Pandas Basic Functionality – 4 Major Functions Used by Data Scientists
Free Pandas course with real-time projects Start Now!!
Python Pandas is popular because of basic functionalities. The panda’s library has many essential basic functions and functionalities which make your everyday work a lot easier. The Pandas basic functionality is highly recommended for a beginner to master in pandas.
Pandas Basic Functionality
Before starting Pandas basic functionality, you must learn to import libraries
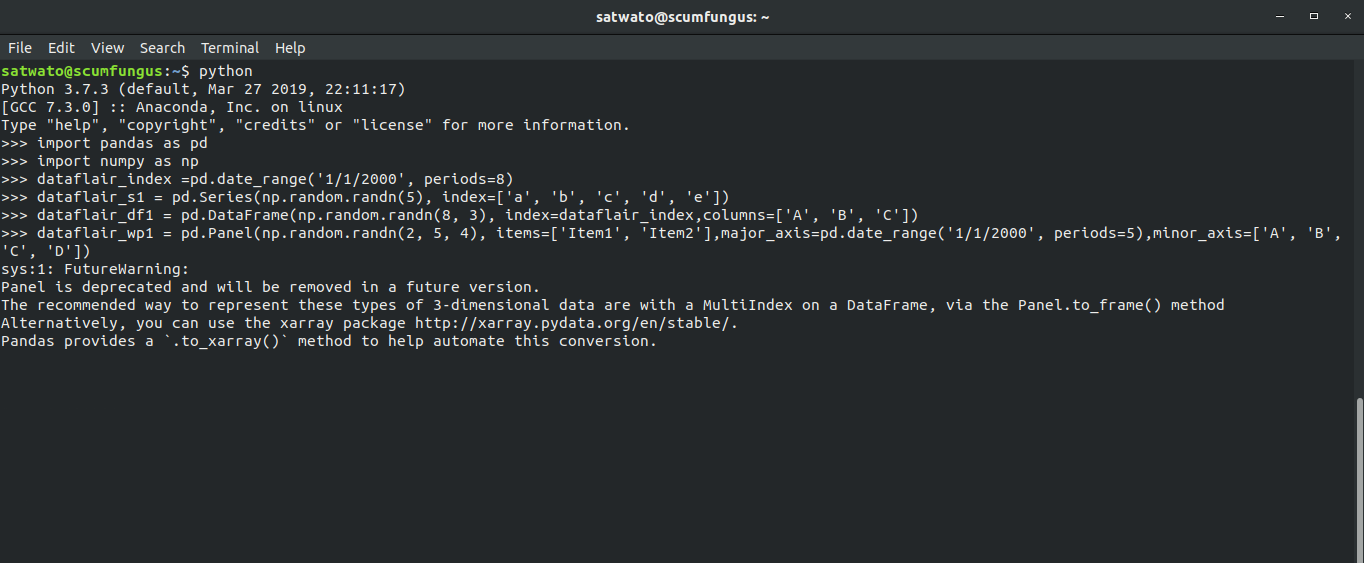
>>> import numpy as np >>> import pandas as pd
Here, we will create the 4 main data structures we work within Pandas.
- Index
>>>dataflair_index =pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=8)- Series
>>>dataflair_s1 = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
- DataFrame
>>>dataflair_df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(8, 3), index=dataflair_index,columns=['A', 'B', 'C'])
- Panel
>>> dataflair_wp1 = pd.Panel(np.random.randn(2, 5, 4), items=['Item1', 'Item2'],major_axis=pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=5),minor_axis=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])Output-
Before we dive into Pandas Basic functionalities, let’s discover the File Hierarchy in Pandas
Now we can start with the basic functionalities of Pandas.
- head() function
- tail() function
- Attributes
- Flexible Binary Operations
To view the starting or the ending of a lengthy series, we can use the head() or tail() function.
1. head() function
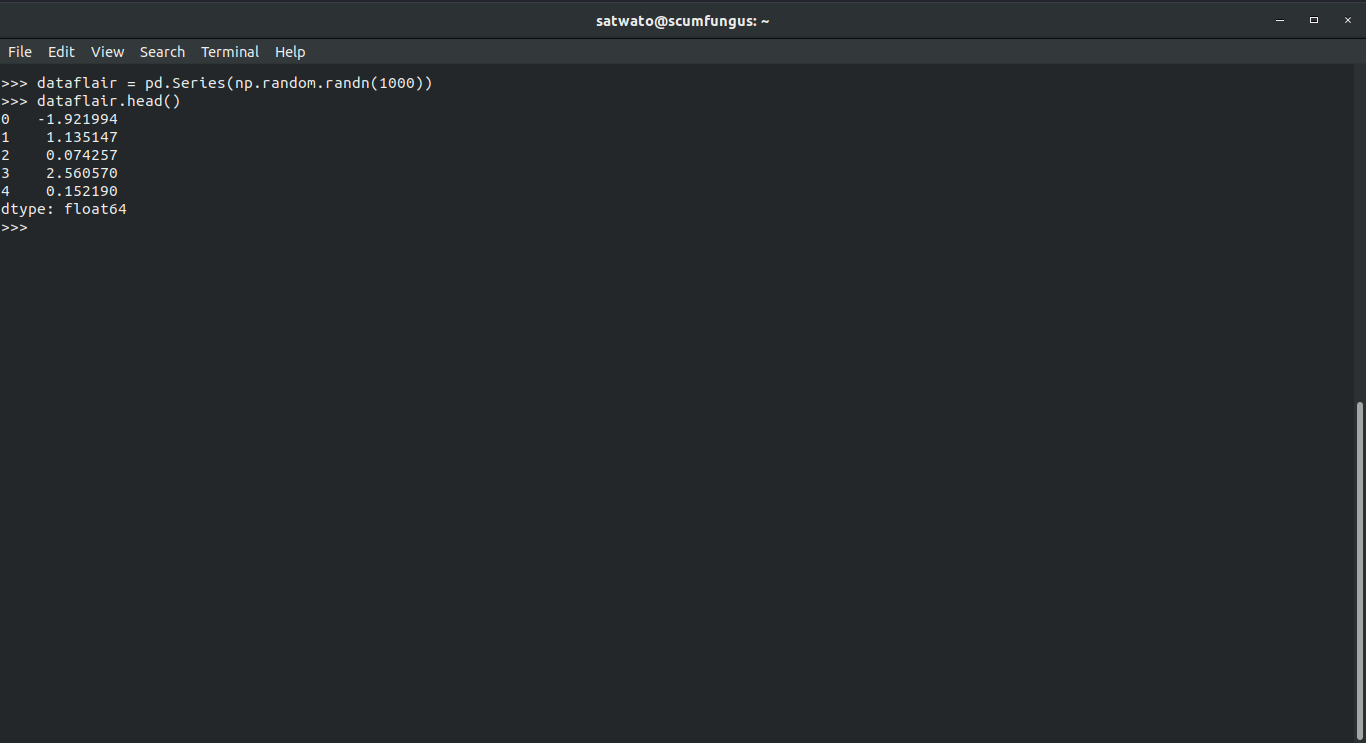
Let us create a series with 1000 random values
>>> dataflair = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000))
Using head() function-
>>> dataflair.head()
Output-
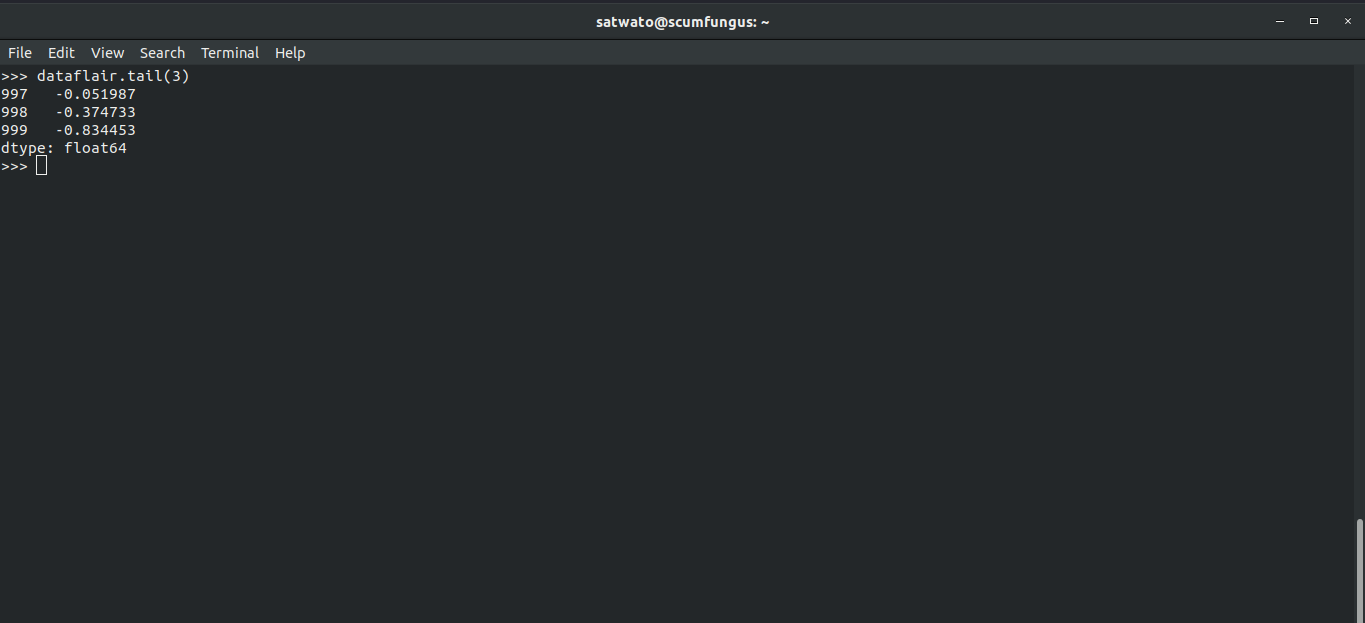
2. tail() function
Now, we use the tail function and set the number of elements to 3:
>>> dataflair.tail(3)
Output-
What makes Python Pandas unique from other libraries?
3. Attributes
Attributes play a major role in the basic functionality of pandas which helps data scientist for fast analyzing, cleaning, and preparation of data. Pandas objects possess a number of attributes which enable you to access the metadata.
Shape: It gives the axis dimensions
Axis labels:
- Series: index (only one axis)
- DataFrame: index (rows) and columns
- Panel: major axis, minor axis and items
- You can safely assign these attributes.
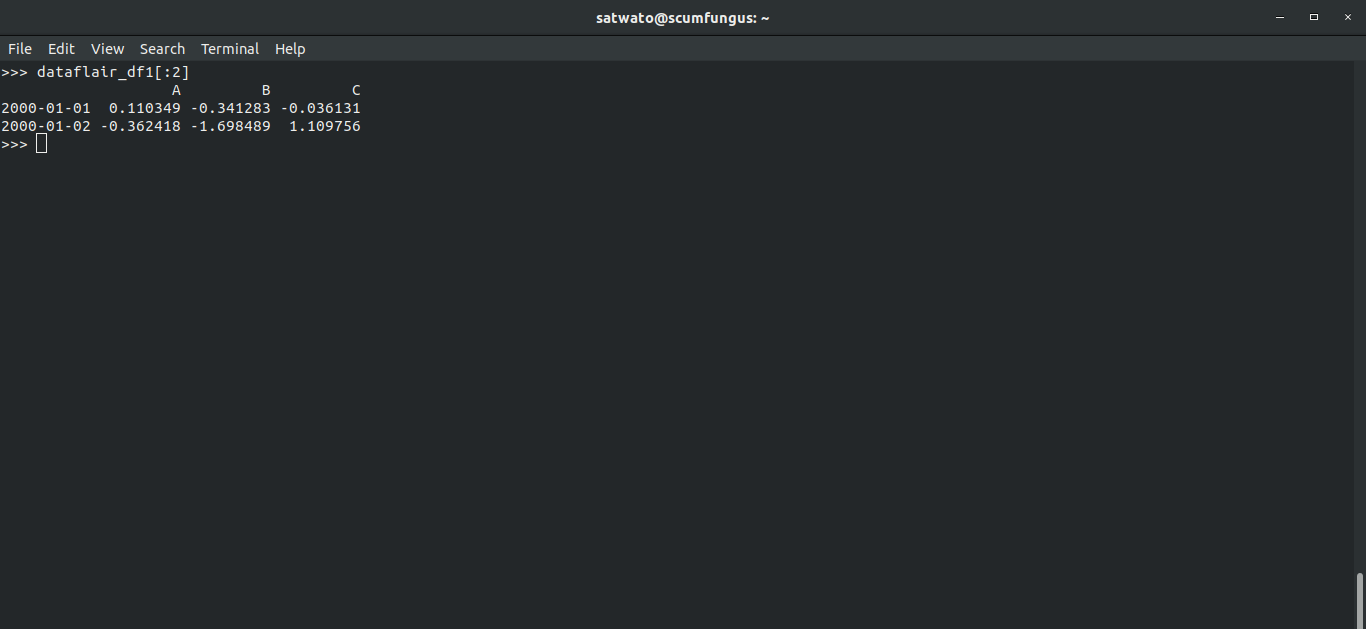
>>> dataflair_df1[:2]
Output-
- This prints the last two values for the DataFrame
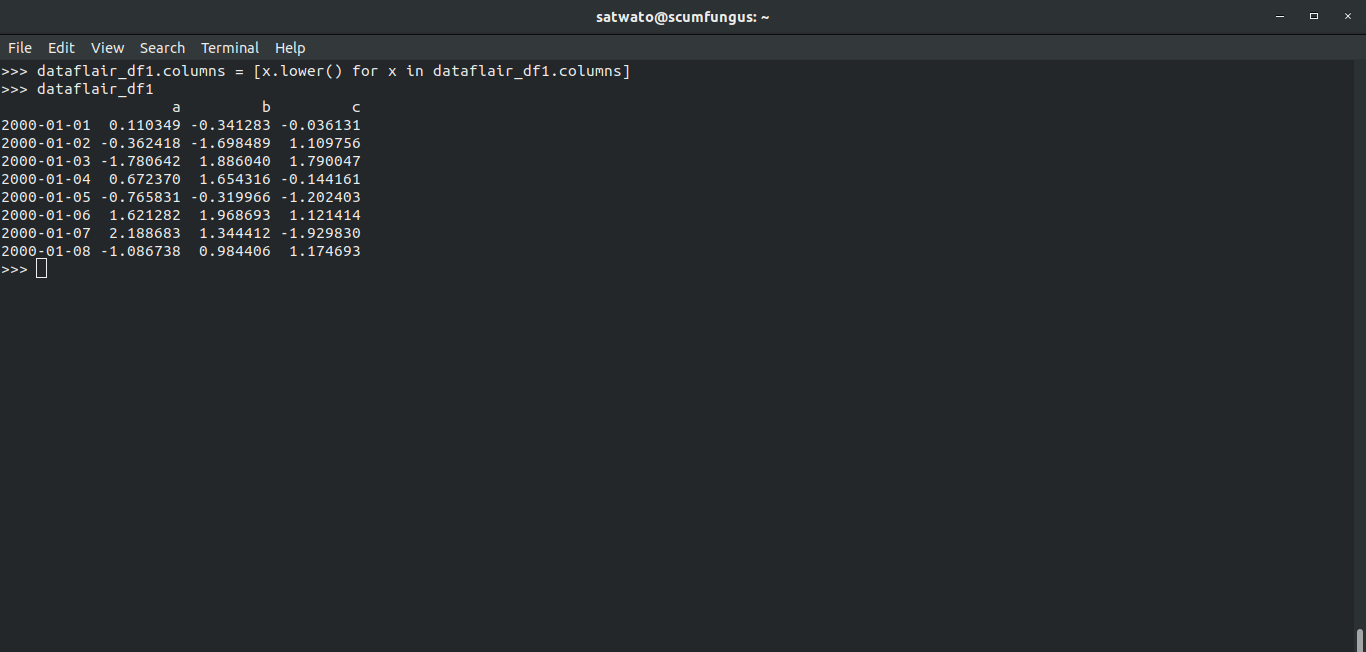
>>> dataflair_df1.columns = [x.lower() for x in dataflair_df1.columns] >>> dataflair_df1
Output-
- Using this function we change the uppercase column names to lowercase.
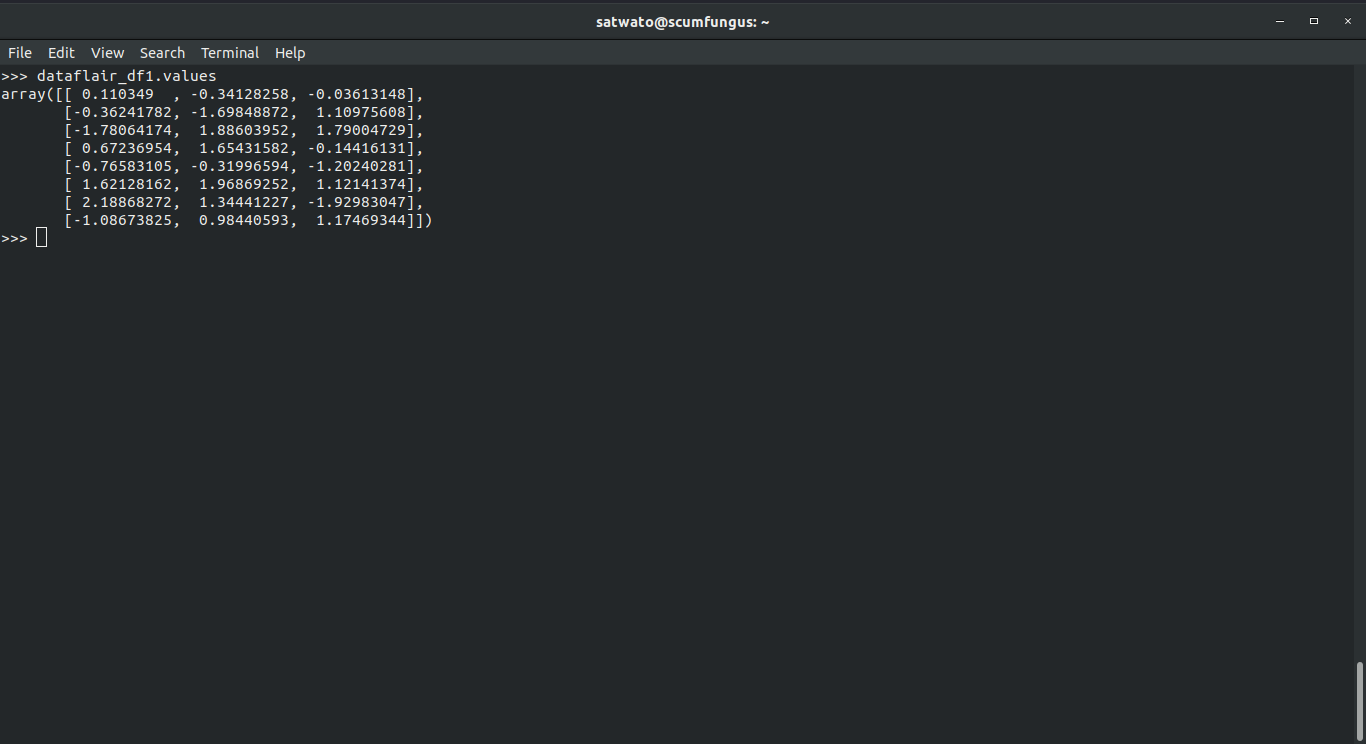
If you have to get the actual data which is inside a Pandas data structure, you only need to use the values property.
>>> dataflair_s1.values
Output-
Input-
>>> dataflair_df1.values
Output-
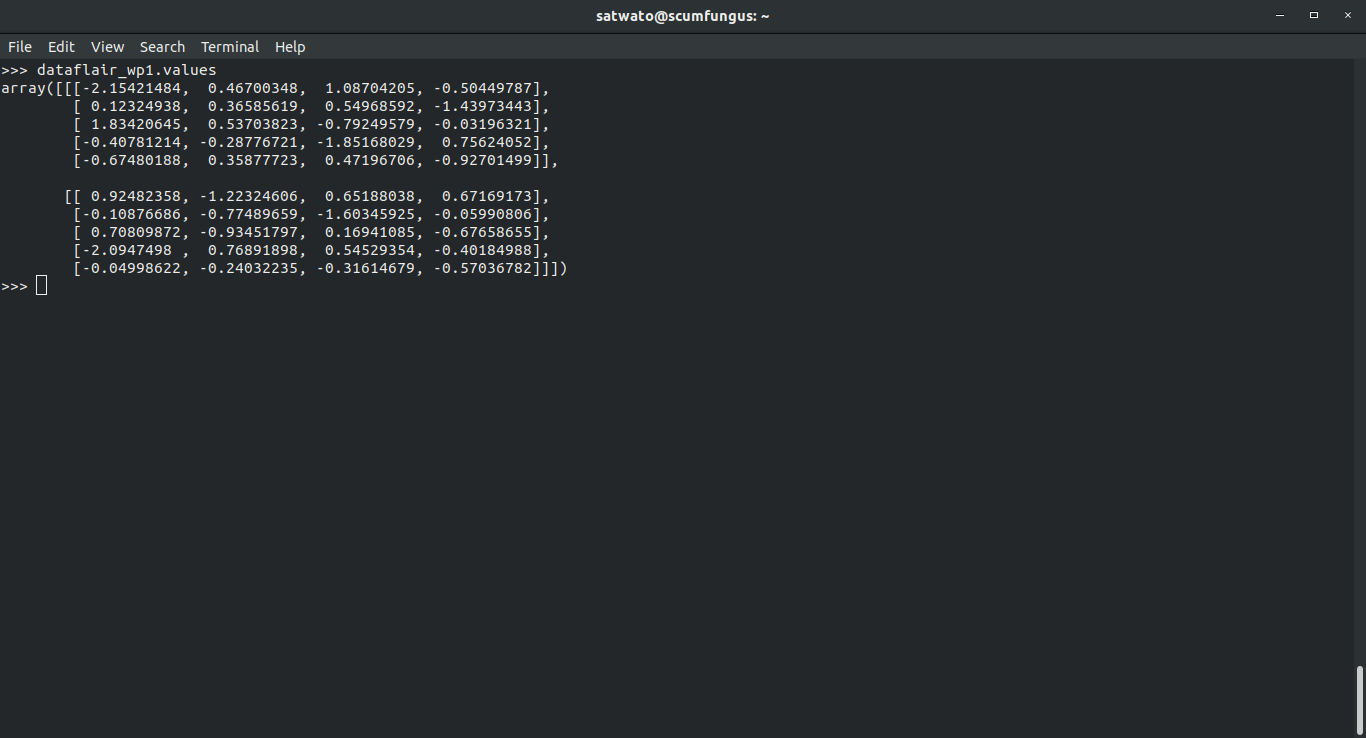
>>> dataflair_wp1.values
Output-
4. Flexible Binary Operations
In the binary operations between data structures in pandas, there are two vital points of interest:
- Broadcasting behavior between lower dimensional objects and higher dimensional objects
- Missing data while computing
We will learn how to manage these two issues independently. They can be dealt with simultaneously though.
4.1 Broadcasting Behaviour
For broadcasting behavior, the Series input is primary. You can match the index or columns by using the axis() keyword.
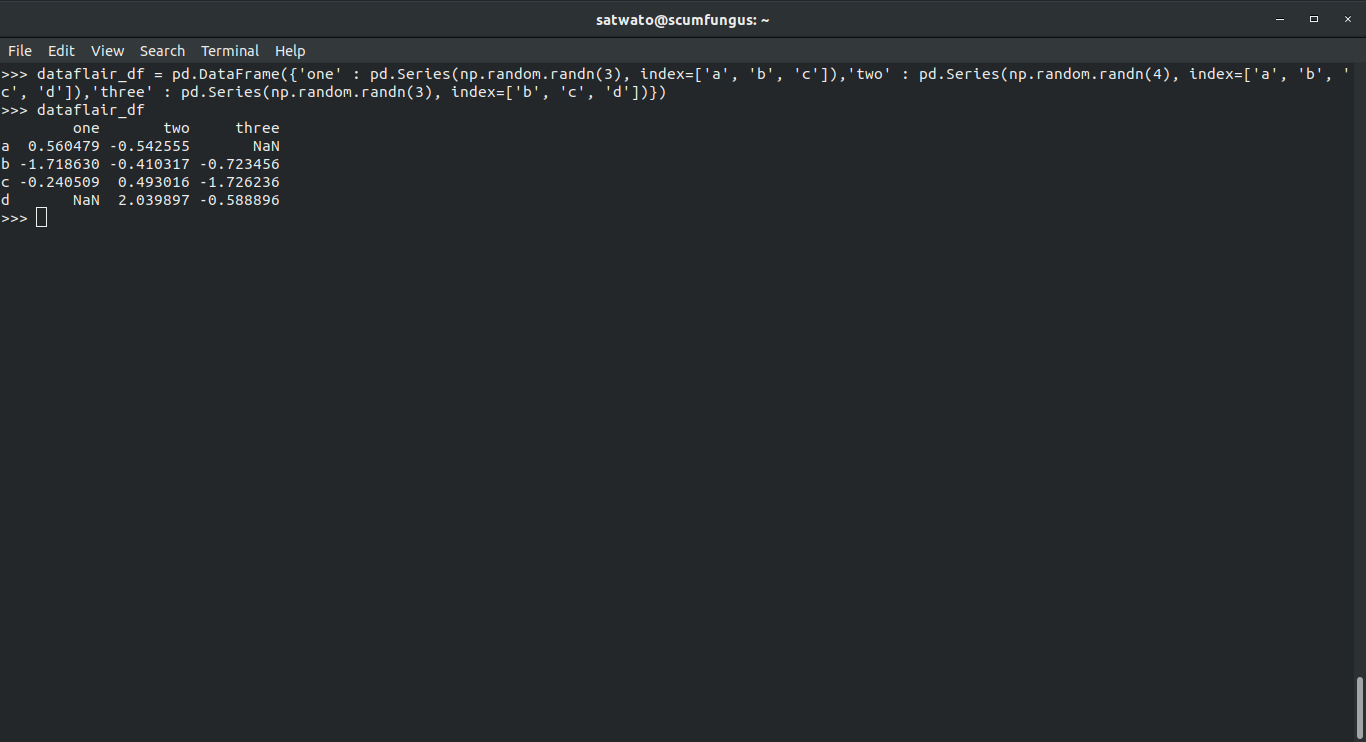
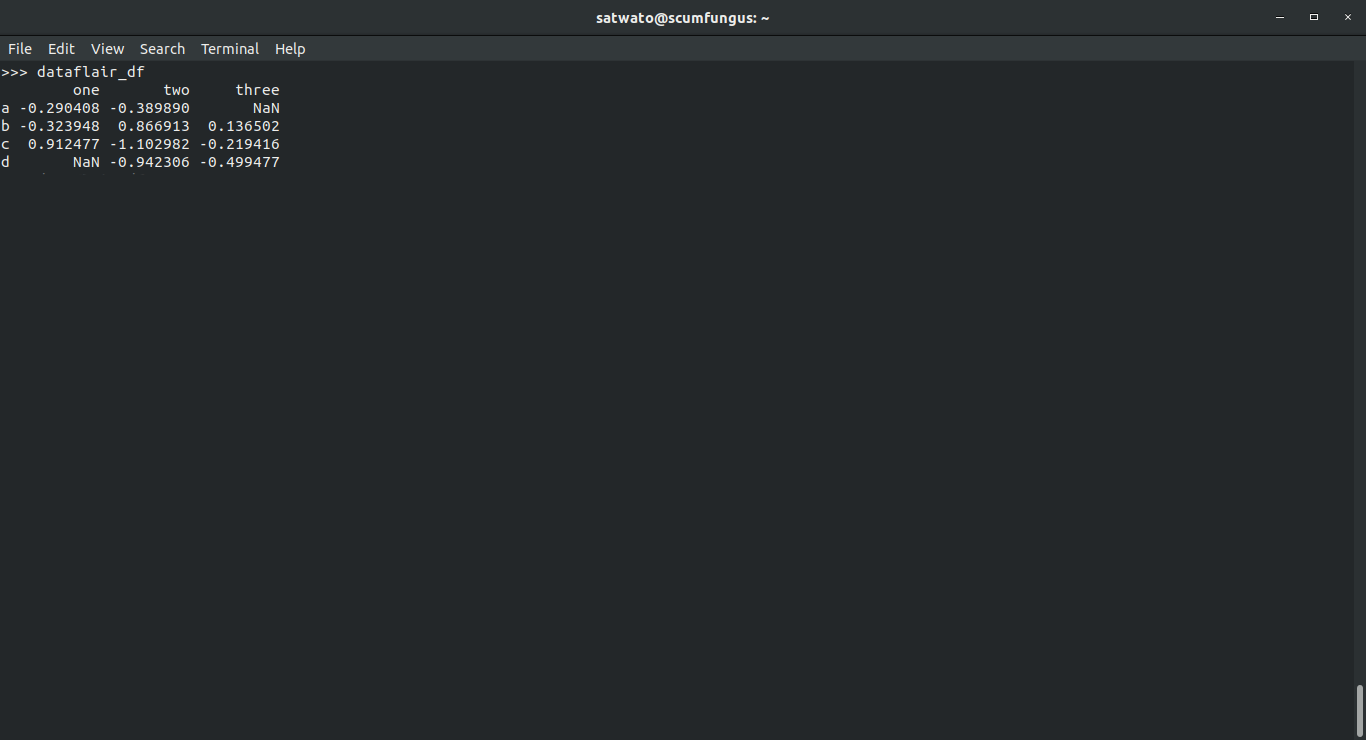
>>> dataflair_df = pd.DataFrame({'one' : pd.Series(np.random.randn(3), index=['a', 'b', 'c']),'two' : pd.Series(np.random.randn(4), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']),'three' : pd.Series(np.random.randn(3), index=['b', 'c', 'd'])})
>>> dataflair_dfOutput-
Input-
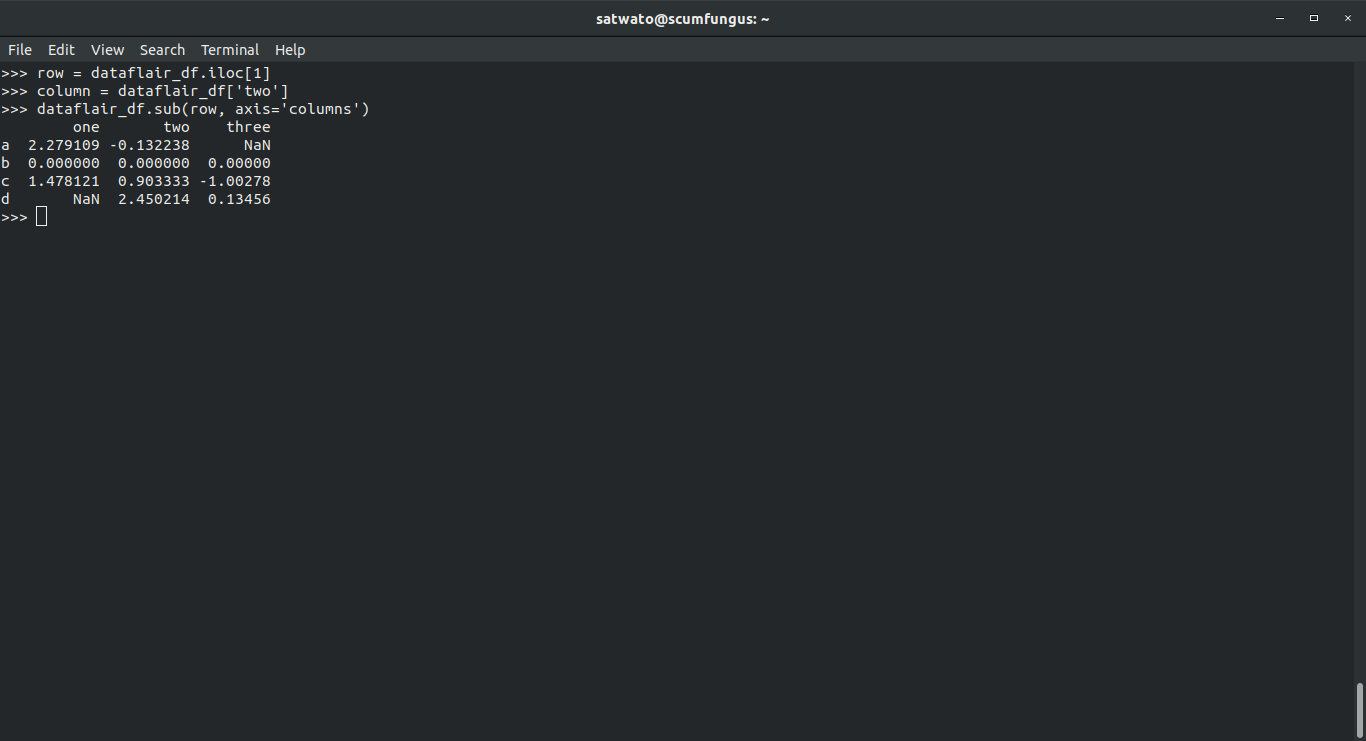
>>> row = dataflair_df.iloc[1] >>> column = dataflair_df['two'] >>> dataflair_df.sub(row, axis='columns')
Output-
Pandas are popular in Data Science but Pandas has different applications in other sectors too.
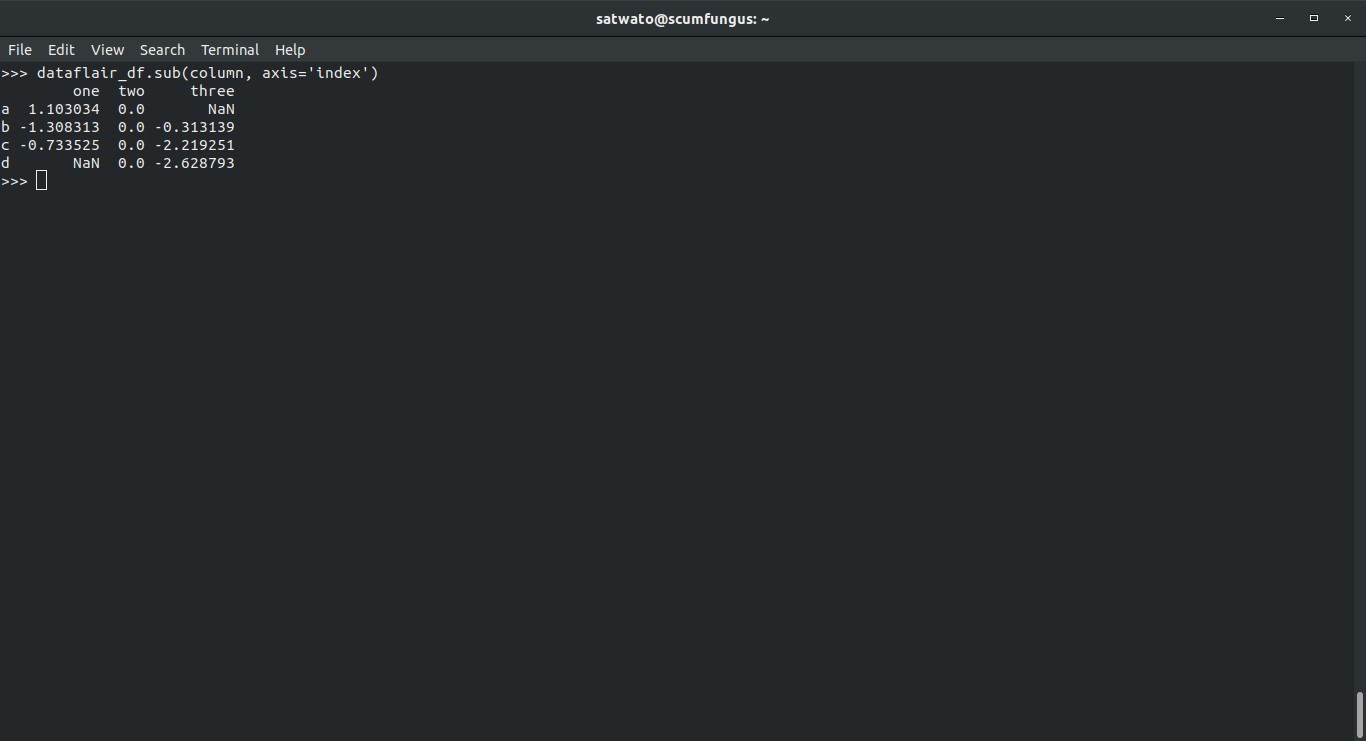
>>> dataflair_df.sub(column, axis='index')
Output-
Input-
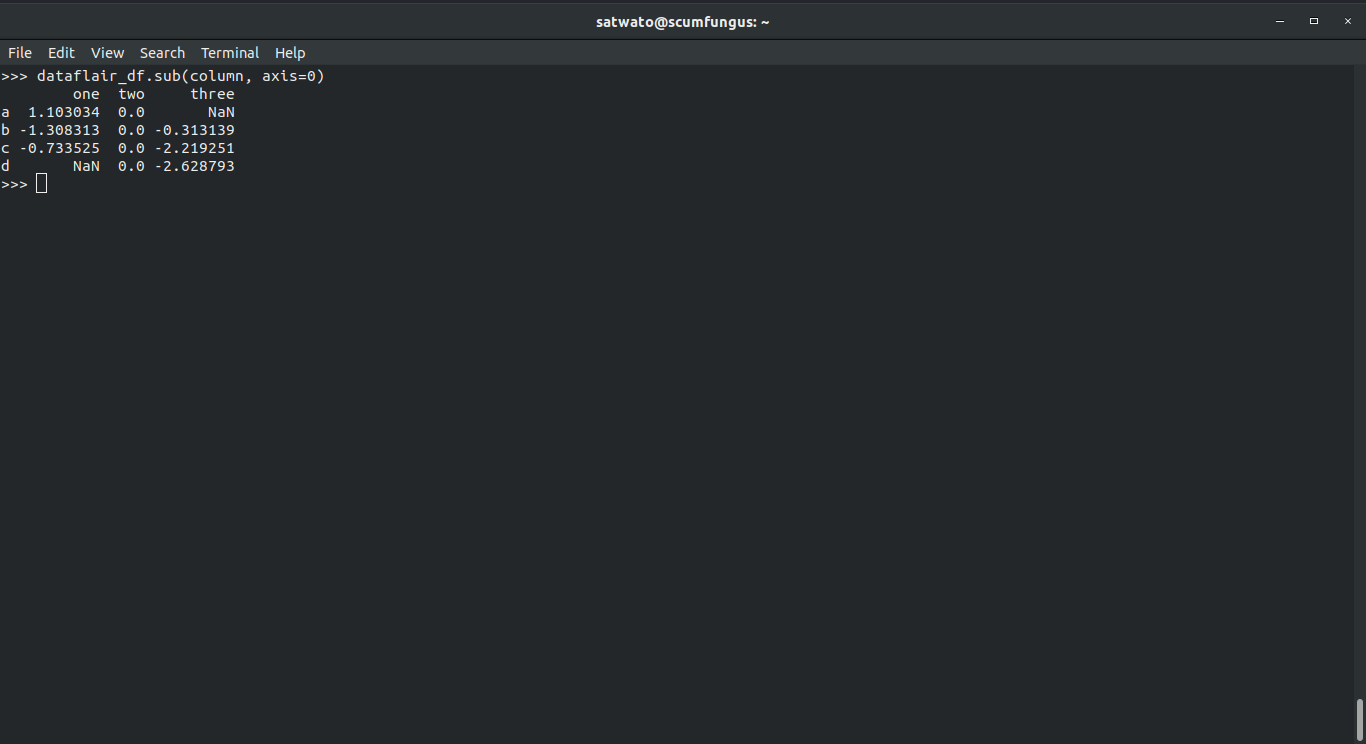
>>> dataflair_df.sub(column, axis=0)
Output-
4.1.1 Multi-indexed DataFrames level
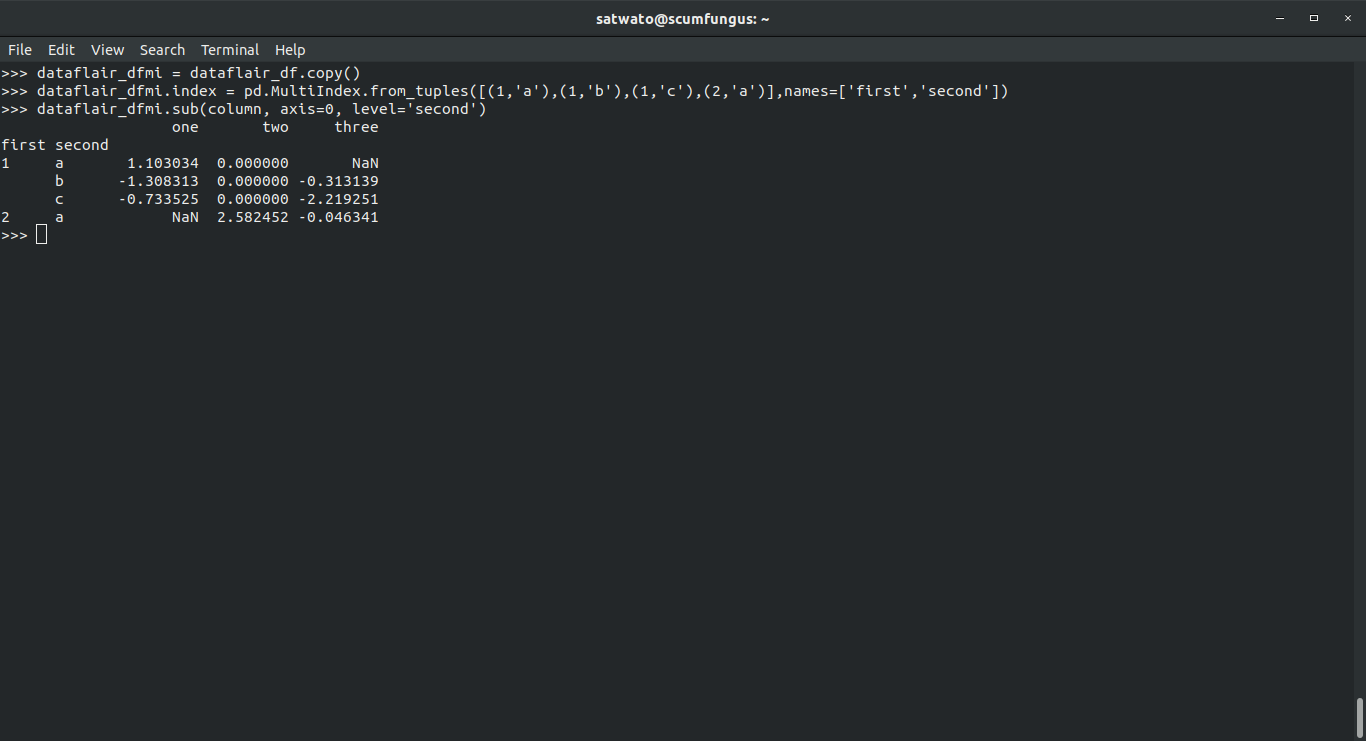
Using a series, you can align a multi-indexed DataFrame’s level.
>>> dataflair_dfmi = dataflair_df.copy() >>> dataflair_dfmi.index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([(1,'a'),(1,'b'),(1,'c'),(2,'a')],names=['first','second']) >>> dataflair_dfmi.sub(column, axis=0, level='second')
Output-
In a Panel, the matching or broadcasting behavior is a little difficult. Hence, the arithmetic methods are used instead, giving you an option to specify the axis of broadcast.
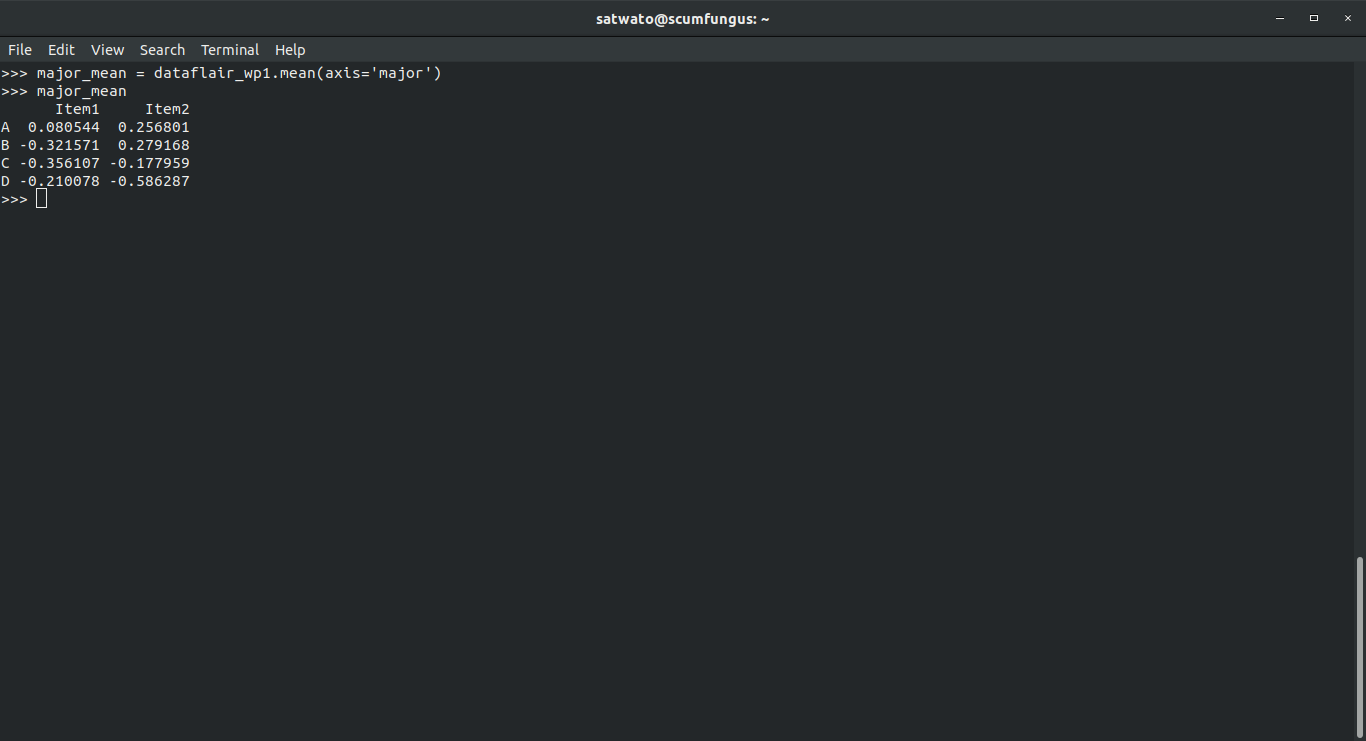
>>> major_mean = dataflair_wp1.mean(axis='major') >>> major_mean
Output-
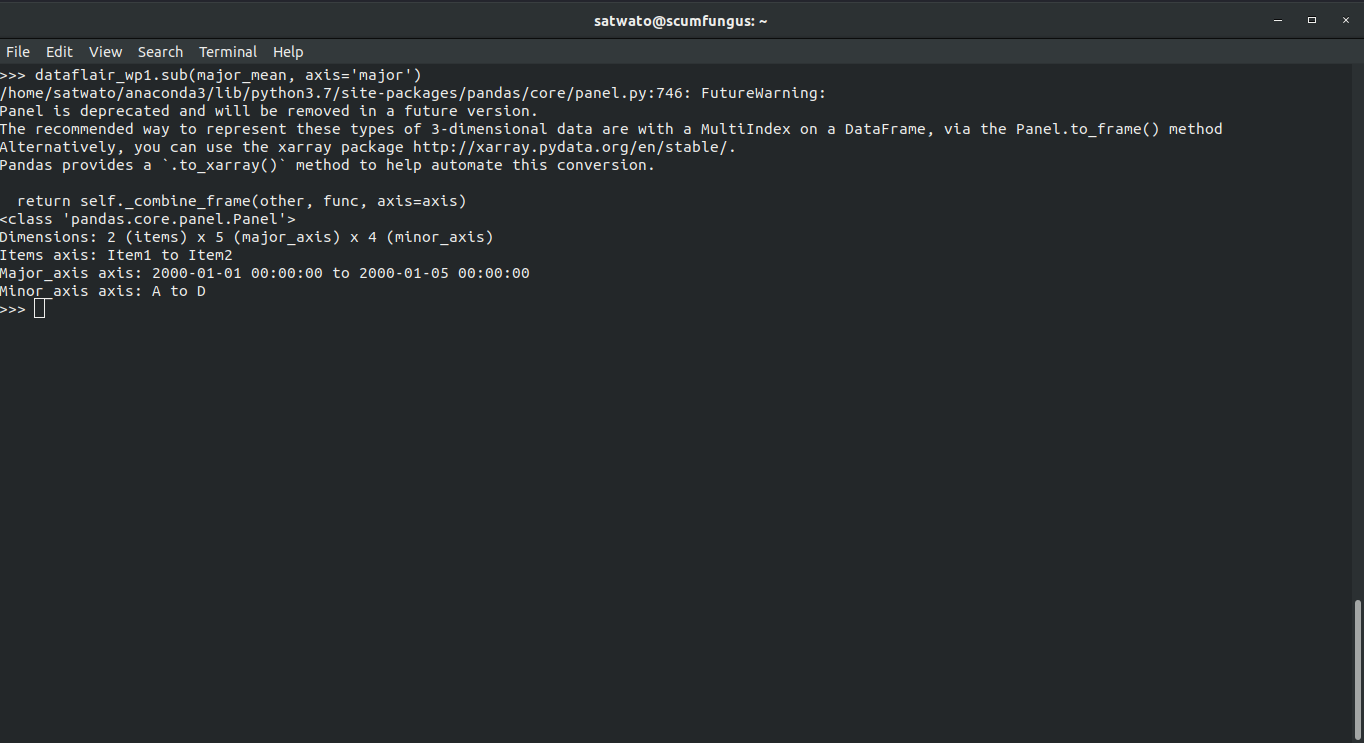
>>> dataflair_wp1.sub(major_mean, axis='major')
Output-
Series and Index support the divmod() built-in function. It takes the floor division along with the modulo operation at the same time and returns a two-tuple of the same type. It returns it as the left-hand side.
Do you know the benefits offered by Python Pandas?
For series
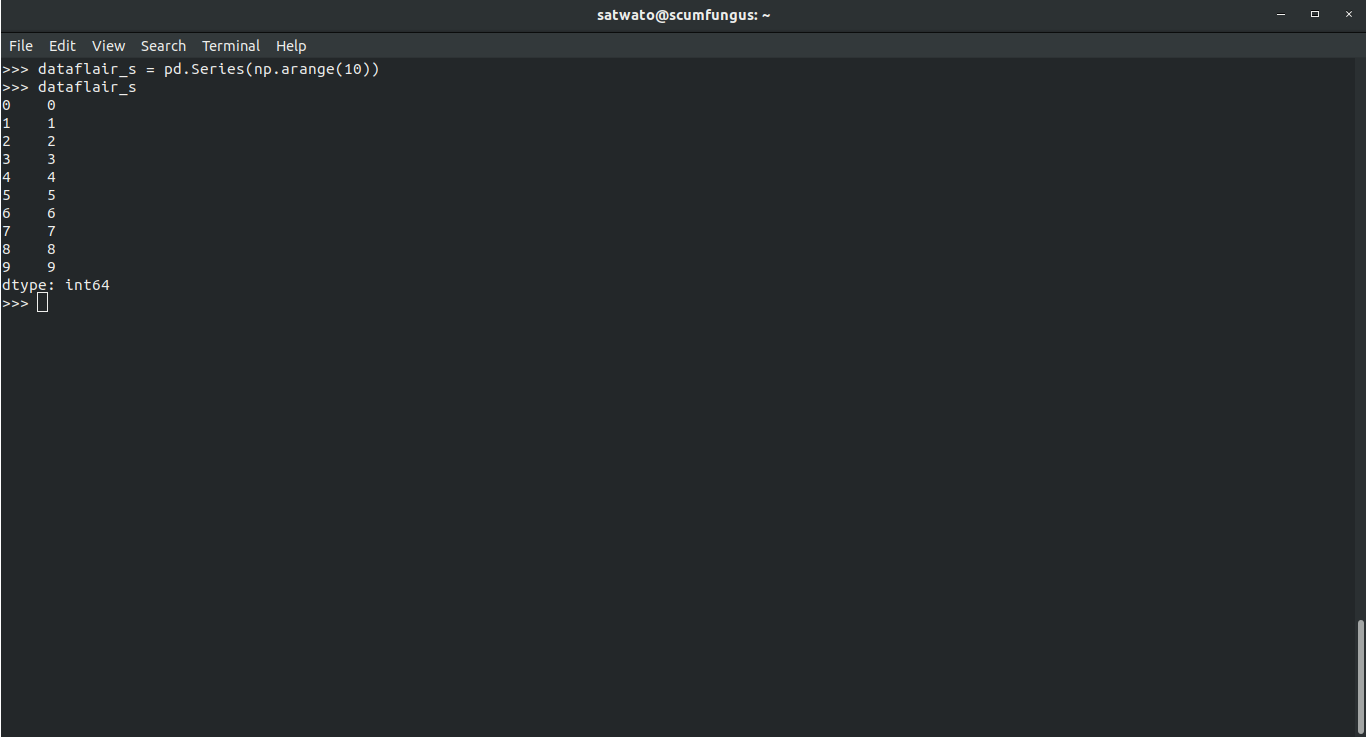
>>> dataflair_s = pd.Series(np.arange(10)) >>> dataflair_s
Output-
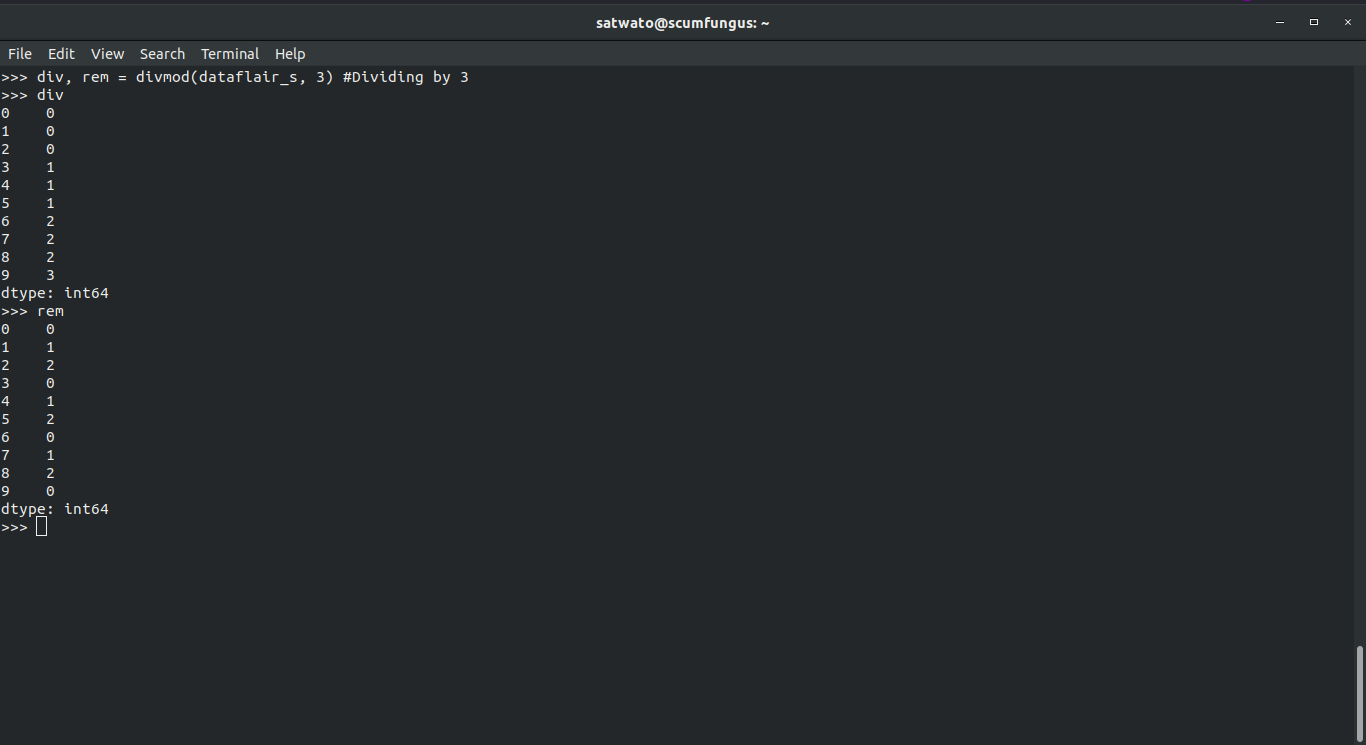
>>> div, rem = divmod(dataflair_s, 3) #Dividing by 3 >>> div
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 1
4 1
5 1
6 2
7 2
8 2
9 3
>>> rem
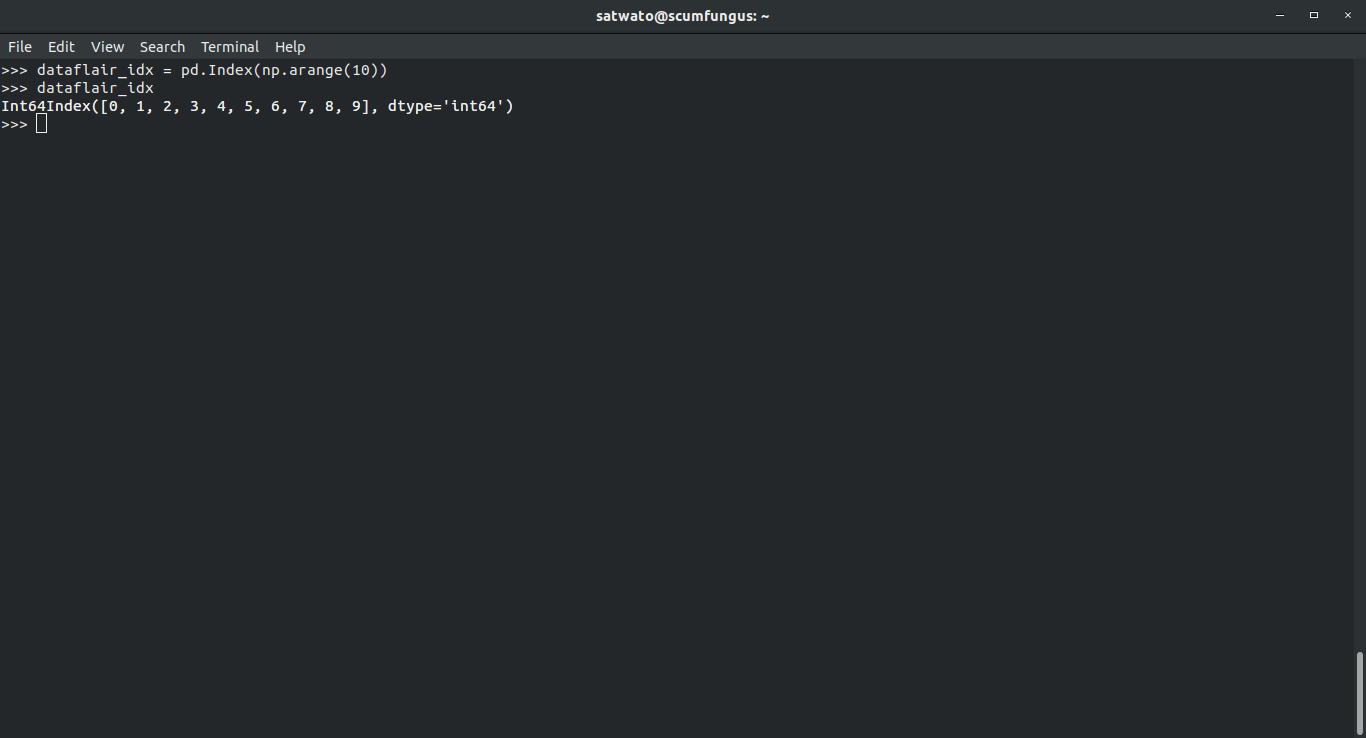
For index
>>> dataflair_idx = pd.Index(np.arange(10)) >>> dataflair_idx
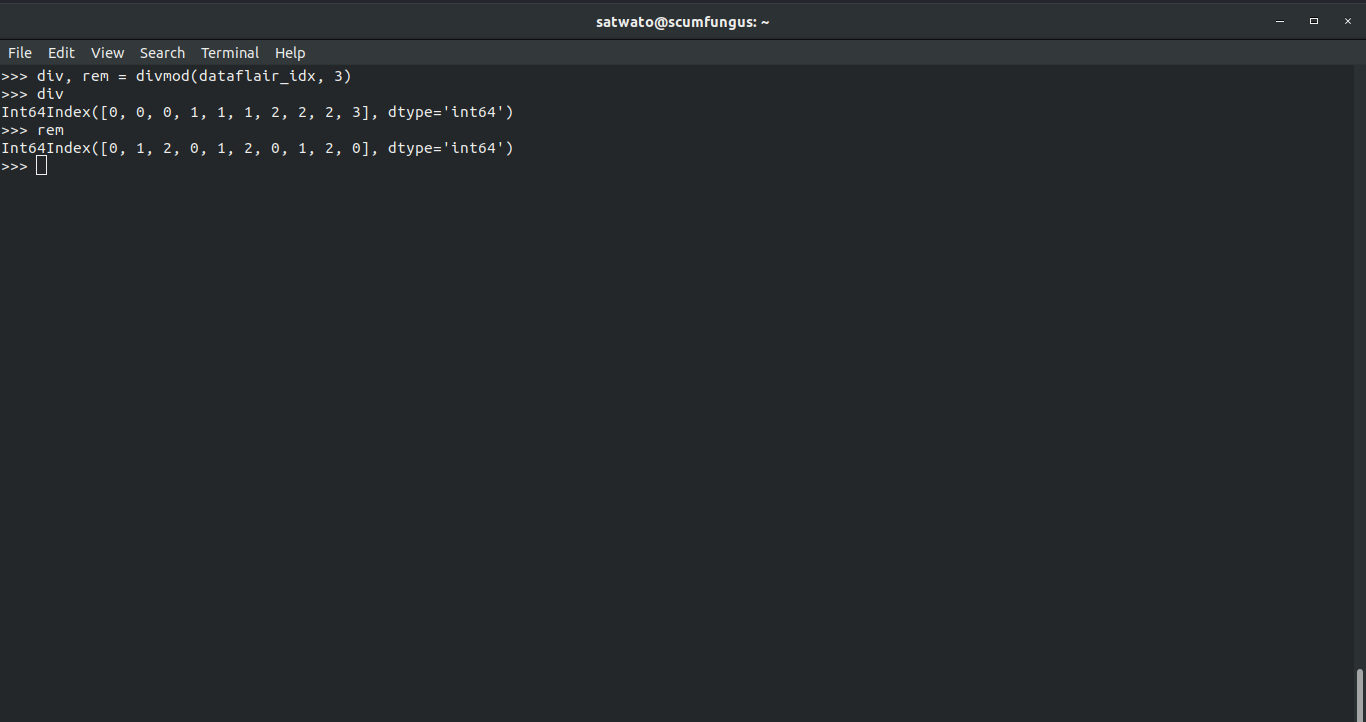
>>> div, rem = divmod(dataflair_idx, 3) >>> div
Int64Index([0,0,0,1,1,1,2,2,2,3], dtype=’int64′)
>>> rem
We can do divmod() elementwise as well.
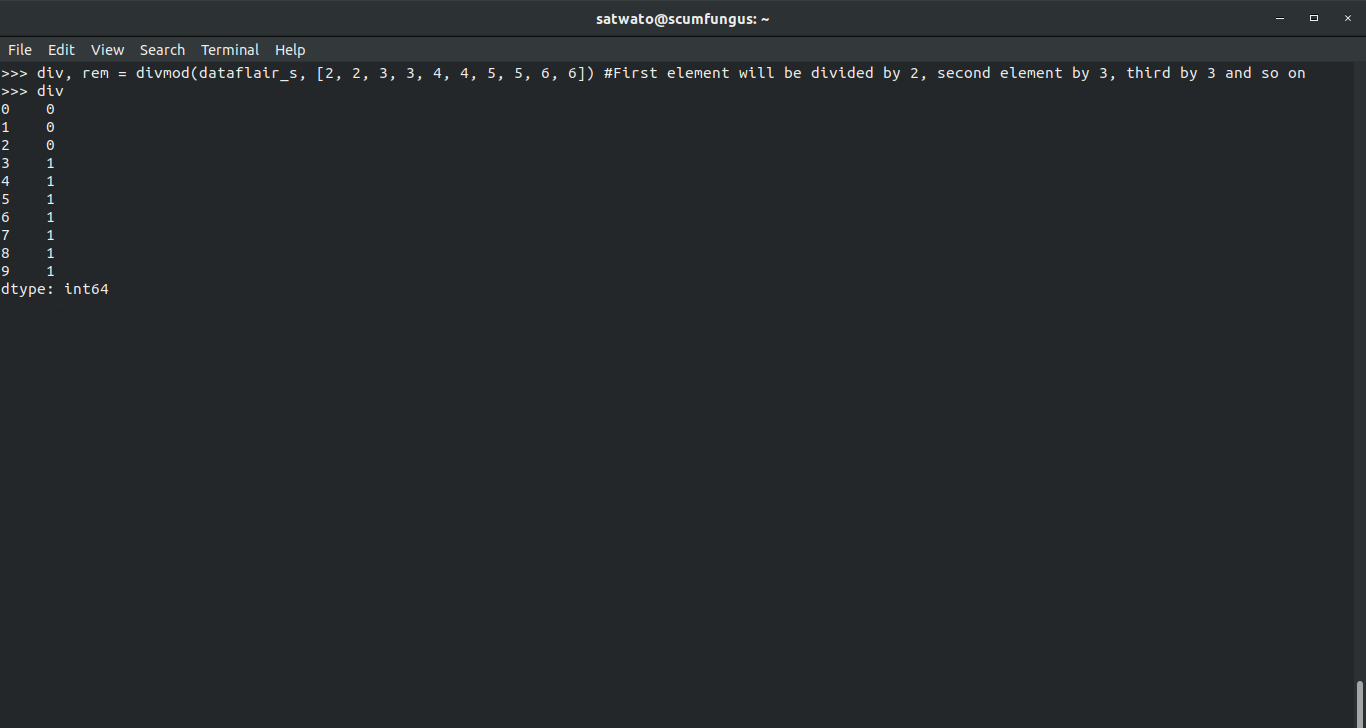
div, rem = divmod(dataflair_s, [2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6]) #First element will be divided by 2, second element by 3, third by 3 and so on
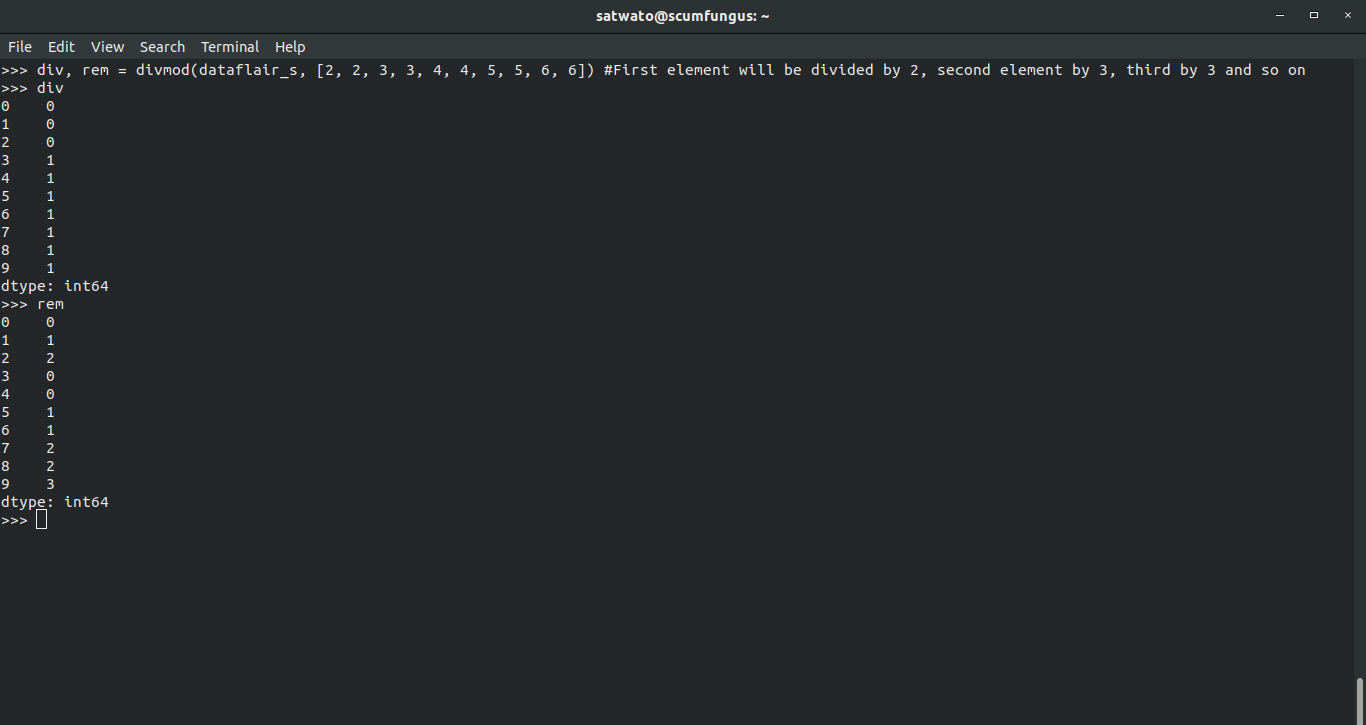
>>> div, rem = divmod(dataflair_s, [2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6]) >>> div
>>> rem
4.2 Missing Values in pandas
In DataFrame and Series, the arithmetic function gives you an option of inputting a fill_value, which basically substitutes a value whenever a value is missing from a location. When you add two DataFrame objects, you can treat NaN as 0. However, if both DataFrames are missing that value the result will be NaN. You can still replace it with some other value by using the fillna function later.
>>> dataflair_df
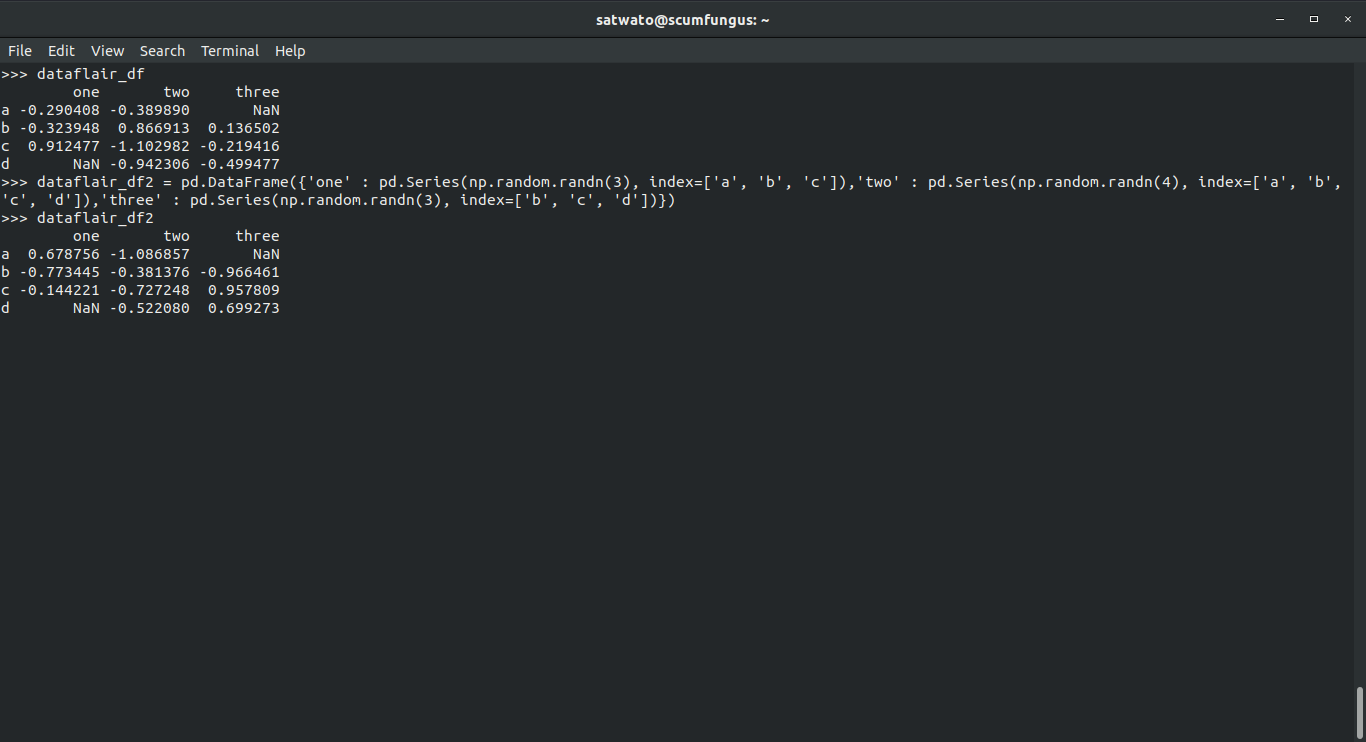
>>> dataflair_df2 = pd.DataFrame({'one' : pd.Series(np.random.randn(3), index=['a', 'b', 'c']),'two' : pd.Series(np.random.randn(4), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']),'three' : pd.Series(np.random.randn(3), index=['b', 'c', 'd'])})
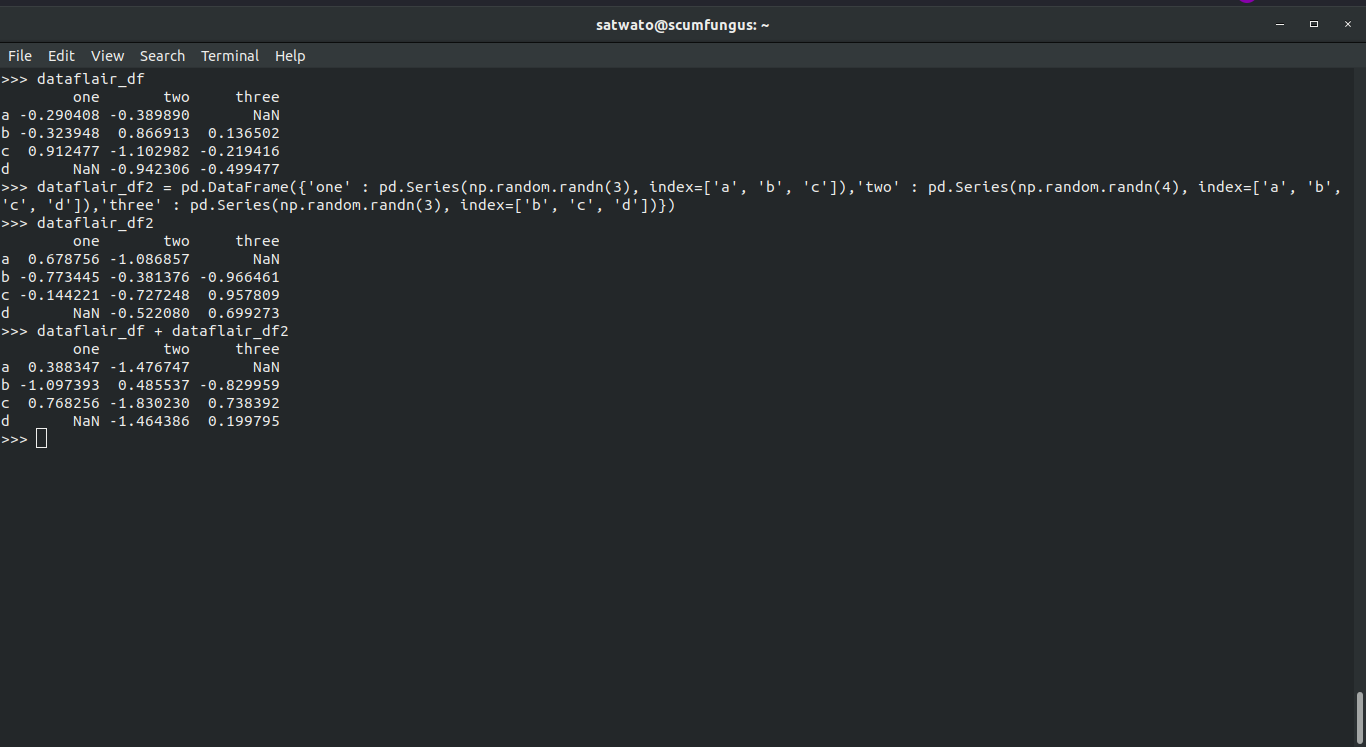
>>> dataflair_df2>>> dataflair_df + dataflair_df2
Input
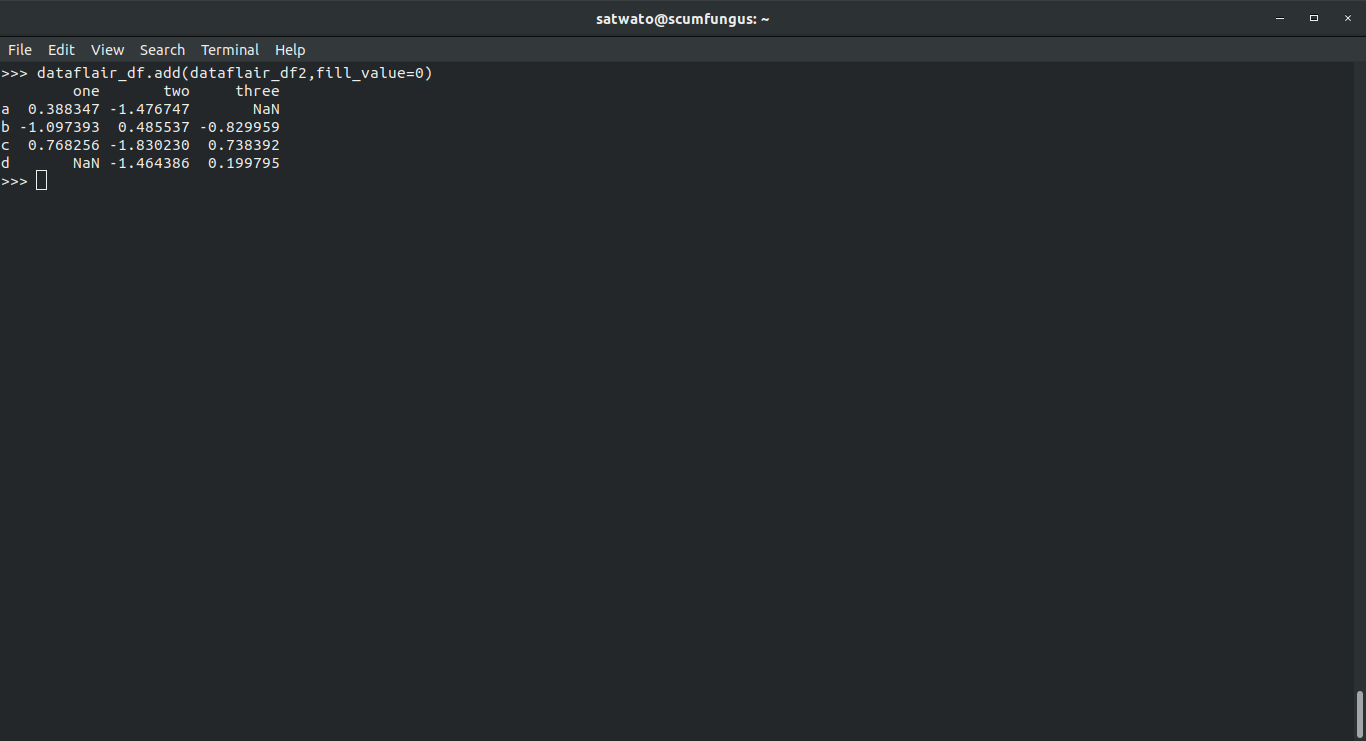
>>> dataflair_df.add(dataflair_df2,fill_value=0) #does the same thing as ‘+’ operator
Summary
In conclusion, we would like to say that basic functionality encompasses a lot of Pandas, but these are the main functions along with some flexible comparisons and Boolean reductions.
I recommend you 7 best Python Pandas books to get more in-depth knowledge of Pandas
If you have any query, feel free to comment below.
If you are Happy with DataFlair, do not forget to make us happy with your positive feedback on Google