Android Application Components with Implementation & Examples
FREE Online Courses: Your Passport to Excellence - Start Now
In this part of Android Tutorial, we will explain various Android Application Components used in Android development. There are four basic components and some additional application components, which we will learn in detail.
Android applications are developed using JAVA, Kotlin, and C++. Application components are very essential for building Applications. They work as an entry point for users or system to enter your application. There are four different types of components. Each component has its own purpose and distinct life cycle.
Android Application Components
The basic components of an Android application are:
1. Activities
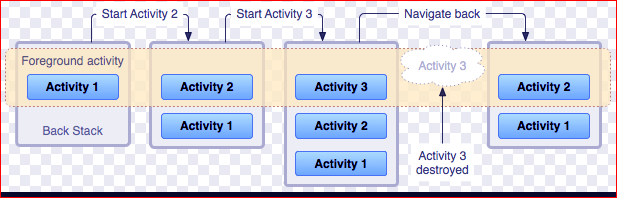
An activity is a class that is considered as an entry point for users that represents a single screen. A messenger application might have an activity that shows a new notification, another activity which reads messages and another which composes a new message.
Each activity is independent of one another. For example – camera application can be started in an email application to compose an email that shares an image. The picture below depicts how each new activity adds an item to back stack and how the current activity is destroyed and previous activity is resumed. We will study the life cycle of activity in detail in our Android Activity article.
To implement an activity, extend the Activity class in your subclass:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
//code
}2. Services
A service is a component that runs in the background, it acts as an invisible worker of our application. It keeps updating data sources and activities. It also broadcasts intents and performs tasks when applications are not active. An example of service is we can surf the internet or use any other application while listening to music.
To execute services, extend the Services class in your sub-class:
public class MyService extends Services {
//code
}Explore Android Services Tutorial and get a detailed insight into the concept
3. Content Providers
Content Provider is a component that allows applications to share data among multiple applications. It hides the details of the database and can be used to read and write private data of the application which is not shared. It would be a mess to access data from other applications without content providers.
For example – you can consider looking for contact details in contact list. Or You might want photos from the gallery which are also provided by Content Provider.
To implement this, extend ContentProvider in your subclass:
public class Provider_Name extendsContentProvider {
//code
}4. Broadcast Receiver
Broadcast Receiver is a component that responds to broadcast messages from another application or the same system. It can also deliver broadcasts to applications that are not running. For example – notify the user that the battery is low. Android developers can use broadcast messages in the application or outside the normal flow.
To implement this, extend BroadcastReceiver to your receiver:
public class Broadcast_Name extendsBroadcastReceiver {
//code
}Get a thorough understanding of Android Broadcast Receiver
Additional Components of Android Application
Some additional components of an android application:
1. Intents
It is an inter-application message passing framework for communication between android components. It is also used for transferring data between different Activities as well as to start a new service and display a list of contacts in ListView. Example – the camera application sends an intent to the operating system when the user decides to share a picture.
2. Widgets
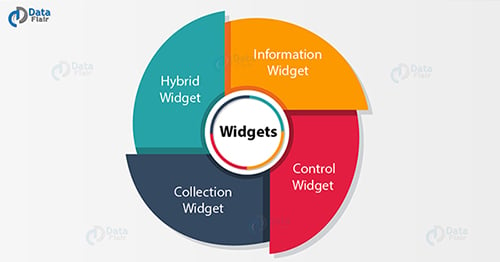
Widgets are variations of Broadcast Receivers and essential aspects of home screen customization. They display data and allow users to perform actions on them. There are various types of widgets:
- Information widget: These widgets display crucial information and track how the information changes over time. Example – Clock widgets and widgets that display weather and time information.
- Collection widget: As the name depicts, collection widgets are a collection of information of the same type. Its use is for browsing information and opening any one of the elements to view details. Example – music widgets, as we can skip pause and play music outside the music application.
- Control widget: These widgets display functionalities and by using them, the user can trigger from home screen without opening the application. Example – pause and play the video outside the application.
- Hybrid widget: These widgets combine features of all the other three widgets. Example – music player widget is a control widget but it also informs the user about which track is playing currently, which means it is a combination of control and information thus it is termed as hybrid widget.
3. Views
View is responsible for drawing and event handling. They are rectangular elements on the screen. Some of the views are EditText, ImageView Button, CheckBox and ImageButton.
4. Notifications
It alerts users when the application is not visible or is inactive. This alert flashes on the screen and then disappears. Example – Notification of the new incoming message popped on the screen.
5. Fragments
A fragment is a portion of the total user interface. Users can combine more than one fragment in a single activity and these fragments can be reused in multiple activities. A fragment generally contains Views and ViewGroups inside them.
6. Layout XML Files
Layout is the structure for the user interface in the application. XML files provide different types of layouts for the different type of screen, it also specifies which GUI component, an activity or fragment holds.
7. App APK files
Apk file is the package file format that contains the program’s code, resources, assets. The Android operating system uses them for installing mobile applications and middleware.
8. Resources
Resources in Android is for defining Images, texts, string values. Everything is defined in the resource file and it can be referenced within the source code. We will learn about Android Resources, in detail in our next upcoming article on Resources.
Summary
In this Android tutorial, we studied basic Android’s Application components and some additional components used for android application development. Also, we tried to explain each application component clearly still if any doubts or feedback related to article, please do comment and let us know.
If you are Happy with DataFlair, do not forget to make us happy with your positive feedback on Google


I feel as if I have discovered a gold mine of knowledge. Thank you so much for sharing all of this!
a-g-r-e-e
what is java tell in detal
idont know
Android is an operating system that is built basically for Mobile phones. It is based on the Linux Kernel and other open-source software and is developed by Google. It is used for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. But nowadays these are used in Android Auto cars, TV, watches, camera, etc. It has been one of the best-selling OS for smartphones.
Thanks for most important details share