SAP HANA Modeling – Attributes, Measures, Privileges, Modeling Objects
FREE Online Courses: Your Passport to Excellence - Start Now
This SAP HANA tutorial is dedicated to learning a very crucial aspect and functionality known as SAP HANA Modeling. A lot of SAP HANA’s applications are based on its capability of creating data models and business logic through modeling practices. In the sections to follow, we are going to learn about attributes and measures of, privileges required and types of modeling objects in SAP HANA.
What is SAP HANA Modeling?
Modeling in SAP HANA showcases data from the databases as a business logic or a model. We can create a data model or a view with this business logic, which we can use in reporting and analytical application such as SAP Lumira, Webi, SBEE, MS Excel etc. We can make this kind of business models by processing, integrating and transforming raw data from data sources.
That is, raw data taken from data sources is converted into business utilizable data by applying business logic on it. SAP HANA modeling is performed via the SAP HANA Studio Modeler (which is an interface) and is applied directly on the database layer (in-memory).
Thus, readymade logics from the database layer of SAP HANA are used on the application layer without transforming data in multiple layers or stages. This saves a lot of system’s time and resources, as raw data is not needed to be transferred between the database and application layer and data models, are created on the fly.
We can create modeling tools in the modeler, in which a data will process from the database according to blueprint offered by the data model. The models create on the HANA database level utilize the processing potentials of multi-core CPUs and parallel processing technologies, which we can execute by the dedicated engines in SAP HANA.
We can create a SAP HANA data model in the modeler perspective of the SAP HANA Studio. You can access the database and tables as the schemas present under the Catalog tab. Once you have created a business model having a combination of information views in it, you can access the entire list of views as a package in the Content tab present in the system view section of the Studio.
These SAP HANA information model views reside under a package name as categories based on view types. Also, within a view, the data tables are structured differently as dimension tables and fact tables (containing primary keys).
What are the attributes and measures?
The business models created in SAP HANA Modeler use data in a particular form. We can use content data within information views, as attributes and measures.
Attributes, as the name suggests, is the descriptive or contextual data which provides information on the data being used in tables. Thus, the attributes are the characteristics of data such as Country, Store, Sales ID, Customer Name, etc. Attributes are the non-measurable data types and cannot be used in calculations.
Whereas, measures are the data entries, which are calculable as well as measurable.
The views that use measures can be utilized for analytical purposes. The data as a measure can be used as Sales Amount, Product Quantity, Profit percentage, etc. There are different types of attributes as discussed below.
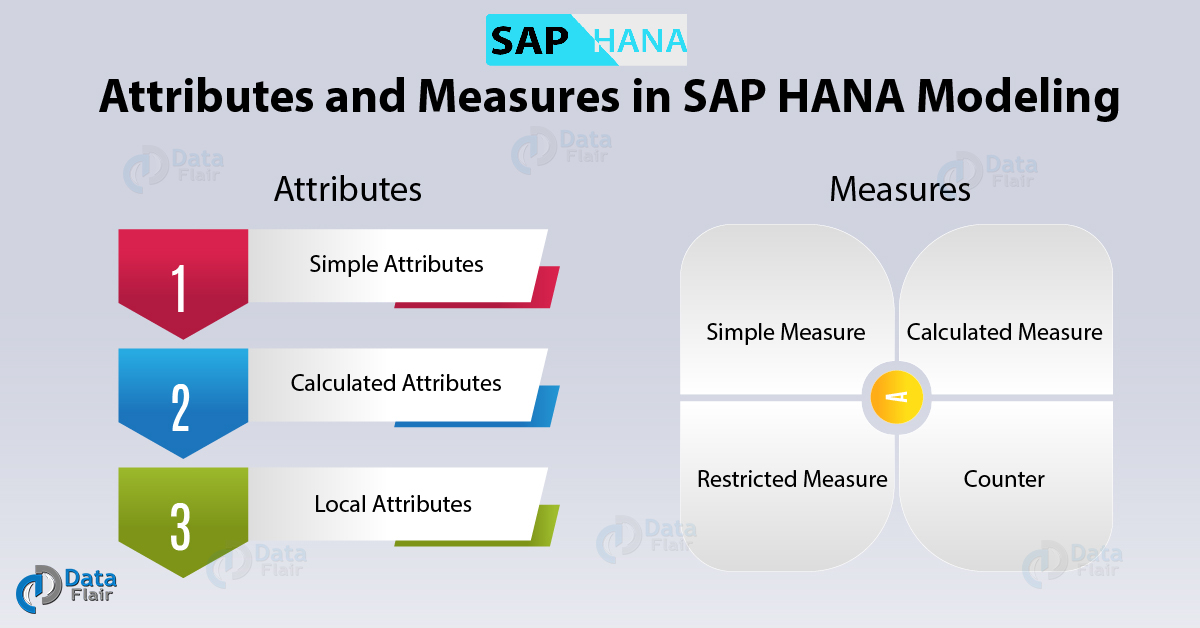
a. Types of Attributes
There are three types of attributes in SAP HANA Modeling.
- Simple Attributes- We can derive it from the data source.
- Calculated Attributes – It is created from existing attributes at the source. Such a full name created from two attributes, i.e. first name and last name.
- Local Attributes – The local or private attributes are used in modeling data in analytical or calculation views. Such attributes can be taken as a private attribute in an analytical view and can only be used in that view or model.
b. Types of measures
There are four types of measures in SAP HANA Modeling as explained below.
- Simple Measure- We can take these measures as it is from the source table.
- Calculated Measure- It is created from a combination of two measures taken from OLAP cubes, arithmetic operators, constants, functions, etc. For instance, a calculated measure would be, Profit obtained from subtracting two measures Sales price – Cost price.
- Restricted Measure- These are the filtered measure values based on a condition put on an attribute. For instance, showing the measure values for only the gross revenue on a particular car in USA (attribute).
- Counter- It is a type of column within an analytical or calculation view, which shows the count or number of attribute columns.
Types of Modeling Objects
Following are the 4 types of SAP HANA Modeling Objects, let’s discuss them one by one:
- Attribute View
- Analytic View
- Calculation View
- Decision Table
i. Attribute View
SAP HANA Attribute view uses attributes, or the non-measurable, non-quantifiable data to design views and models according to the business logic. The data in attribute view also call as ‘Master data’ and we can use it as a piece of reference information in other views (analytic and calculation). The tables in attribute view do not contain any facts or measure.
That is entries like sales amount, transaction amount, quantity sold, profit incurred etc. We can analyze all these measures by different characteristics such as year, quarter, month, vendors, sales departments, product groups etc. These characteristics also call as dimensions.
ii. Analytic View
In the SAP HANA analytic view, you can create star schemas, having a central transaction or fact table and multiple dimension tables linked to it via primary keys. We can join or group the measures, which contain in only the central transaction table with multiple dimension tables as per the logic’s requirement. An analytic view is the next layer or level of a model after the attribute view.
iii. Calculation View
SAP HANA Calculation view is a more complex model using both attribute and analytic view elements in it to make a complete business logic. Thus, it is the next level of SAP HANA modeling for more advanced transformations and logic.
In order to perform complex operations such as combining two data sets into one, we need to use the calculation view. As we inform about analytic view can measure only a transaction table.
So, if we have transaction data from two tables, say, Sales and Finance, and we wish to combine both in one data set, we can only do it in the calculation view.
iv. Decision Table
We can use Decision table for business planning and decision-making purposes. With the help of these tables, we can analyze business scenarios and situations. It answers a lot of if and else conditional queries, which helps in decision making by the enterprise. We can use to carry out such an if-else situational analysis using a graphical interface.
Privileges required for Modeling
We can use these 3 types of SAP HANA Modeling privileges, which are offering permission to a user for secure access contents from the database.
- Object Privileges
- Packages Privileges
- Analytic Privileges
i. Object Privileges
Such privileges are the read/write privileges given for SQL used to access a database. The object privileges are:
- ELECT privilege on _SYS_BI Schema.
- SELECT privilege on _SYS_BIC Schema.
- EXECUTE privilege on REPOSITORY_REST (SYS).
- SELECT privilege on Table Schema.
ii. Package Privileges
We can use package privileges to authorize an action to perform on packages. It is necessary for the data modeling:
- REPO.MAINTAIN_NATIVE_PACKAGES (a privilege on Root Package).
- REPO.READ, REPO.EDIT_NATIVE_OBJECTS & REPO.ACTIVATE_NATIVE_OBJECTS (on package used for Content Objects).
iii. Analytic Privileges
We can use analytic privilege, to access the SAP HANA information view. If you want to get full data access to use in all the information view types, select the privilege “_SYS_BI_CP_ALL”.
So, this was all about SAP HANA Modeling Tutorial. Hope, you liked our explanation.
Summary
Thus, we can do SAP HANA modeling via the Data Modeler view in SAP HANA Studio. As it is very important for you to understand the basics of data modeling in SAP HANA in order to further understand the working of systems like information modelers and its different views in the SAP HANA Studio.
Furthermore, if you have a query or doubt, feel free to ask in the comment section.
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google


What kind of requirements we will get? What kind of error you have faced in Your work?