MongoDB Tutorial – Learn What is MongoDB?
FREE Online Courses: Enroll Now, Thank us Later!
MongoDB is a numerous nonrelational database technology from the mid-2000s use in big data applications. This MongoDB tutorial is specially designed for the beginners, who are new to the IT industry and want to be a part of it.
Here, we will study what is MongoDB with NoSQL Database and it’s an introduction to the world of the existing database management system. Moreover, we will discuss MongoDB Features, History, applications and Installation process with some MongoDB example.
So, let’s start MongoDB Tutorial for beginners.
What is NoSQL Database?
NoSQL databases, commonly referred to as “Not Only SQL,” are a subset of database systems that deviate from the conventional relational database paradigm to effectively manage massive amounts of unstructured, semi-structured, or structured data. NoSQL databases provide schema flexibility, permitting the storing of many data types inside the same database and allowing data to be saved without following a preset format.
In order to handle enormous volumes of data and adjust to expanding data needs, they are built for horizontal scalability, spreading data over several nodes or servers. These databases are ideal for real-time applications and high-traffic situations because they excel at high-speed data access and retrieval.
Contrary to relational databases, NoSQL databases often stay away from complicated joins and maintain data relationships using different methods like denormalization or embedding. NoSQL databases come in a variety of forms, each suited to a particular data format, such as document databases, key-value stores, column-family stores, and graph databases.
Due to their versatility in handling different data types, horizontal scalability, and superior performance compared to conventional relational databases, they have found wide adoption in contemporary applications such as web applications, social media platforms, IoT systems, real-time analytics, and big data processing.
What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is an open source platform written in C++ and has a very easy setup environment. It is a cross-platform, document-oriented and non-structured database. MongoDB provides high performance, high availability, and auto-scaling.
It is a NoSQL database and has flexibility with querying and indexing. MongoDB has very rich query language resulting in high performance.
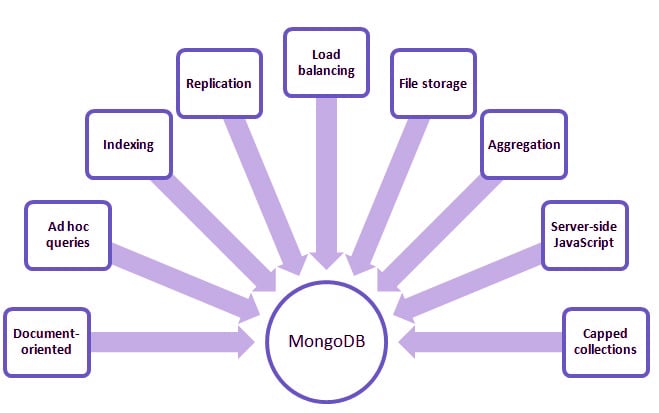
MongoDB Features
Here, in this part of the MongoDB Tutorial, we discuss some key features of MongoDB:
i. Ad-hoc Queries
MongoDB supports ad-hoc queries by indexing.
ii. Schema-Less Database
It is very flexible than structured databases. There is no need to type mapping.
iii Document Oriented
It is document oriented, JSON like a database.
iv. Indexing
Any document can index with primary and secondary indices.
v. Replication
It has this powerful tool. Every document has one primary node which further has two or more secondary replications.
vi. Aggregation
For efficient usability, MongoDB has aggregation framework for batch processing.
vii. GridFS
It has grid file system, so it can use to store files in multiple machines.
viii. Sharding
For the larger data sets sharding is the best feature. It distributes larger data to multiple machines.
ix. High Performance
Indexes support faster queries leading to high performance.
MongoDB History
Known as MongoDB, the well-known NoSQL database management system was created by MongoDB Inc., originally known as 10gen, and was formed in 2007 by Dwight Merriman and Eliot Horowitz. It was made available as an open-source document-oriented database in 2009 with a focus on performance, scalability, and schema flexibility to meet the demands of contemporary online applications. The document-based data format used by MongoDB, which can manage unstructured and dynamic data, soon became popular.
Major versions gradually included crucial components like replica sets and sharding, boosting high availability and horizontal scalability. With a free Community Edition and a premium Enterprise Edition with more features and support options, MongoDB Inc. was founded to oversee the database’s development and maintenance. With its steady growth and popularity, MongoDB has emerged as a top choice across a wide range of applications and sectors, supporting big data initiatives, real-time data processing, and cutting-edge web development initiatives.
MongoDB Applications
This part of MongoDB Tutorial covers, the Applications of MongoDB:
- In E-commerce product catalogue.
- Big data
- Content management
- Real-time analytics and high-speed logging.
- Maintain Geolocations
- Maintaining data from social websites.
How to Install MongoDB?
MongoDB is available for Windows, Linux, and MacOS. You can download the setup directly from the MongoDB website. Download any version after checking the hardware requirements. MongoDB runs by commands in all three major OS. You have to select any folder at the time of installation.
This was all about MongoDB Tutorial. Hope you liked our explanation.
Summary of MongoDB Tutorial
Hence, in this MongoDB Tutorial, we studied what is MongoDB, what is NoSQL database. In addition, we see MongoDB features with MongoDB history. At last, discussed MongoDB applications and Environment setup.
Furthermore, if you have any query regarding MongoDB Tutorial, feel free to ask in a comment section.
Your opinion matters
Please write your valuable feedback about DataFlair on Google




Le didacticiel est léger. Il devrait aller plus en profondeur: Que fait Grids?