Spark Machine Learning with R: An Introductory Guide
1. Objective
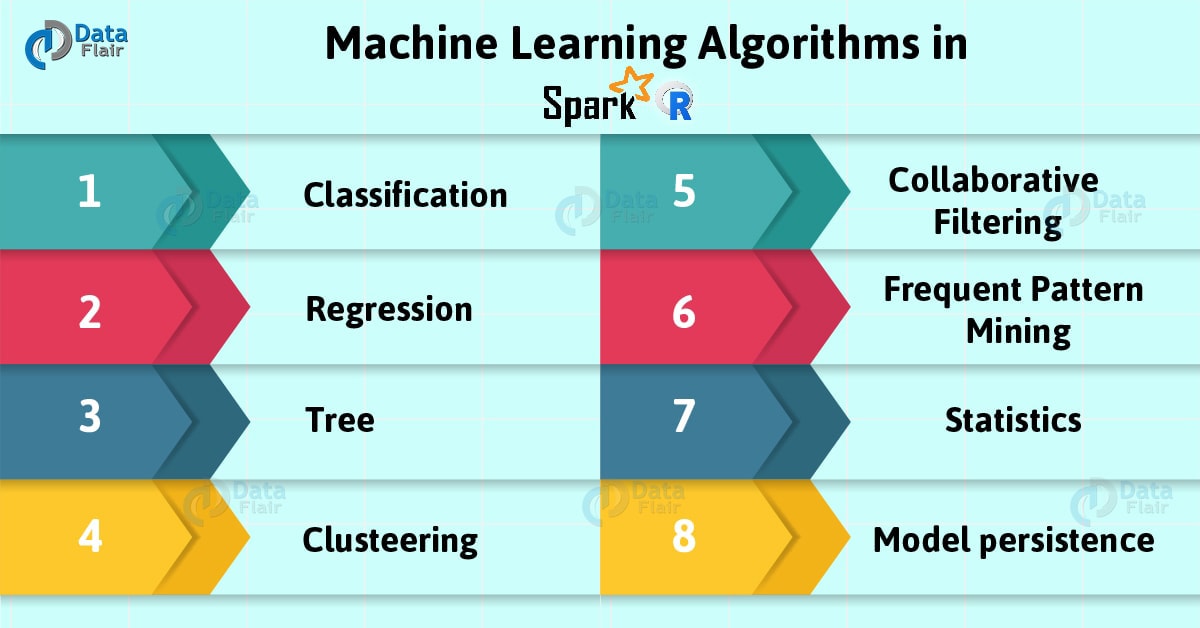
Today, in this Spark tutorial, we will learn several SparkR Machine Learning algorithms supported by Spark. Such as Classification, Regression, Tree, Clustering, Collaborative Filtering, Frequent Pattern Mining, Statistics, and Model persistence. we will learn all these in detail. Moreover, we will learn a few examples to understand Spark Machine Learning with R in a better way.
So, let’s start Spark machine Learning with R.
2. Spark Machine Learning with R
The following Spark machine learning algorithms using R supports currently are,
a. Machine Learning Classification
spark.logit: Logistic Regression
spark.mlp: Multilayer Perceptron (MLP)
spark.naiveBayes: Naive Bayes
spark.svmLinear: Linear Support Vector Machine
b. Machine Learning Regression
spark.survreg: Accelerated Failure Time (AFT) Survival Model
spark.glm or glm: Generalized Linear Model (GLM)
spark.isoreg: Isotonic Regression
Let’s have a look at Apache Spark Machine Learning Algorithm
c. Machine Learning Tree
spark.gbt: Gradient Boosted Trees for Regression and Classification
spark.randomForest: Random Forest for Regression and Classification
d. Machine Learning Clustering
spark.bisectingKmeans: Bisecting k-means
spark.gaussianMixture: Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM)
spark.kmeans: K-Means
spark.lda: Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
e. Machine Learning Collaborative Filtering
spark.als: Alternating Least Squares (ALS)
Frequent Pattern Mining
spark.fpGrowth : FP-growth
f. Statistical Machine Learning
spark.kstest: Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
Basically, SparkR uses MLlib to train the model. Moreover, it supports a subset of the available R formula operators. For example, model fitting, including ‘~’, ‘.’, ‘:’, ‘+’, and ‘-‘.
g. Model persistence in Machine Learning
Here, below example shows how to save/load an MLlib model by SparkR.
For example,
training <- read.df(“data/mllib/sample_multiclass_classification_data.txt”, source = “libsvm”)
# Fit a generalized linear model of family “gaussian” with spark.glm
df_list <- randomSplit(training, c(7,3), 2)
gaussianDF <- df_list[[1]]
gaussianTestDF <- df_list[[2]]
gaussianGLM <- spark.glm(gaussianDF, label ~ features, family = “gaussian”)
Let’s discuss Data Types in Spark Machine Learning
# Save and then load a fitted MLlib model
modelPath <- tempfile(pattern = “ml”, fileext = “.tmp”)
write.ml(gaussianGLM, modelPath)
gaussianGLM2 <- read.ml(modelPath)
# Check model summary
summary(gaussianGLM2)
# Check model prediction
gaussianPredictions <- predict(gaussianGLM2, gaussianTestDF)
head(gaussianPredictions)
unlink(modelPath)
3. Conclusion
As a result, we have seen all the Spark machine learning with R. Also, we have seen various examples to learn machine learning algorithm using spark R well. However, if you feel for any query, feel free to ask in the comment section.
See also –
RDD Lineage in Spark
For Reference.
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google