Method Overloading in Java with Example [Updated]
Free Java courses with 37 real-time projects - Learn Java
In Java Polymorphism, we heard the term Method Overloading which allows the methods to have a similar name but with the difference in signatures which is by input parameters on the basis of number or type. Method Overloading in Java supports compile-time (static) polymorphism.
In this article, we will talk about Method Overloading with its rules and methods. We will discuss each and every concept with an example for a clear understanding. So, let’s start!
Example of Methods Overloading in Java-
class Calculator
{
int addition(int operand1, int operand2)
{
return operand1+operand2;
}
int addition(int operand1, int operand2, int operand3)
{
return operand1+operand2+operand3;
}
}
public class CompileTimePolymorphism
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Calculator obj = new Calculator();
System.out.println("Addition of two operands is "+obj.addition(10, 20));
System.out.println("Addition of three operands is "+obj.addition(10, 20, 30));
}
}
Output-
1. Different Methods of Method Overloading in Java
Method overloading can be done by 3 methods in Java:
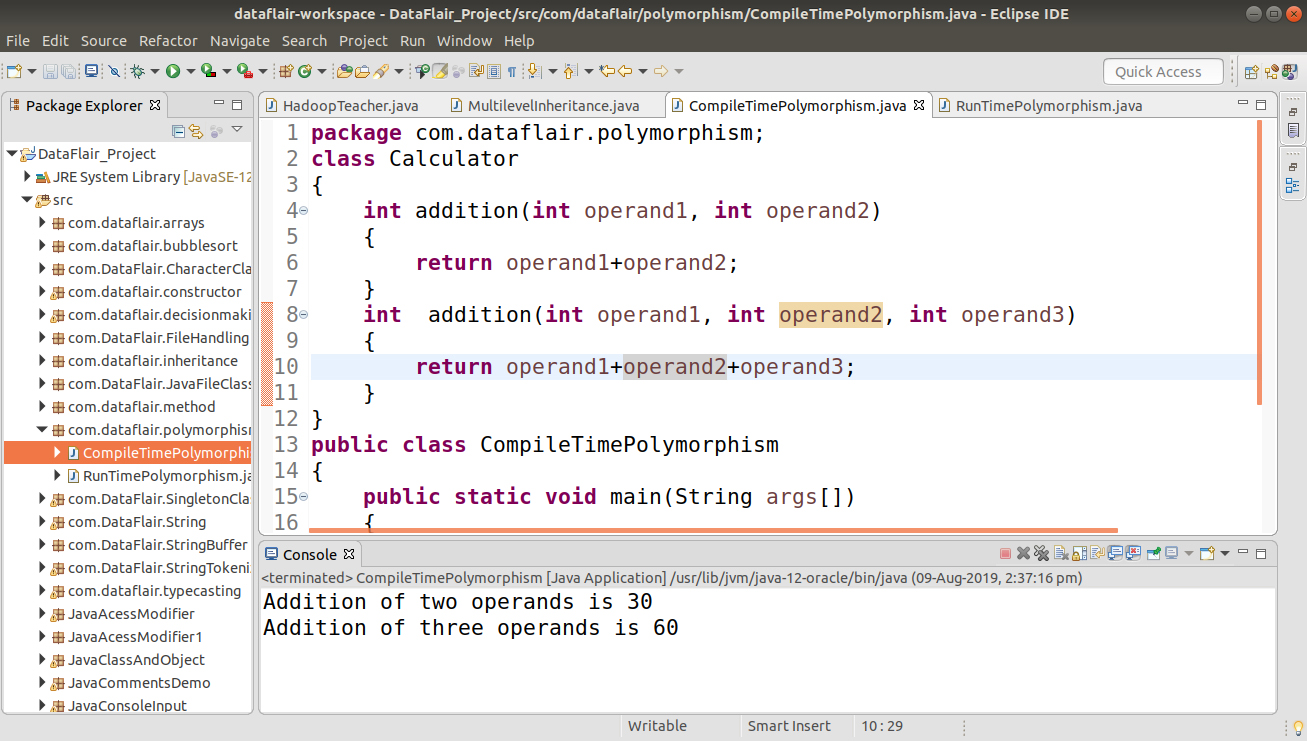
1.1 By a number of parameters in two methods.
The following example shows how method overloading is done by using a different number of parameters
class Calculator
{
int addition(int operand1, int operand2)
{
return operand1+operand2;
}
int addition(int operand1, int operand2, int operand3)
{
return operand1+operand2+operand3;
}
}
public class CompileTimePolymorphism
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Calculator obj = new Calculator();
System.out.println("Addition of two operands is "+obj.addition(10, 20));
System.out.println("Addition of three operands is "+obj.addition(10, 20, 30));
}
}Output-
Recommended Reading – DataTypes in Java with Examples
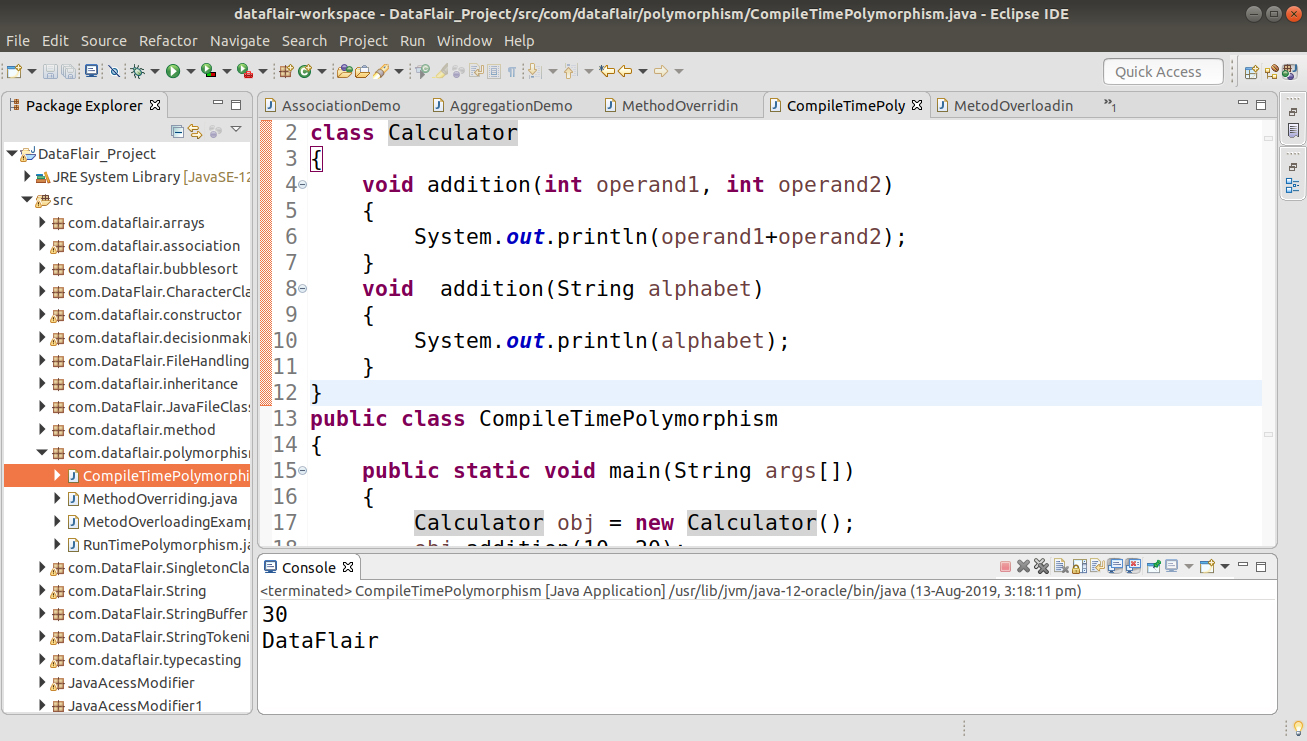
1.2 By data types of the parameters of methods
In the following example, method addition() is overloaded based on the data type of parameters – We have two methods with the name addition(), one with the parameter of int type and another method with the parameter of string type.
class Calculator
{
void addition(int operand1, int operand2)
{
System.out.println(operand1+operand2);
}
void addition(String alphabet)
{
System.out.println(alphabet);
}
}
public class CompileTimePolymorphism
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Calculator obj = new Calculator();
obj.addition(10, 20);
obj.addition("DataFlair");
}
}
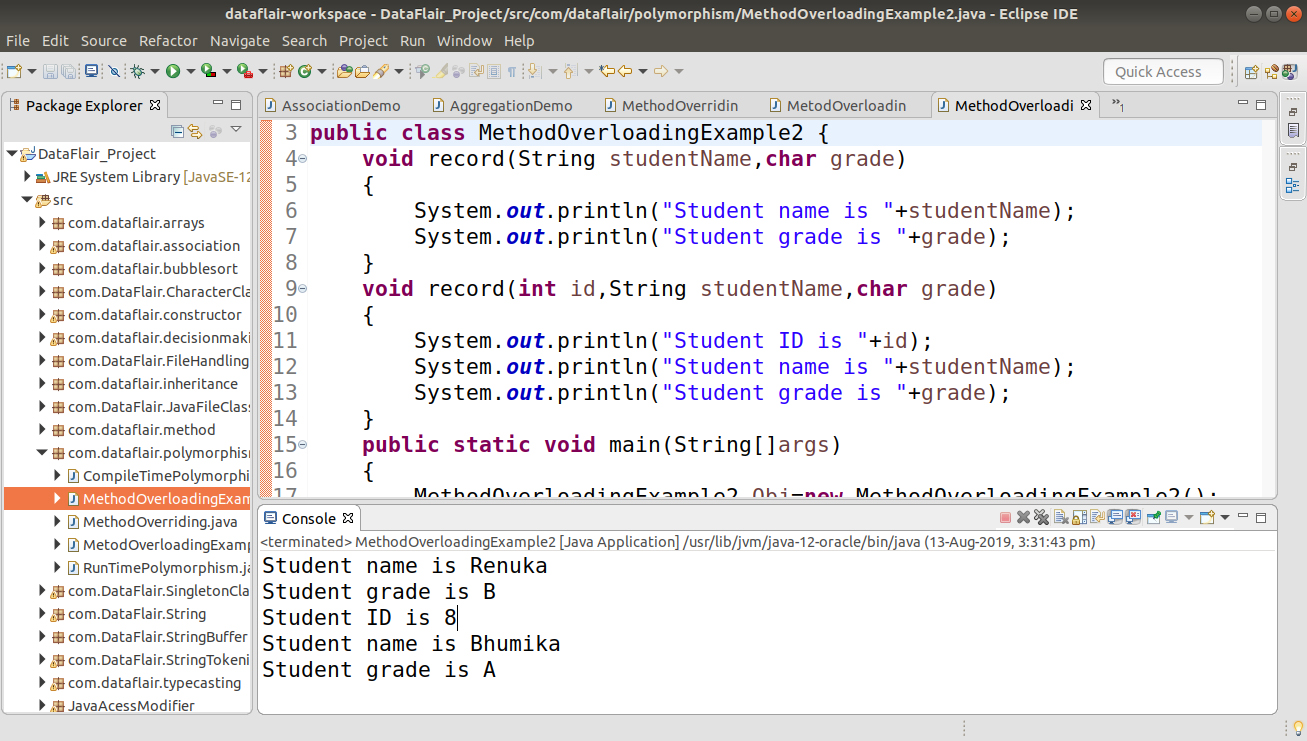
1.3 By order of the parameters of methods
Here both methods have a different sequence of data type in an argument list. The first method is having argument list as (String, char) and second is having (int, String, char). Since the sequence is different, the method can be overloaded without any errors.
It’s right time to explore about Command Line Argument in Java
public class MethodOverloadingExample2
{
void record(String studentName,char grade)
{
System.out.println("Student name is "+studentName);
System.out.println("Student grade is "+grade);
}
void record(int id,String studentName,char grade)
{
System.out.println("Student ID is "+id);
System.out.println("Student name is "+studentName);
System.out.println("Student grade is "+grade);
}
public static void main(String[]args)
{
MethodOverloadingExample2 Obj=new MethodOverloadingExample2();
Obj.record("Renuka",'B');
Obj.record(8, "Bhumika", 'A');;
}
}Output-
2. Important Points of Method Overloading in Java
2.1 The advantage of Method Overloading
The advantage of method overloading in Java is that it makes easier for us deal with methods as we don’t have to remember different names for the same operation, we can just change the parameters of a method.
Have you heard about Method Overriding in Java?
2.2 Overloading on methods for a different return type
We cannot perform method overloading for different return types in Java.
Example-
public class Main
{
public int number()
{
return 10;
}
// compiler error: number() is already defined
public char number()
{
return 'a';
}
public static void main(String args[])
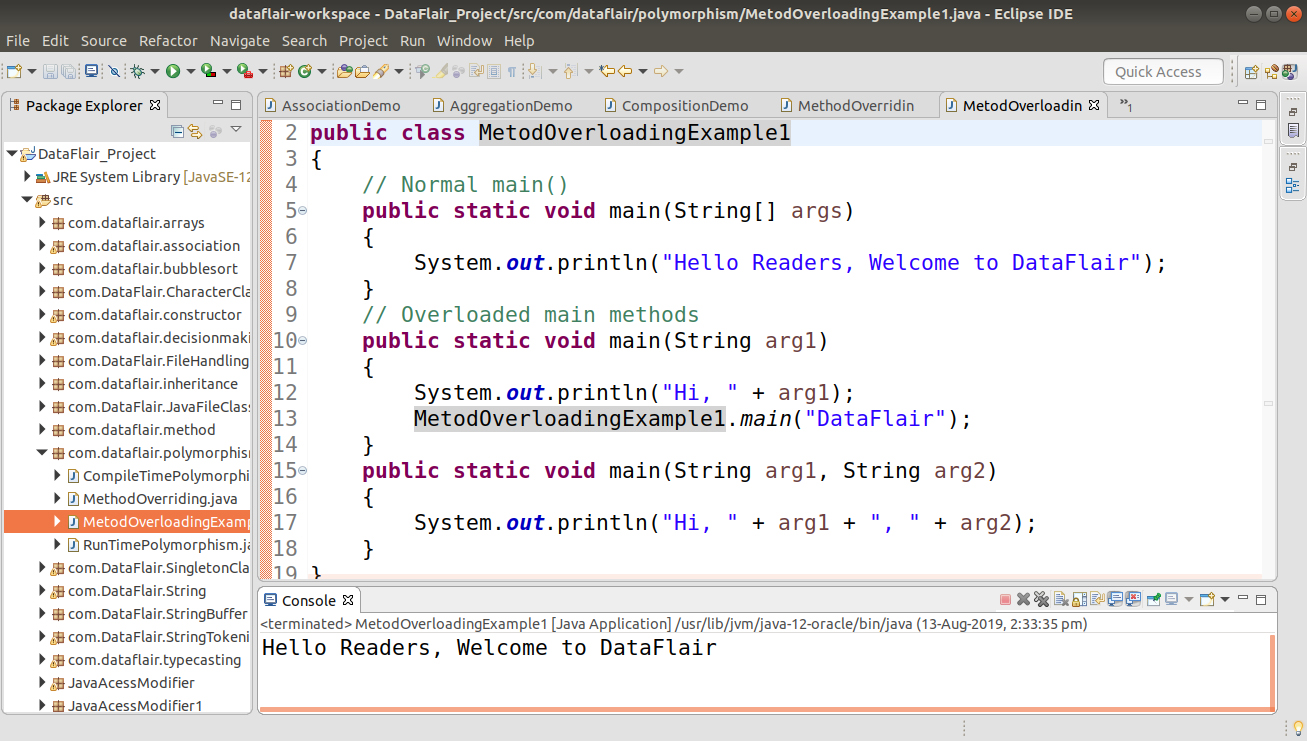
}2.3 Overloading of the main() method
Java supports overloading of the main() method.
Example –
public class MetodOverloadingExample1
{
// Normal main()
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello Readers, Welcome to DataFlair");
}
// Overloaded main methods
public static void main(String arg1)
{
System.out.println("Hi, " + arg1);
MetodOverloadingExample1.main("DataFlair");
}
public static void main(String arg1, String arg2)
{
System.out.println("Hi, " + arg1 + ", " + arg2);
}
}3. Summary
Wrapping up, method overloading can be done by 3 methods – by the number of parameters in two methods, data types of the parameters, and order of parameters of methods. It is not an easy task, you have to remember some important points, which we discussed above.
Don’t forget to check Constructor Overloading in Java
In order to give suggestions and feedback, please approach our comment section.
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google


Pages of helpful information. Thanks