30 Most Asked Django Interview Questions – Unlock Your Success in 2023
Python course with 57 real-time projects - Learn Python
FREE Online Courses: Enroll Now, Thank us Later!
Django is a great framework and will be in high demand in 2023. You may get the job opportunity in the field of Django that you desire.
So, this tutorial will help you to practice some Django interview questions and answers, which are very important to showcase your understanding in an interview.
Bookmark the complete series of Django interview questions for your interview preparation:
- Django Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
- Django Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
Let’s start your interview preparation with some tricky Django interview questions.
Latest Django Interview Questions and Answers for 2023
Below are the top Django interview questions and answers that will surely boost your confidence in interview preparation.
Q.1 What is Django? Elaborate some technical features of Django.
Ans. Django is a high-level web application framework based on Python.
This framework is one of the best in the industry for rapid development, pragmatic design without compromising on features.
Some of the technical features of Django include:
- Admin Interface
- Code Reusability
- CDN Integration
- Security Features
- ORM
- A huge number of third-party applications
There are many features which Django community has been developing over the years and therefore it’s called “Batteries-Included” framework, as it has lots of features built-in which otherwise would be time-consuming and expensive to make.
Check out other unique features of Django in detail
Q.2 What is Django Admin Interface?
Ans. Django Admin is the preloaded interface made to fulfill the need of web developers as they won’t need to make another admin panel which is time-consuming and expensive.
Django Admin is application imported from django.contrib packages.
It is meant to be operated by the organization itself and therefore doesn’t need the extensive frontend.
Django’s Admin interface has its own user authentication and most of the general features.
It also offers lots of advanced features like authorization access, managing different models, CMS (Content Management System), etc.
Q.3 How is Django’s code reusability feature different from other frameworks?
Ans. Django framework offers more code-reusability than other frameworks out there.
As Django Project is a collection of different applications like login application, signup application.
These applications can be just copied from one directory to another with some tweaks to settings.py file and you won’t need to write new signup application from scratch.
That’s why Django is a rapid development framework and this level of code reusability is not there in other frameworks.
Q.4 Explain the file structure of a typical Django project?
Ans. A Django project is a collection of web-applications that coordinate together to serve the request of the user.
These applications have one assigned feature and shall do only that.
A typical Django project consists of these four files:
- manage.py
- settings.py
- __init__.py
- urls.py
- wsgi.py
The last four files are inside a directory, which is at the same level of manage.py.
Here the structure is very logical, and the names of these files and their purpose should remain intact.
manage.py is the command-line utility of your Django project and this file is used to control your Django project on the server or even to begin one.
When Django server is started, the manage.py file searches for settings.py file, which contains information of all the applications installed in the project, middleware used, database connections and path to the main urls config.
The urls.py file is like a map of your whole web-project, this file examines URL and calls the right view function or transports the URL to another application-specific urls-config file.
This is like the main URL linker and any app installed in the settings.py which you wish to be searched by the URL should have a link here.
The __init__.py file is an empty file which is there to make the python interpreter understand that the directory consisting settings.py is a module/ package.
The wsgi.py file is for the server format WSGI, which Django supports natively. We can customize that for other server formats.
Note – This one is the most popular Django interview question.
Q.5 Django is an MVC based framework, how this framework implements MVC?
Ans. Django is based on MTV architecture which is a variant of MVC architecture.
MVC is an acronym for Model, View, and Controller.
There are different parts of a website so that they can develop and execute in different machines to achieve faster and more responsive websites.
Django implements MTV architecture by having 3 different components and they are all handled by Django itself.
Models are the part which is models.py file in a Django application, which defines the data structure of the particular application.
View are the mediators between models and templates, they receive the data from the Model and make it a dictionary and return the same as a response to a request to the Template.
The Template is the component with which user interacts, and it generates both statically and dynamically in the Django server.
That’s how the Django implements 3 components and work in coordination with each other.
Q.6 What happens when a typical Django website gets a request? Explain.
Ans. When a user enters a URL in the browser the same request is received by the Django Server.
The server then looks for the match of the requested URL in its URL-config and if the URL matches, it returns the corresponding view function.
It will then request the data from the Model of that application, if any data is required and pass it to the corresponding template which is then rendered in the browser, otherwise, a 404 error is returned.
There are multiple phases required in processing a request that is sent to a standard Django website in order to get a response. An outline of what transpires when a request is made to a Django website is provided below:
Mapping URLs: Finding the URL of the incoming request is the first step. To match the given URL to a specific view function that will handle the request, Django employs its URL dispatcher.
Viewing Method: Django invokes the matching view function linked to that URL pattern after mapping the URL to a view function. The request must be processed and a response must be produced by the view function.
Processing of Requests:When a request comes in, it comprises information like the requested URL, HTTP method (GET, POST, etc.), form data, and any other data supplied in the request headers. These pieces of information are given to the view function.
Processing data: The view function may need to obtain or alter data from the database or carry out additional data processing operations, depending on the nature of the request.
rendering of a template: The template engine of Django is frequently used by the view function to render dynamic content. It could send information to a template file that combines HTML markup with variables and template elements.
Creation of Responses: The view function produces a response after processing the request and rendering the template (if necessary). The reply may come in HTML, JSON, XML, or plain text, among other forms.
Execution of middleware: The response passes through a number of middleware components before it is returned to the client. Middleware may handle functions like authentication, caching, and error handling and provides a mechanism to process requests and responses worldwide.
Client response sent: Django sends the response back to the client (often a web browser) through HTTP as soon as it has been entirely processed.
Customer Contact: After receiving the Django server’s response, the client (web browser) displays the content for the user. The browser shows the user the answer if it was an HTML page.
Q.7 What is the Controller in the MVC framework of Django?
Ans. As Django implements in MTV framework, these three components communicate with each other via the controller and that controller is actually Django framework.
Django framework does the controlling part itself.
Q.8 Is Django’s Admin Interface customizable? If yes, then How?
Ans. Django’s Admin is just one of the applications and very customizable, also you can download a different third-party application and install it for a totally different view.
You can make your own Admin Application if you want complete control over your Admin.
Although you can customize the Django Admin site like changing the properties of admin.site object.
We can also make some changes in particular models and apply them in our Django Admin for particular apps like we can add a search bar for particular applications.
The Django Admin Interface is fully customizable to the lowest level, but instead of customizing that much, we can rather create a new Admin Interface.
So those who don’t like Django Admin Interface, prefer making a new one from scratch then editing the previous one.
Q.9 Why is Django called a loosely coupled framework?
Ans. Django is called a loosely coupled framework because of the MTV architecture it’s based on.
Django’s architecture is a variant of MVC architecture and MTV is useful because it completely separates server code from the client’s machine.
Django’s Models and Views are present on the client machine and only templates return to the client, which are essentially HTML, CSS code and contains the required data from the models.
These components are totally different from each other and therefore, front-end developers and backend developers can work simultaneously on the project as these two parts changing will have little to no effect on each other when changed.
Therefore, Django is a loosely coupled framework.
Note – This one is the favorite Django interview question of many interviewees.
Q.10 What is Django Rest Framework (DRF)?
Ans. Django REST is a framework which lets you create RESTful APIs rapidly.
This framework has got funding by many big organizations and is popular because of its features over Django frameworks like Serialisation, Authentication policies and Web-browsable API.
RESTful APIs are perfect for web applications since they use low bandwidth and are designed such that they work well with communications over the Internet like GET, POST, PUT, etc.
Q.11 Explain the importance of settings.py file and what data/ settings it contains.
Ans. When Django server starts, it first looks for settings.py. As the name settings, it is the main settings file of your web application.
Everything inside your Django project like databases, backend engines, middlewares, installed applications, main URL configurations, static file addresses, templating engines, allowed hosts and servers and security key stores in this file as a list or dictionary.
So, when your Django server starts it executes settings.py file and then loads particular engines and databases so that when a request is given it can serve the same quickly.
Q.12 Why Django uses regular expressions to define URLs? Is it necessary to use them?
Ans. Django uses a very powerful format for storing URLs, that is regular expressions.
RegEx or regular expression is the format for sophisticated string searching algorithms. It makes the searching process faster.
Although it’s not necessary to use RegEx when defining URLs.
They can be defined as normal string also, Django server should still be able to match them, but when you need to pass some data from the user via URL, then RegEx is used.
The RegEx also makes much cleaner URLs then other formats.
Q.13 What is Django ORM?
Ans. Django ORM is one of the special feature-rich tools in Django. ORM is an acronym for Object-Relational Mapper.
This ORM enables a developer to interact with a database in a pythonic way.
Django ORM is the abstraction between models (web application data-structure) and the database where the data is stored.
It makes possible to retrieve, save, delete and perform other operations over the database without ever writing any SQL code.
It also covers many loopholes and takes all the field attributes and gives you more control over your code in Python rather than any database language.
Q.14 What is a Model in Django and what is the Model class?
Ans. A Model in Django is a python class which derives from Model class that imports from the django.db.models library.
The concept of Django Models is to create objects that can store data from the user in a user-defined format.
Therefore, python class is used for the process and that class is generally defined in models.py file of the particular application.
The model class is a pre-defined class of Django framework and every class which is a model must derive from the same.
The model class has lots of benefits like you can define the field with specific attributes as you would do in SQL, but now the same can be achieved in Python.
Django Model class is parsed by the Django ORM or backend engine and you won’t need to do anything related to the database, like creating tables and defining fields afterward mapping the fields with the attribute of the class.
Q.15 How does Django Templating Work?
Ans. Django Templates are Django’s answer to generate dynamic web pages. Templates, in general, are the HTML or the formats which can return as an Http response.
Django templating engine handles templating in the Django framework.
There are some template syntaxes which declares variables, control logic, filters, and comments.
After putting these inside the HTML structure, when the web page is requested and called upon by the view function, the Django Template engine gets two things, the HTML structure with variables in place and the data to replace with those variables.
It replaces the variables with data while also executing the control logic and generating filters.
It renders the required HTML and sends it to the browser when all the work gets complete.
Q.16 What are View functions? Can we directly import a function in URL?
Ans. The View is the middle component in Django that receives data from the Django models and pass the same to the Templates.
Every application in Django comes with views.py file, this file contains the View functions.
The View functions are functions which receive an argument and they return a browser-renderable format or a redirect.
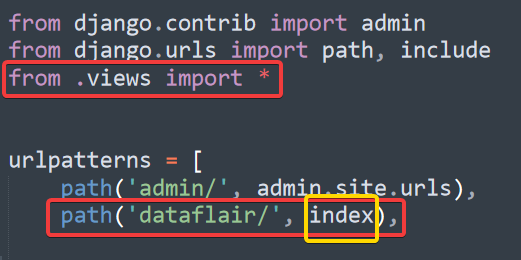
Django Views function can import directly in the urls file.
For that, we have to first import the view function in the urls.py file and then add the path/ URL which browser should request to call that View function.
Here as you can see that we imported all the functions from our View module which is in the same folder.
We added the URL in the urlpatterns list (red box). When the ‘dataflair/’ gets searched in the yellow box, we have called a function named index.
Q.17 What is django.shortcuts.render function?
Ans. When a View function returns a webpage as HttpResponse rather than a simple string, we use render().
Render function is a shortcut function which lets the developer to easily pass the data dictionary with the template.
This function then combines the template with data dictionary via templating engine.
Finally, this render() returns an HttpResponse with the rendered text, which is the data returned by the models.
Thus, Django render() bypasses lots of work for the developer and lets him use different templating engines.
It is because this function provides the same functionality with other templating systems.
The basic render Syntax:
render(request, template_name, context=None, content_type=None, status=None, using=None)
The request is the parameter which generates the response, the template_name containing the value where the template is stored.
The template name and other parameters are for passing the dictionary.
If you want more control, you can specify the content type, status of the data you passed and the render you are returning. That is the render().
Note – This one is a bit difficult Django interview question. Make sure to prepare it thoroughly.
Q.18 List some ways by which we can add our View functions to urls.py file?
Ans. We can add our view to the main urls config in two ways:
1. Adding a function View
In this method, we import our view as function.
We import the function itself from the particular view and then, add the particular URL to the urlpatterns list.
2. Adding a Class-based view
The class-based view is a more object-oriented approach.
To begin, import the class from the views.py and then add the URL to the urlpatterns. This time we will need an inbuilt method to call the class as a view.
In the name of the function on the previous method, write
class_name.as_view()
This will pass your view class as view function.
Both class-based views and function-based views have their own pros and cons and we can use them in the appropriate situations to get the right results.
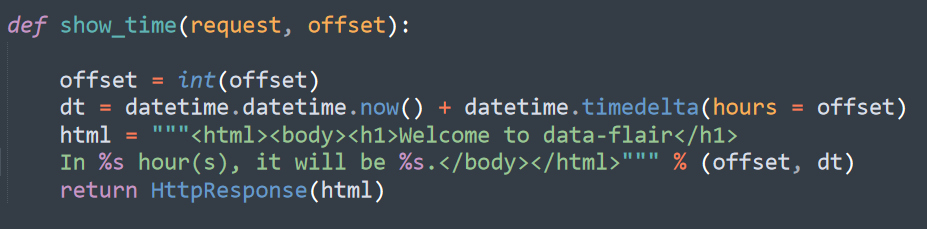
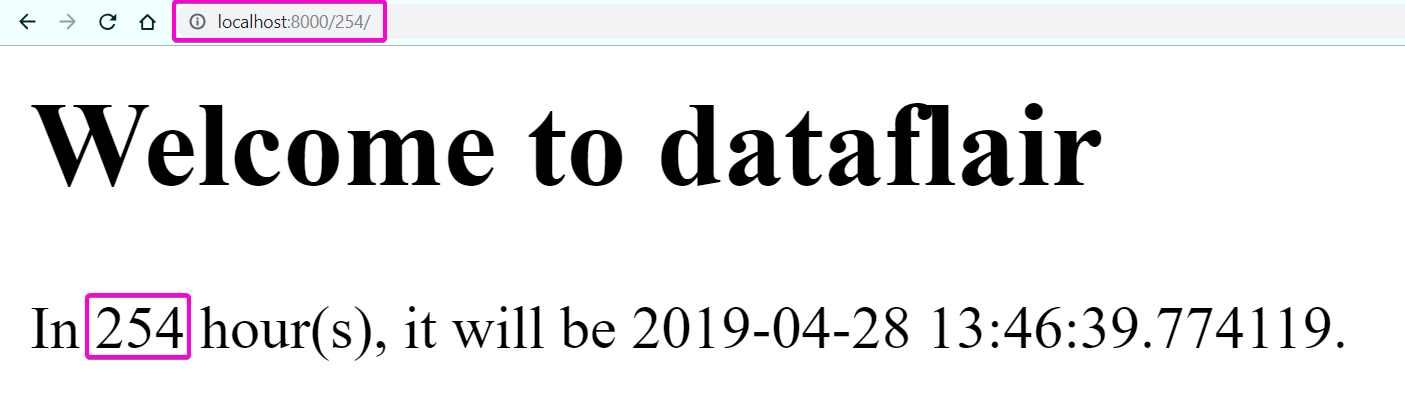
Q.19 How can we extract the data from the request/ URL and pass the same to the View function?
Ans. We can very easily take some input via URL request and generate something dynamically via the same input.
Here focus on the pink box, where a regular expression as URL is present. It will perform an important task that is checking the URL which has 3 or fewer digits.
That code will call the show_time() in the Views file and here as you can see we are passing two values in the request.
The other one is offset, which is a variable containing the numerical value which we entered after the URL.
So when the Django server gets the URL, it snips off the rest part and compares it with regex by automatically passing the numerical part or the part which is random in RegEx.
After that, it transfers to the function, where we are converting the same in integer type as, by default, python takes the URL requests as strings.
Then we execute regular python statements and we get a rendered application.
Q.20 What does urls-config file contain?
Ans. The URLs-config in Django contains the list of urls and the mappings to view functions for those urls.
The urls can map to view functions, Class-based views and urls-config of another application. All these methods have their use-cases.
For example – If we want to keep all the URLs of our application sorted, we will use the URL-config mapping. Inside urls file, we will use view function mapping and class-based views if we require some data from the user.
Q.21 How does Django compare to other popular frameworks like Laravel?
Ans. Django has many unique features, the top-line is that Django allows for rapid development of applications without any security loopholes or performance lacking.
Some of the features which Laravel doesn’t have but Django implies are:
- Laravel is PHP based while Django is Python-based, which is clearly more powerful and robust then PHP.
- The performance of Django is better than Laravel because of the different programming languages it uses.
- Django is based on MTV architecture, a more robust and loosely coupled architecture while Laravel is strictly based on MVC architecture.
- Django can use RegEx (as used in the previous answer), while Laravel doesn’t provide you with that functionality.
Q.22 Django is too monolithic. Explain this statement.
Ans. Django framework is too monolithic, which is true to some extent.
Django is MTV architecture-based framework and since Django is the controller of the architecture, it requires some rules that the developer should follow so that the framework can find and execute appropriate files at the right time.
Therefore, Django is one of the frameworks where file structure is as important as its architecture.
In Django, you get great customizability with the implementations.
There is just one condition that you cannot change the file names, the pre-defined lists, and variable names.
You can create new ones but you can’t change the predefined variables for which people say that they always have to follow a certain pattern while working on Django.
Django’s file structure is one of the most logical workflows.
The monolithic behavior is actually helping the developers to easily understand the project.
Even, when the company changes, the project layout remains the same.
Therefore, the developer would take less time to understand every aspect, will be able to perform more work productively.
Q.23 What is the latest release of Django framework? What are its features?
Ans. Django’s latest version is Django 3.0. Some new features of Django 3.0 are:
- ASGI Support for Async Programming
- It supports MariaDB 10.1 and higher
- Custom enumeration types TextChoices, IntegerChoices, and Choices are now available as a way to define model field choices
- Exclusion constraints on PostgreSQL
- Filter expressions
Q.24 What is Jinja Templating?
Ans. Django supports many popular templating engines and by default, it comes with one very powerful templating engine.
Jinja Templating is a very popular templating engine for Python, the latest version in the market is Jinja 2.
There are some features of Jinja templating that make it a better option than the default template system in Django.
- Sandbox Execution – This is like a sandbox or a protected framework for automating the testing process.
- HTML Escaping – Jinja 2 provides automatic HTML Escaping, as <, >, & characters have special values in templates and if used as regular text, these symbols can lead to XSS Attacks which Jinja deals with automatically.
- Template Inheritance
- Generates HTML templates much faster than default engine
- Easier to debug, compared to default engine.
Q.25 Why permanent redirecting is not a good option?
Ans. Permanent redirecting is not a good option because the browser caches the response generated by the permanent redirect.
This is the difference between permanent and temporary redirect. It causes all sorts of issues when you change that redirect to something different.
Since the browser has cached the redirect before, this time it won’t look on the server for the changed redirection and will load the previously saved redirect.
So, even though the developer might have redirected the user to a different page, it will still load the same page.
It is browser/ client-side operation, therefore, the user can’t even do anything about the same.
Because of this reason, permanent redirecting is not a good option as informing the users to clear their internal caching data is not good for any website.
Q.26 Why is Django better than Flask?
Ans. Django has its own unique qualities over Flask which is also a Python Framework. The key differences between them are:
- Django is a high-level Python framework while Flask is a low-level Python Framework providing you with the minimum functionality, a server would require.
- Django comes with lots of built-in functionality like Django ORM, Admin Panel, Web-templating System, Inheritance, serialization while Flask comes with a development server, NoSQL support, support for unit testing, which are already there in Django.
- Flask is more customizable than Django as Flask comes with no pre-defined structure or scaffold while Django’s file structure is fixed.
- Flask settings are user made and can be altered completely by the user. Django settings are not customizable to that degree, it has variables where only values are modifiable.
- Flask has more speed than Django when it comes to processing requests but that comes without any APIs or functionality which Django gives you in-built.
- Flask is for the developers who want more flexibility on their website and don’t need lots of built-in extra functions, while Django is for developers who want rapid development of their applications that can sustain dynamic changes to its environment.
Note – Comparison questions are very popular in the Django interview. Prepare this one nicely.
Q.27 Explain user authentication in Django?
Ans. Django comes with a built-in user authentication system, which handles objects like users, groups, user-permissions, and some cookie-based user sessions.
Django’s User authentication not only authenticates (verifying the user identity) the user but also authorizes him (determines what permissions the user have).
The system consists and operates on these objects:
- users
- Permissions
- Groups
- Password Hashing System
- Forms Validation
- A pluggable backend system
There are many third-party web applications that we can use in place of the default system as they provide much more control over user authentication with more features.
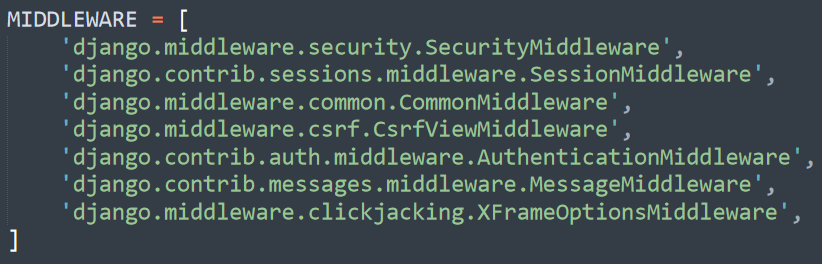
Q.28 Middleware in Django is useful for which purpose?
Ans. Middleware in the Django framework is the component that operates on request and transfers it to the view and before passing it to the template engine, it starts operating on a response.
This is the list of middleware that installs by default in your Django framework.
It serves many different purposes like session management, user authentication, etc.
Q.29 What is the use of the djangopackages.org website?
Ans. Django packages website is the place where all the third-party applications upload.
After that, you can install them in your system or in the Django project very easily.
Almost all the things that we want to implement in Django has been implemented by someone else or some organization.
The Django Software organization has made this platform for 3rd party applications.
It has all sorts of applications and organizations.
For example – Facebook and Instagram have their code open sourced on the site, therefore, we can say that the site shares some pretty decent code.
Q.30 Name some popular websites or apps using Django?
Ans. Django is a very powerful framework and there are many websites that use this framework.
Some of the highly trafficked websites using Django are:
- Disqus
- Mozilla
- Bitbucket
- YouTube
- Spotify
- NASA
- Eventbrite
There are many other websites that have shifted towards Django.
The djangosites.org is the website that shows you the list of websites registered using Django.
Summary
These are some of the Django interview questions which you won’t find on any other site.
There are some descriptive answers that will help you a lot in your understanding of the framework and to crack the interview easily.
Time to practice the Advanced Django Interview Questions and Answers
All the best for your interview!
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google



Question no 9 got incorrect answer.
Django’s Models and Views are present on the client machine but the answer should be Django’s Models and Views are present on the server machine.
I did not come here for ages and Have to say that Data flair lightened my way since I begin using Django, I took my first tutorial here about 3 years ago, and now I came by chance and found out great new inf for anyone who wants to learn Django.
Data-Flair (Big fat THANK UUUU)