Reflection in Java | Java Reflection API Tutorial
Free Java courses with 37 real-time projects - Learn Java
1. Objective
In our previous Java tutorial, we looked at Iterators in Java. Today, in this article we are going to discuss Reflection in Java. Here, we will see what is Java Reflection & how it can utilize to get data. Moreover, we will look at the pros and cons of reflection in Java. Along with this, we will understand the sample code using reflection in Java and Java reflection class. Finally, we will see the reflection in Java with Java reflection invoke a method.
So, let’s start Reflection in Java.
2. What is Reflection in Java?
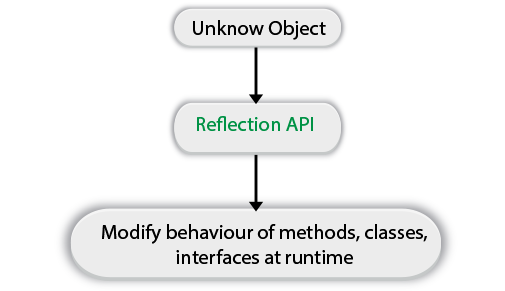
Reflection in Java is an Application Programming Interface(API) which is utilized at the runtime to change classes, methods, and interfaces.
Java Reflection is an API which is utilized to look at or change the conduct of methods, classes, interfaces at runtime.
- The required classes for reflection in Java are given under java.lang.reflect package.
- Reflection gives us data about the class to which an object has a place and furthermore the methods for that class executes by utilizing the object.
- Through reflection, we can summon method at runtime independent of the access specifier utilized with them.
Do you know the Working of Java Packages?
3. How to Get Data By Java Reflection?
Reflection can utilize to get data about –
- Class- The getClass() method is utilized to get the name of the class to which an object has a place.
- Constructors- The getConstructors() technique is utilized to get the public constructors of the class to which an object has a place.
- Strategies- The getMethods() technique is utilized to get the public methods for the class to which an object has a place.
Let’s revise Java Copy Constructor | Constructor Overloading in Java
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
class Test
{ private String s;
public Test() { s = "DataFlair"; }
public void method1() {
System.out.println("The string is " + s);
}
public void method2(int n) {
System.out.println("The number is " + n);
}
private void method3() {
System.out.println("Private method invoked");
}
}
class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
Test obj = new Test();
Class cls = obj.getClass();
System.out.println("The name of class is " +
cls.getName());
Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
System.out.println("The name of constructor is " +
constructor.getName());
System.out.println("The public methods of class are : ");
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
for (Method method:methods)
System.out.println(method.getName());
Method methodcall1 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("method2",
int.class);
methodcall1.invoke(obj, 19);
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("s");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, "JAVA");
Method methodcall2 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("method1");
methodcall2.invoke(obj);
Method methodcall3 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("method3");
methodcall3.setAccessible(true);
methodcall3.invoke(obj);
}
}Output for java reflection
The name of class is Test
The name of constructor is
Test The public methods of class are:
method2
method1
wait
wait
equals
wait
toString
hashCode
getClass
notify
notifyAll
The number is 19
The string is JAVA
Private method invoked
Learn Singleton Class in Java – Two Simple Ways For Implementing
Important points –
- We can summon a strategy through reflection on the off chance that we know its name and parameter composes. We use underneath two strategies for this reason
getDeclaredMethod(): To make a question of a method to conjure.
A Syntax for Java Reflection get declared method–
Class.getDeclaredMethod(name, parametertype) name- the name of method whose object is to be created parametertype - parameter is an array of Class objects
invoke(): At the runtime to invoke a method of class, we use the following method-
A Syntax for invoke method-
Method.invoke(Object, parameter)
Java Wildcard – Types of Wildcard in Java
So, if the Java reflection class method doesn’t accept any parameter then an argument passes by null.
- Through reflection, we can get to the private methods and variables for a class with the assistance of its class question and summon the method by utilizing the object as talked about above. We use underneath two strategies for this reason.
Class.getDeclaredField(FieldName): Used to get the private field.
Field.setAccessible(true): It allows, getting to the field independent of the entrance modifier utilized with the field.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Java Reflection
a. Advantages of Java Reflection –
Extensibility Features: An application may make utilization of outer, user-defined classes by making examples of extensibility objects utilizing their completely qualified names.
Debugging and testing devices: Debuggers utilize the property of reflection to look at private members on classes.
b. Disadvantages of Reflection in Java–
Execution Overhead: Reflective tasks have slower execution
Introduction of Internals: Reflective code breaks deliberations.
Learn about Collection Framework in Java – Hierarchy, Need & Advantages
5. Conclusion
Hence, we have a complete understanding of reflection in Java. Moreover, in this Java Reflection tutorial, we discussed an introduction to reflection in Java. Along with this, we saw the advantages and disadvantages of Java Reflection. At last, we learned Java reflection class and java reflection invokes a method with the help of an example. Furthermore, if you have any query, feel free to ask through the comment section.
Did you like this article? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google