Learn 5 Major Components of SAP HANA In-Memory Computing Environment
FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
In the previous tutorial, we learned about Reporting in SAP HANA; now, we are going to learn about the in-memory computing of SAP HANA. All the technical capabilities and efficiencies are possible due to the proficient in-memory computing engine working on the back side.
Let’s explore how SAP HANA becomes a popular in-memory database technology by virtue of in-memory computing in this article.
What is In-Memory Computing?
In-memory computing stores oceans of data as information in the Random-Access Memory (RAM) of the systems operating in an environment. This technology replaces the conventional way of storing data in disks and using relational database management methods to fetch and process it.
The traditional method is much slower than in-memory storage and computing. In-memory computing technology serves a large customer base ranging from industries, finance, manufacturing to retail, banking, utility, etc.
It is used in both managing and manipulating data through fast and efficient processing.
Also, in-memory computing technology is much cheaper than the traditional database system. The most popular and widely used application for in-memory technology is SAP HANA.
It is because of this why SAP HANA is also called a High-speed Analytical Appliance. In a technology like SAP HANA, you can perform real-time analytics on big data as well as develop real-time applications.
What makes an in-memory computing technology like SAP HANA so widely accepted?
Well, the answer lies in the question. The primary reason for its success is the in-memory storage and computing technology. Earlier, traditional database management methods were used in enterprise applications where data was stored and fetched from the storage disks.
It added an extra process which is the movement of data from the database (hard-disk) to the respective application server. This made the entire process slow and inefficient.
In efforts to improve this, applications in SAP HANA is developed in close association with the database, and there is close to no data movement in it.
Thus, SAP HANA keeps an original copy of the data ready in in-memory storage which results in the quick query response, data access, and processing for ad-hoc reporting and analysis of real-time data.
Along with keeping data ready in memory, SAP HANA technology also reduces the complexity of data models for ERPs. It is done by using columnar storage methods of arranging data in-memory.
Column-oriented organizing makes data processing faster along with allowing high data compression rates and cache-efficient processing. No data redundancy is there in the SAP HANA database resulting in simpler data models.
Also, SAP HANA is a unique technology because it integrates OLTP and OLAP functionalities.
Both analytical and transactional data gets accessed, processed and analyzed in real-time with the help of SAP HANA which improves the data analysis.
This integration also allows the addition of some new features of processing and analyzing semi and unstructured data along with the general structured data. Thus, due to all these reasons, it is evident that SAP HANA is a break-through technology in database management.
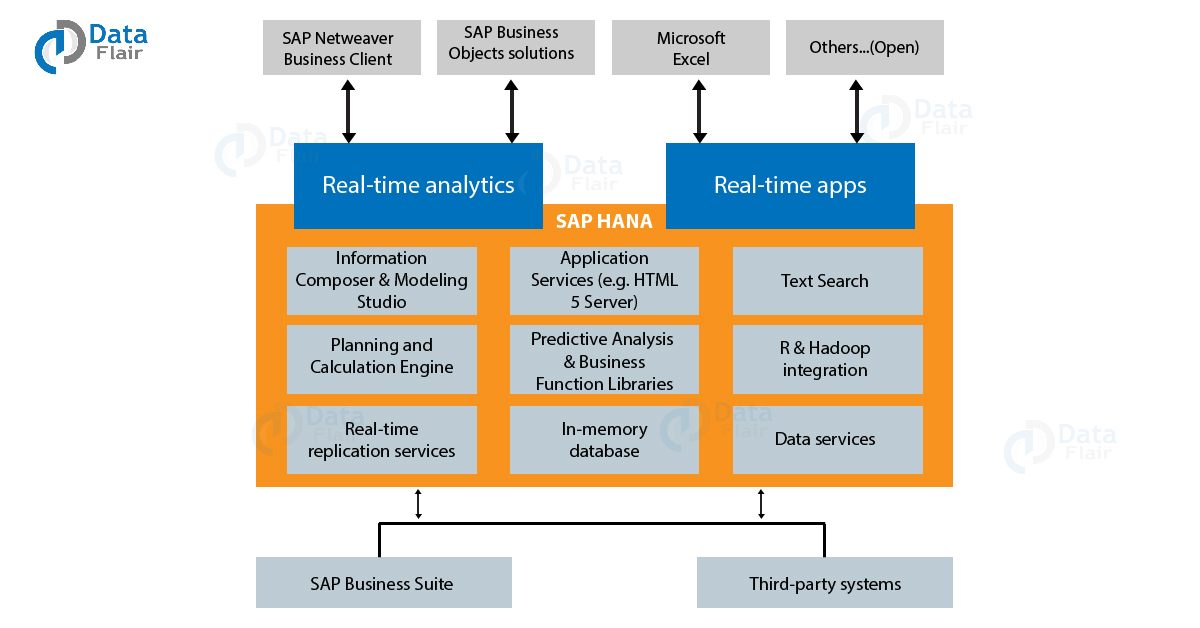
The diagram below shows the connection between the SAP HANA database with other SAP tools.
SAP HANA In-Memory Computing Environment
SAP HANA is an in-memory computing technology which comprises of both hardware and software to process large amounts of real-time data. It is a platform which you can deploy both on-premise as well as on the cloud.
Here, everything from developing applications to performing analysis achieves in real-time because of the in-memory computing.
SAP HANA provides a multi-engine query processing environment where multi-core CPUs, multiple CPUs per board and various boards on an application server are used. It makes data processing about a million times faster than that from the disk.
The conventional or traditional database systems fetched data in 5 milliseconds whereas the in-memory database engine does it in 5 nanoseconds. Also, in SAP HANA massive parallel processing is possible due to efficient database partitioning.
There is no need to use aggregate tables for removing data redundancy and duplication. Data can compress up to 10 times. Also, the data is written only in delta storage (fast loading), and both row and column-oriented data organizing are possible.
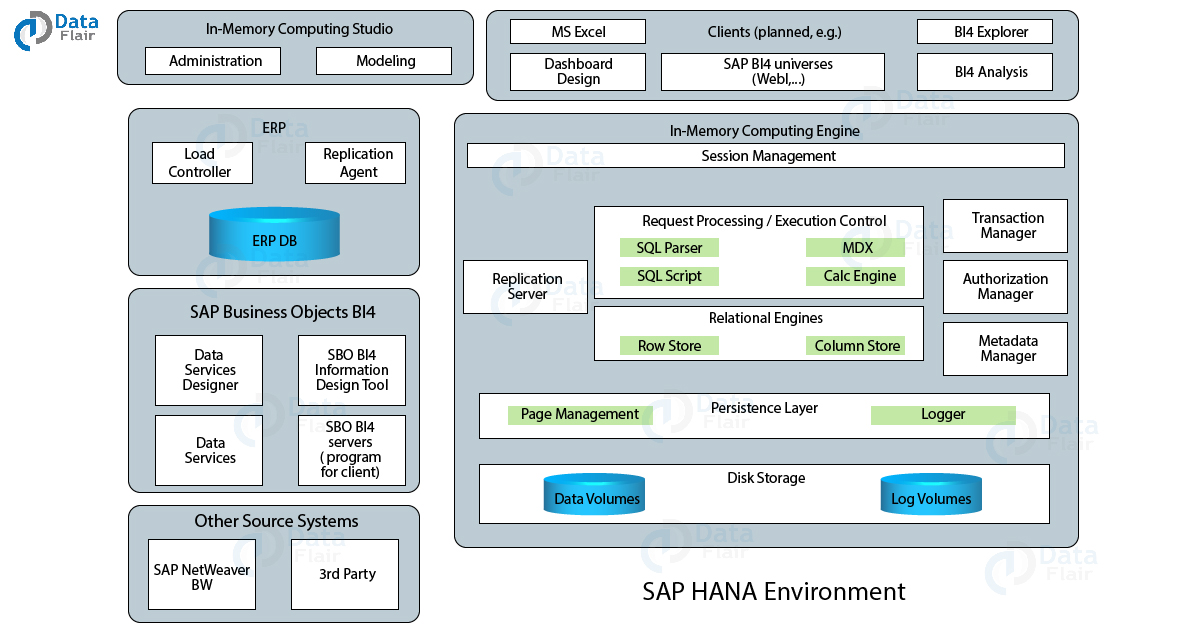
In the above diagram, it is the SAP HANA environment where operations carry on with the in-memory computing engine at its core. The in-memory computing engine takes care of memory management during sessions and transactions, data persistence, etc.
A computing engine surroundes by different servers and applications which fetches data from the database with the help of the data engine. Data replication implements in this environment, where data replicates from a source (SAP or Non-SAP) using appropriate replication techniques.
Various business objects tools interact with the computing engine through query languages like SQL, MDX, BICS, etc. It also performs session and user management, data persistence, etc.
Let us discuss some of the additional servers and components working with the computing engine:
1. SAP HANA In-Memory Computing Engine
It is a component residing within the Index Server in SAP HANA. It has got several sub-components such as Session Management, Request Processing, and Execution Control, Relational Engine, Planning Engine, Disk Storage, etc. Let us learn about them in detail.
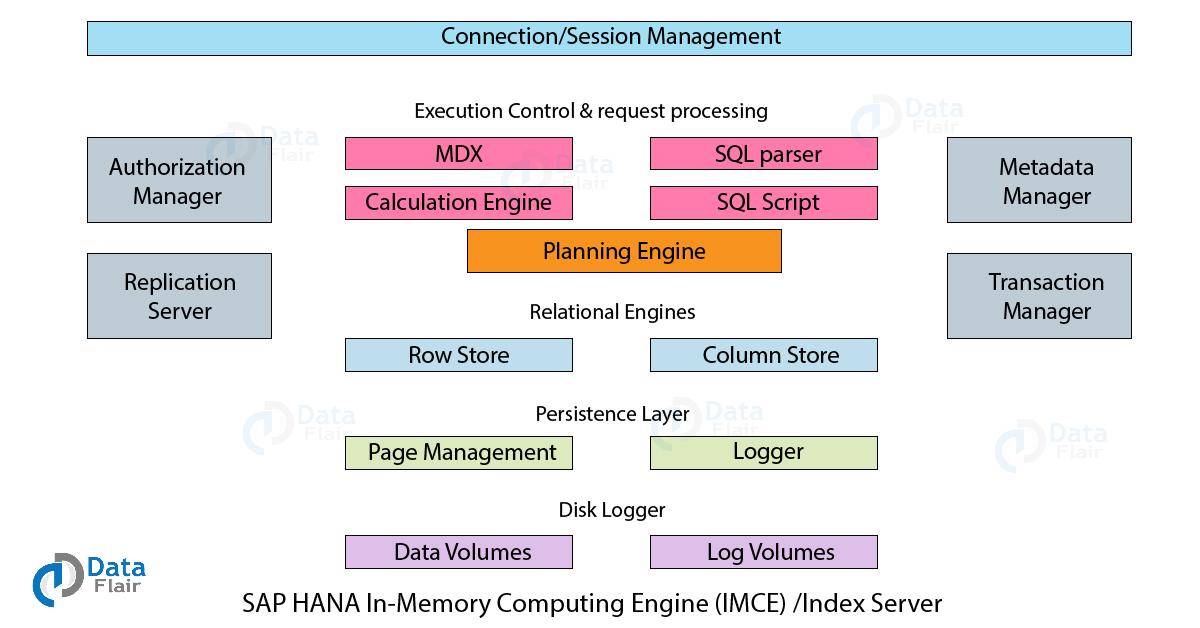
- Connection and Session Management: Creates and manages the connection session between clients and SAP HANA database. These sessions establish for the user to communicate with the database using different query languages.
- Authorization Manager: This component allows only authorized users with a legible user ID. It makes sure that the users access, manipulate and share only that data which they are allowed to access.
- Replication Server: This is responsible for managing the replication of table data as well as metadata from the data source.
- Planning Engine: This creates an execution plan to apply on the database depending on the query sent to the computing engine.
- Metadata Manager: It stores all the information, i.e., metadata about the data table structures, views, data types, field descriptions, etc.
- Transaction Manager: It manages data transactions and keeps track of Commits and Rollbacks.
- Request Processing and Execution Control: This component receives queries or requests from client applications and directs it towards the respective component in the SAP HANA environment. It consists of an SQL Parser, SQL Script, MDX and Calculation Engine.
- SQL Processor: It processes the incoming queries or SQL statements and manipulates (insert, delete, update) data accordingly.
- Persistence Layer and Disk Logger: In in-memory computing, RAM stores data which makes it volatile (can erase due to system malfunctioning). Thus, the persistence layer is responsible for taking data backups periodically and store it permanently. It is known as Savepoints and by default, the savepoint frequency is in every 5 minutes. The data stores as log volumes and data volumes.
2. ERP Database
It has raw data residing in the ERP database which is sent to the HANA database. Replication Agent (in ERP DB) and Replication Server (in the computing engine) facilitates this data movement. This component provides log-based data provisioning.
3. SAP Business Object BI 4
This component involves tools like Data Services Server, Data Services Designer, SBO BI Information Designer tool and Data servers, etc. These components are mainly for job-based data provisioning.
Thus, they create and execute a job on data and store the reports generated as a result. Therefore, it also acts as a repository.
4. In-memory Computing Studio/SAP HANA Studio
It is a user interfacing platform with an Eclipse-based tool where you can manage, administer and manipulate data. You can work on several views like Analytic View, Calculation View, and Attribute View in SAP HANA.
5. Clients
These are different reporting tools which connect to the computing engine using specific drivers. You can create and share reports using these client applications and tools.
Key Features of SAP HANA In-Memory Computing
Let us discuss some key features and capabilities that in-memory computing technology brings to SAP HANA:
1. Application development capabilities like web server, JavaScript compatibility, SAP Fiori user experience, Graphic Modeler, and Application lifecycle management.
2. Advanced analytical processing capabilities like spatial, graphs, predictive analysis, smart search, text analytics, streaming analytics, series data, and business functions.
3. Data integration and quality by virtue of data visualizations, ETL and replicate, Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark integration, and remote data sync.
4. Database management capabilities such as the columnar store, multicore processing and parallelization, advanced compression, multitenancy, multi-tier storage, data modeling, administration and security, high availability and disaster recovery.
Benefits of SAP HANA In-Memory Computing
1. Reduce the complexity of data by bringing all your data onto one platform; SAP HANA. It prevents data redundancy, data footprint, hardware and IT cost. Also, it enables quick real-time processing and analysis of real-time data.
2. Run anywhere as it provides flexible deployment options to the users. You can deploy the software on-premise or on-cloud, on a public or private cloud that configures to various applications and hardware easily.
3. Get real results which are closest to the reality of the market and enables an enterprise to make informed decisions and get better ROI. It also helps reduce the data management costs for the company.
Summary
It is fair to say that SAP HANA is a revolutionary new-age technology due to its in-memory computing engine working at its core. It has given SAP HANA a vast and stable customer base.
Companies all over the world use SAP HANA such as Adobe, Infosys, BASF, Bosch, INTEL, Lenovo, Cisco, Colgate, Deloitte, Hilti, P&G, etc.
We hope this explanation was helpful. If you have any queries or feedbacks related to SAP HANA In-Memory Computing Tutorial, you can ask in the comment section.
Did you like this article? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google