SQL Join – Inner, Left, Right & Full Joins
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Skills, Zero Cost. Enroll Now!
We have large units of data stored in our database, consisting of thousands of tables. When we need to look into a specific set of data satisfying various conditions, we face problems while combining a large amount of data.
The data is spread into multiple tables, and thus to extract the data from multiple tables we use various joins to convert the tables into one table.
What are Joins in SQL and Use of SQL Joins?
SQL join statements help us to combine the rows and columns and parts of various tables and view them as one. By the use of joins, we can easily combine and present data into a single table.
This makes it easy for us to perform queries and transactions on the data needed by us. We perform joins based on one or more common fields in the two or more tables.
Let us try to understand by using the example of a school student’s data.
We have a table storing the data of the student with all the personal details including the parent’s details and health details of the student. On the other side, we have a table that stores the data on the performance of the student.
Now suppose we want to run a survey on our school students which requires the data of the parents and the performance of the student over time. To do any sort of analysis, we require data to be present in the same table.
To obtain this we use joins on the tables. By using join we can combine data that satisfies various conditions and logics we specify and require.
When we use joins, they are done on multiple parameters and conditions passed. Here we will discover more about the types and uses of the available joins in SQL.
Demo Database
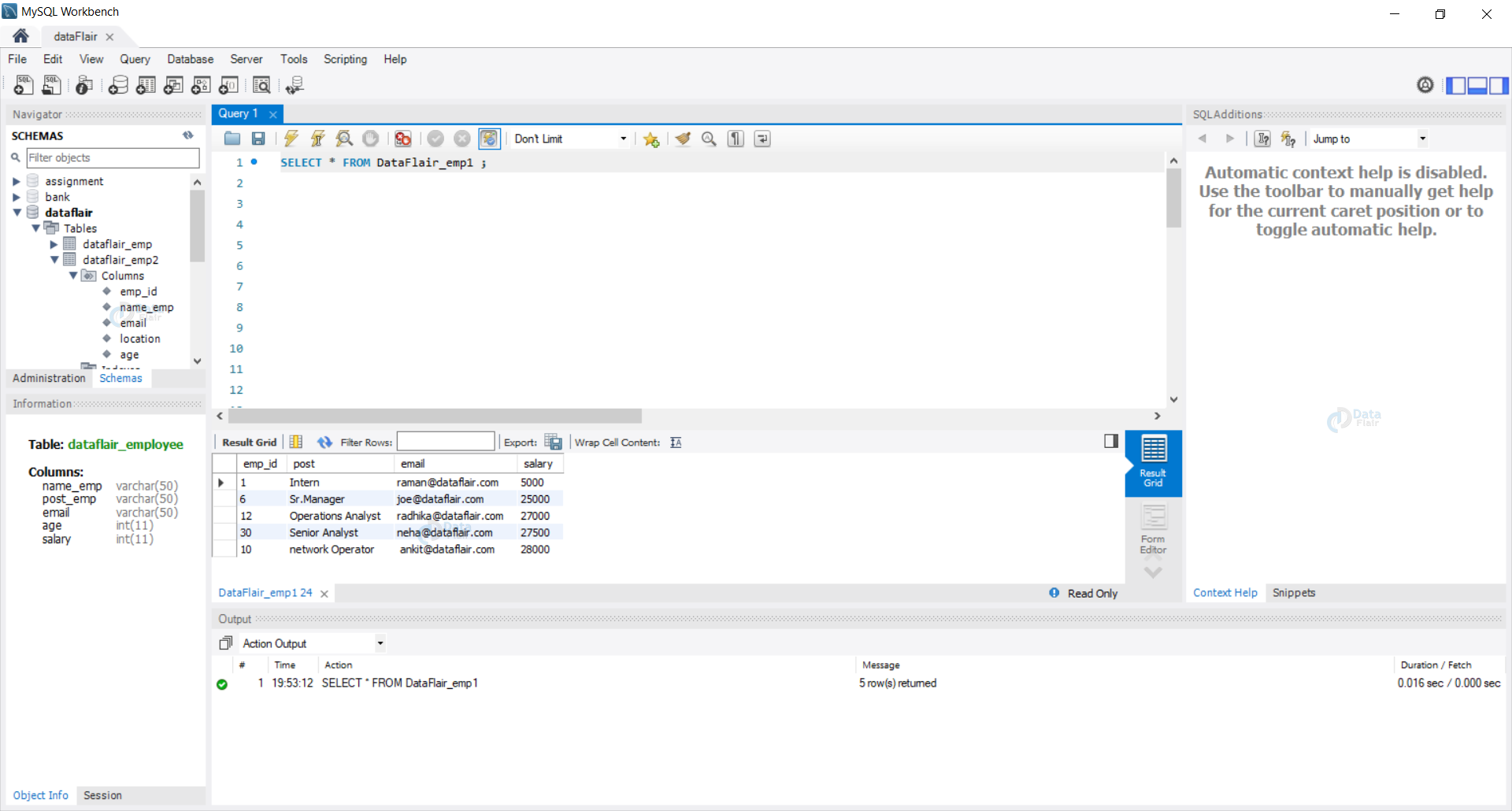
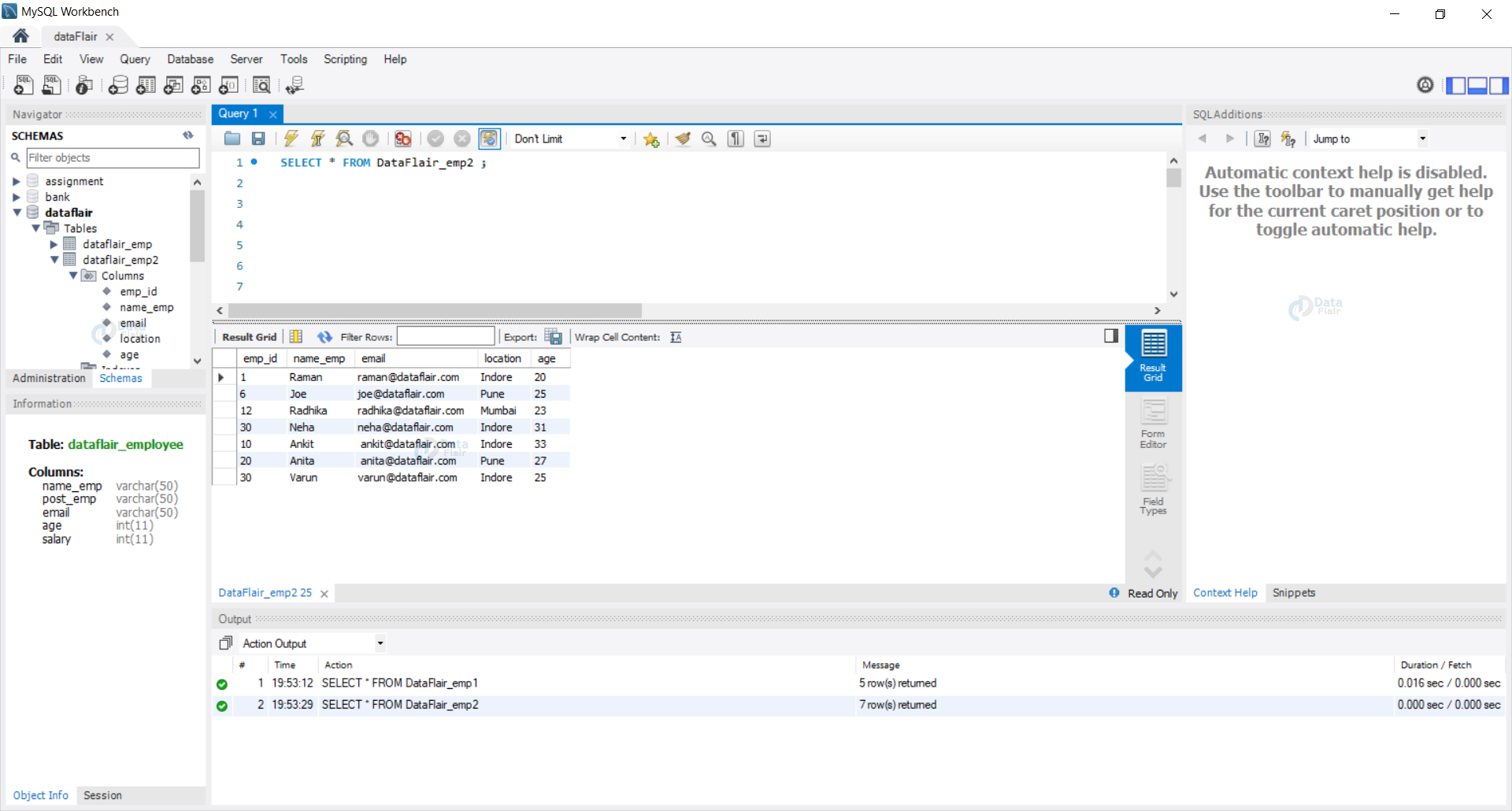
Let us view our tables, i.e. DataFlair_emp1 and DataFlair_emp2.
Query:
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp1 ;
Query:
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp2 ;
Types of SQL Joins
We have four types of joins in SQL, and they are as follows:
| Sr.No | JOIN | Description |
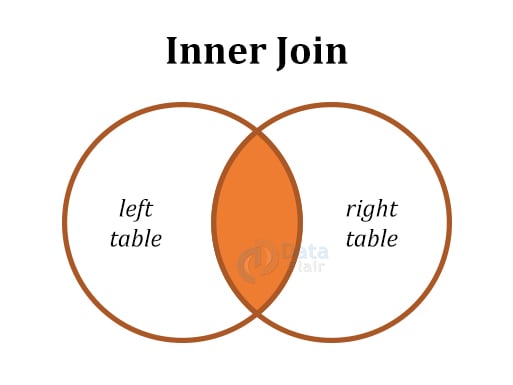
| 1 | Inner Join | Fetches value common in all the tables. |
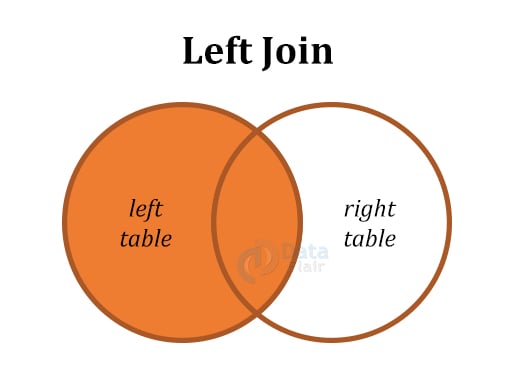
| 2 | Left (Outer) Join | Fetches all values from the left table and matching records from the right table. |
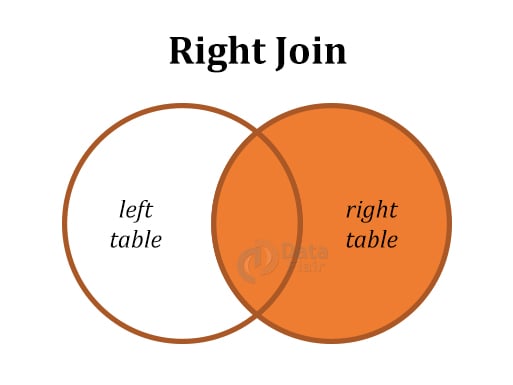
| 3 | Right (Outer) Join | Fetches all values from the right table and matching records from the left table. |
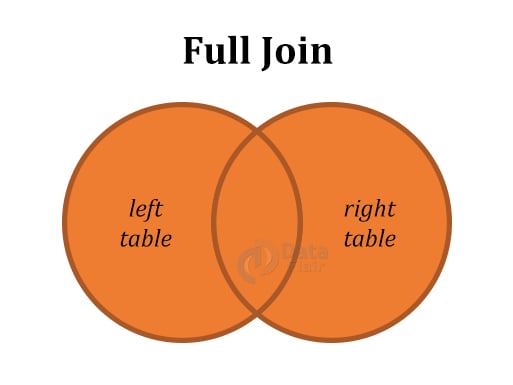
| 4 | Full (Outer) Join | Fetches value when there is a match in the right or left table. |
Below are the diagrammatic representations of all the SQL Joins:
SQL Inner Join Syntax
SELECT * FROM tableName1 INNER JOIN tableName2 ON tableName1.matchingColumn = tableName2.matchingColumn ;
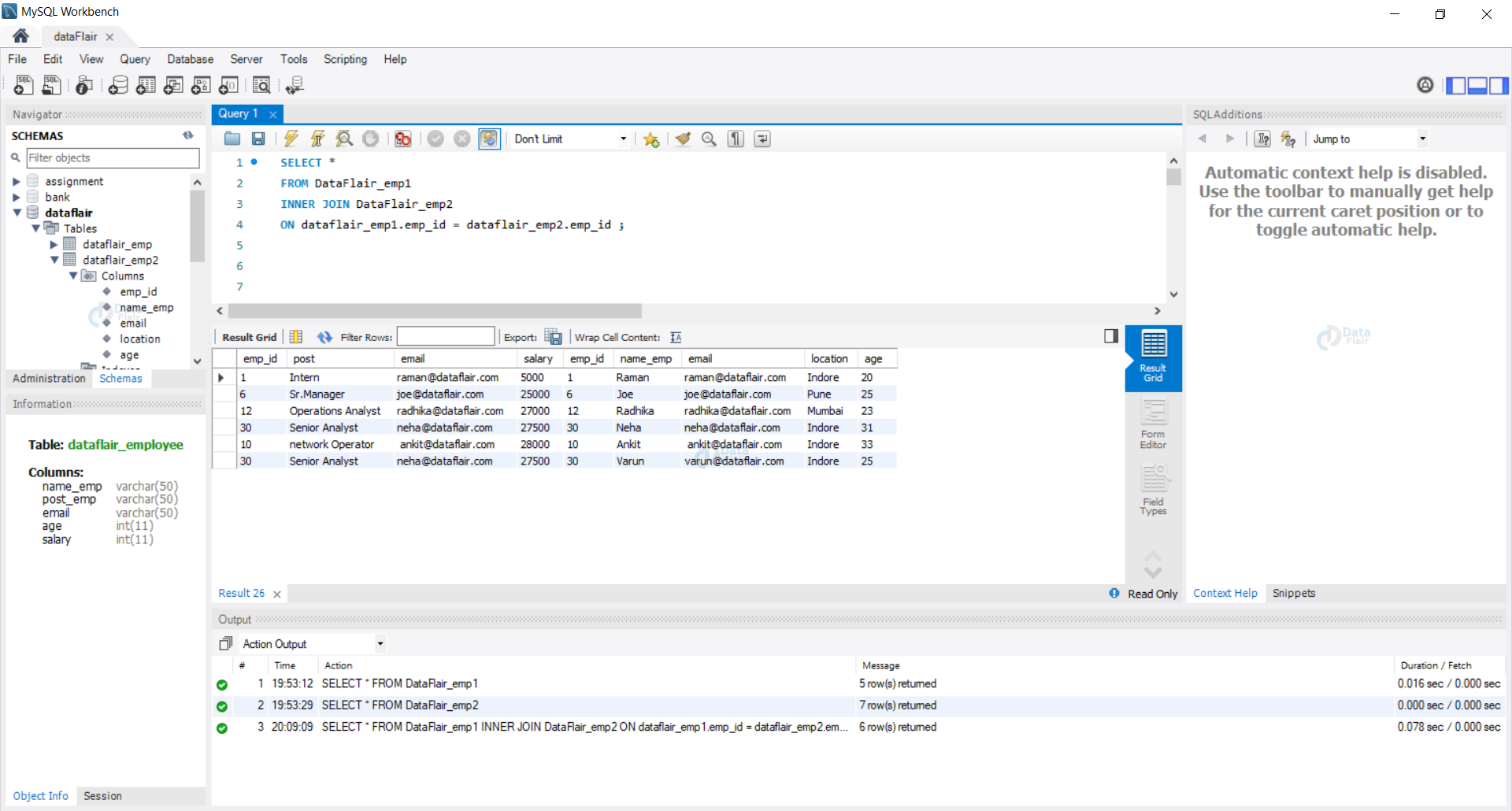
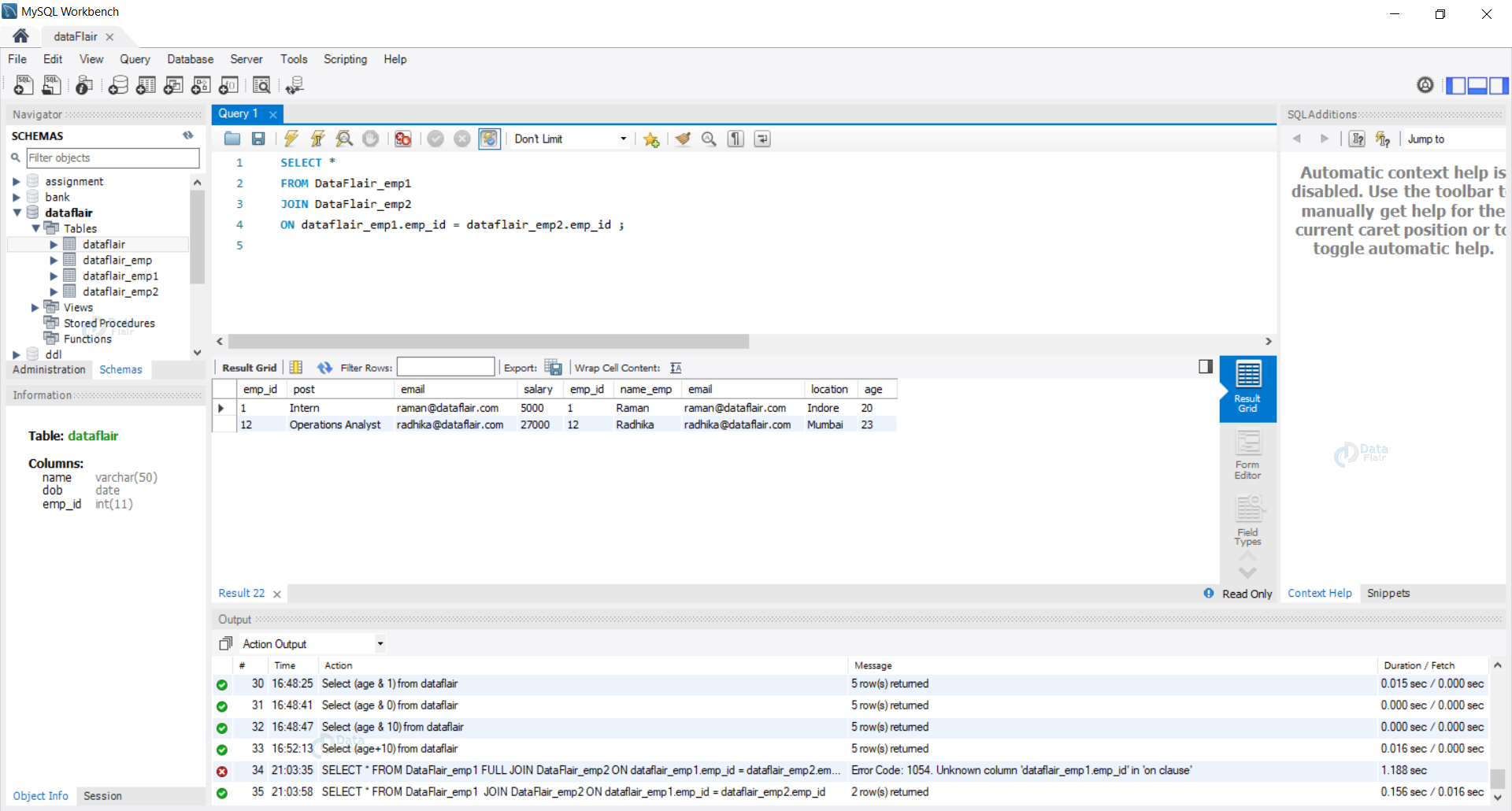
Example 1: [Inner Join] Let us view all the data in both of our tables using the inner join.
Query:
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp1 INNER JOIN DataFlair_emp2 ON dataflair_emp1.emp_id = dataflair_emp2.emp_id ;
SQL Left (Outer) Join Syntax
SELECT * FROM tableName1 LEFT JOIN tableName2 ON tableName1.matchingColumn = tableName2.matchingColumn ;
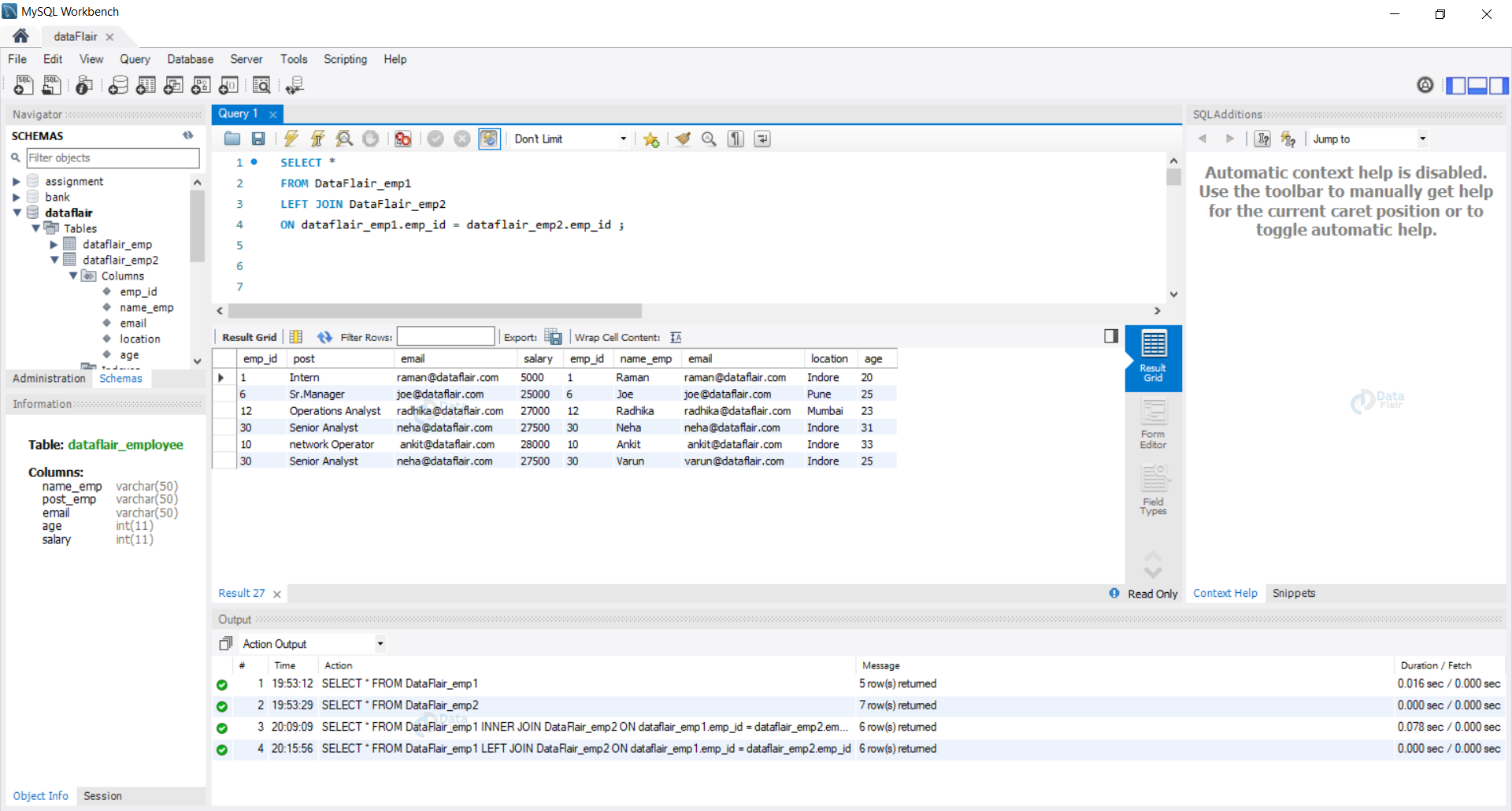
Example 2: [Left (Outer) Join] Let us use the left join on both of our tables.
Query:
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp1 LEFT JOIN DataFlair_emp2 ON dataflair_emp1.emp_id = dataflair_emp2.emp_id ;
SQL Right (Outer) Join Syntax
SELECT * FROM tableName1 RIGHT JOIN tableName2 ON tableName1.matchingColumn = tableName2.matchingColumn ;
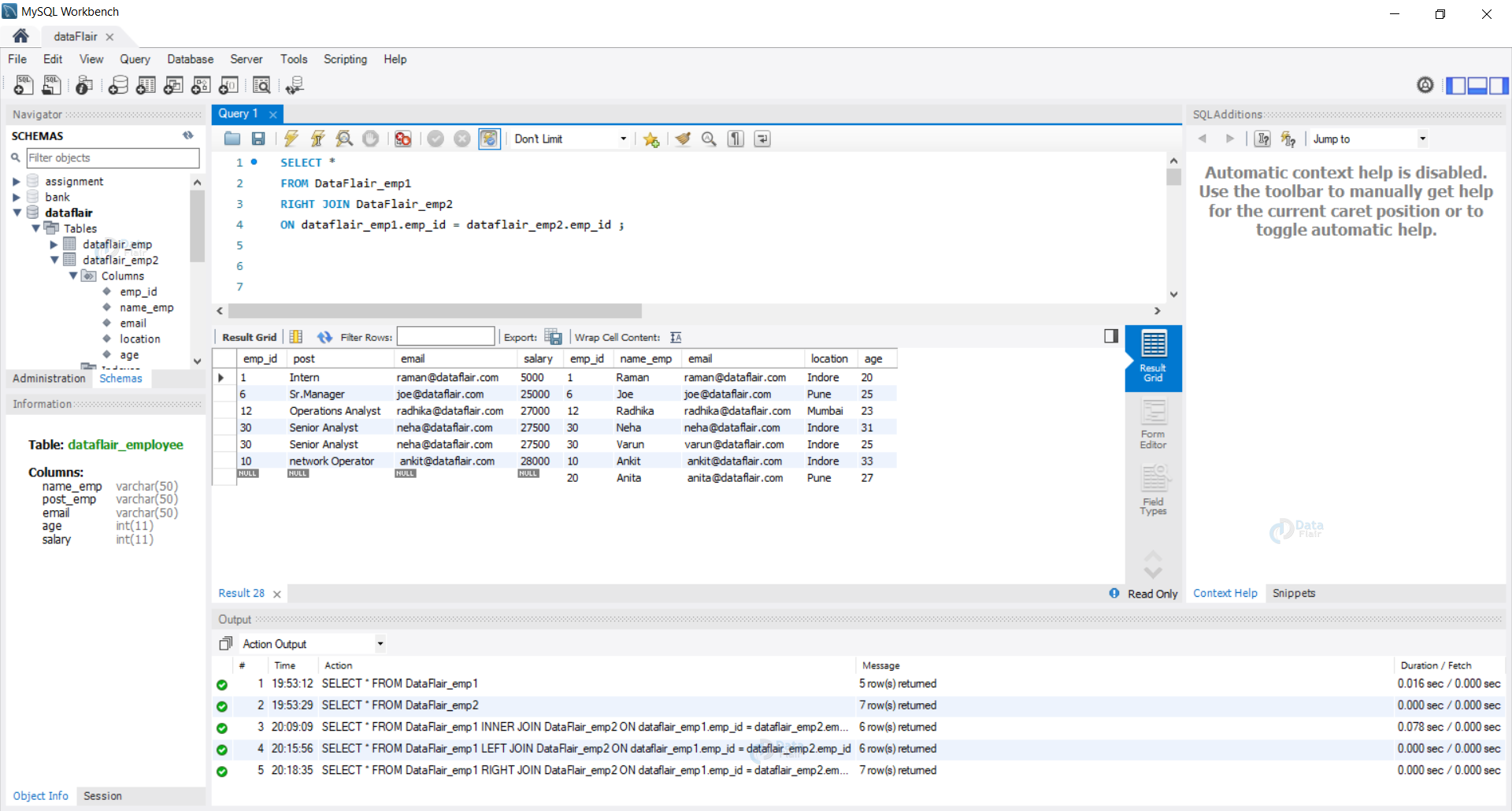
Example 3: [Right (Outer) Join] Let us use the right join on both of our tables.
Query:
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp1 RIGHT JOIN DataFlair_emp2 ON dataflair_emp1.emp_id = dataflair_emp2.emp_id ;
SQL Full (Outer) Join Syntax
SELECT * FROM tableName1 RIGHT JOIN tableName2 ON tableName1.matchingColumn = tableName2.matchingColumn ;
Example 4: [Full (Outer) Join] Let us use the full join on both of our tables.
Query:
SELECT * FROM DataFlair_emp1 FULL JOIN DataFlair_emp2 ON dataflair_emp1.emp_id = dataflair_emp2.emp_id ;
Summary
When we have to deal with large volumes of data, we need to do a lot of modifications and tweaks in our data to extract some meaningful knowledge.
With the help of joins, we are able to easily combine the data and draw useful insights out of it. We have discussed four significant types of joins, i.e. Full outer join, Left outer join, Right outer join, and inner join.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google


To display easy words to understand
Do you allow to print your content, and how much will the fee. (I am a student).
There is a mistake on “SQL Full (Outer) Join Syntax” snippet. Line 3 should have been “FULL JOIN tableName2” instead of “RIGHT JOIN tableName2”