2 Easy Ways To Create Pandas Series – The Ultimate Guide
Free Pandas course with real-time projects Start Now!!
Pandas series is the most important part of the data structure. Pandas series can be defined as a column in an excel sheet. We can create series by using SQL database, CSV files, and already stored data. There are many ways to create a series in Pandas but, we are going to practice in these two ways-
- With ndarray or numpy array
- With Python Dictionary
By the end of this pandas series tutorial, I am sure you can create and perform any task on series.
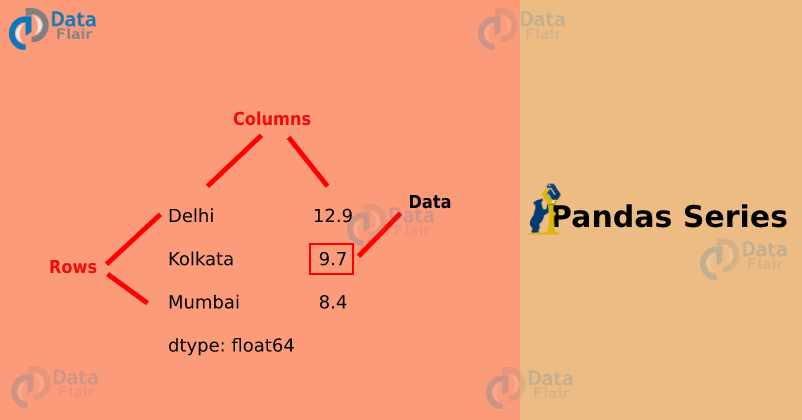
1. What is pandas series?
A series in pandas can be thought to be the fundamental piece of data structure. It is basically nothing but a one-dimensional array-like structure, which can be used to handle and manipulate data. What makes it special is its index attribute, which has incredible functionality and is heavily mutable.
Parameters in pandas series:
- data: This the value you want your series to possess.
- index: This is the index related to the value you use for the series.
- dtype: This specifies the type of values in the series.
- copy: This copies the data which was input.
Do you know what makes python pandas unique?
Let’s start to code in pandas series-
To begin, we import the pandas library.
>>> import pandas as pd
2. How to create a pandas series?
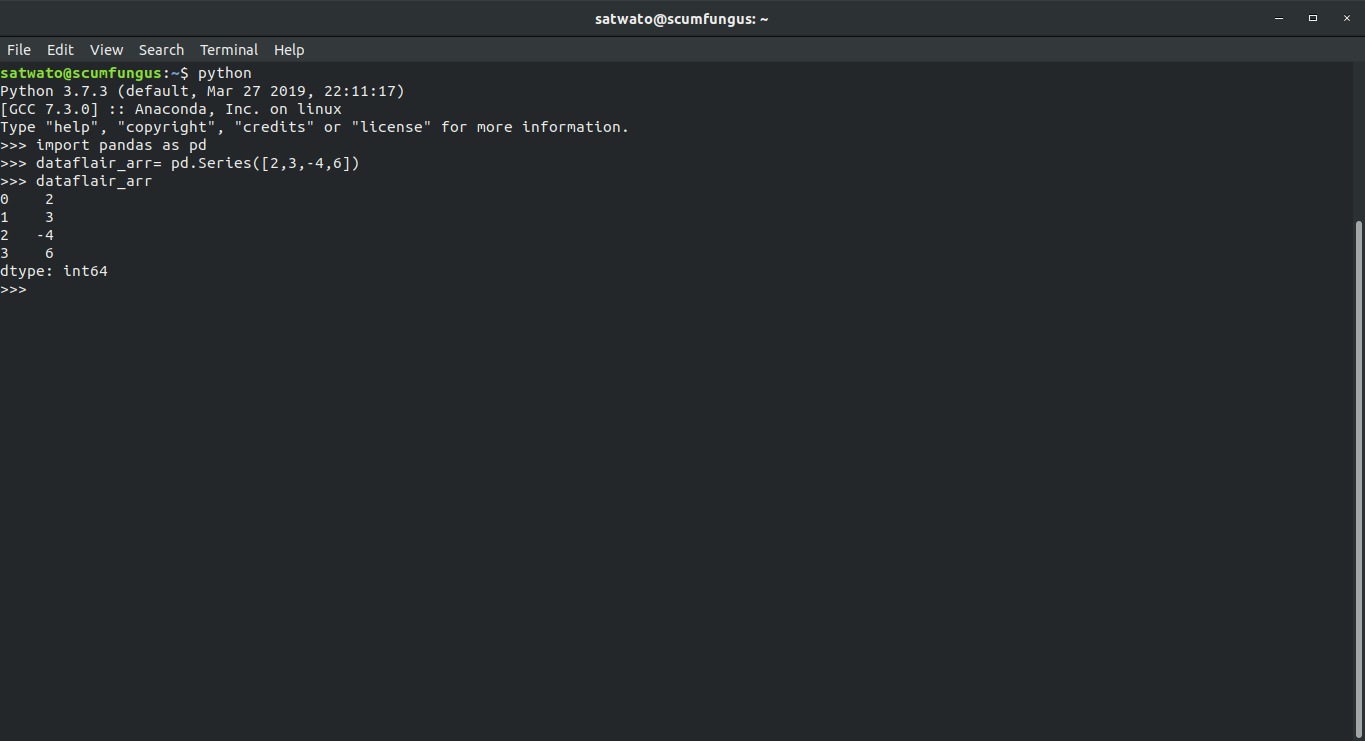
In your second code box after importing the library, go ahead and enter the following code-
>>> dataflair_arr= pd.Series([2,3,-4,6])
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
This will create your series.
To access the series, code the below code-
>>> dataflair_arr
Output-
0 2
1 3
2 -4
3 6
dtype: int64
Congratulations! You have created your first own series in pandas.
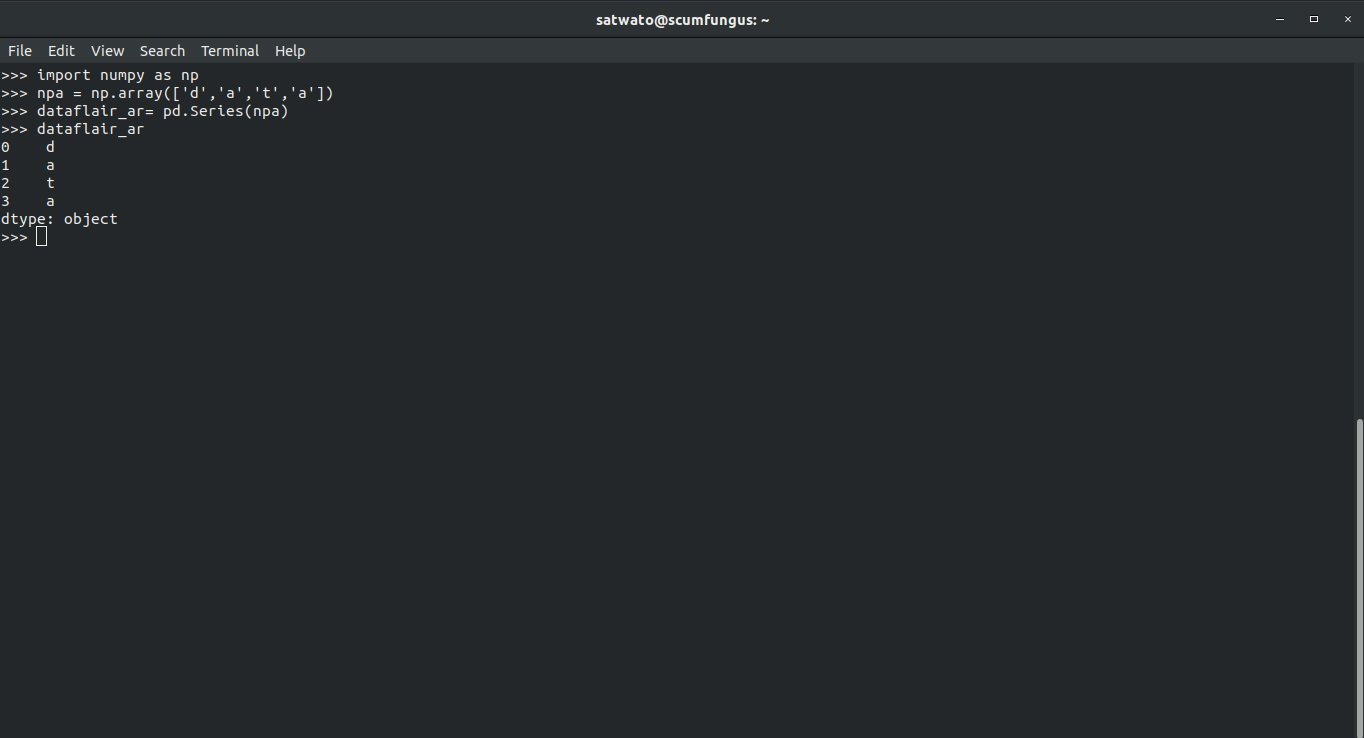
2.1 Create a series with ndarray or numpy array
We can also create a series using a ndarray or numpy array:
First, we will import the numpy library:
>>> import numpy as np
This lets us refer to the library as np. After initializing, we create a numpy array and then turn it into a series.
>>> npa = np.array(['d','a','t','a']) >>> dataflair_ar= pd.Series(npa) >>> dataflair_ar
The first line creates the numpy array and the second line turns the array into pandas series.
Output-
0 d
1 a
2 t
3 a
dtype: object
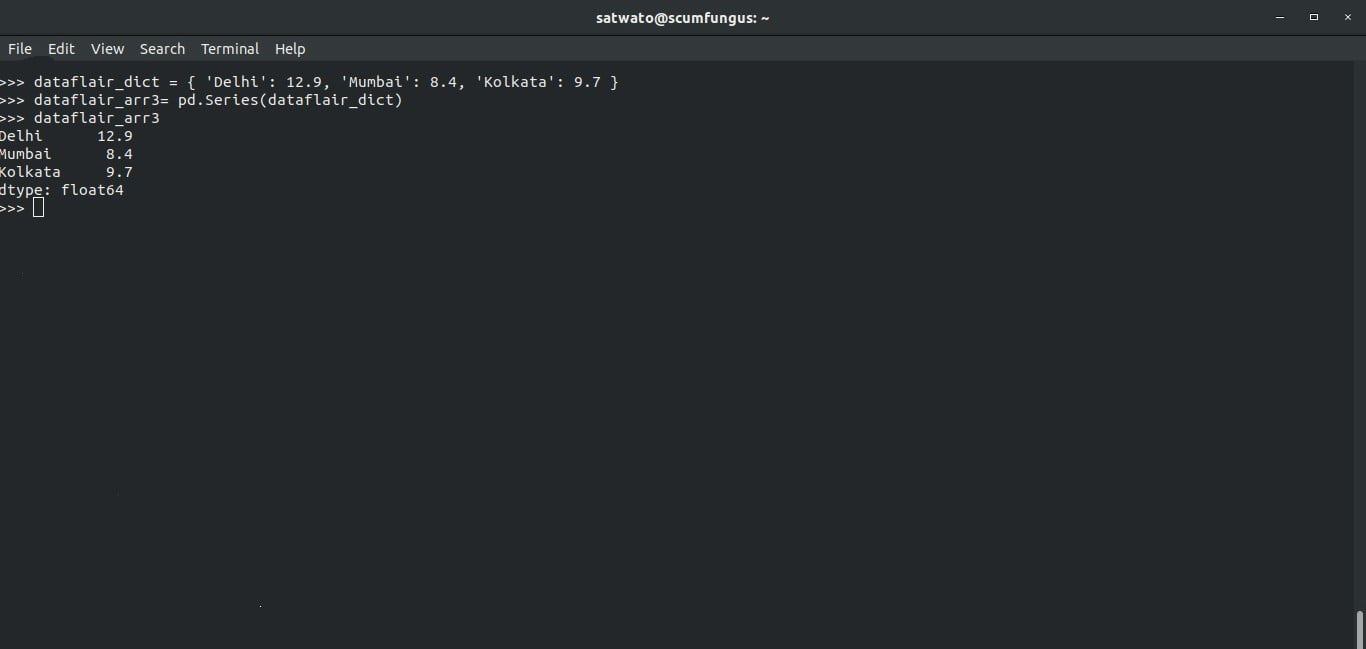
2.2 Create a series from a python dictionary
We can create a series from python dictionaries To do this, we first need to create a dictionary:
>>> dataflair_dict = { 'Delhi': 12.9, 'Mumbai': 8.4, 'Kolkata': 9.7 }To turn this dictionary into a pandas series, all we have to do is:
>>> dataflair_arr3= pd.Series(dataflair_dict) >>> dataflair_arr3
Output-
Delhi 12.9
Mumbai 8.4
Kolkata 9.7
dtype: float64
3. How to change the index of pandas series?
For indexing in pandas series first, we will create a list.
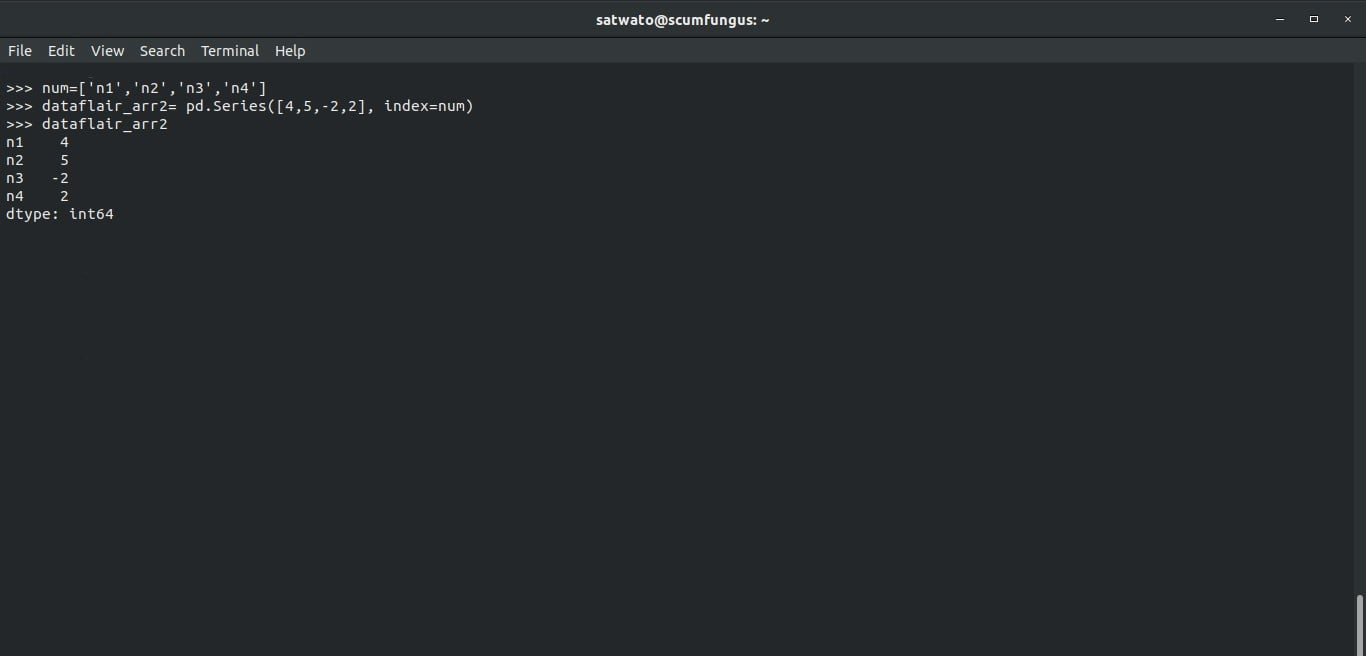
>>> num=[‘n1’,’n2’,’n3’,’n4’]
This is our list, and we want this to be the index to the values (we have provided). So, we write the following code and run it:
>>> dataflair_arr2= pd.Series([4,5,-2,2], index=num >>> dataflair_arr2
Output-
4. How to perform mathematical operations on a series?
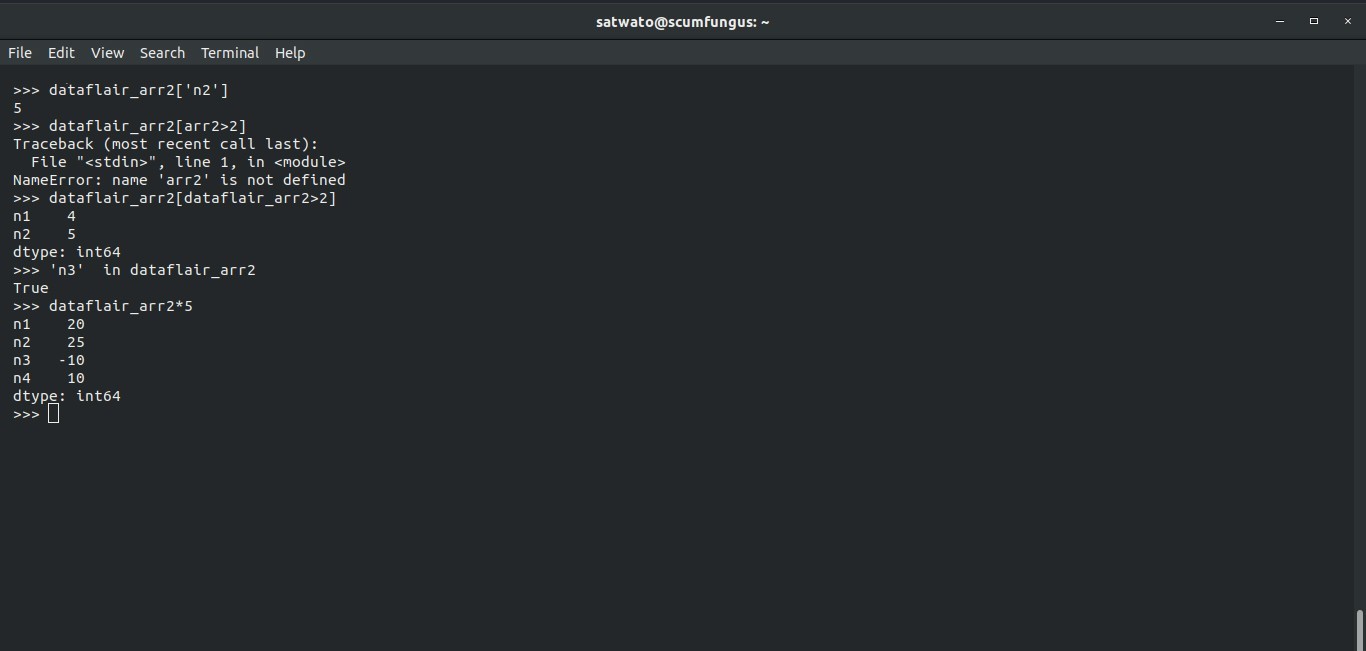
If you want to check the value to a corresponding index, simply use the following command
>>> dataflair_arr2[‘n2’]
This will return the value 5.
We can use parameters to filter values in a series. For this, let’s take the following example:
>>> dataflair_arr2[dataflair_arr2>2]
What does this mean? This basically is telling the series that you want a list of all the values that are greater than 2.
Running the code given above, we get:
n1 4
n2 5
dtype: int64
Check out pandas basic functionality to enhance your skills
Because 4 and 5 are the only values in the pandas series, that is more than 2. If a certain index is present inside a series or not, then use the ‘in’ parameter from python’s native code.
>>> ‘n3’ in dataflair_arr2
This will return “True”.
Example of Mathematical operations on Pandas Series
>>> dataflair_arr2*5
Output-
n1 20
n2 25
n3 -10
n4 10
dtype: int64
5. Demonstration of missing values
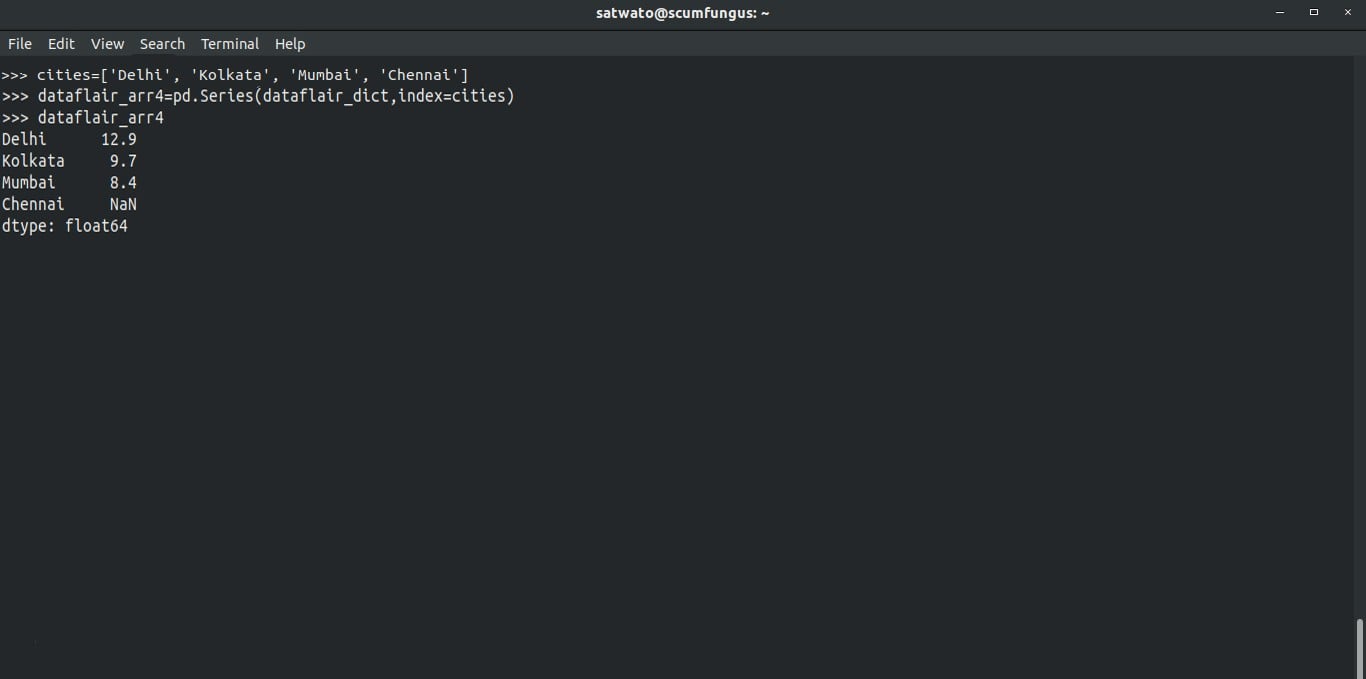
Let’s create a list of cities and implement it into a series as index:
>>> cities=['Delhi', 'Kolkata', 'Mumbai', 'Chennai'] >>> dataflair_arr4=pd.Series(dict,index=cities) >>> dataflair_arr4
Did you notice something? Chennai is a new addition and there is no value pertaining to it in the original series. Here, the value for Chennai is represented as NaN.
Delhi 12.9
Kolkata 9.7
Mumbai 8.4
Chennai NaN
dtype: float64
NaN is Pandas way to represent missing values.
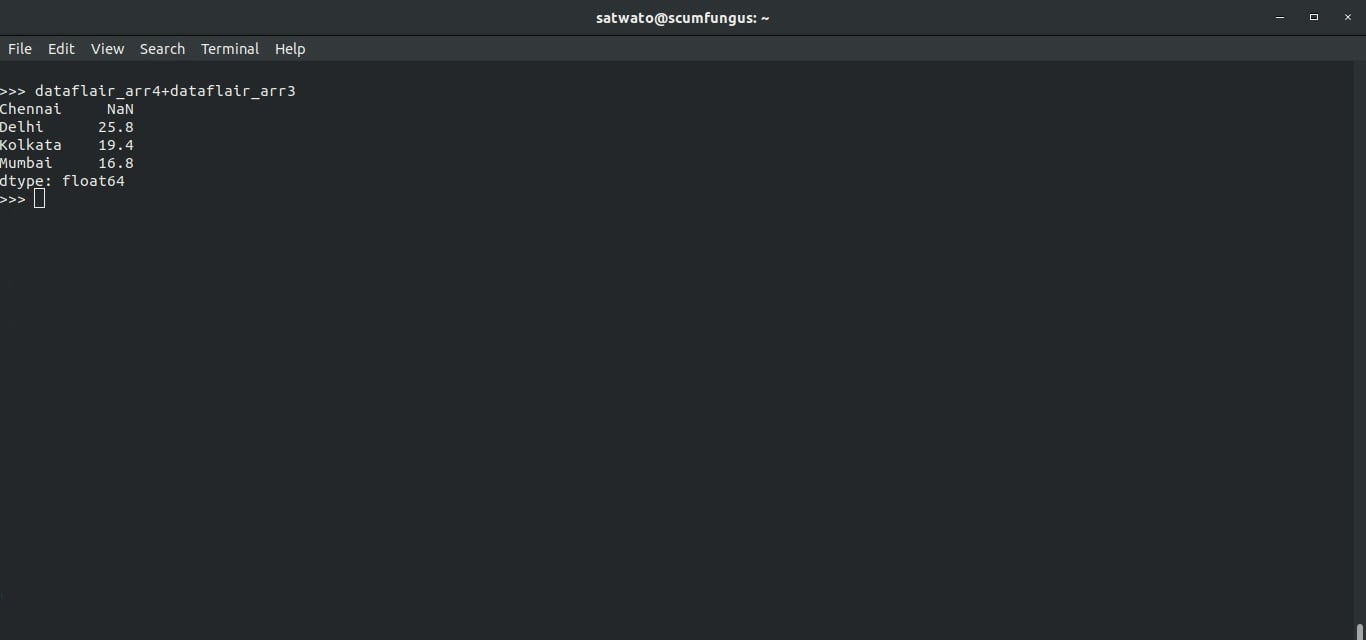
6. How to add two series in pandas?
Yes, it’s possible to add two series in pandas.
>>> dataflair_arr4+dataflair_arr3
Output-
Chennai NaN
Delhi 25.8
Kolkata 19.4
Mumbai 16.8
dtype: float64
Now, it’s time to learn how to sort in pandas series
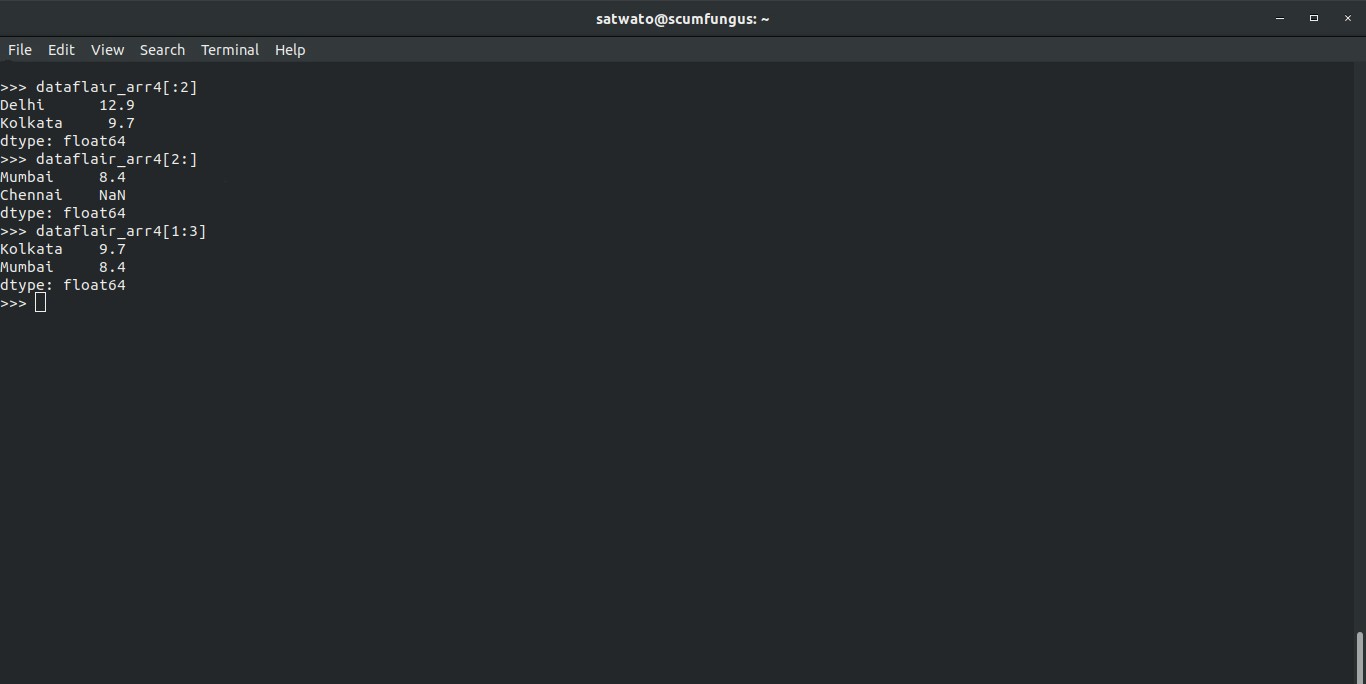
7. How to access a range of elements in a pandas series?
Let’s say, we want to access the first 2 elements of arr4. All we have to do is use the range function in pandas, which we can use with the help of ‘:’
The code to access the first two elements will be:
>>> dataflair_arr4[:2]
Output-
Delhi 12.9
Kolkata 9.7
dtype: float64
The code for the last two is:
>>> dataflair_arr4[2:]
Output-
Mumbai 8.4
Chennai NaN
dtype: float64
Therefore, the function basically works in the way series[x:y] where x is the number for the first row of the range and y is the last row of the range. Let’s try :
>>> dataflair_arr4[1:3]
Output-
Kolkata 9.7
Mumbai 8.4
dtype: float64
Summary
Now, you can create and perform any task on pandas series. It is very important to learn a series concept to become a master in pandas. With the help of pandas series, you can gain expertise in the other two data structures; dataframes, and panels.
The next step towards mastering pandas is dataframes
If you have any issues or questions, please drop a comment below.
You give me 15 seconds I promise you best tutorials
Please share your happy experience on Google


important basics of pandas