Create SQL Sequence – Syntax and Example
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Skills, Zero Cost. Enroll Now!
In this tutorial, we will learn about the Sequences in SQL. Let us now dive deep into SQL sequences and understand them in detail.
What are Sequences in SQL?
When we talk about sequences they are numerical series which helps us to identify each row of the table with a unique identity.
With the help of sequences, we can provide identification for even the data which otherwise can’t be identified using one parameter.
Using the series we can easily create single parameters which identify each row of our database. Examples could be Adhaar Card numbers of each citizen or roll numbers in a class.
In SQL for generating the sequences, we use Autoincrement.
With the help of autoincrement, we can generate sequences that are integers and can decide the starting and endpoint such that they always remain unique.
Why do we need SQL Sequences?
When we have data that doesn’t provide unique identifiers, we create sequences that actually help us to create identification marks for each row.
We can consider the situation when we have data that has some similar entries, in such cases, we need identification and for that we use sequences.
Thus, creating sequences helps us to create identification points for each row or the tuple.
What is Auto Increment in SQL?
The data which we store in our database does not always have unique properties to enable the identification of each record uniquely.
To ensure that we can uniquely identify each record we need to create an external unique identification attribute, which enables us to identify each row.
We create an additional attribute of numeric type and set it to Auto Increment, ones set to auto-increment the values are automatically incremented and stored in the database.
This helps us to identify each record easily. We need to set a column as Auto Increment in the Create statement itself as otherwise, problems would arise.
We assign the auto-increment to the Primary Key attribute to ensure that the unique identity of data is maintained.
Syntax:
1. To create an Auto Increment Column.
CREATE TABLE tableName ( col1 NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, Col2, col3,...... PRIMARY KEY(col1));
2. To alter the starting point of the Auto Increment Column.
ALTER TABLE tableName AUTO_INCREMENT = n;
3. To alter the amount of increment of each column.
CREATE TABLE tableName ( col1 NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT(n,m), Col2, col3,...... PRIMARY KEY(col1) );
Where n is the starting point and m is the gap between each created record.
Features of Auto Increment in SQL
Some of the features of Auto Increment are as follows:
1. Allows us to create Primary Key in data that doesn’t have any unique identification attribute.
2. We can set the starting value explicitly and modify the same at any particular time.
3. Helps us to create unique identification in the records.
4. Provides us with the flexibility to handle the gap between each record.
5. We can leave the attribute set to auto-increment empty as it will automatically take its values.
Steps to create SQL Auto Increment Attribute
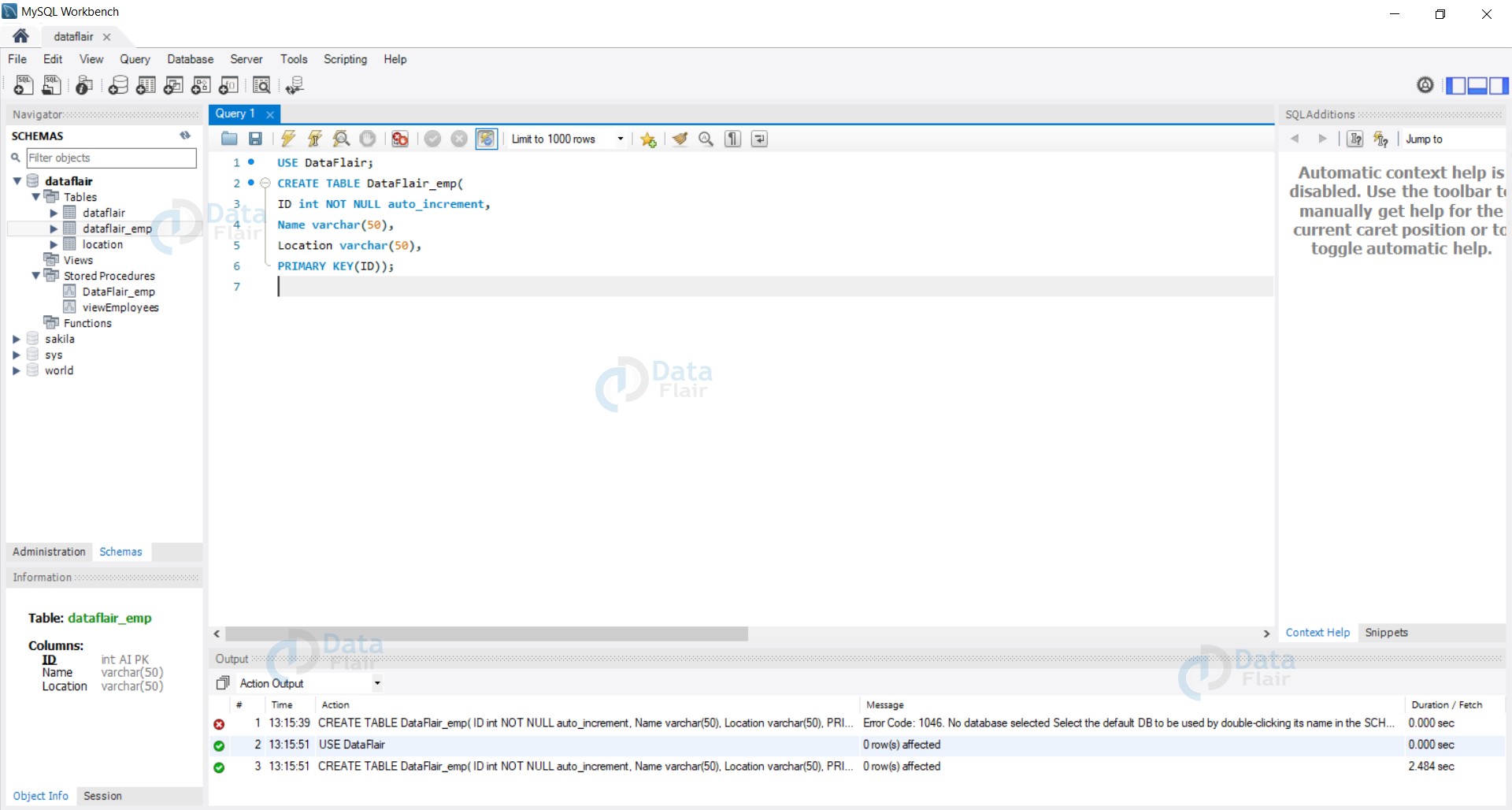
1. Let us create a new database called DataFlair_emp with the following columns.
- ID int Auto Increment NOT NULL
- Name varchar(50)
- Location varchar(50)
Query:
USE DataFlair; CREATE TABLE DataFlair_emp( ID int NOT NULL auto_increment, Name varchar(50), Location varchar(50), PRIMARY KEY(ID));
Output:
We can see that our database with ID as the Auto Increment attribute is created.
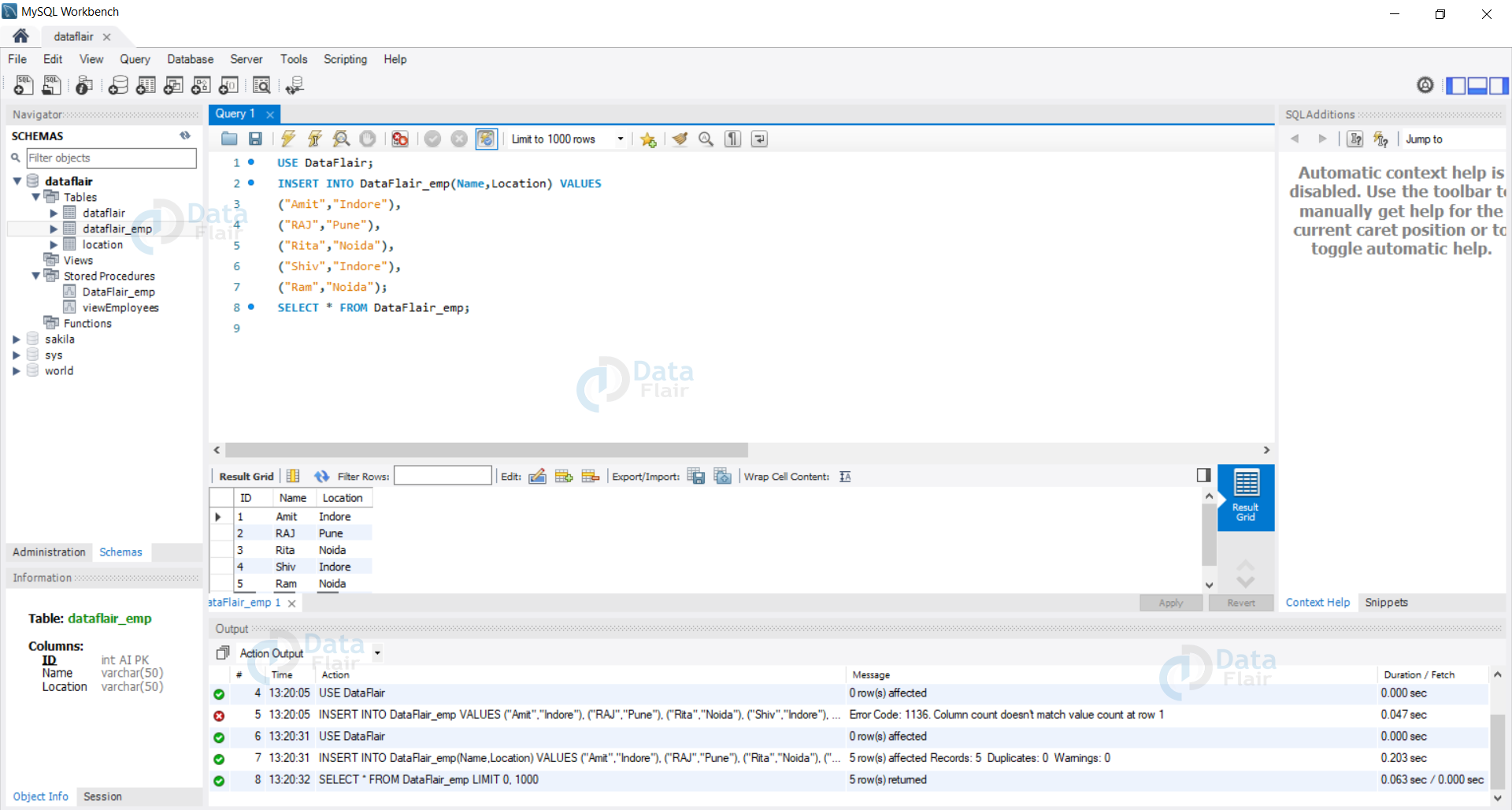
2. Let us now insert data in our database.
Query:
USE DataFlair;
INSERT INTO DataFlair_emp(Name, Location) VALUES
("Amit","Indore"),
("RAJ","Pune"),
("Rita","Noida"),
("Shiv","Indore"),
("Ram","Noida");
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp;
Output:
We can see that despite having not passed any value or ID column the values are automatically incremented and inserted in our database.
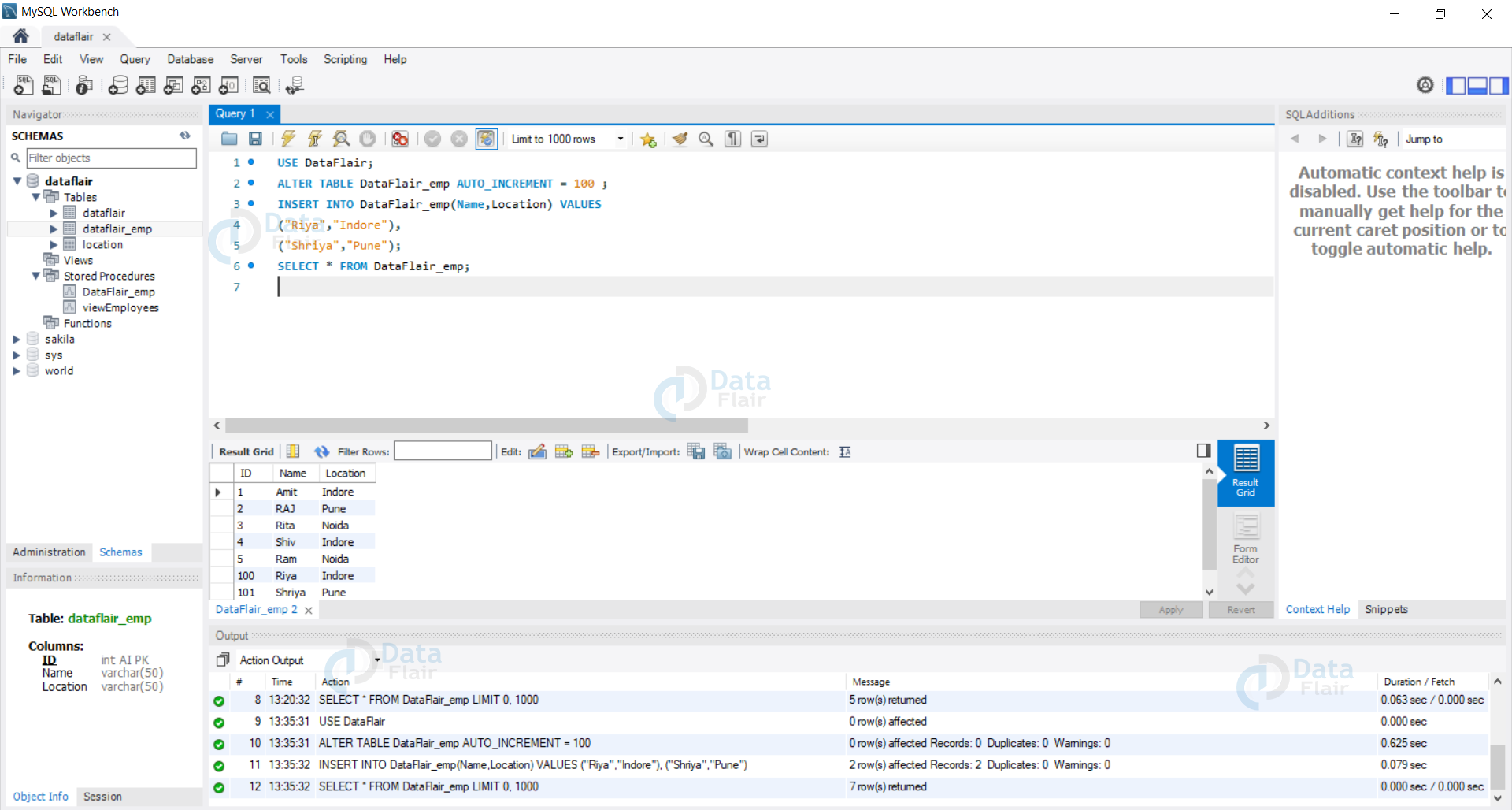
3. Let us now alter the starting value of Autoincrement and then again insert some new records in our database.
Query:
USE DataFlair;
ALTER TABLE DataFlair_emp AUTO_INCREMENT = 100 ;
INSERT INTO DataFlair_emp(Name,Location) VALUES
("Riya","Indore"),
("Shriya","Pune");
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp;
Output:
We can see that now the Auto Increment value is set to 100, also by inserting multiple records we can see that the values are being incremented by 1 and are being stored in our database as Primary Key.
Summary
In this tutorial, we have seen what is a sequence and why do we need a sequence. We have seen how we create a sequence with various examples.
When we generate a sequence we create a unique identification for the database.
With the help of unique attributes, the rows are identified easily and the data becomes more usable and efficient. Also by using the sequences we can easily make our database more flexible and fast to query.
If you are Happy with DataFlair, do not forget to make us happy with your positive feedback on Google