R List – Learn what all you can do with Lists in R!
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Skills, Zero Cost. Enroll Now!
Now in this R programming DataFlair tutorial series, we will see one of the major R data types that is R list in detail. First of all, we will learn about R list, then we will discuss how to create, access and modify lists in R with the help of examples.
What is R List?
R list is the object which contains elements of different types – like strings, numbers, vectors and another list inside it. R list can also contain a matrix or a function as its elements. The list is created using the list() function in R. In other words, a list is a generic vector containing other objects.
For example:
The variable x is containing copies of three vectors n, s, b and a numeric value 3.
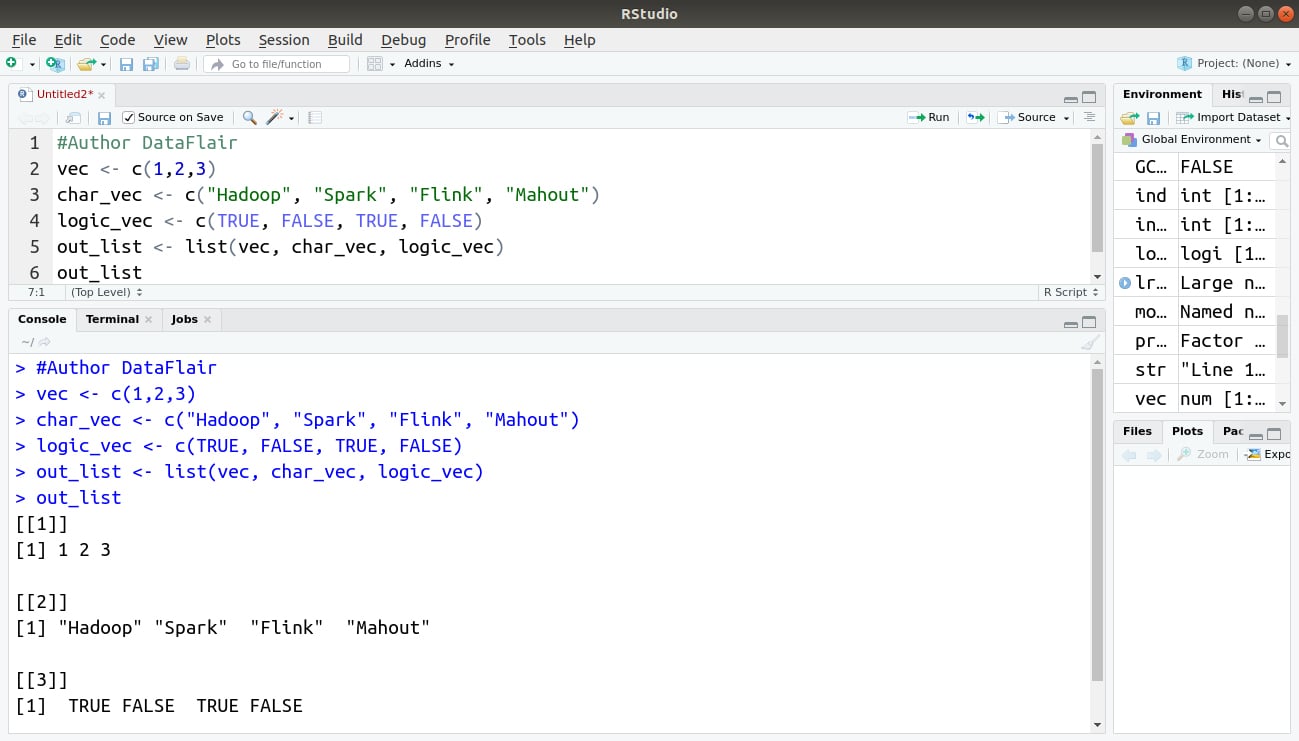
#Author DataFlair
vec <- c(1,2,3)
char_vec <- c("Hadoop", "Spark", "Flink", "Mahout")
logic_vec <- c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE)
out_list <- list(vec, char_vec, logic_vec)
out_listOutput:
Wait! Have you checked – Guide on R Vector Operations
How to Create Lists in R Programming
In this section of the R list tutorial, we will create R list with the help of an example.
Let’s create a list containing string, numbers, vectors and logical values.
For example:
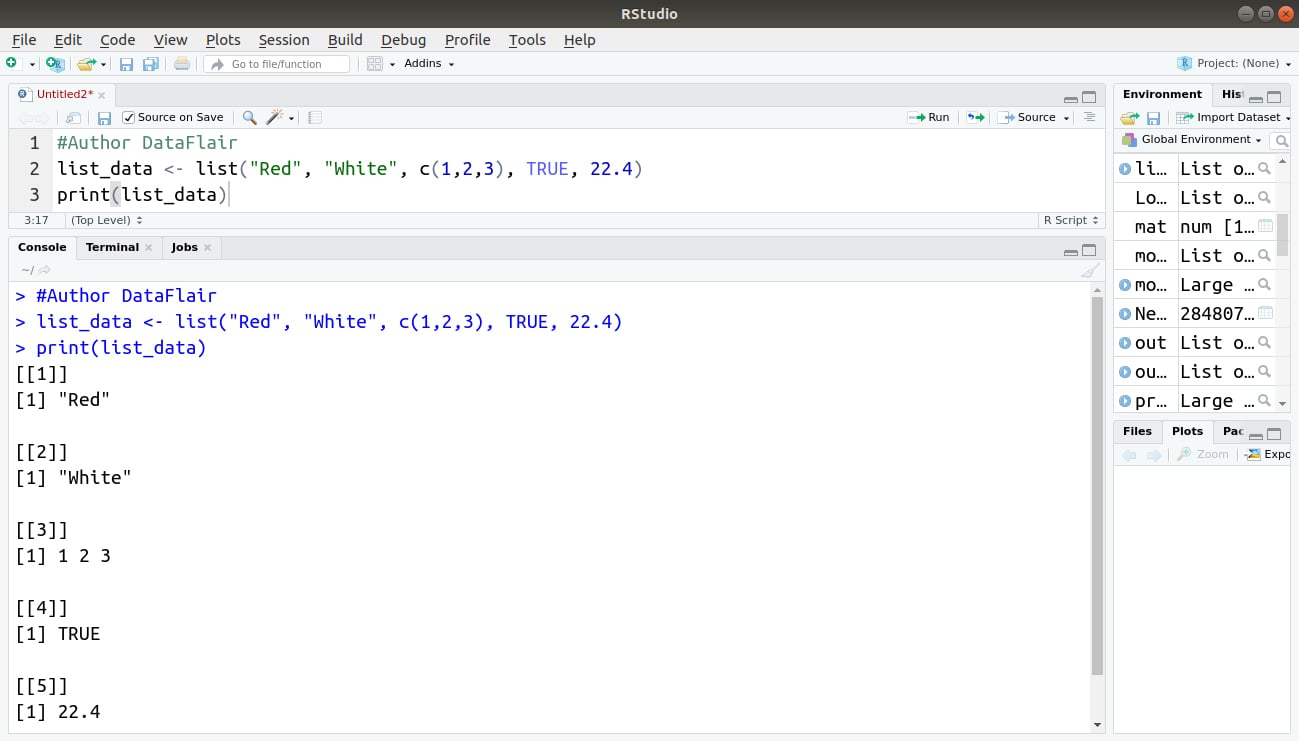
#Author DataFlair
list_data <- list("Red", "White", c(1,2,3), TRUE, 22.4)
print(list_data)Output:
How to Name List Elements in R Language
In this section, we will learn to name the R list elements with the help of an example.
Let’s create a list containing a vector, matrix, and list.
For example:
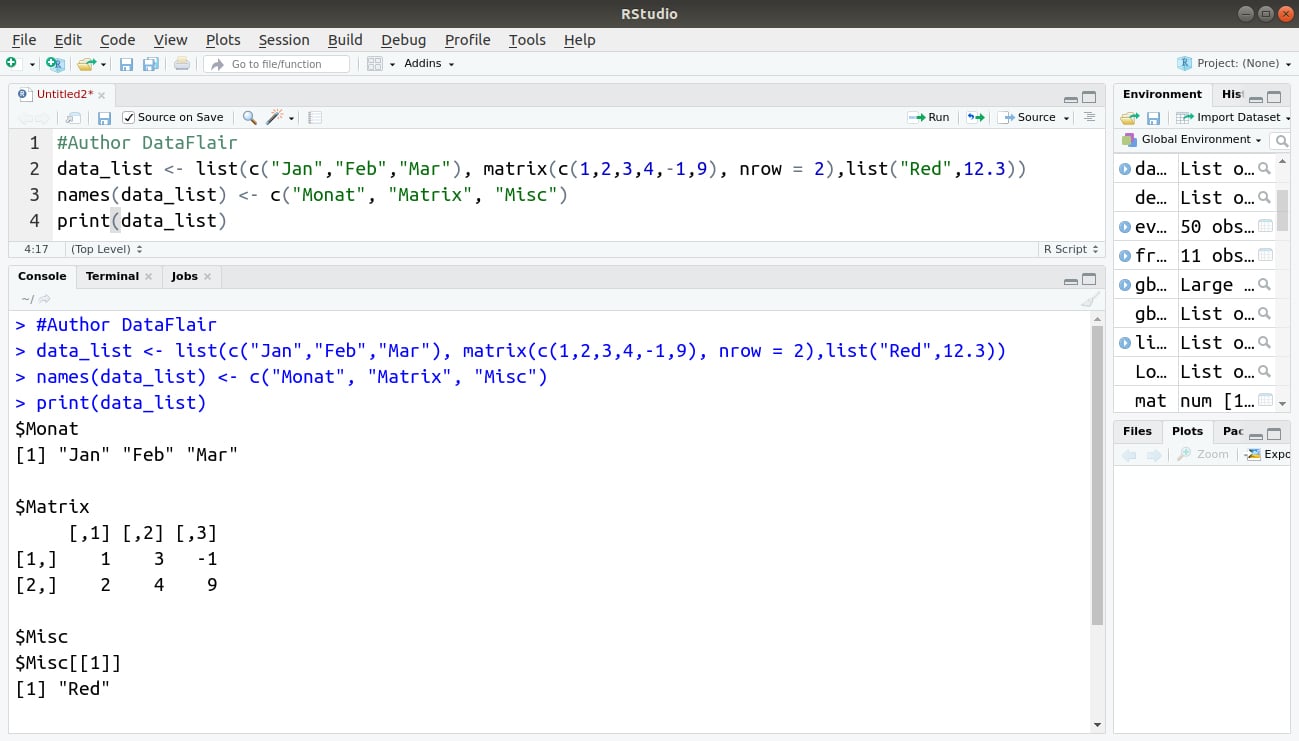
#Author DataFlair
data_list <- list(c("Jan","Feb","Mar"), matrix(c(1,2,3,4,-1,9), nrow = 2),list("Red",12.3))
names(data_list) <- c("Monat", "Matrix", "Misc")
print(data_list)Output:
You must definitely learn to Create and Access R Matrix
How to Access R List Elements
Let’s now understand how to access lists elements in R programming.
Create an R list containing a vector, list and matrix. We will use the list that we created in the previous section ‘data_list’.
In order to give names to the elements of the list:
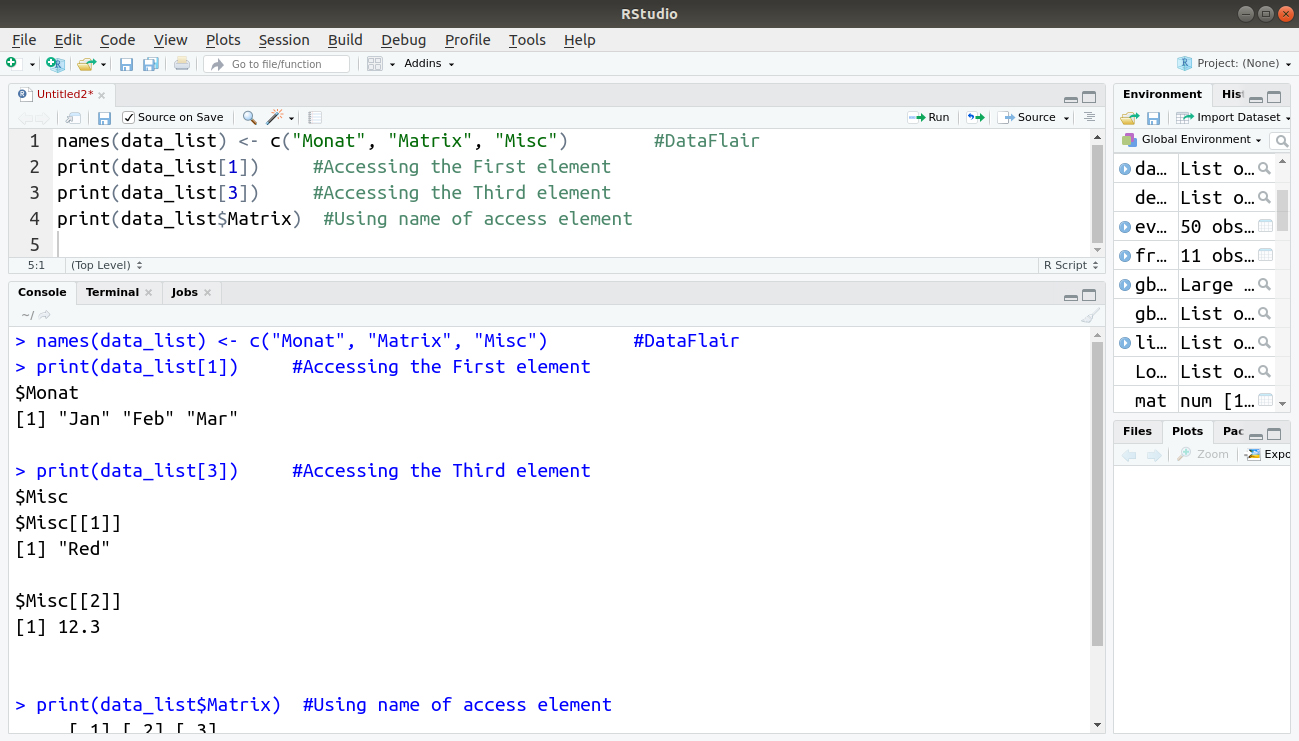
names(data_list) <- c("Monat", "Matrix", "Misc")Access the first element of the list.
print(data_list[1]) #Accessing the First element
Access the third element. As it is also a list, all its elements will print.
print(data_list[3]) #Accessing the Third element
By using the name of the element access the list elements.
print(data_list$Matrix) #Using name of access element
Output:
How to Manipulate List elements in R Programming
Let’s now discuss how to manipulate the R list elements with the help of an example.
Create a list containing a vector, a matrix and a list.list_data <- list(c(“Feb”,”Mar”,”Apr”), matrix(c(3,9,5,1,-2,8), nrow = 2),list(“green”,12.3))
For example:
Give names to the elements in the list.
names(data_list) <- c("Monat", "Matrix", "Misc")
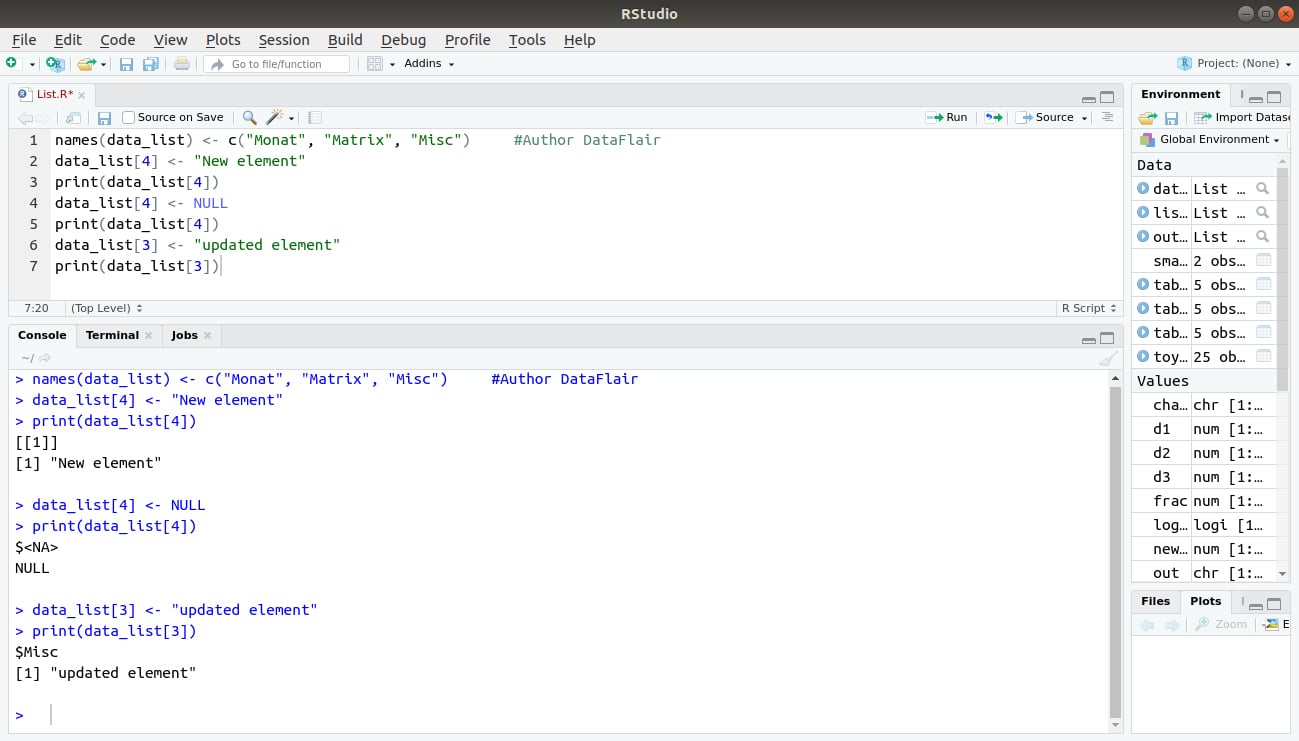
Add an element at the end of the list.
data_list[4] <- "New element" print(data_list[4])
Remove the last element.
data_list[4] <- NULL print(data_list[4])
Update the 3rd Element.
data_list[3] <- "updated element"
Output:
Don’t forget to explore the R Data Frame tutorial
How to Merge Lists in R Programming language
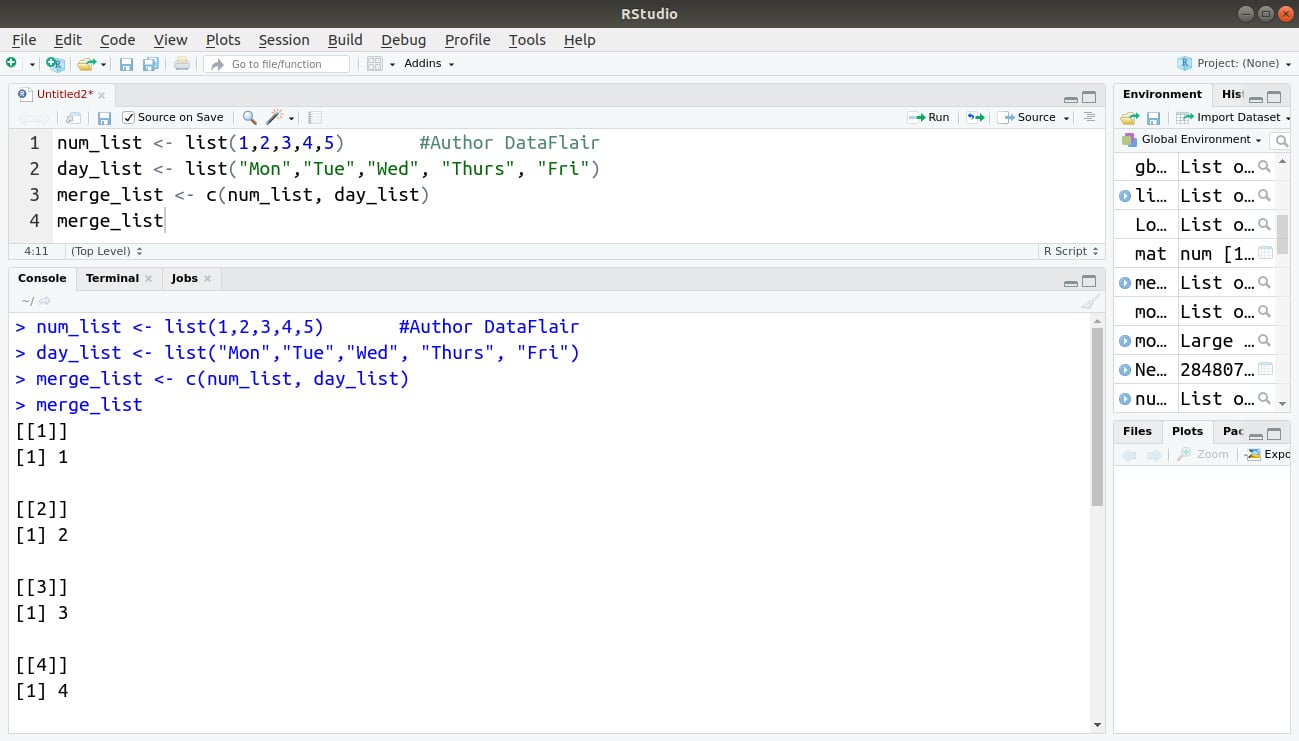
We can merge many lists into one list by placing all the lists element inside one list() function.
For example:
num_list <- list(1,2,3,4,5) #Author DataFlair
day_list <- list("Mon","Tue","Wed", "Thurs", "Fri")
merge_list <- c(num_list, day_list)
merge_listOutput:
How to Convert R List to Vector
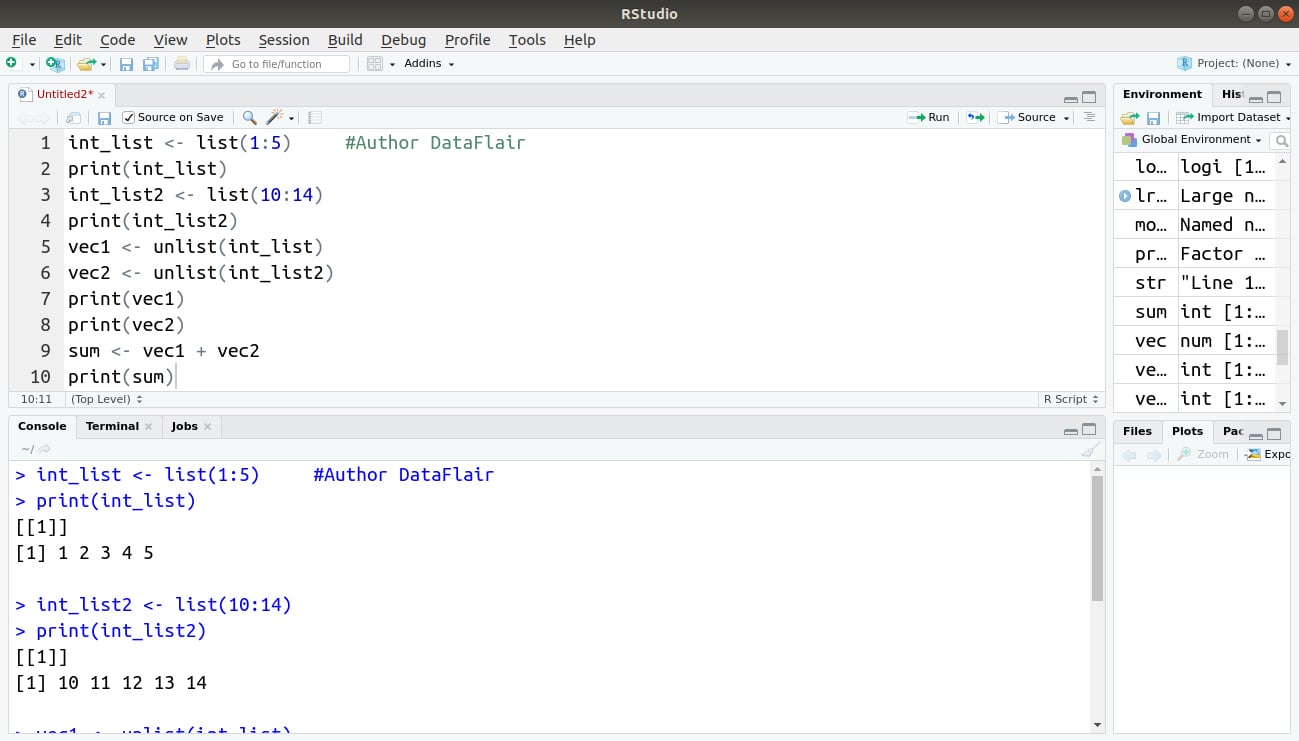
A list can be converted to a vector so that the elements of the vector can be used for further manipulation. All the arithmetic operations on vectors can be applied after the list is converted into vector. To do this conversion, we can use the unlist() function. It takes the list as input and produces a vector.
For example:
Create lists.
int_list <- list(1:5) #Author DataFlair print(int_list) int_list2 <- list(10:14) print(int_list2)
Convert the lists to vectors.
vec1 <- unlist(int_list) vec2 <- unlist(int_list2) print(vec1) print(vec2)
Now add the vectors.
sum <- vec1 + vec2 print(sum)
Output:
Must Learn – R Vector Functions Tutorial
How to Generate Lists in R
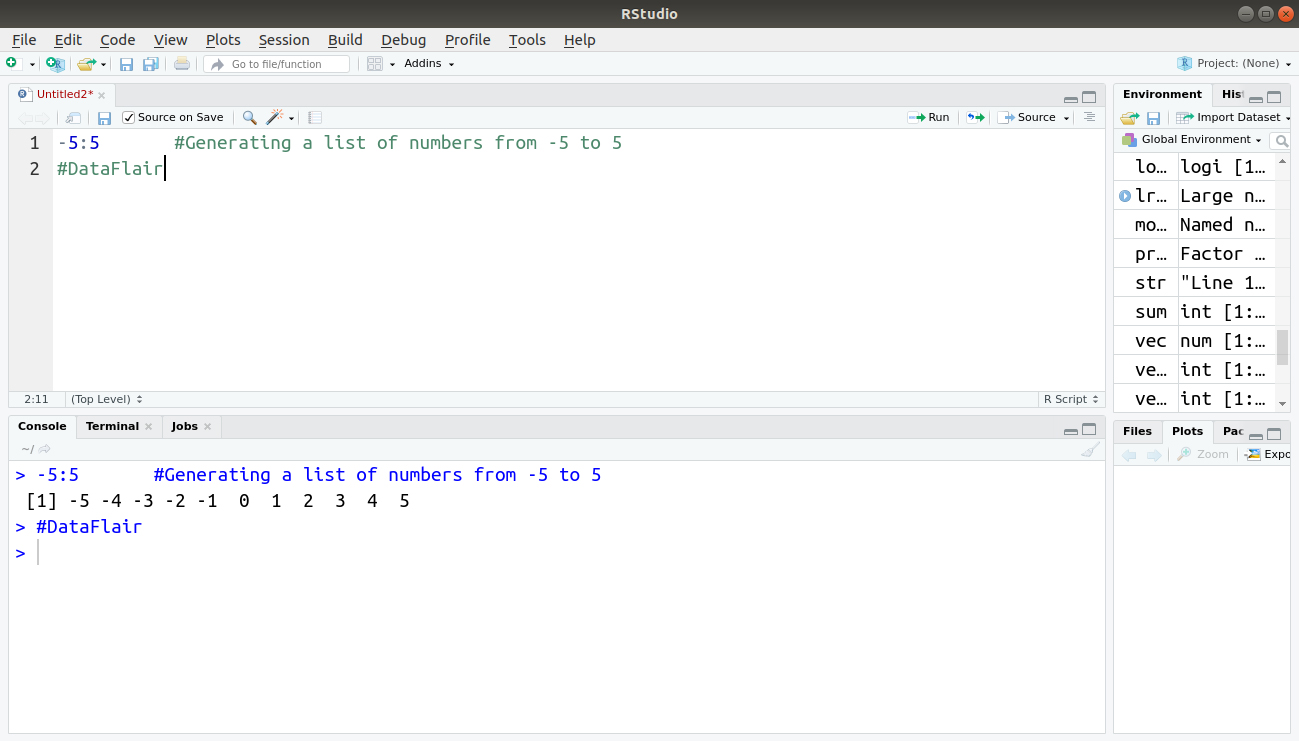
We can use a colon to generate a list of numbers.
For example:
> -5:5 #Generating a list of numbers from -5 to 5
Output:
Operating on Lists in R
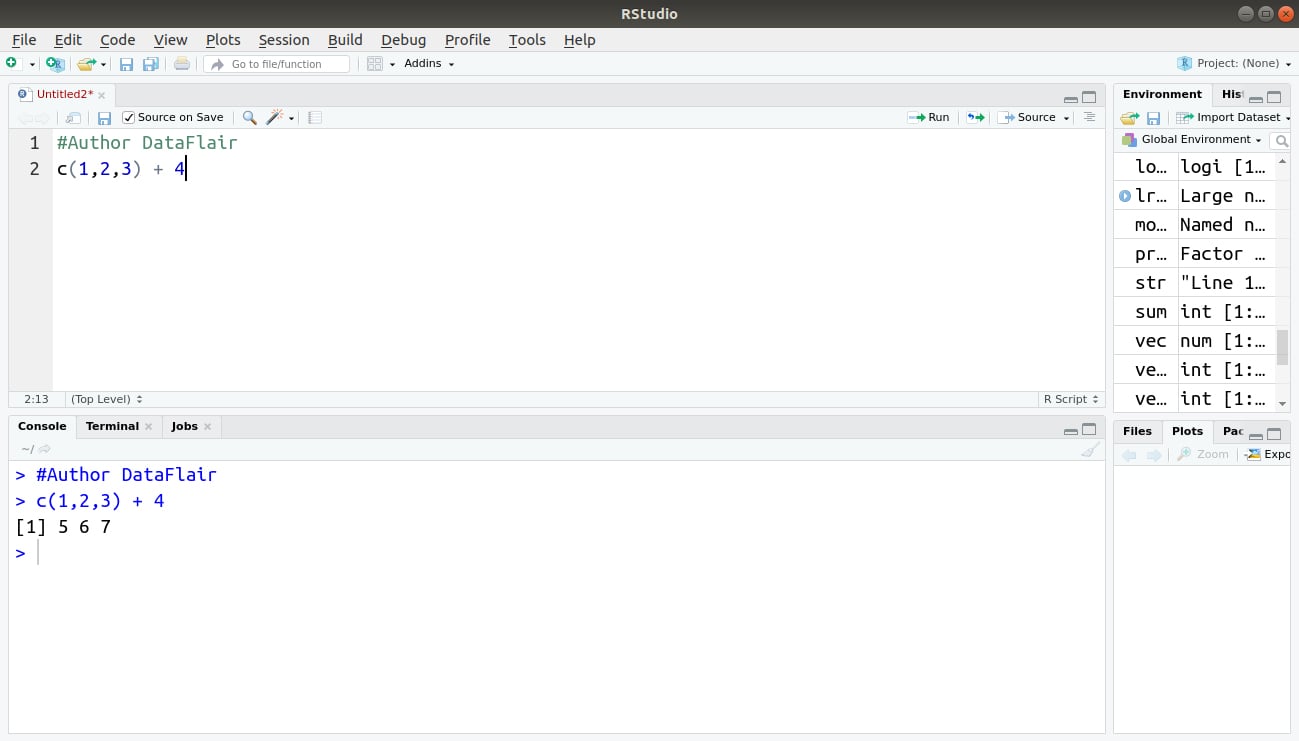
R allows operating on all list values at once.
> #Author DataFlair > c(1,2,3) + 4
This and the Apply function allow you to avoid most for loops.
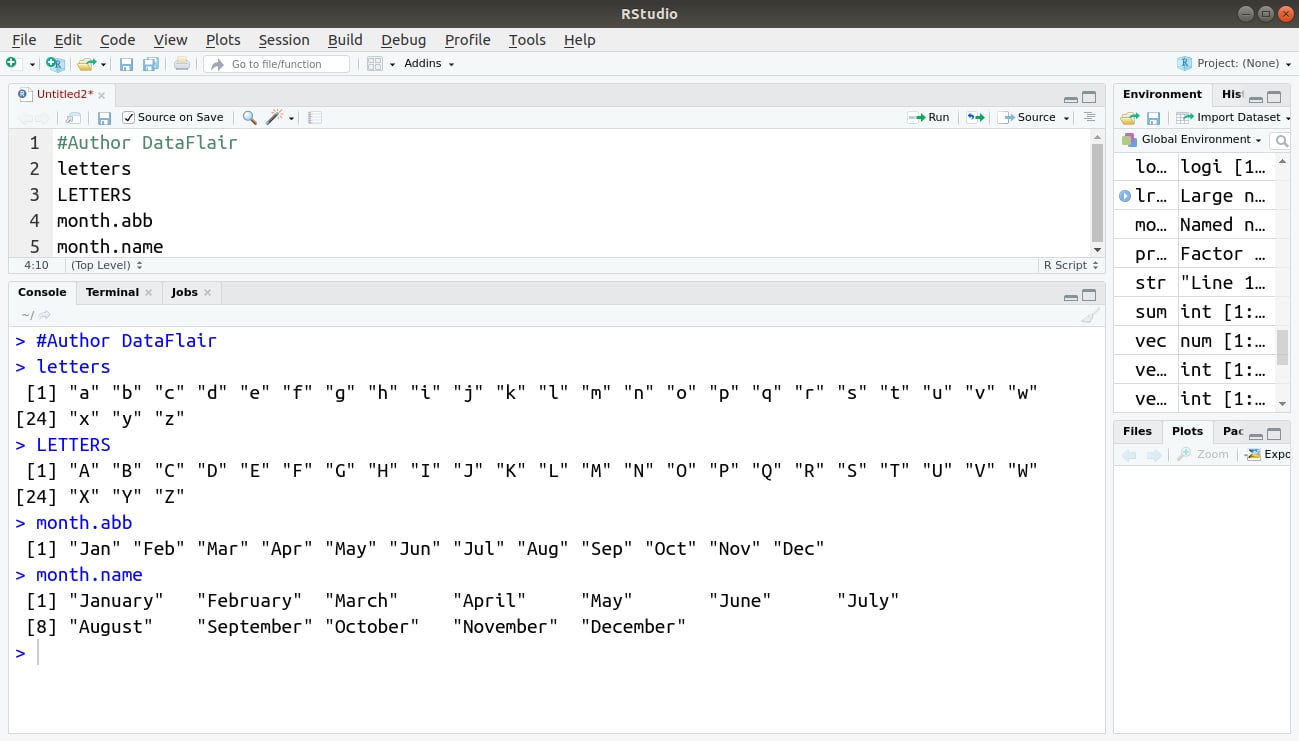
R Predefined Lists
Lists for letters and month names are predefined:
#Author DataFlair letters LETTERS month.abb month.name
Output:
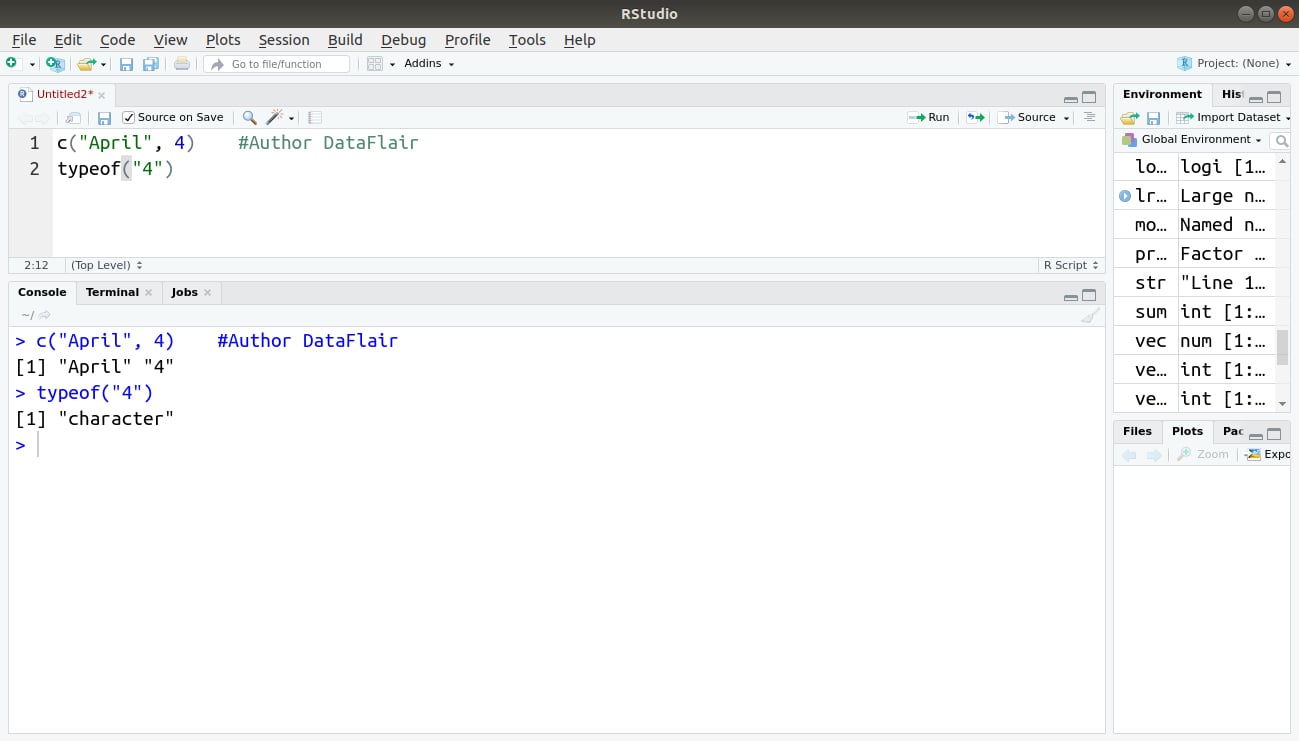
c function in R
The c function in R combines the parameter into a list and converts them to the same type.
For example:
> c("April", 4) #Author DataFlair
> typeof("4")Here 4 is converts into a string.
Summary
We have studied the R list in the above-mentioned information. We all are aware, that lists are the object which contains elements of different types like strings, numbers, and vectors. Thus, it is necessary to learn how to apply different operations on list elements.
Now, it’s the turn of R Array Function Tutorial
If you like this post on R list, or you have any query to understand Lists in R. So, please drop me a comment below.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder
Please share your happy experience on Google



I’m having trouble filling a list with other lists dynamically – that’s what I would like to see.
Can you please share the particular code in which you are facing issues?
Hi, I’m having difficulty mutating the list.
See the code below
vec <- c(1:4)
str <- c('Joy', 'Peace', 'Long-suffering', 'Love')
make_list <- list(vec, str)
names(make_list) <- c('vector', 'string')
make_list[2] <- c('God', 'Jesus', 'Holy Spirit', 'Love')
#This is where the problem is. It only takes the first character 'God', whereas I expect it to take all the characters
print(make_list)
Hey Mc Quirer,
Here is the solution to your problem.
To access and replace elements of a list, you should use double square brackets. Therefore, this should work:
Make_list[[2]] <- c('God', 'Jesus', 'Holy Spirit', 'Love')
Hi, I’m having difficulty mutating the list.
See the code below
vec <- c(1:4)
str <- c('Joy', 'Peace', 'Long-suffering', 'Love')
make_list <- list(vec, str)
names(make_list) <- c('vector', 'string')
make_list[2] <- c('God', 'Jesus', 'Holy Spirit', 'Love')
#This is where the problem is. It only takes the first character 'God', whereas I expect it to take all the characters
print(make_list)
under “Update the 3rd Element” what is the difference between:
data_list[3] <- "updated element"
and
data_list[[3]] <- "updated element"
The second looks more consistent since the rhs ain't a list
In Python we can add 2 lists
but in R why i am not able to add them..?
#operation
L=list(1,23,4,56,100)
#L[5]=100
L3=list(23,4,5,67,700)
#L3[5]=700
#Adding
Add=L+L3
R does not recognize lists as being numeric so you can’t perform numeric operations on them. You would need to coerce them to numeric vectors and then you could add them together.
This would add each element to each corresponding element and output a new vector of the same length as the original lists.
Add = as.numeric(L) + as.numeric(L3)
Or you could add individual elements
Add2 = as.numeric(L[3]) + as.numeric(L[5])
Hi! Can you please explain how to export the list of lists, created by a function in R? Something similar to save.csv(). Thanks!
‘number of items to replace is not a multiple of replacement length’.What does this error mean?