Pandas Merge and Join – Strategies For Beginners
Free Pandas course with real-time projects Start Now!!
The last tutorial ended with the question- How is Pandas Concatenation different from Pandas Merging and Joining? Hope, you all remember that. Today, we will come up with an answer to this question and discuss the various functions offered by pandas merge and join for the dataframes.
Pandas Merge and Join Functions
Pandas merging and joining functions allow us to create better datasets. This helps to get efficient and accurate results when trying to analyze data.
To perform pandas merge and join function, we have to import pandas and invoke it using the term “pd”
>>> import pandas as pd
- Now, we will create a dictionary and convert it into a pandas dataframe.
Print the dataframe.
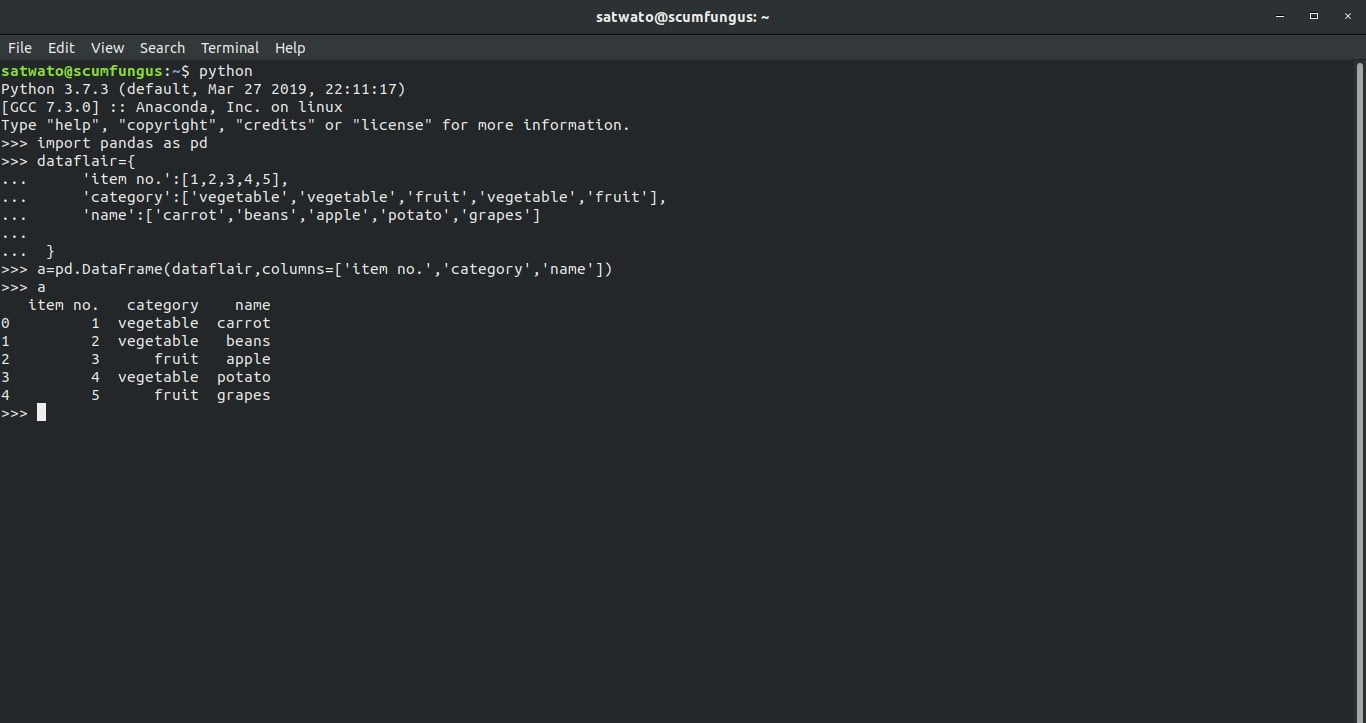
>>> dataflair={
... 'item no.':[1,2,3,4,5],
... 'category':['vegetable','vegetable','fruit','vegetable','fruit'],
... 'name':['carrot','beans','apple','potato','grapes']
...
... }
>>> a=pd.DataFrame(dataflair,columns=['item no.','category','name'])
>>> aOutput-
We saw that the DataFrame has 3 columns and 5 rows.
- Next, create another dictionary and make a DataFrame from it.
>>> dataflair2={
... 'item no.':[4,5,6,7,8],
... 'category':['vegetable','fruit','fruit','vegetable','fruit'],
... 'name':['gourd','mango','peach','peas','watermelon']
...
... }
>>> b=pd.DataFrame(dataflair2,columns=['item no.','category','name'])
>>> bOutput-
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
Again, we have 3 columns and 5 rows.
- We create the third and final dictionary to form the last DataFrame.
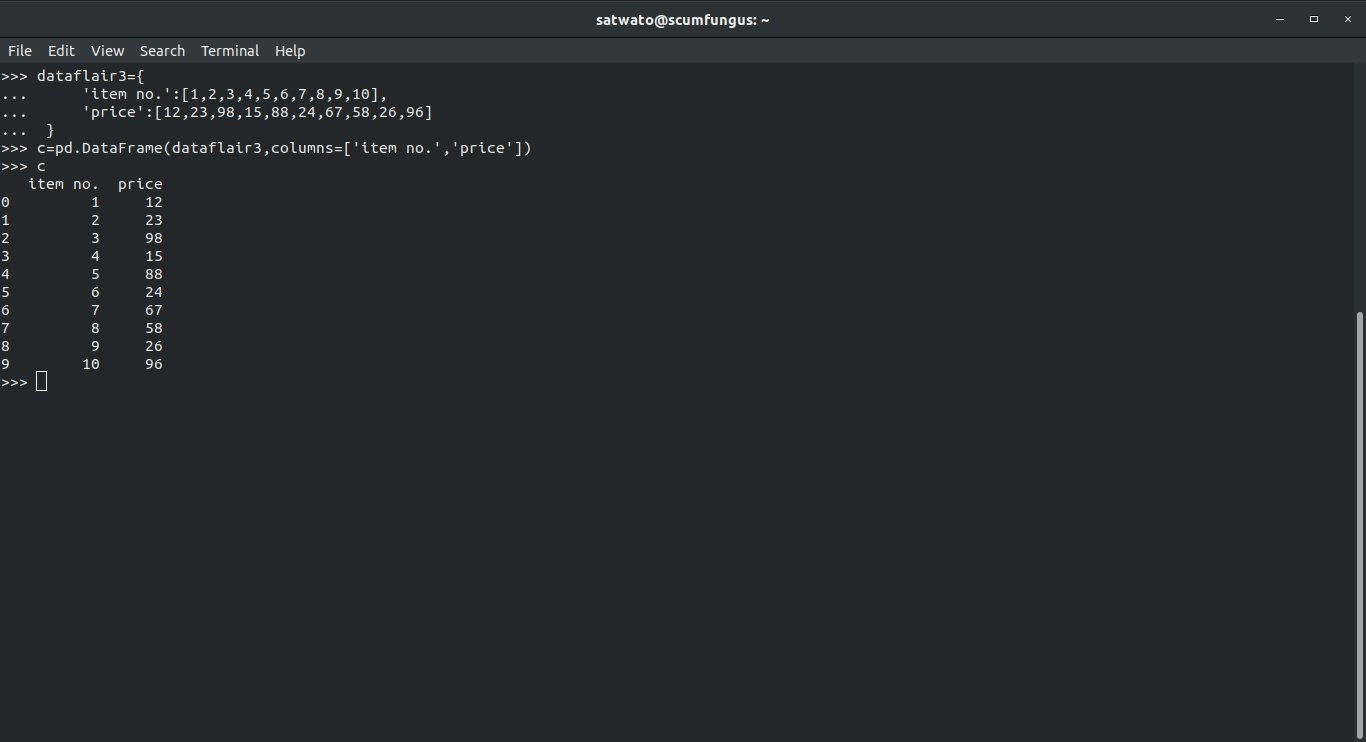
>>> dataflair3={
... 'item no.':[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],
... 'price':[12,23,98,15,88,24,67,58,26,96]
... }
>>> c=pd.DataFrame(dataflair3,columns=['item no.','price'])
>>> cOutput-
Here, we got the 2 columns, but 10 rows.
1. Pandas Concatenation
Using the concat function, we can concatenate two DataFrames in Pandas:
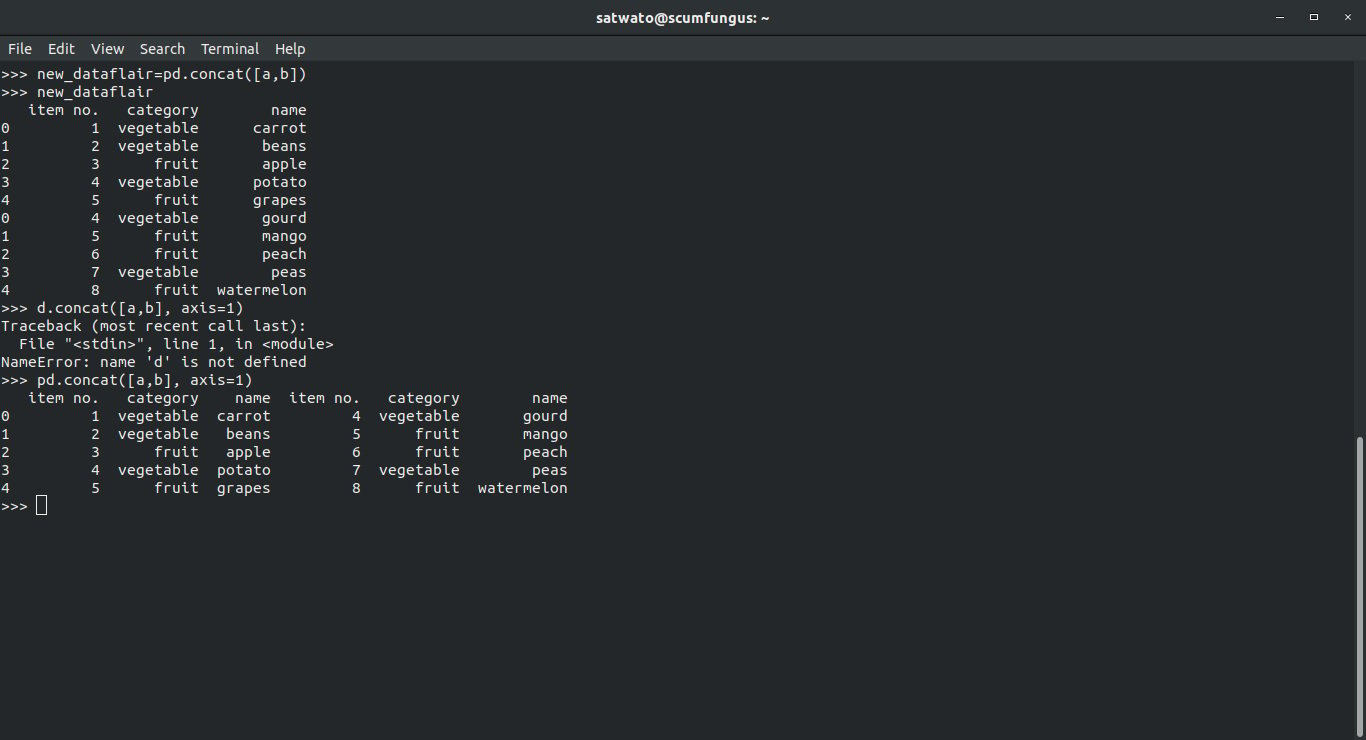
>>> new_dataflair=pd.concat([a,b]) >>> new_dataflair
This gives us a DataFrame, with a and b together. But this is vertical; to add horizontally, we use the following function:
- Horizontal Concatenation
>>> pd.concat([a,b], axis=1)
Using the axis=1 parameter, we are able to concatenate on the horizontal axis.
Output-
2. Pandas Merge
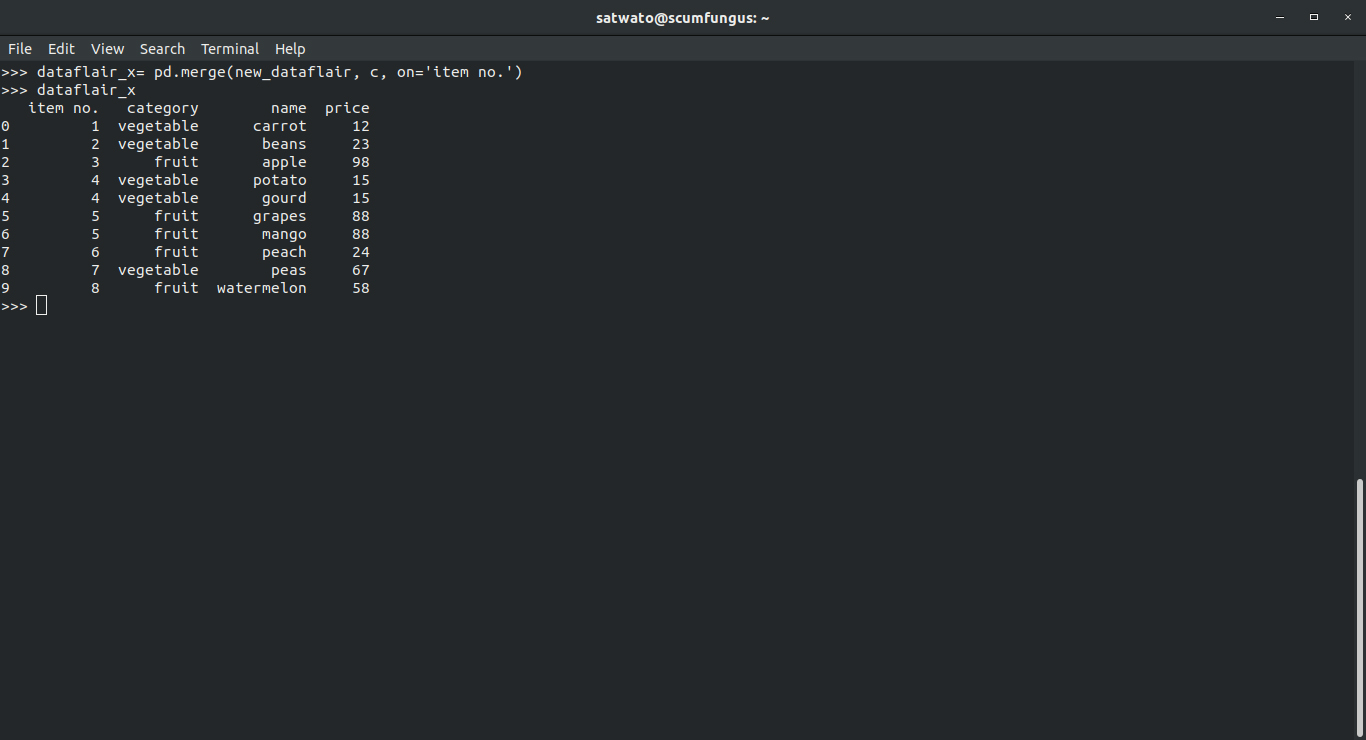
>>> dataflair_x pd.merge(new_dataflair, c, on='item no.') >>> dataflair_x
The Pandas merge function lets us merge the dataframe of items with their corresponding elements. This is achieved by the parameter “on” which allow us to select the common column between two dataframes.
Output-
2.1 Pandas Merging Using Multiple Keys
We can also merge dataframes using multiple keys using the following instruction.
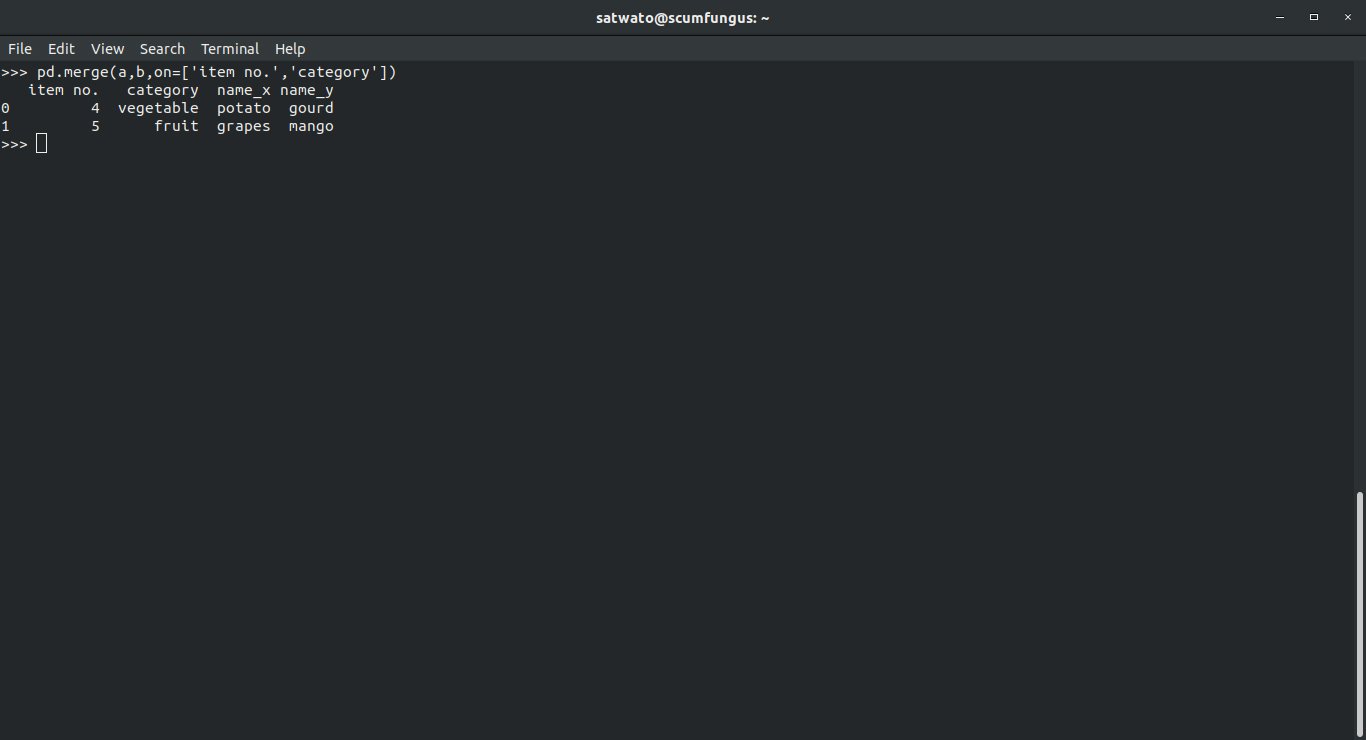
>>> pd.merge(a,b,on=['item no.','category'])
This will yield the common rows between the two dataframes for the corresponding column values.
Output-
2.2 Pandas Merging on the Basis of Index
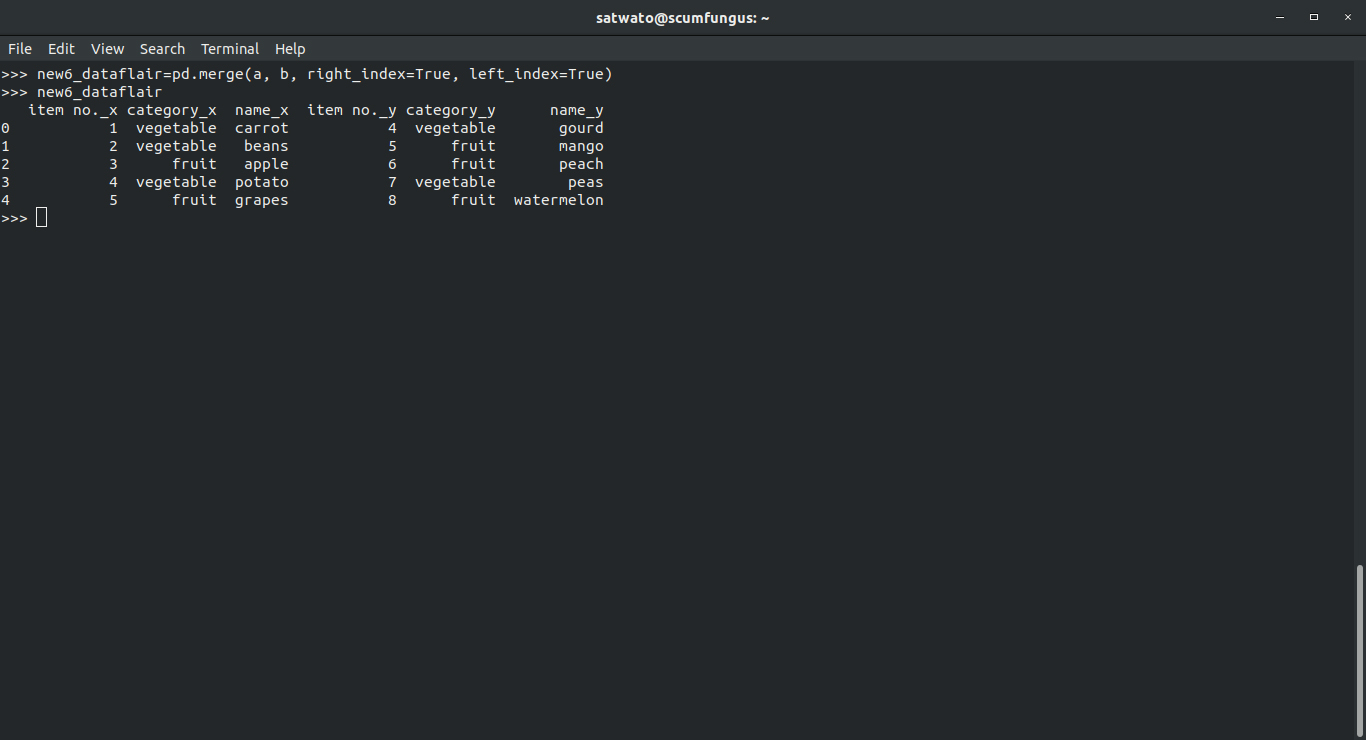
This function helps to merge two dataframes, based on the index of both of them.
>>> new6_dataflair=pd.merge(a, b, right_index=True, left_index=True) >>> new6_dataflair
Get a trick to Index the Pandas Dataframes
Output-
3. Pandas Join
There are 4 types of joins available in Pandas, let’s discuss one by one with an example-
3.1 Pandas Outer Join
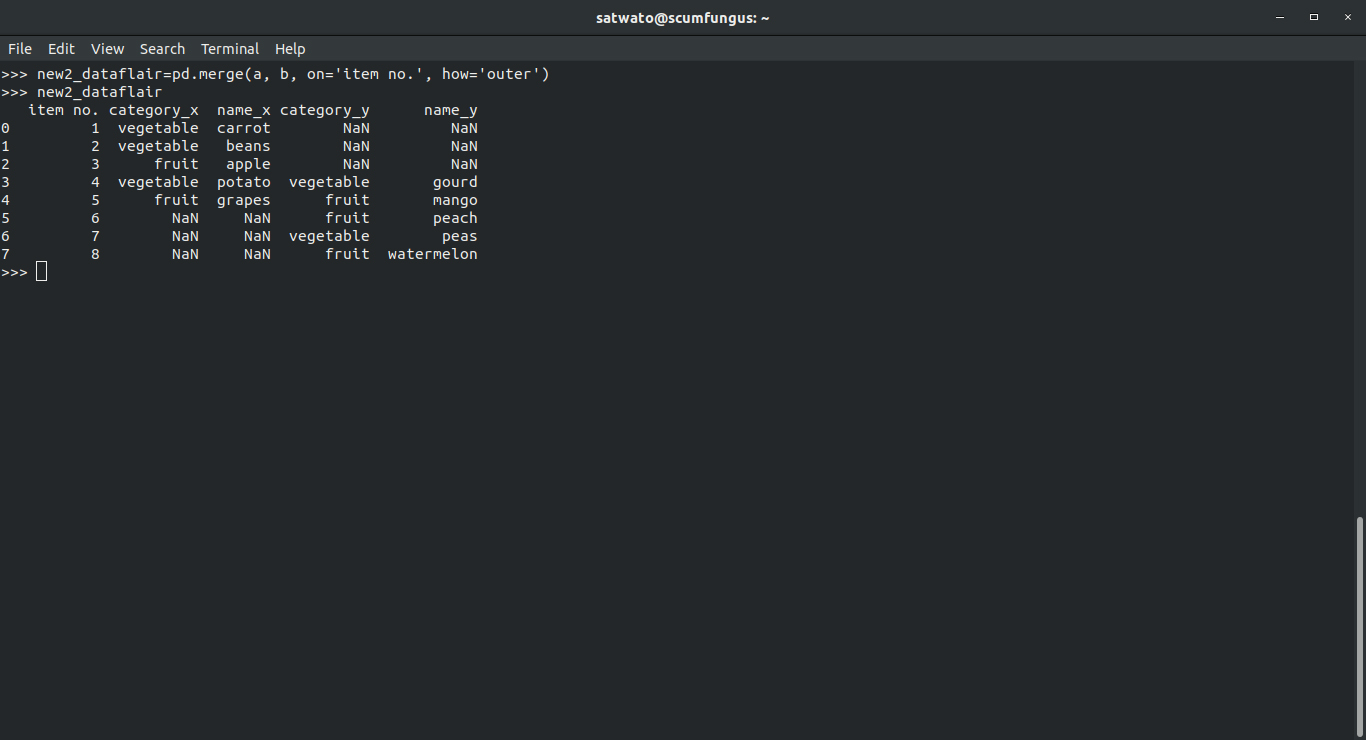
With an outer join in Pandas, we tend to achieve a dataframe with all records of elements from both a and b.
For each column attribute, we get an x and a y version. The x version belongs to the first dataframe and consists of members from its own dataset, including the ones common with the second dataframe. The other values are treated as missing values. For the y version, it’s the same.
>>> new2_dataflair=pd.merge(a, b, on='item no.', how='outer') >>> new2_dataflair
Output-
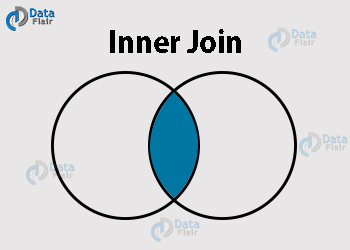
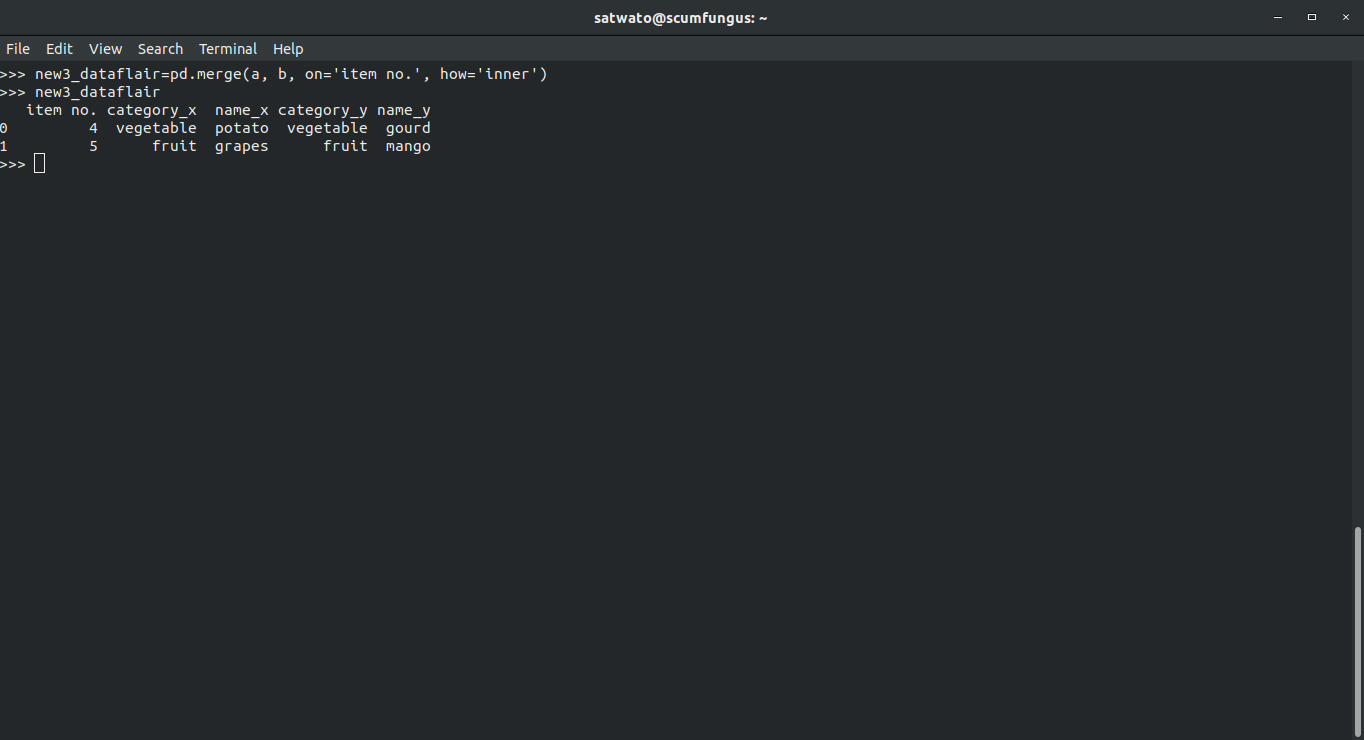
3.2 Pandas Inner Join
In an inner join, only the common values between the two dataframes are shown.
>>> new3_dataflair=pd.merge(a, b, on='item no.', how='inner') >>> new3_dataflair
Output-
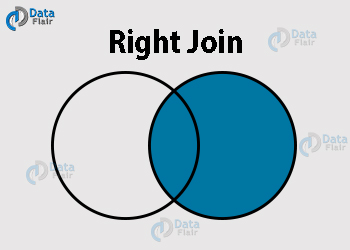
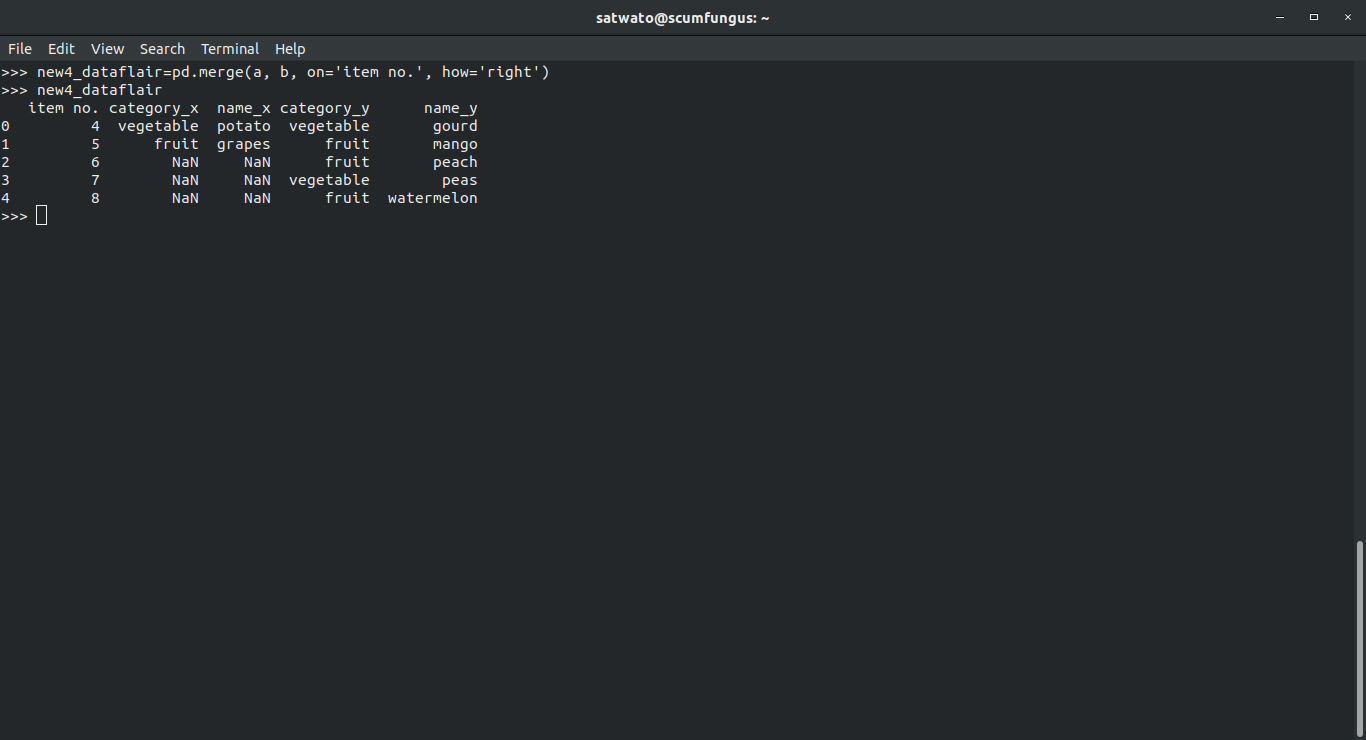
3.3 Pandas Right Join
In this, the x version of the columns show only the common values and the missing values. The y version shows all the values that are both- common and unique to the second dataframe.
>>> new4_dataflair=pd.merge(a, b, on='item no.', how='right') >>> new4_dataflair
Output-
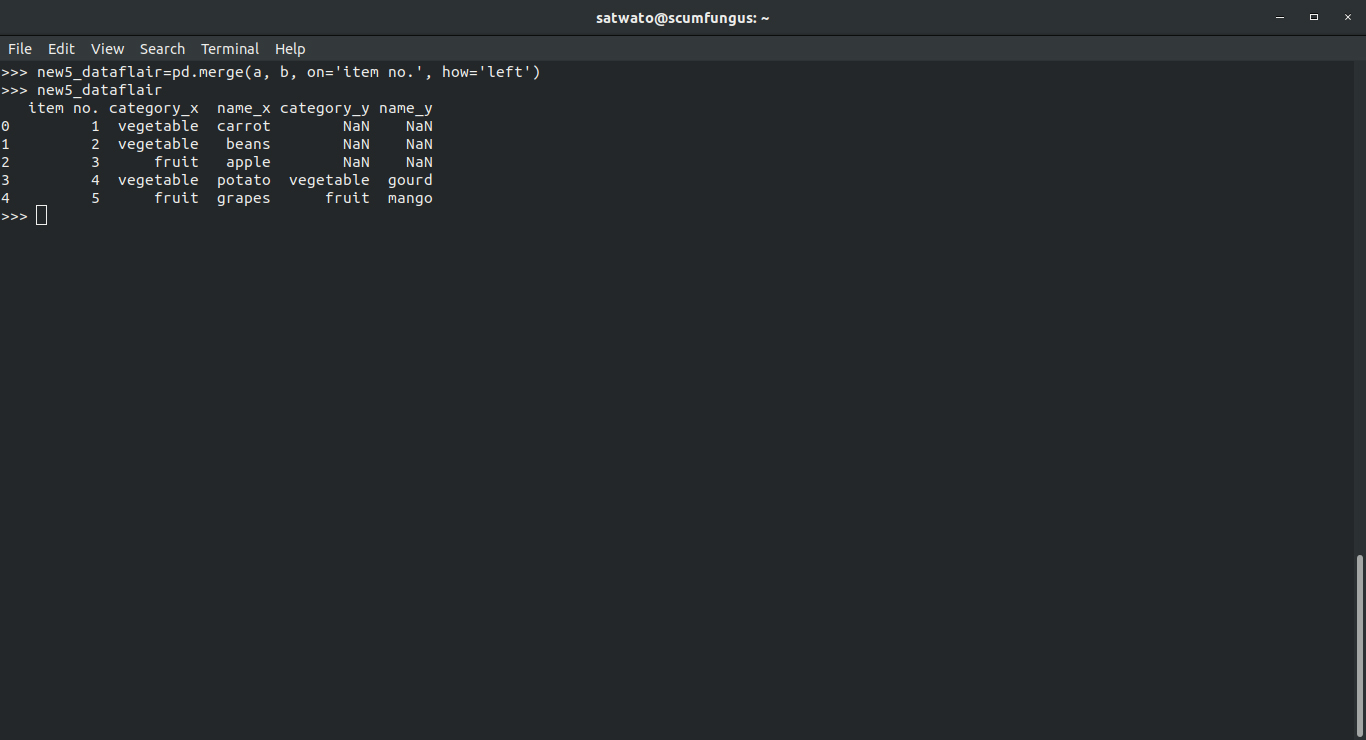
3.4 Pandas Left Join
In this, the x version consists of all the unique and common values from the first dataframe, but the y version only has the common values and missing values.
>>> new5_dataflair=pd.merge(a, b, on='item no.', how='left') >>> new5_dataflair
Output-
Summary
Through this article, we come across the various kinds of merge and join functions offered by pandas. This helps us manipulate data better. Hope you understood the differences between concatenation, merging, and joining in pandas.
Has this tutorial on pandas merging and joining been helpful to you? Let us know your suggestions, if any, and leave your feedback in the comments.
Did you like this article? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google