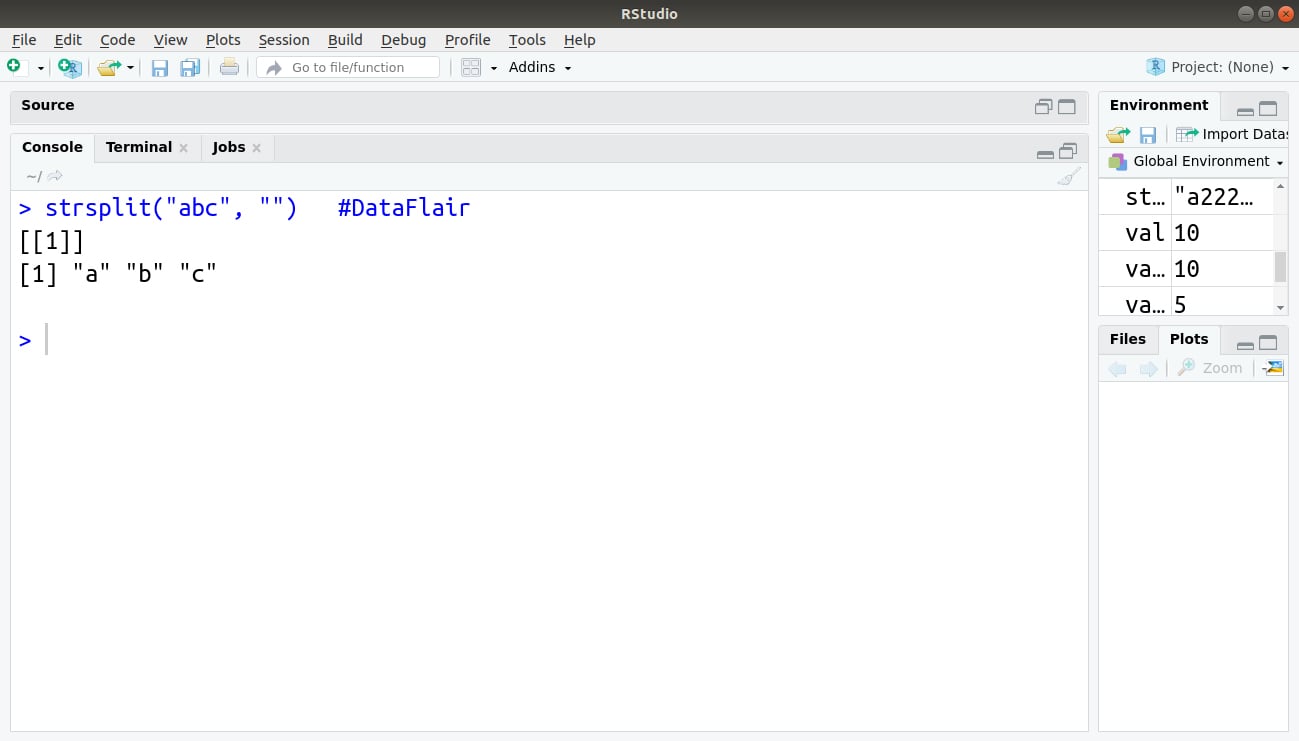
3. strsplit
> strsplit("abc", "")Output:
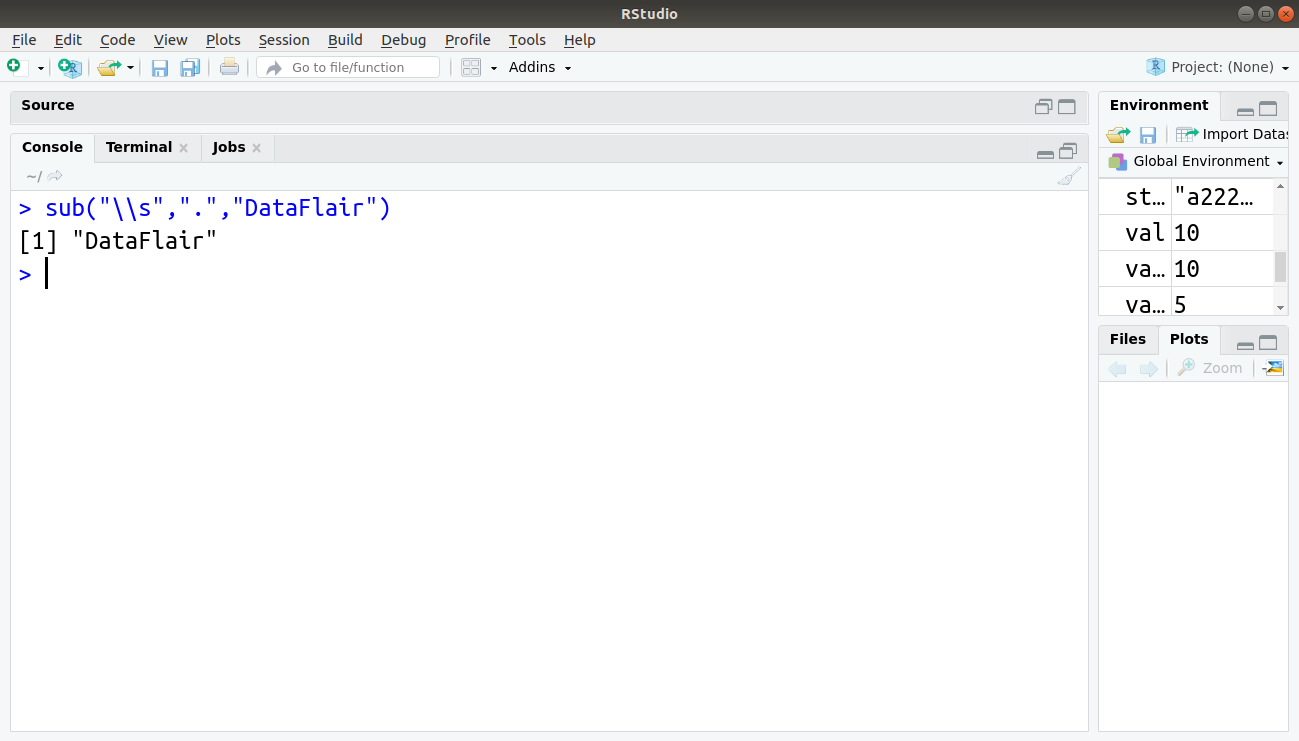
4. sub(pattern, replacement, x, ignore.case =FALSE, fixed=FALSE)
Description:
- Find a pattern in x and replace it with the replacement text.
- If a fixed = FALSE, then a pattern is a regular expression.
- If fixed = TRUE, then a pattern is a text string.
sub("\\s",".","DataFlair")Output:
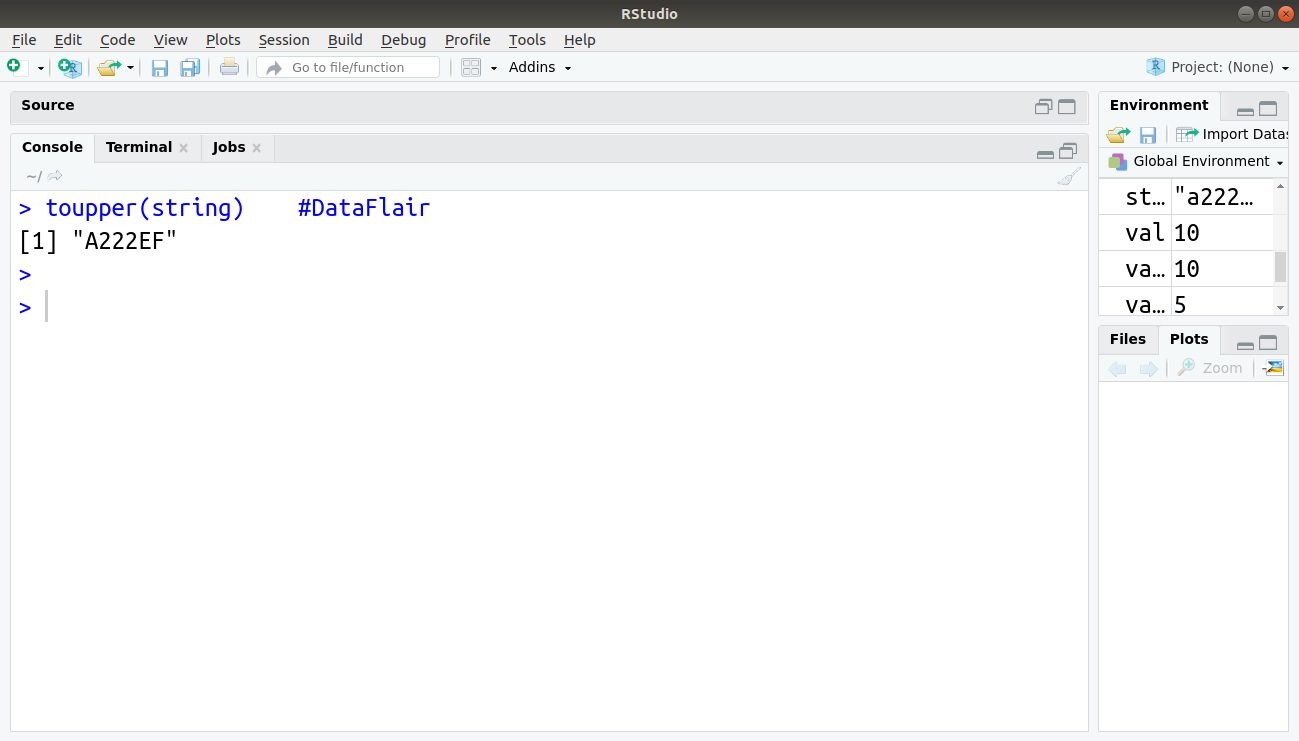
5. toupper(string)
Description:
Uppercase
> toupper(string)
Output:
Do you know about Object Oriented Programming in R
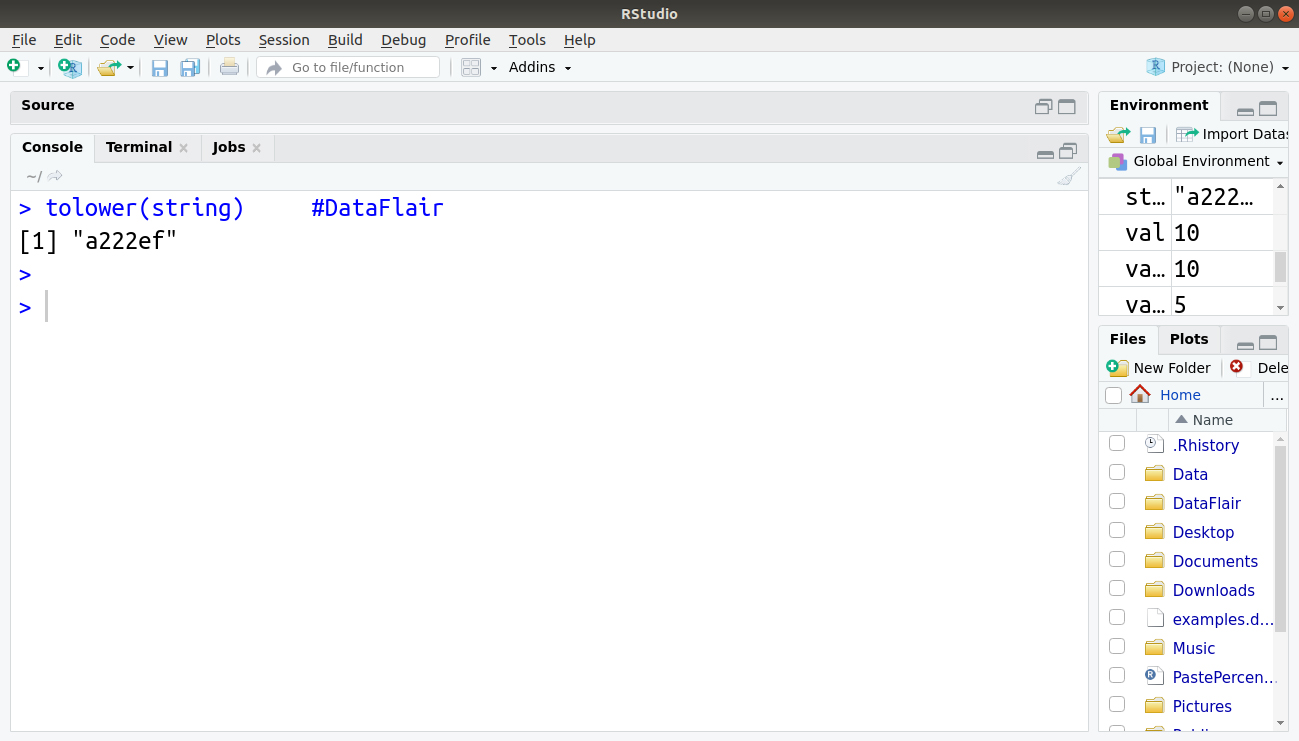
6. tolower(string)
Description:
Lowercase
> tolower(string)
Output:
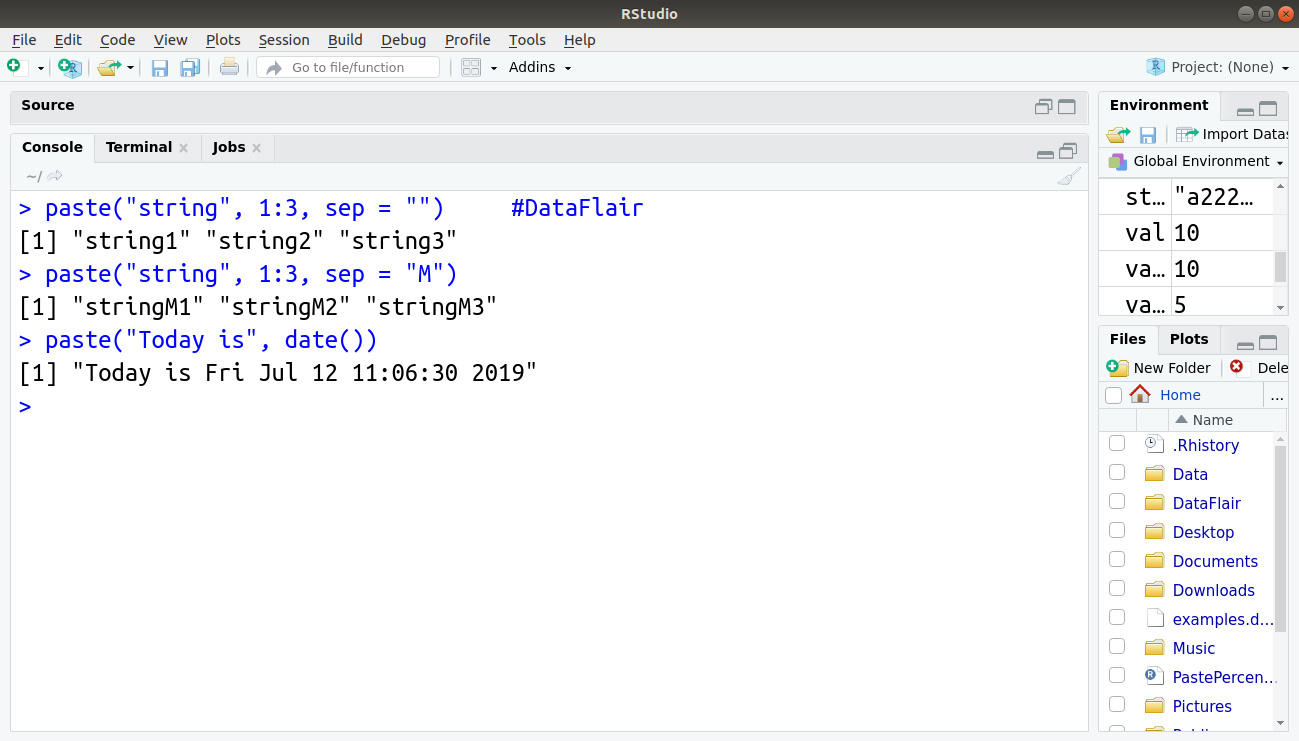
7. paste(…, sep=””)
Description:
Concatenate strings after using sep string to separate them.
> paste("string", 1:3, sep = "")
> paste("string", 1:3, sep = "M")
> paste("Today is", date())Output:
R Character Function – Create Strings
In R, we store strings in a character vector. We can create strings with a single quote/ double quote.
For example – y = “Hadoop at DataFlair”
1. Convert Object into Character type
We use an as.character function that converts arguments to a character type.
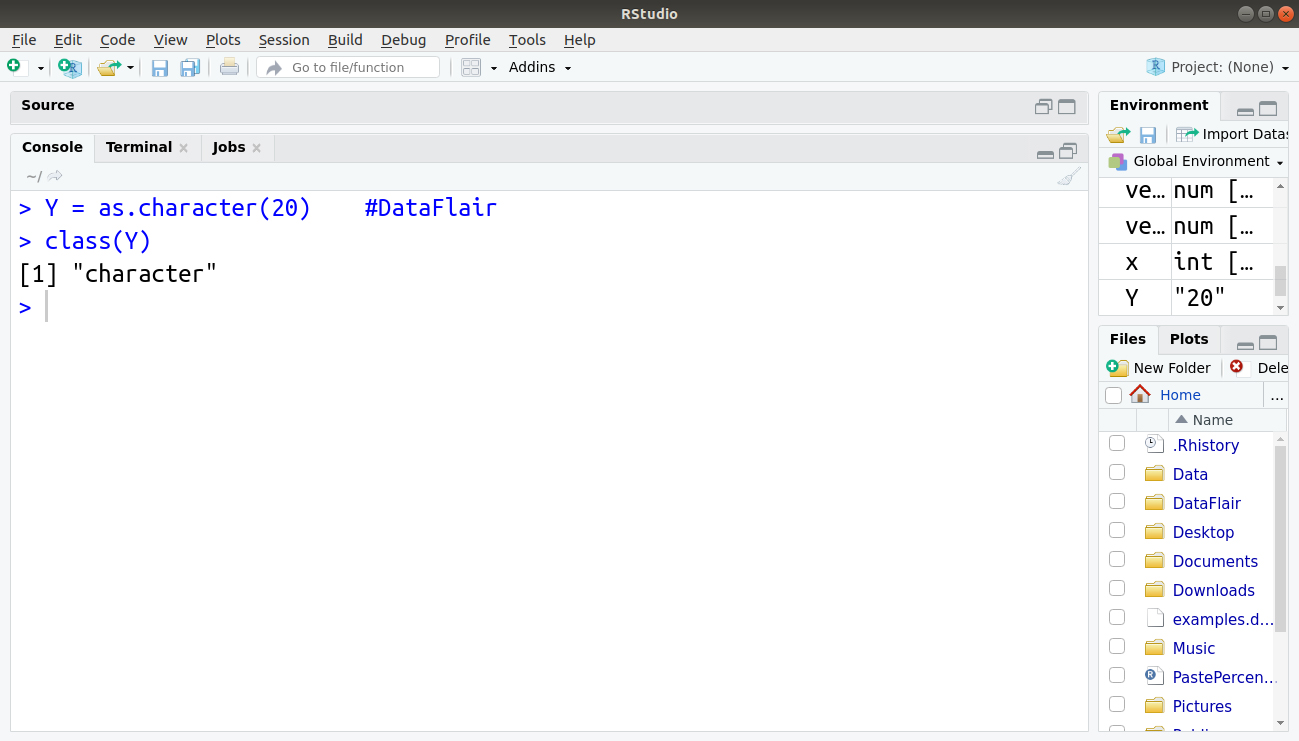
For example – We are storing 20 as a character.
Y = as.character(20) class(Y)
Output:
The class(Y) returns character as 20 and is stored as a character in the above code.
Explore all the Types of Arguments in R
2. Check the character type
> X = “Hadoop at DataFlair” > is.character(X)
Output:
There are other functions that are similar to is.character such as is.integer, is.array and is.character for validating integer, array and character data types respectively.
3. Concatenate Strings in R
In order to join the two strings (also known as concatenation), we make use of the paste function. It is one of the most important strings manipulation task. Every analyst performs it almost daily to structure the data.
Paste Function Syntax:
paste (objects, sep = " ", collapse = NULL)
- sep – Keyword which denotes a separator or delimiter.
- default separator – A single space.
- collapse – Keyword which is used to separate the results.
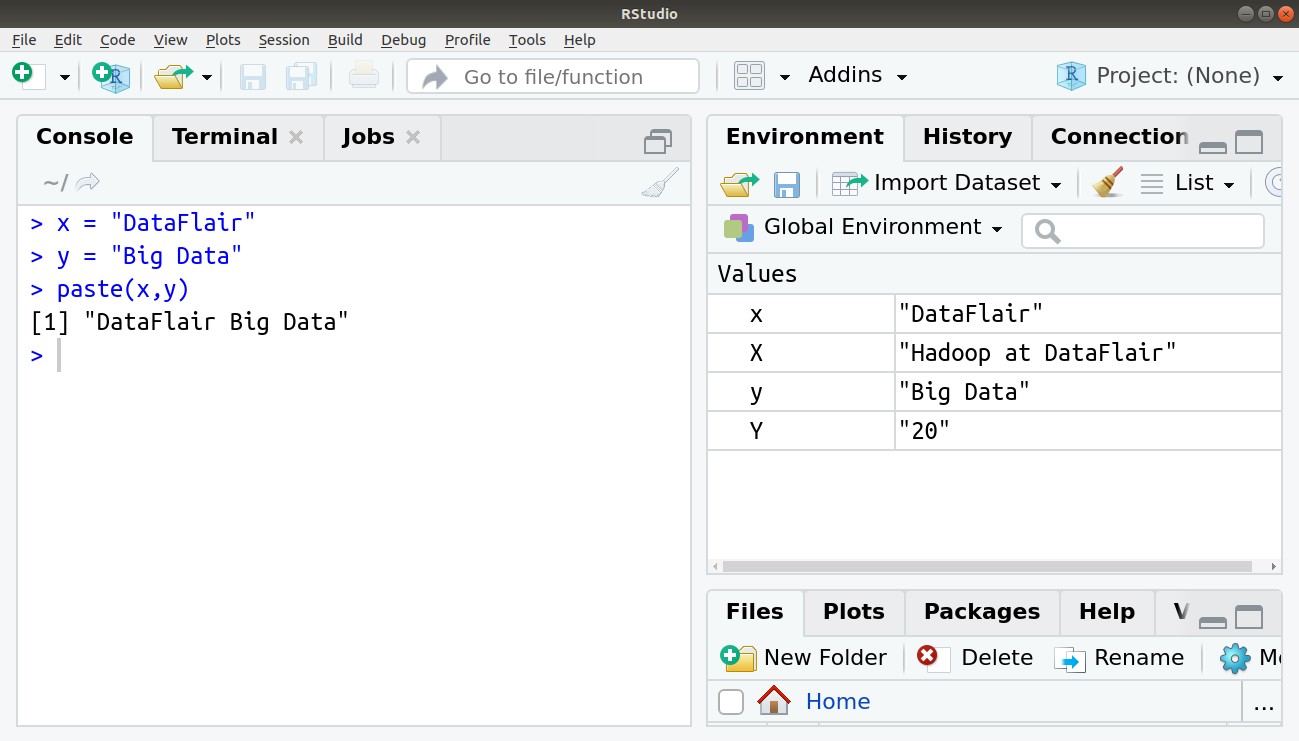
For example:
> x = "DataFlair" > y = "Big Data" > paste(x,y)
Output:
Understand the String Manipulation Function in R
4. String Formatting in R
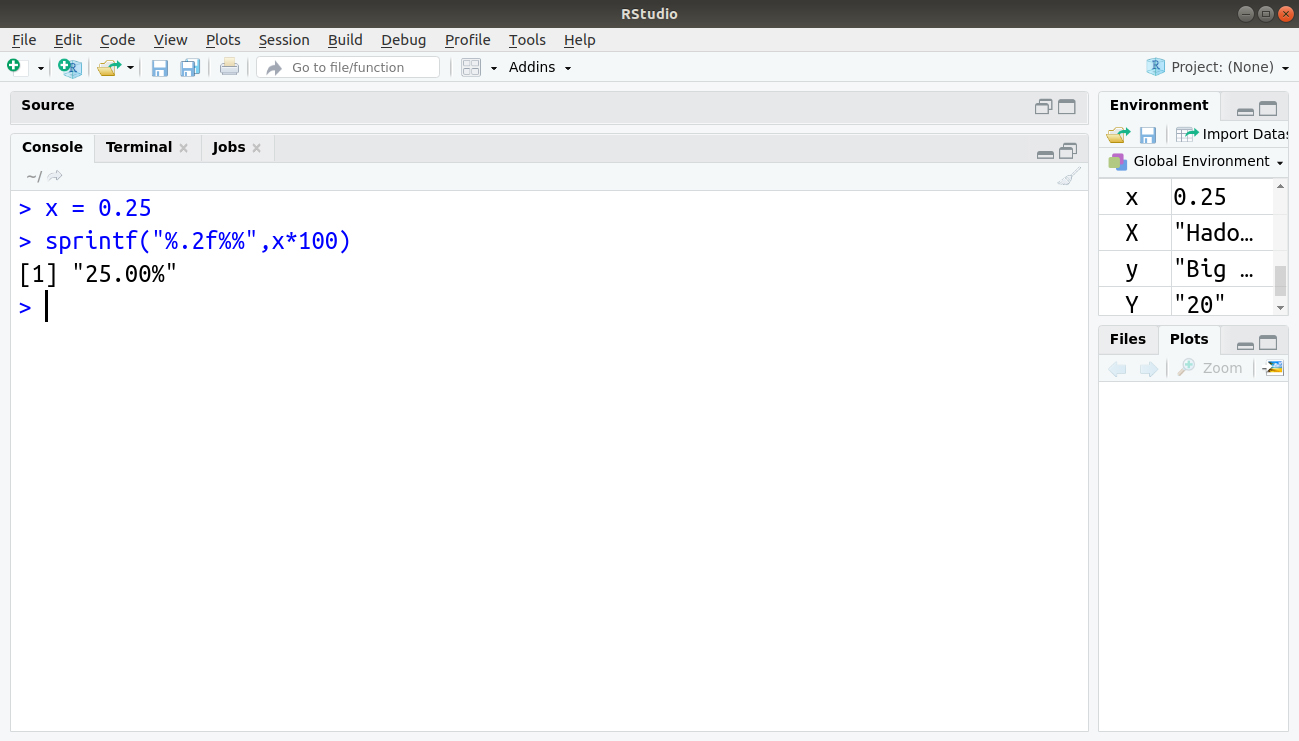
Suppose the value is stored in fraction and you need to convert it to percentage. In order to format our string in a C-style, sprintf function is used.
Sprintf Function Syntax:
sprintf(fmt, ...)
The keyword fmt denotes string format. The numbers and letters in the format start with the % symbol.
x = 0.25
sprintf("%.2f%%",x*100)Output:
5. Extract or replace substrings in R
substr Syntax –
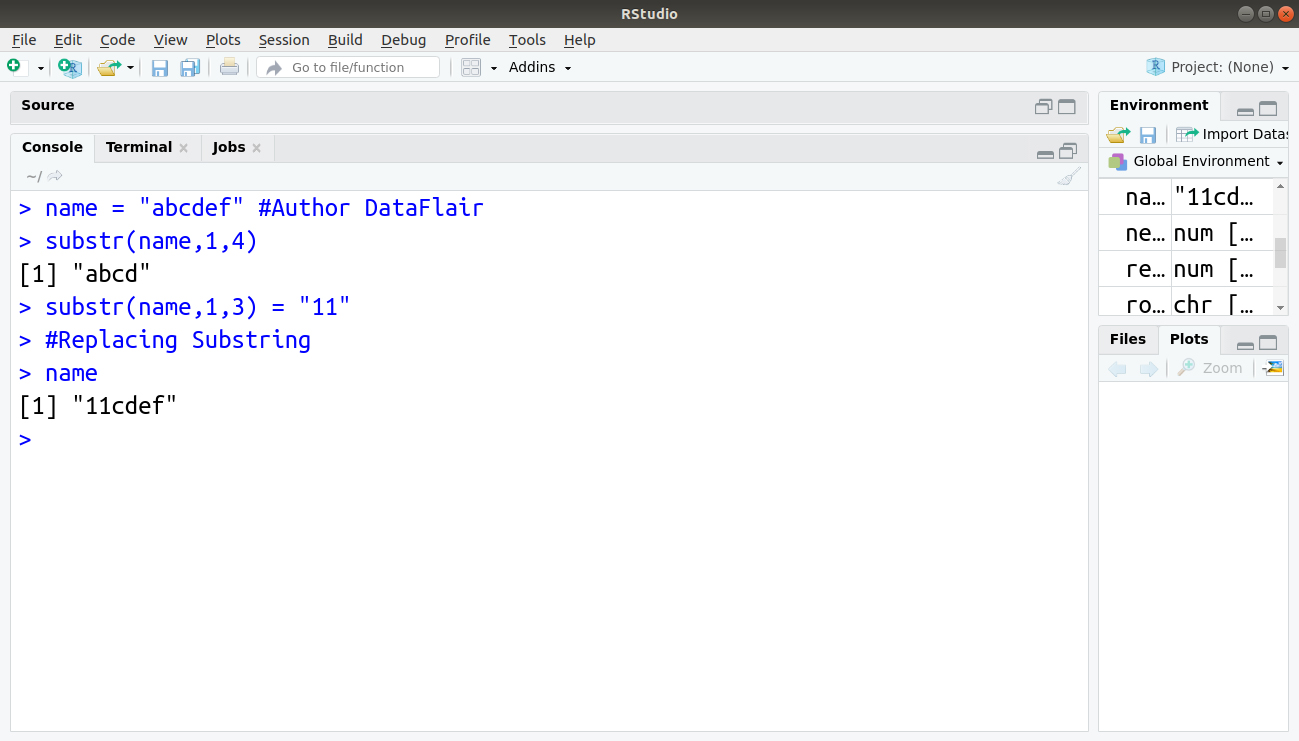
> name = "abcdef" #Author DataFlair > substr(name,1,4)
In the above example, we are telling R to replace first 3letters with 111.
Replace Substring – substr(x, starting position, end position) = Value
> substr(name,1,3) = "11" #Replacing Substring > name
Output:
6. String Length
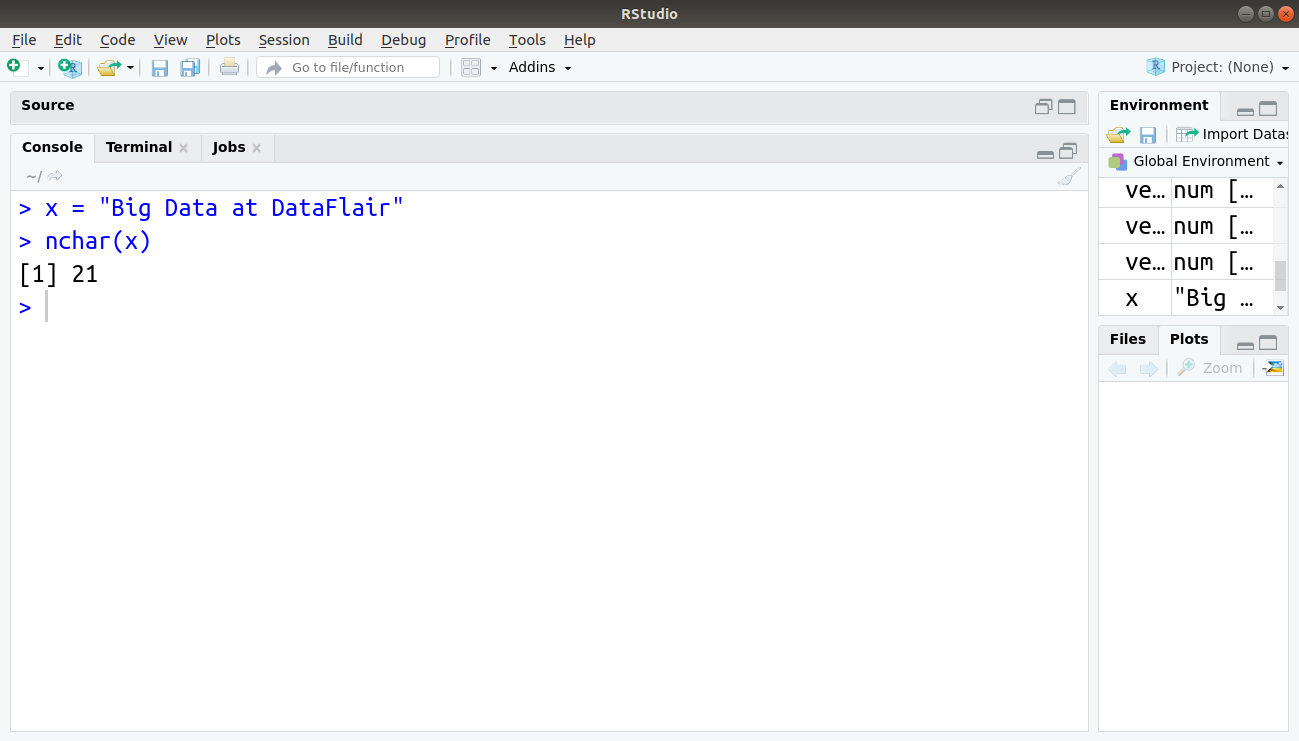
The nchar function is used to compute the length of a character value.
> x = "Big Data at DataFlair" > nchar(x)
Output:
It returns 14 as the vector ‘x’ contains 14 letters (including 2 spaces).
Don’t forget to check the R Statistics Tutorial
7. Extract word from a programming
Suppose you need to pull a first or last word from a character string.
Word Function Syntax (Library : stringr)
word(string, position of word to extract, separator)
For example:
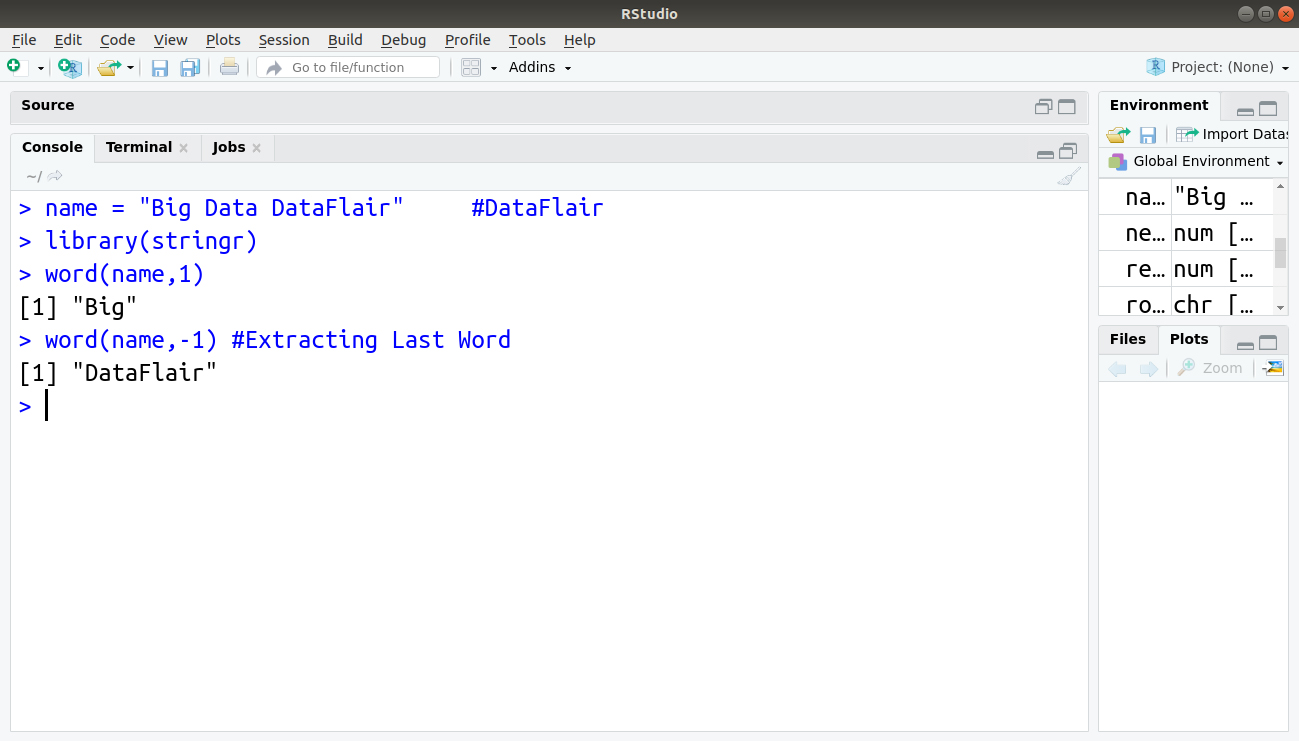
> name = "Big Data DataFlair" > library(stringr) > word(name,1)
In the example above, ‘1’ denotes the first word to be extracted from a string.
Extract Last Word
> word(name,-1) #Extracting Last Word
In the example above, ‘-1’ denotes the first word to be extracted from the right of the string.
Output:
8. Convert Character to Uppercase / Lowercase /Propercase
At many times, we need to change the case of a word.
For example: convert the case to uppercase or lowercase.
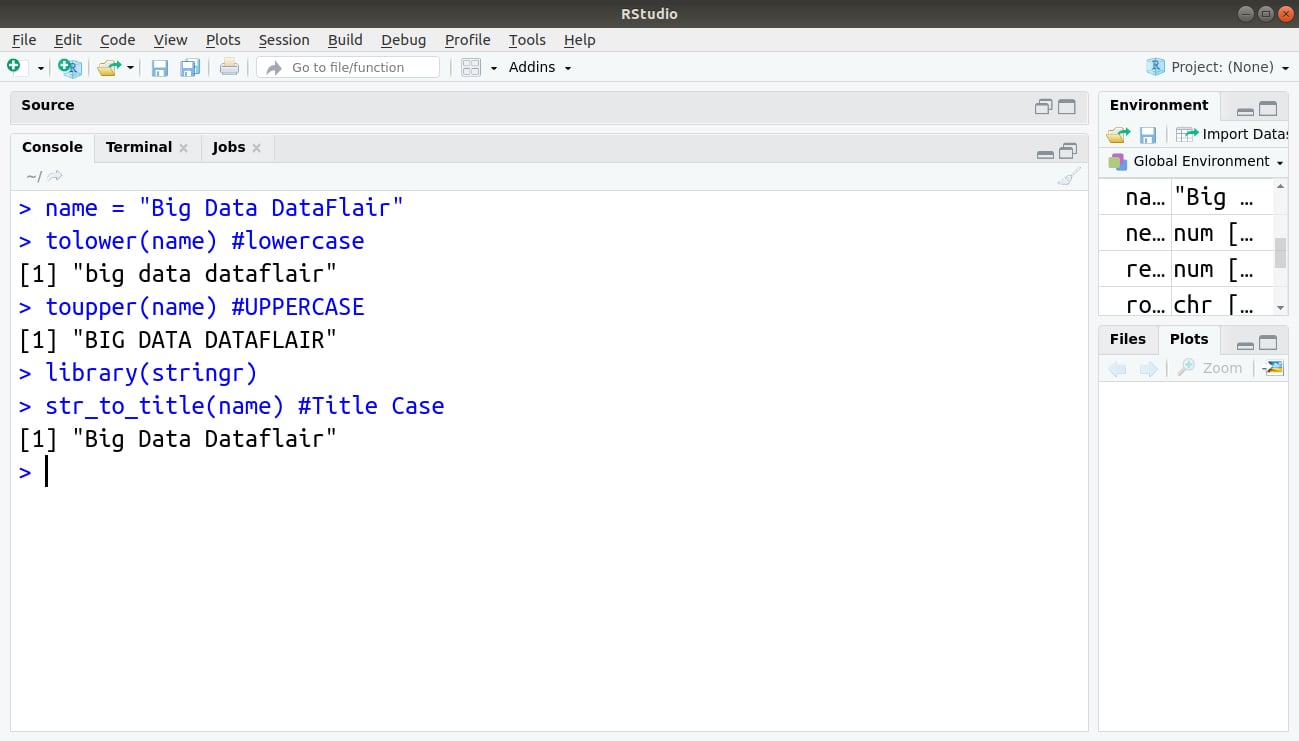
> name = "Big Data DataFlair" > tolower(name) #lowercase
The tolower() function converts letters in a string to lowercase.
toupper(x)
> toupper(name) #UPPERCASE
The toupper() function converts letters in a string to uppercase.
library(stringr)
> library(stringr) > str_to_title(name) #Title Case
The str_to_title() function converts the first letter in a string to uppercase and the remaining letters to lowercase.
Output:
Grab the list of R Debug Functions
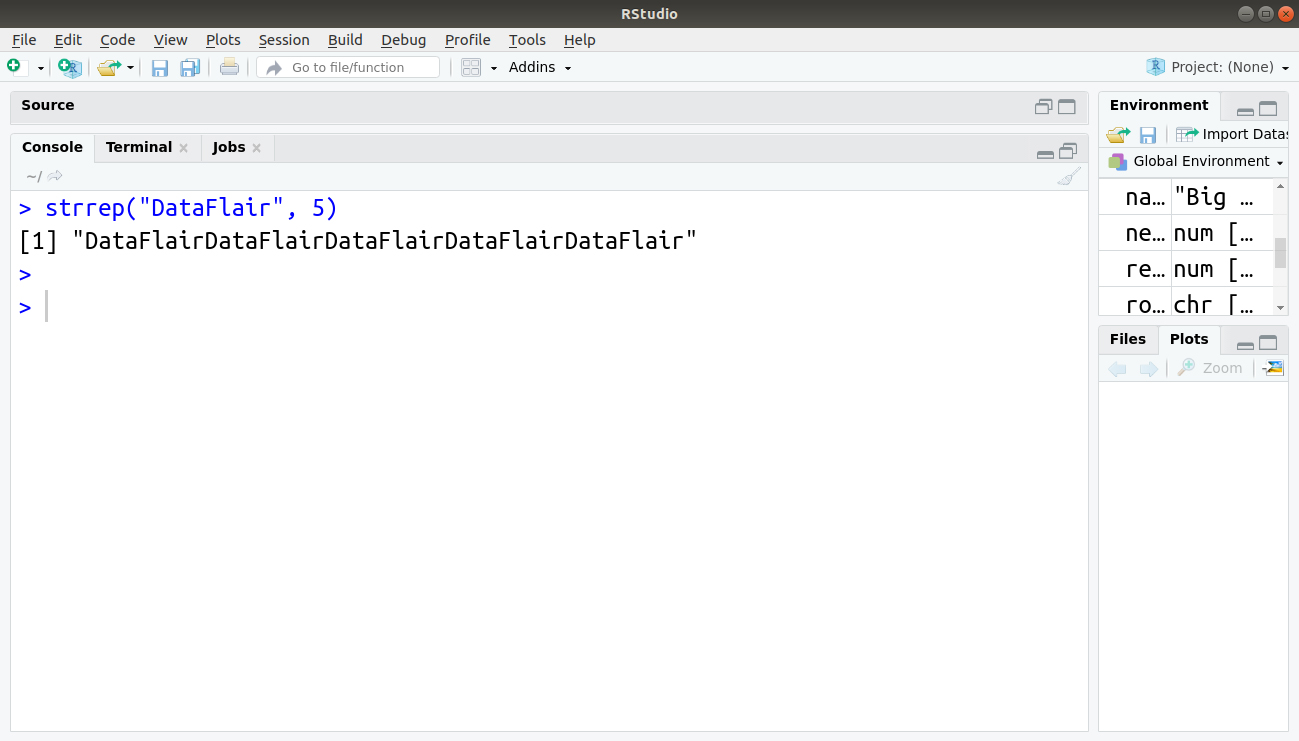
9. Repeat the character N times
We can use strrep base R function to repeat the character N times.
> strrep("DataFlair", 5)Output:
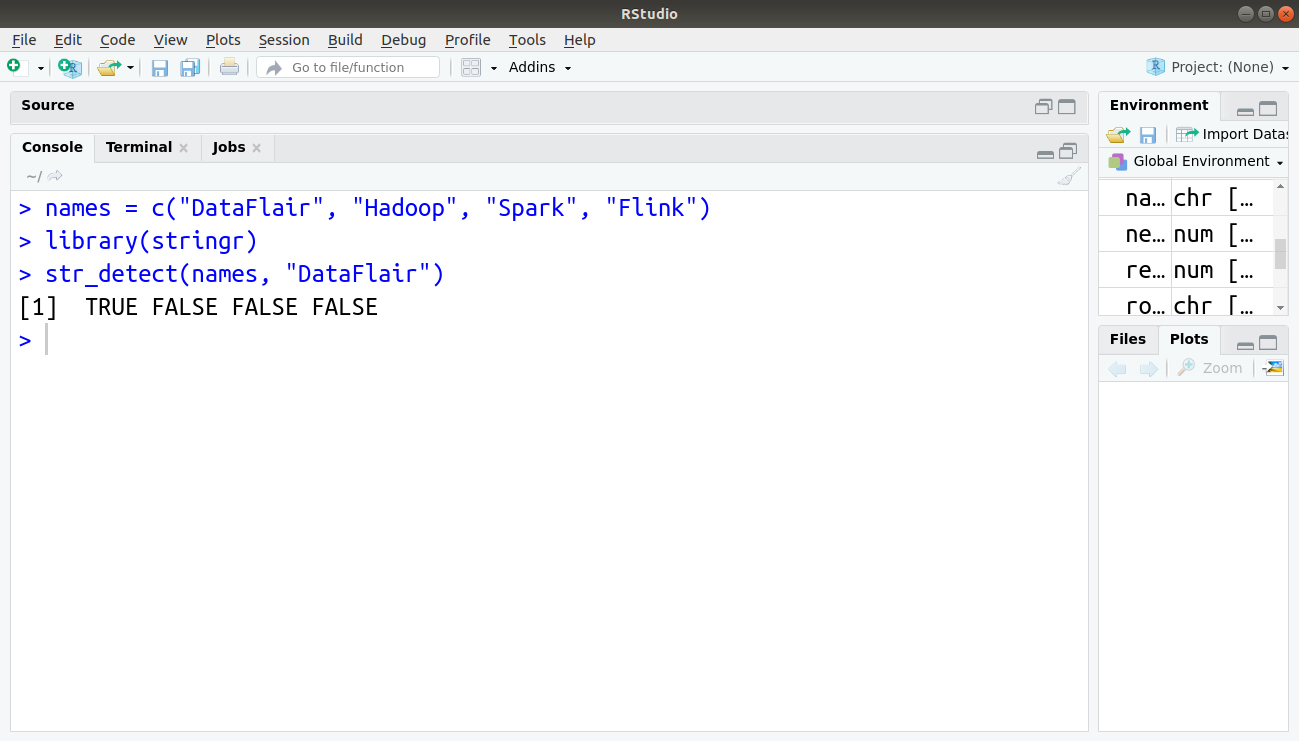
10. Find String in a Character Variable
The str_detect() function helps to check whether a substring exists in a string. It is equal to ‘contain’ function of SAS. It returns TRUE/FALSE against each value.
> names = c("DataFlair", "Hadoop", "Spark", "Flink")
> library(stringr)
> str_detect(names, "DataFlair")Output:
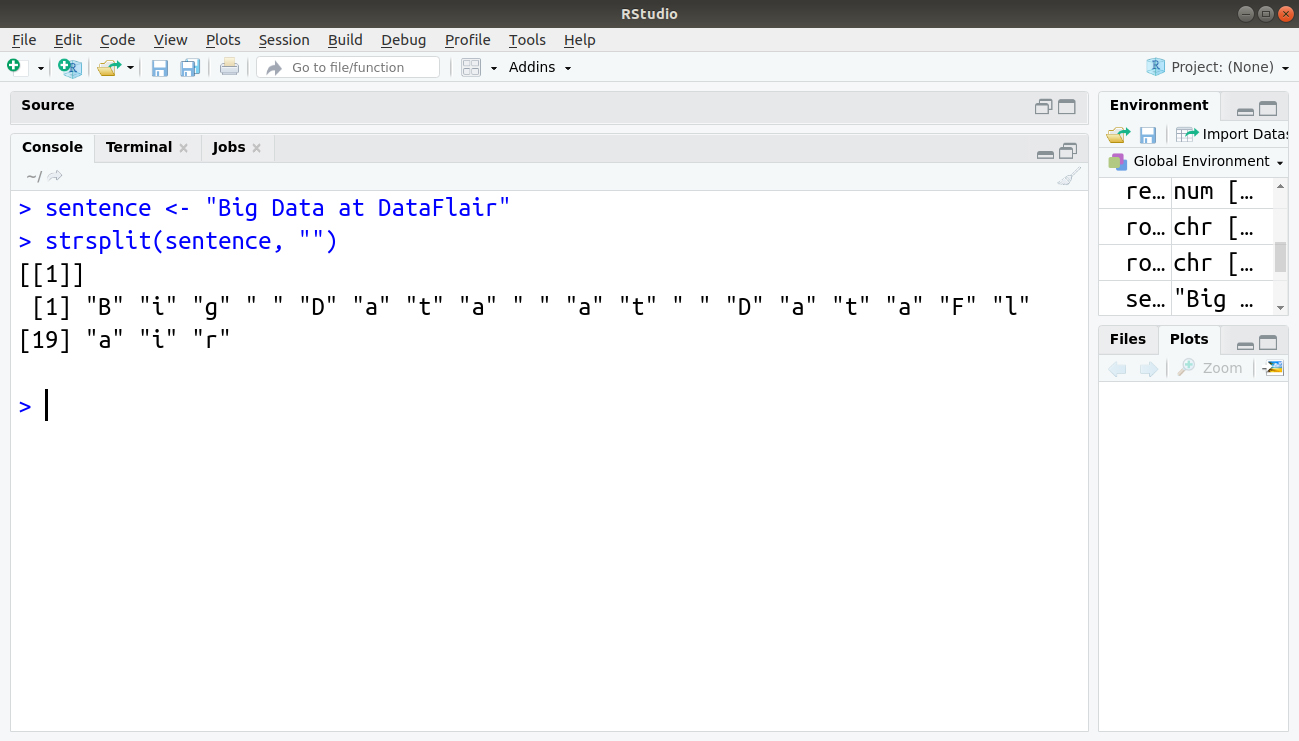
11. Splitting a Character Vector
In the case of text mining, it is required to split a string to calculate the used keywords in the list. We use ‘strsplit()’ in base R to perform this operation.
> sentence <- "Big Data at DataFlair" > strsplit(sentence, "")
Output:
Summary
We have studied in deep about various numeric and character functions in R and also learned different properties of these functions which help a lot in R programming.
Next tutorial in our learning box of R DataFlair Tutorial Series – R Matrix Functions
Still, if any doubt regarding Numeric and Character Functions, ask in the comment section.
Your opinion matters
Please write your valuable feedback about DataFlair on Google



I m not able to find few syntax on my Rstudio
they are: str_to_title(), str_detect(), word().
Any specific thing we are supposed to follow make it possible?