SAP HANA Auditing – All the aspects that you need to know!
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Skills, Zero Cost. Enroll Now!
The another important topic of SAP HANA security is auditing in SAP HANA. With this tutorial, you will learn how you can audit processes and activities in SAP HANA. So stay with us to understand the concept and process of auditing in SAP HANA.
What is Auditing in SAP HANA?
Auditing is the process of monitoring and recording specific user activities in the SAP HANA system. Through auditing, SAP HANA administrator will be able to know which user performed what activity on the HANA system or database and at what time.
For better monitoring, “Audit Policy” is created that decides which events in SAP HANA you have to audit. Audit policies can be enabled on individual systems in a multiple database setup. The audit policy is defined in a nameserver.ini file for system database and in a global.ini file for tenant database.
An important aspect of auditing is to be able to trace the action performed and store all the details related to it at a target. This storage target is the “Audit trail target”.
Until SAP HANA’s SPS6, the default Audit trail target of complete audit information was Syslog of the system. But with newer versions of SAP HANA, you can also store the audit information in database tables in HANA.
Actions for SAP HANA Auditing
In SAP HANA, some typical actions performed on database or in the HANA system which are generally audited are:
- User’s authorization changes
- Creating or deleting database objects
- Authentication of users
- System configuration changes
- Audit configuration changes
- Accessing and altering sensitive information
- Logon monitoring
- SYSTEM User events
- Technical users’ actions
- Activities of exceptional users
Audit Policies in SAP HANA
The audit policies define and thus decide which activities or events in SAP HANA will be audited. The audit policies in SAP HANA also specifies the actions which are relevant for auditing. The administrators need to enable a newly created audit policy.
As the policy will not get triggered on an assigned action unless enabled manually and explicitly by the administrator. The administrator is free to enable or disable an audit policy as per requirement. To enable or disable an audit policy, the administrator must have AUDIT ADMIN privilege.
In addition to this, any user who has system privileges like AUDIT ADMIN, CATALOG READ or DATA ADMIN can view and check the existing audit policies in public view named AUDIT_POLICIES.
Activating an Audit Policy
To activate an existing audit policy in SAP HANA Studio, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Security option given under the Security node of a SAP HANA system.
2. Open Auditing tab in the window that opens.
3. Notice the Global Settings section. Change the Auditing Status from Disabled to Enabled.
4. You can also select the Audit Trail Target from the three given options i.e. Database Table, Syslog, CSV Text. Click on the green deploy button given on the top bar to implement the changes.
This is how you can enable an audit policy.
In addition to this, you can add or create new policies from the Audit Policy section. Click on the green + sign and add an existing policy or create a new one by entering the name of the policy, select audited actions for it, select audited actions status, audit level, users, target objects, audit trail target, etc.
Also, from this section, you can disable a policy or delete a policy using the red cross button.
Auditing in SAP HANA Cockpit
To create and manage auditing policies for SAP HANA system, you can use SAP HANA Cockpit as well. The SAP HANA Cockpit contains an auditing app using which you can carry out auditing activities for a specific HANA system.
Using the auditing option, you can create a new audit policy. The steps include naming a new policy, then selecting an action in SAP HANA on which auditing will take place.
Next, you will select a location, “Audit trail target” where the results of auditing process will save. To perform auditing activities in SAP HANA Cockpit, you need to have the role
“sap.hana.security.cockpit.roles::MaintainAuditPolicy” beforehand.
Let’s learn the process in detail.
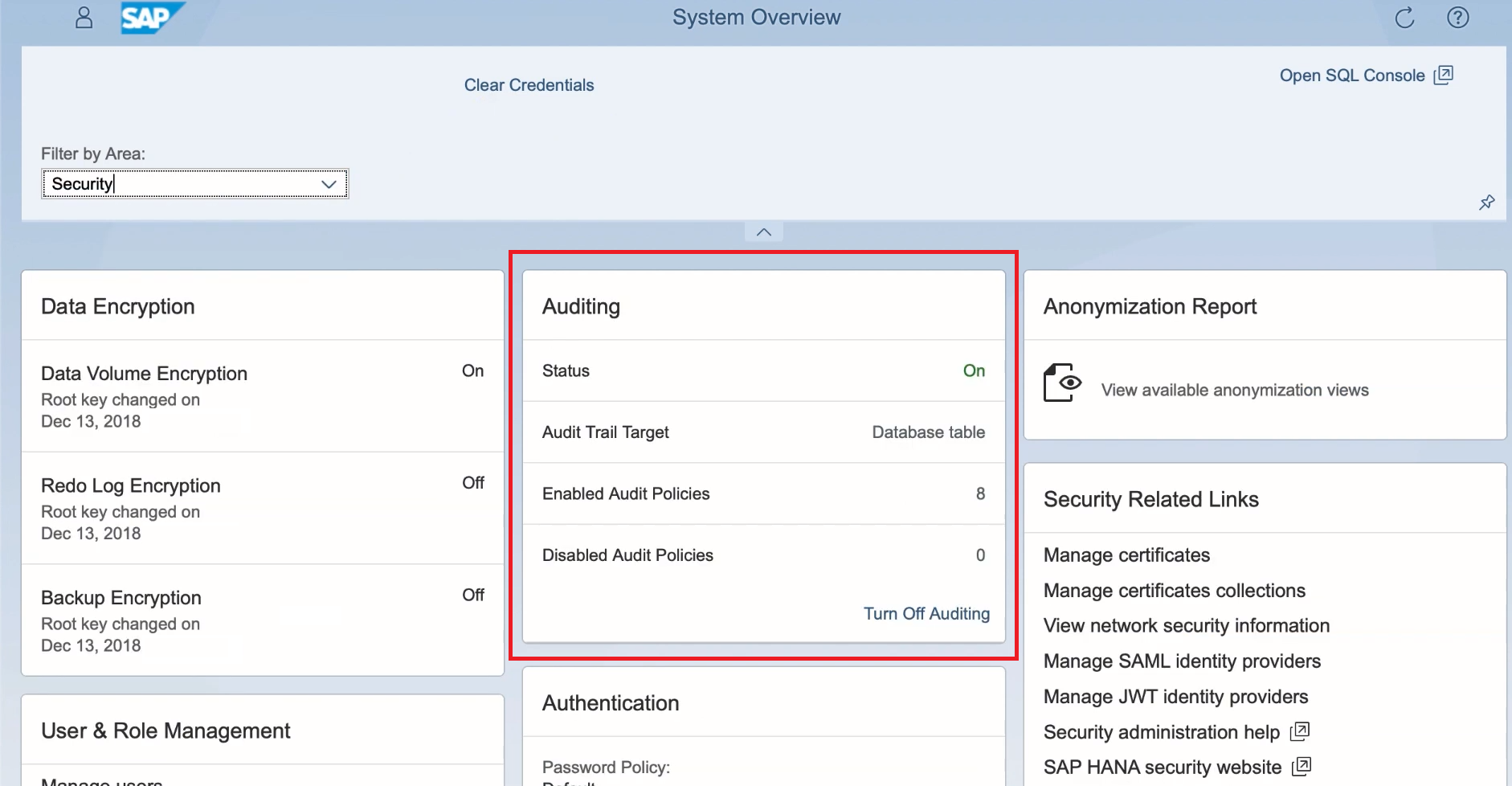
1. Open SAP HANA Cockpit. In the System Overview tab, select the Security option.
2. On the security page, there is an Auditing tile which shows general information regarding a HANA system auditing. It shows the status of auditing process, audit trail target (i.e. the location where auditing results save), number of enabled audit policies, disabled policies, etc. You can also turn off auditing from here.
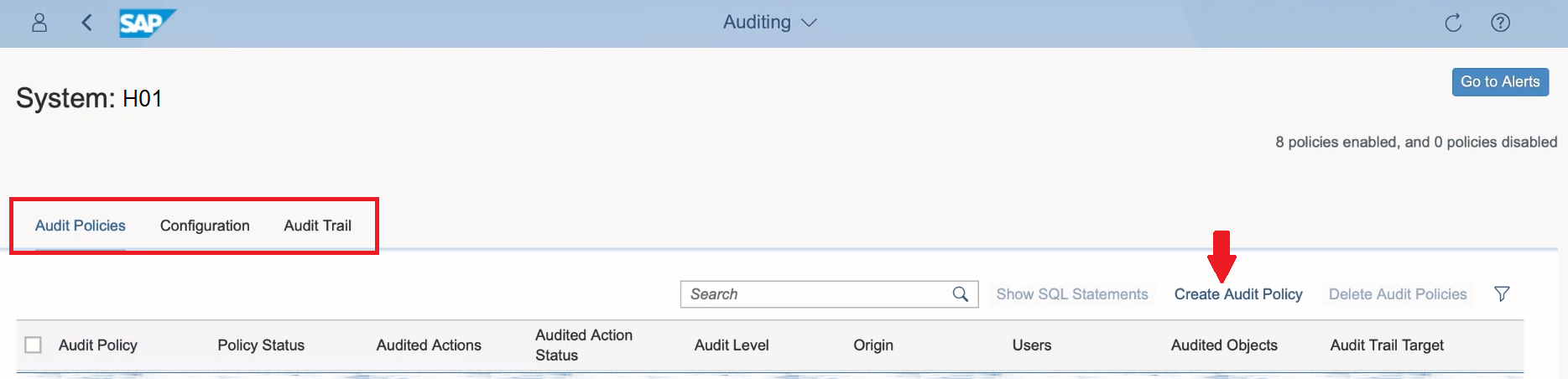
3. Click on the tile to open the auditing app. In the auditing app window, you have three tabs (Audit Policies, Configuration, Audit Trail) to manage the auditing policies and actions related to it. To create a new audit policy, select the Create Audit Policy option.
4. In the next few steps you will have a wizard like guided experience to create a new audit policy.
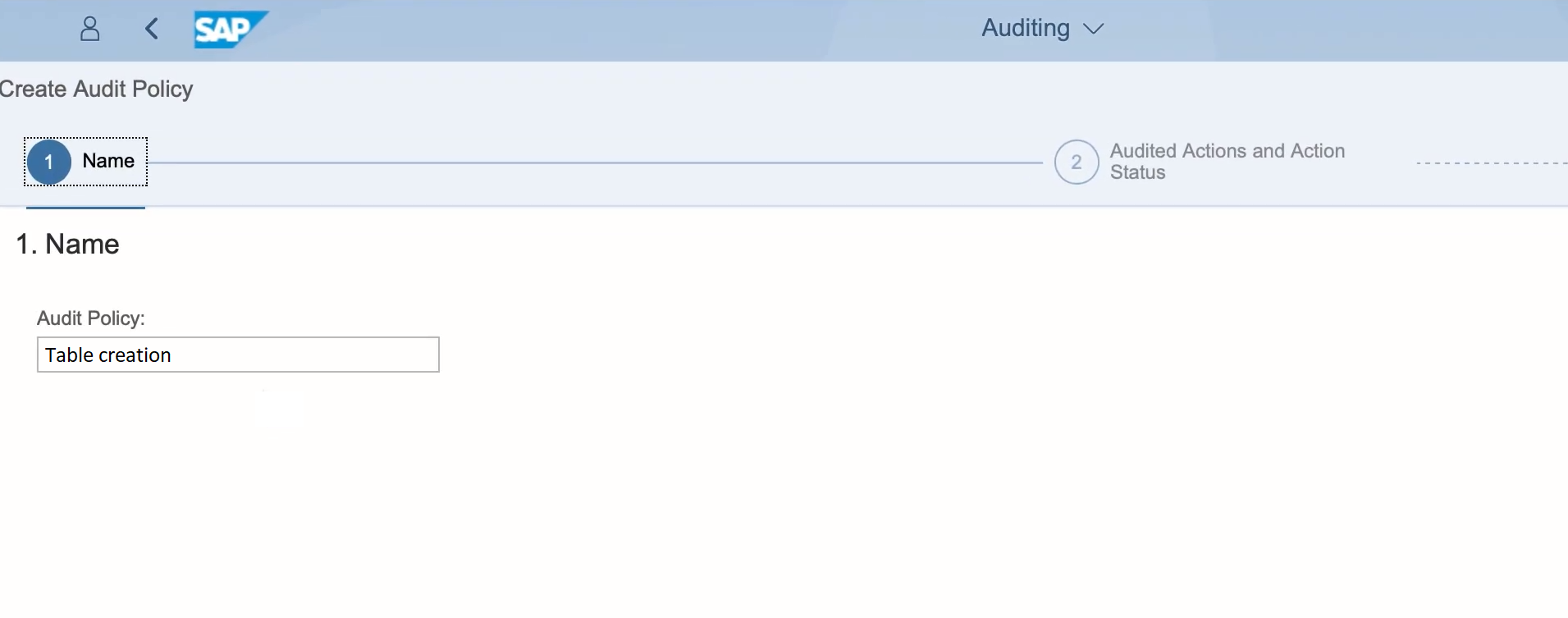
Name: Assign a name to the new audit policy. Then click on Step 2.
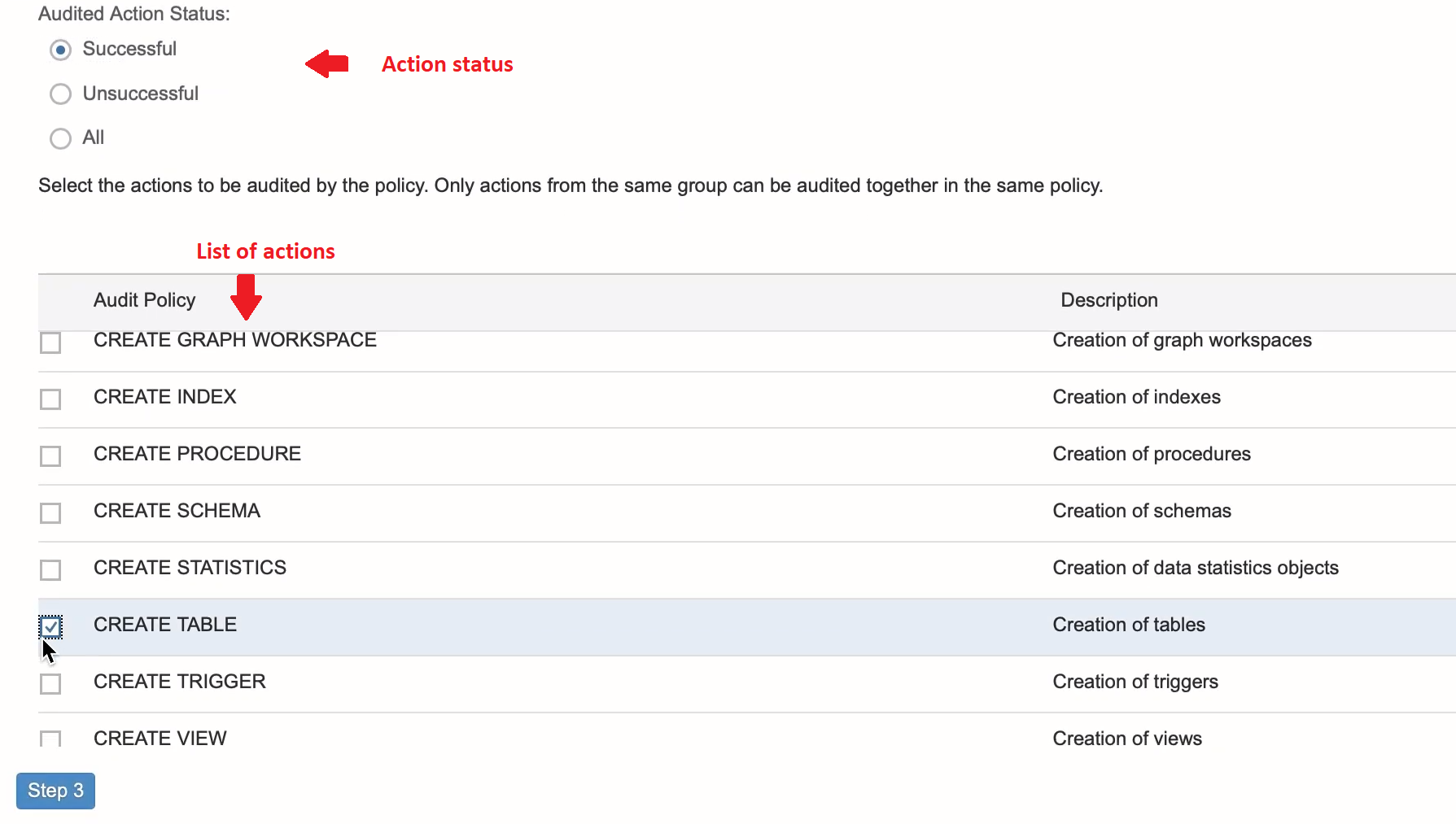
Audited actions and Action Status: Select the action status as SUCCESSFUL, UNSUCCESSFUL or ALL.
- If you select SUCCESSFUL, then the action is audited only when the SQL statement is executed successfully.
- If you select UNSUCCESSFUL, then the action is audited when the SQL statement execution is unsuccessful.
- If you select ALL, then the selected action is audited if the SQL statement is successful or unsuccessful.
Next, select the action on which auditing should apply. There is a list of actions in the lower section. Click on Step 3.
Audited Users: Select the type of users which you want to audit under this policy. Click on Step 4.

Audit Trail: In this step, you get to specify two things. The first is Audit Level which specifies the severity of the auditing action taking place. We have selected Info as the audit level.
Second is selecting Audit Trail Target, that is selecting the location to save auditing results. The default target is Database table. You can change it to Syslog or a text file. Click on Step 5.
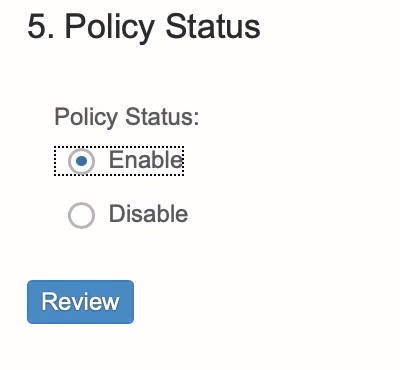
 Policy Status: Select the policy status as Enable or Disable in this step as per your requirement. Click on Review. Then click Save from the bottom of the page.
Policy Status: Select the policy status as Enable or Disable in this step as per your requirement. Click on Review. Then click Save from the bottom of the page.
5. The policy will successfully create. You can confirm it in the Audit Policies section on the Auditing app main page. Now, every time you create a table using SQL console, a new log entry in the Policy Audit Trail will show the details of auditing action done on “Create table” action.
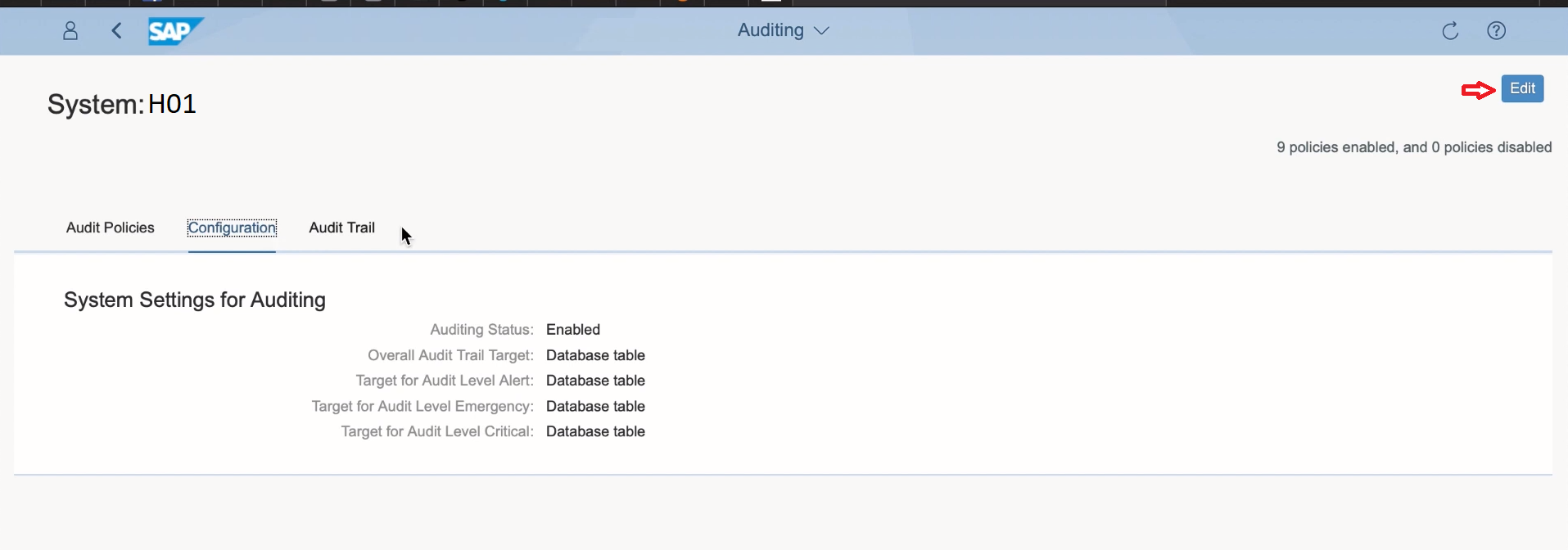
6. You can check the configuration details of the audit policies.
Image Source – SAP HANA Academy
You can change the Audit Status from Enable to Disable or vice versa from the Edit option.
Also, from the Audit Trail tab, you can view all the details on SAP HANA auditing logs. The logs will help you to monitor when was an action performed, who performed the action, the status of auditing, on which object was auditing performed and the SQL statement used.
Summary
We can conclude that auditing is an important process of SAP HANA system which ensures data security by close monitoring and record maintaining. We hope our explanation was helpful in understanding SAP HANA security further. Stay tuned as we plan on bringing more such interesting topics of SAP HANA for you.
Was the article useful? Do share your views in the comment section below.
Did you like this article? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google