HTML Attributes with Examples
Free Web development courses with real-time projects Start Now!!
In order to provide additional and extra bits of information related to an element such as ‘href’ to specify the URL of a link using <a> element, HTML attributes are used. We are going to learn HTML attributes in detail now. So let’s start!!!
HTML Attributes
HTML attributes structure the elements and manipulate their behavior as per the user’s jurisdiction and preferences. Attributes are inserted in the opening tags of the elements and have a name-value pair.
- name – It is used to specify the property that needs to be added or manipulated. For example, the height of an image.
- value – This is for defining the value of the property. For example, image height should be 20 px.
<img height=”20px”>
Here, <img> is a non-container element whose attribute height(name) has been set to 20 px(value).
Let us learn the same with an example. We will set the align property of a paragraph as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DataFlair-Attributes</title>
</head>
<body>
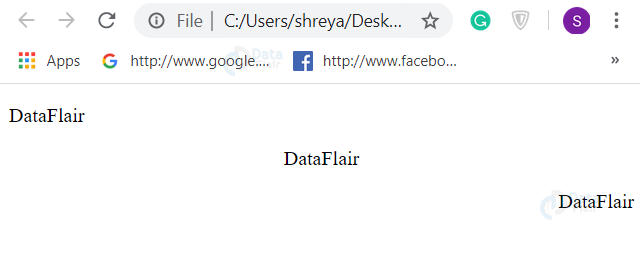
<p align = "left">DataFlair</p>
<p align = "center">DataFlair</p>
<p align = "right">DataFlair</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
Major HTML Attributes
Some of the major HTML attributes that we frequently use are as follows-
1. Class in HTML
The class attribute can be accessed by any element and is useful to identify a group of elements in a HTML document together. These elements can be styled using CSS or actions can be performed on them using JavaScript.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.country {
background-color: black;
color: white;
padding: 8px;
font-weight: bold;
font-family: monospace;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2 class="country">DataFlair</h2>
<p>HTML Attributes</p>
<h2 class="country">Article on</h2>
<h2 class="country">The Class attribute</h2>
</body>
</html>
(Here, the class attribute is accessed with CSS using the dot operator i.e. ‘.’).
Output
2. Id
We use HTML id attribute to uniquely identify a particular element in the HTML document. It can be used with at most one element. It also acts as a distinguisher between two or more elements with the same name.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DataFlair id attribute</title>
<style>
#DataFlair {
font-size:50px;
font-weight:bold;
text-align:center;
}
#Article {
text-align:center;
font-size:50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
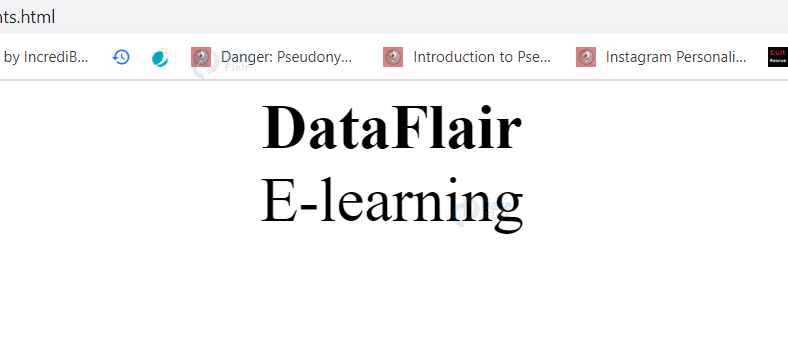
<div id="DataFlair">DataFlair</div>
<div id="Article">E-learning</div>
</body>
</html>
(Here, two divisions with id DataFlair and Article have been created and styled with CSS. ‘#’ is used to access these elements with id).
Output
3. HTML Style
The style attribute is for inline styling of HTML elements using CSS.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
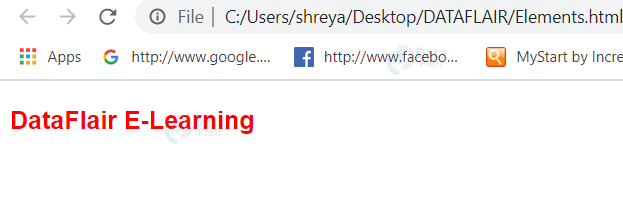
<p style = "font-family:arial; color:#FF0000; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px">DataFlair E-Learning</p>
</body>
</html>Output
4. HTML Title
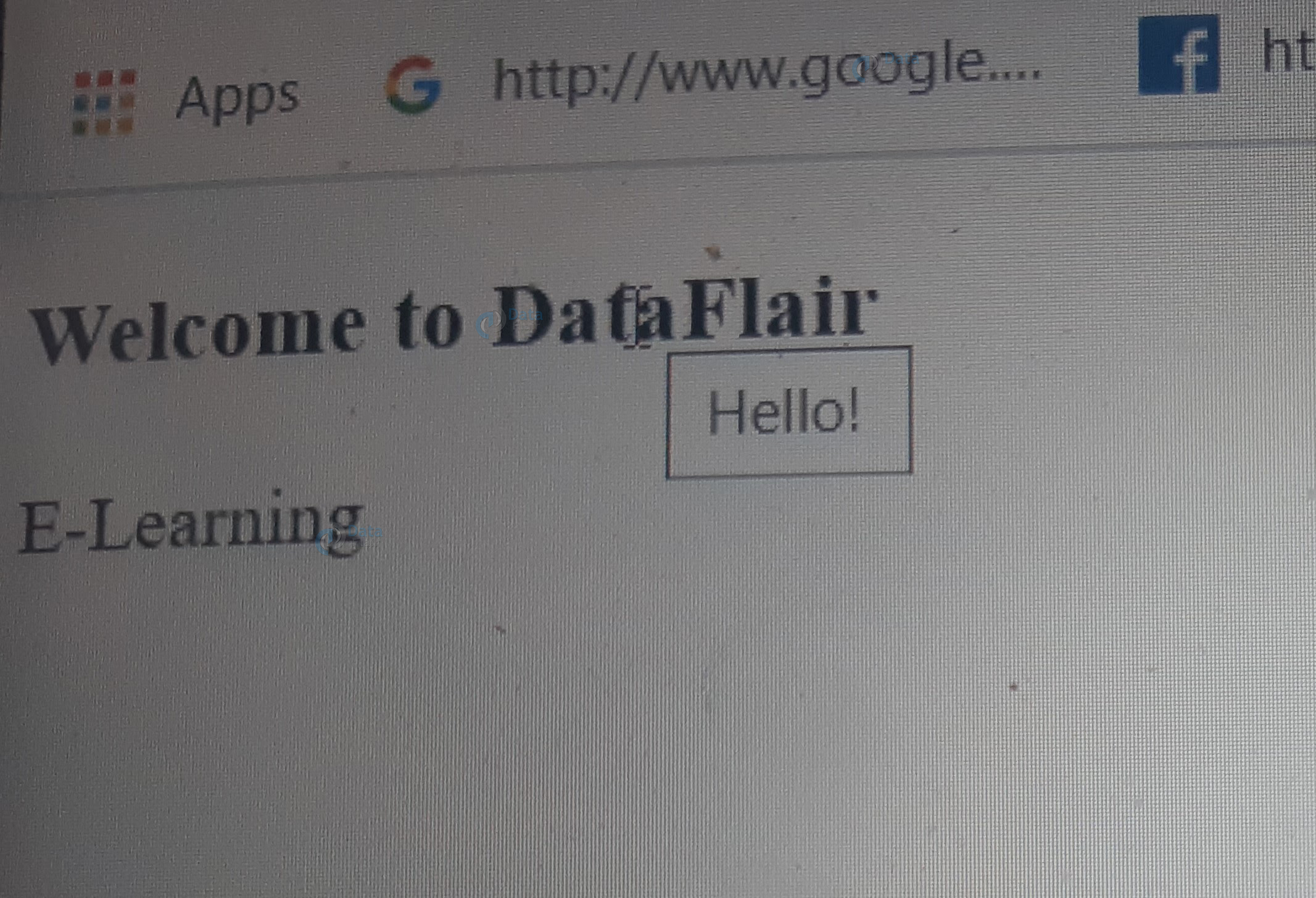
The title attribute is useful to give a title for the element. Everytime you mouse-over that particular element, the value of the title attribute will be displayed on its tooltip.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <h3 title = "Hello!">Welcome to DataFlair</h3> <p title="DataFlair"> E-Learning </p> </html>
Output
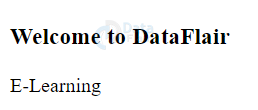
5. HTML Lang Attribute
This attribute is used to specify the language of the HTML document and is used with the <html> element.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en-US"> <head> </head> <body> <h3>Welcome to DataFlair</h3> <p> E-Learning </p> </html>
Output
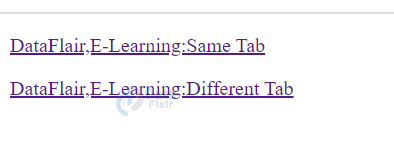
6. Href HTML attribute
HTML href attribute is used to specify the URL of the destination address i.e. link, as defined by the <a>,anchor,element. On using the value of another attribute i.e. ‘target’ and setting it to ‘_blank’, the link will be redirected to another window or tab.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en-US"> <head> </head> <body> <p><a href="https://data-flair.training">DataFlair,E-Learning:Same Tab</a></p> <p><a href="https://data-flair.training" target="_blank">DataFlair,E-Learning:Different Tab</a></p> </p> </html>
Output
7. HTML Image Attributes
- src – The src attribute is used to specify the location or URL of a particular image (defined by the <img> element).
- alt – We use it to specify some alternative text related to the image which is displayed if the user cannot view the image due to some inevitable reasons.
- height – It is for specifing the height of the image in pixels.
- width – It is useful to specify the width of the image in pixels.
<html>
<head>
<title>DataFlair</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Here is an image</h1>
<img src="C:\Users\shreya\Desktop\DATAFLAIR\DataFlair.png" alt="DataFlair" height="400px" width="400px">
</body>
</html>
Output
Note:
- For attribute values, both single and double quotes can be used. We can write href attribute’s value without quotes as well.
- If the attribute value contains double quotes, it should be contained within single quotes.
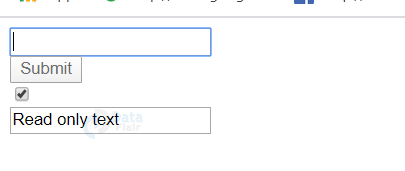
- Some attributes of HTML 5 that do not have name-value pairs are boolean attributes. For example – checked, disable, required, readonly, etc.
Following is an example with HTML boolean attributes in a form:
<html> <head> <title>DataFlair</title> </head> <body> <form> <input type="email" required><br> <input type="submit" value="Submit" disabled><br> <input type="checkbox" checked><br> <input type="text" value="Read only text" readonly><br> </form> </body> </html>
Output
Summary
HTML Attributes are useful to manipulate HTML elements and in this article, we have discussed some of the major HTML attributes – class, id, style, href, src, alt, height, width and some boolean attributes. The use of HTML attributes facilitates the creation and development of web-pages. It is important to have a gist of these widely used attributes, we would delve further into their details and more attributes in the preceding articles.
Do not forget to share your feedback in the comment section!!!
You give me 15 seconds I promise you best tutorials
Please share your happy experience on Google