List of RBI Governors – Governors of Reserve Bank of India
Are you ready for UPSC Exam? Check your preparation with Free UPSC Mock Test
The Reserve Bank is the Central bank of India. It is responsible for controlling the production and supply of the Indian rupee. It is the regulator of the banking system of India. RBI is the leader and the boss of all commercial and other finance companies in India.
It came into being on 1 April 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act. The governor is the chief executive of the Reserve bank of India. He is the ex-officio chairperson of the Central Board of Directors.
Their tenure is usually of three years but can be extended to two more years. India has seen 25 Governors of the RBI till the date.
Roles and Responsibilities of RBI Governors
- He maintains monetary stability in the Indian economy. The governor plays an active role in formulating the programs and policies of the Reserve Bank of India.
- He issues the required licenses to start new foreign and private banks in India.
- Also, he holds the power to control different interest rates on loans and deposits of all the banks in India.
- It is his duty to regulate and administer the financial system of India.
- Under the foreign exchange management act (1999), RBI Governors manage the foreign exchange market including external payment and trade transactions.
- The governor issues and monitors the currency notes and coins to supply in the country.
- He also monitors the rules and regulations to offer more customer-friendly services in the Indian banking system.
- He facilitates and monitors the flow of credit to all working sectors of India.
List of Governors of the Reserve Bank of India
Below is the List of RBI Governors of India:
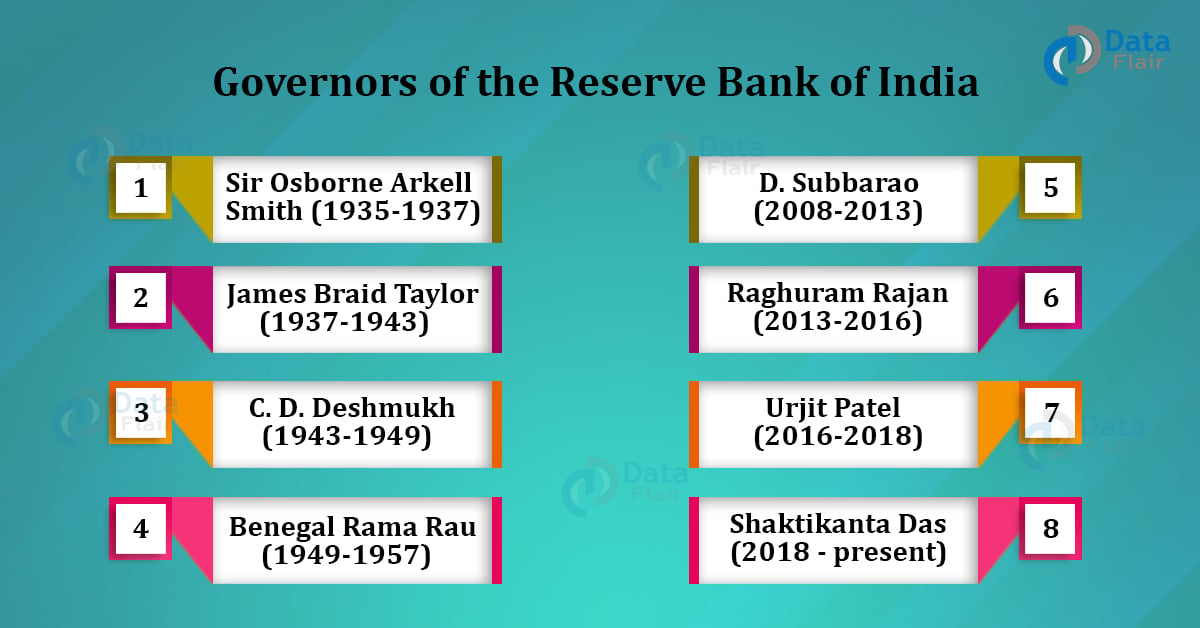
1. Sir Osborne Arkell Smith (1935-1937)
He was the first governor of the Reserve Bank of India. He was a professional banker from Australia. In 1926, he came to India and became the Managing Governor of the Imperial Bank of India.
Due to his different take on policy issues like the exchange rates and interest rates, he became the first governor of RBI in 1935. He did not sign any rupee during his tenure.
2. James Braid Taylor (1937-1943)
He was the second governor of the Reserve bank of India and was an Indian Civil Service officer as a profession. He also served as the Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India and Controller of Currency.
James Braid played an active role in preparing the Reserve Bank of India Bill. He was the first governor to sign on the Indian currency. He served as the governor for two terms.
3. C. D. Deshmukh (1943-1949)
He was the first Indian Governor of the Central Bank of India. He was a member of Indian Civil Services. Before becoming the governor, he served as Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India and Custodian of Enemy Property.
In 1943, British authority made him the governor of RBI. His second term ended in 1949. He then served as the Finance Minister in the Union Cabinet.
4. Benegal Rama Rau (1949-1957)
He was the fourth governor of the Central bank of India. He was an Indian Civil Services Officer too. Benegal Rama Rau served as the Ambassador of India to the United States, Ambassador of India to Japan, and the Chairman of Bombay Port Trust.
He became the governor of RBI in 1949 and served the longest till 1957.
5. K. G. Ambegaonkar (1957)
He was the fifth governor of the Central bank of India. He was an Indian Civil Service member and served the RBI for only 45 days. His tenure was the third shortest of all. He was a finance secretary and then deputy governor of RBI before joining the governor’s office.
6. H. V. R. Iyengar (1957-1962)
He was the sixth governor of the Central Bank of India. He was a part of the Indian Civil Service from 1926 and was the Chairman of State Bank of India before joining the RBI. in 1957, he became the governor of RBI.
The idea of cash reserve ratio and selective credit control entered the banking system during his tenure. He also received the Padma Vibhushan in 1962.
7. P. C. Bhattacharya (1962-1967)
He was the seventh Governor of the Central Bank of India. He was an Indian Audit and Accounts Service officer and served as the Chairman of the State Bank of India and Secretary in the Ministry of Finance. In 1962, he became the governor of RBI.
He saw the introduction of the Industrial Development Bank of India, the Agricultural Refinance Corporation, and the Unit Trust of India. The reduction of denominations 5, 10, and 100 took place during his tenure.
8. Lakshmi Kant Jha (1967-1970)
He was the eighth governor of the Central Bank of India. He was an Indian Civil Service officer and served as a secretary in the Ministries of Industries and Commerce and Finance and Secretary to the Prime Minister of India.
In 1967, he became the governor of RBI. He saw the introduction of Rs 2, 5, 10, and 100 notes in 1969. During his tenure, the nationalization of 14 major commercial banks, social controls over commercial banks, and establishment of the National Credit Council took place.
9. B. N. Adarkar (1970)
He was the ninth governor of the Central Bank of India. He was an economist and a civil service officer and served as the Executive Director at the International Monetary Fund. B.N.Adarkar became the governor of RBI in 1970 and served only for 42 days.
His report on the health insurance scheme for industrial workers became the Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948. He was an active member of the establishment of the National Institute of Bank Management.
10. Sarukkai Jagannathan (1970-1975)
He was the tenth governor of the Central bank of India. He was an Indian Civil Service officer and became the governor of RBI in 1970. The establishment of Credit Guarantee Corporation of India and State Level Bankers’ Committee took place during his tenure.
He saw the introduction of notes of Rs20 and Rs50 denomination. He left his office to join the position of India’s Executive Director at the International Monetary Fund.
11. N. C. Sen Gupta (1975)
He was the eleventh governor of the Central Bank of India. He served as a secretary to the Department of Banking of the Ministry of Finance. N.C.Sen Gupta became the governor of RBI in 1975 and served for only 92 days. His signature was seen on 1000 rupees note only.
12. K. R. Puri (1975-1977)
He was the twelth governor of the Central Bank of India. He was the chairman of Life Insurance Corporation of India before this. His signature was also last seen on a 1000 rupees note. His tenure saw the introduction of Regional Rural Banks and the announcement of a twenty point economic program.
13. M. Narasimham (1977)
He was the thirteenth governor of the Central bank of India and first from the Reserve bank Cadre. He was the Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India before this. M. Narasimhan became the governor of RBI in 1977 but served only for 211 days.
He then became India’s executive director at the World Bank and then of the International Monetary Fund. He received Padma Vibhushan in 2000.
14. I. G. Patel (1977-1982)
He was the fourteenth governor of the Central bank of India. He was an economist who served as Director of the London School of Economics, Deputy Administrator of the United Nations Development Programme, and Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India.
I.G.patel became the governor of RBI in 1977. The demonetization of Rs 1000, 5000, and 10,000 notes took place during his tenure. He received Padma Vibhushan in 1991.
15. Manmohan Singh (1982-1985)
He was the fifteenth governor of the Central Bank of India. He is an economist and served as Secretary in the Ministry of Finance and Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India. Manmohan Singh became the governor of RBI in 1982.
His tenure saw new legal reforms for the banking sector and establishment of the Urban Banks Department. He became the prime minister of India in 2004.
16. Amitav Ghosh (1985)
He was the sixteenth governor of the Central Bank of India. He is a banker and served as Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India and Chairman of the Allahabad Bank.
Amitav Ghosh became the governor of RBI in 1985 but served only for 20 days. After this, he served as the Director of the IDBI Bank.
17. R. N. Malhotra (1985-1990)
He was the seventeenth governor of the Central bank of India. He was an Indian Administrative Service officer and served as the Finance Secretary and Executive Director at the International Monetary Fund. Also, He became the governor of RBI in 1985 and saw the introduction of Rs 500 note.
18. S. Venkitaramanan (1990-1992)
He was the eighteenth governor of the Central bank of India. He was an IAS officer and served as the Finance Secretary in the Ministry of Finance before joining RBI. Venkitaramanan became the governor of RBI in 1990 and dealt with the balance of payments crisis before the LPG policy.
19. C. Rangarajan (1992-1997)
He was the nineteenth governor of the Central bank of India. He is an economist and served as Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India. Rangarajan became the governor of RBI in 1992 and saw central bank activism and the establishment of a unified exchange rate.
He became the Chairman of the Prime Minister’s Economic Advisory Council in 2009.
20. Bimal Jalan (1997-2003)
He was the twentieth governor of the Central Bank of India. He is an economist and served as Finance Secretary, Banking Secretary, and Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India.
Bimal Jalan became the governor of RBI in 1997. He saw the Asian Crisis and struggle of forex reserves and balance of payments.
21. Y. Venugopal Reddy (2003-2008)
He was the twenty-first governor of the Central Bank of India. He is an economist and was an IAS officer and served as the Executive Director at the International Monetary Fund and Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India.
Venugopal Reddy became the governor of RBI in 2003. He contributed to financial sector reforms, trade finance, center-state financial relations, and regional planning. He received Padma Vibhushan in 2010.
22. D. Subbarao (2008-2013)
He was the twenty-second governor of the Central Bank of India. He is an economist and ex IAS officer who served as a Finance Secretary and Member-Secretary of the Prime Minister’s Economic Advisory Council.
Subbarao became the governor of RBI in 2008. He worked on raising financial awareness in all parts of the country. He also handled the global financial crisis of 2008 and maintained the economy during tough times.
23. Raghuram Rajan (2013-2016)
He was the twenty-third governor of the Central Bank of India who served as the Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India and Chief Economist of the International Monetary Fund.
He became the governor of RBI in 2013 and became the Vice-Chairman of the Bank for International Settlements during his tenure. Raghuram is known for bringing down inflation and increasing foreign exchange reserves in India.
24. Urjit Patel (2016-2018)
He was the twenty-fourth governor of the Central Bank of India and worked at IMF till 1995. He is an economist and served as the Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank. Urjit Patel became the governor of RBI in 2016. The demonetization of Rs 500 and Rs1000 notes took place during his tenure.
25. Shaktikanta Das (2018 – present)
Shaktikanta Das is the current and twenty-fifth governor of the Central Bank of India. He was an IAS officer and served as Member of the Fifteenth Finance Commission, Sherpa of India to the G20, Economic Affairs Secretary, and Revenue Secretary.
He became the governor of RBI in 2018 and is also the chairperson of the Monetary Policy Committee of the central bank.
Conclusion
The Governors of the Reserve Bank of India have certain roles and responsibilities. This article will help you study details about RBI Governors, their tenure, roles/responsibilities, and their achievements.
India has seen 25 RBI governors including 2 Britishers. They all saw different economic phases of the country. Each of them was different from the other.
Competitive exams like UPSC, RRB, SSC, etc. are interested in this topic about RBI Governors. The questions around this topic are present in the general knowledge section.
Aspirants are expected to know basic information about RBI and its Governors. This article should help you cover this topic with all the important information.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google