Functions of a Commercial Bank in India
Are you ready for UPSC Exam? Check your preparation with Free UPSC Mock Test
A bank is defined as a legalized institution that acquires monetary deposits that can be extracted on demand. These are established for financial aid, protection, and storage of public fiscal assets.
These organizations ensure the security of the deposited amount along with the provision of the deposited amount when demanded. These also provide interests on the deposited amount which encourages more people to invest with the banks and also helps them save their earnings.
This boosts the economic development of a country. Let us see various functions of Bank in India.
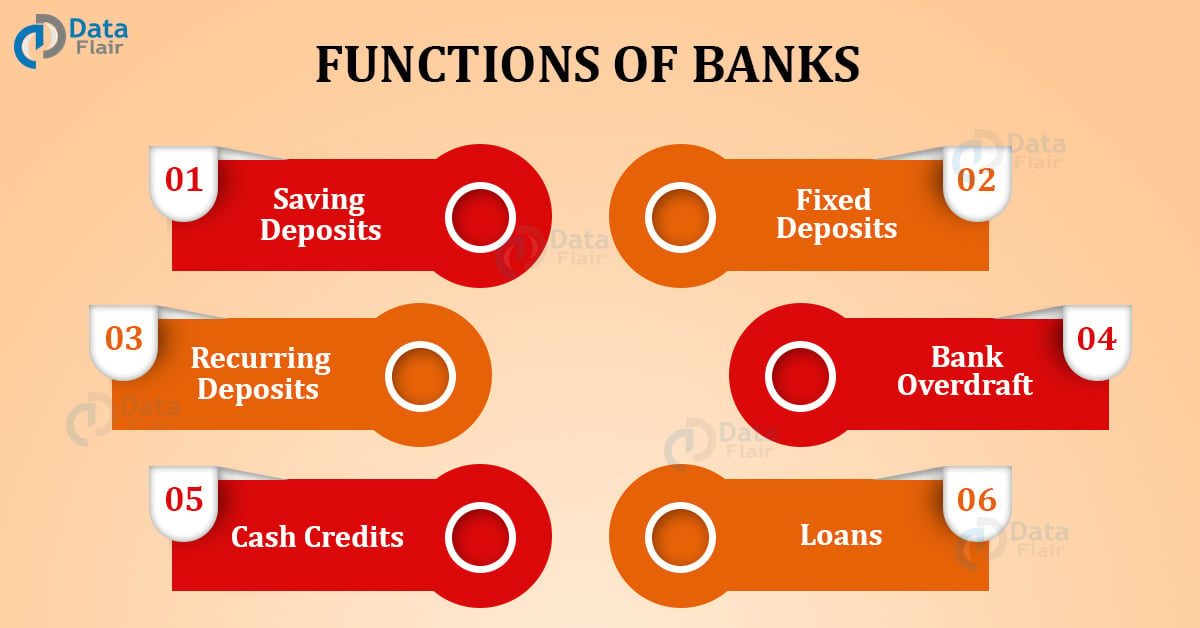
Functions Of The Banks in India
A bank has both – primary and secondary functions.
A. Primary Functions of a Bank
These include 2 major roles:
1. Acquiring Deposits
This includes mustering public investment and providing security to the collected funds. They also offer interests on the deposited amount which in turn encourages people to invest in banks. There are many types of investment deposits:
Saving Deposits
- Appropriate for those receiving remuneration and wages.
- These have a low fare of interest.
- Unlimited withdrawals can take place.
- The account can have any – a single holder or a joint holder.
- A minimum amount always needs to remain deposited in the bank account – which is different for different banks.
- This promotes a culture of saving amongst the bank users.
- Withdrawal, additions, or transactions may be made through ATM Debit cards, several types of cheque books, or internet banking
- provisions.
Fixed Deposits
- These are also known as ‘Term Deposits’.
- An amount is deposited for a predetermined fixed term.
- These have a high fare of interest, which also varies with the duration of the fixed term for which the amount is deposited.
- Withdrawals are not permitted during this term.
- When withdrawal of deposits takes place before the term is over, there is a penalty fine sanctioned which is to be submitted to the bank.
Current Deposits
- Appropriate for business people and entrepreneurs.
- There is a provision of overdraft to those holding these accounts.
- Deposits act as loans for a short period of time in urgent situations.
- Bank imposes a high rate of interest added to which are charges of the overdraft provision.
- This helps maintain a pool of assets which further act as a resource for overdrafts.
Recurring Deposits
- Appropriate for people receiving remuneration and trivial traders.
- Deposits are made at consistent intervals.
- Withdrawal of deposits can take place only after a certain interval of time.
- These have a very high fare of interest due to the presence of compounded interest rate.
- This makes possible the collection of large amounts of assets deposited.
2. Provisions of Loan, Down Payments and Deposits
This includes the usage of deposited amounts as loan payments made to those members who applied for it. The interest fair difference between that taken on the loans and the one offered on the deposits is how the bank obtains profit. There are many types of loans and advances:
Bank Overdrafts
- This provision is for bank account holders.
- This permits the withdrawal of amounts more than that present in the account, however only to a certain extent.
- There is a provision of the overdraft facility offered against a collateral asset.
- The interest paid depends on the duration term of the loan along with the amount.
Cash Credits
- Appropriate for both – account holders and non-account holders in the bank.
- This is a provision for loans up to a certain extent for a short duration of time.
- The loan is passed against a collateral asset or property which acts as assurance.
- Interest is only on the extra amount withdrawn.
- This credit offers a larger loan when compared to an overdraft.
Loans
- Loans are lent to bank associates for a duration of about 1-5 years or a longer-term against a collateral asset.
- The debtor can either repay the entire loan amount at once or pay it in small installments over a fixed duration of time.
- Interest is charged on the sanctioned amount of loan which is comparatively less to the fare decided for overdrafts and credit facilities.
Discounting The Bill Of Exchange
- This provision is of loans for a short duration.
- The dealer discounts the final charge or bill from the bank in return for a particular fee.
- The bank pays the amount by discounting or buying the bill.
- The bank cuts the discount charges while paying the bill on behalf of the buyer.
- Later, the bank makes the buyer look into the bill payment.
B. Secondary Functions of a Bank
These include 2 major roles:
1. Agency Functions of Bank
Banks are the representatives, negotiators, and hence the agents of their members. Due to this, they have to perform several functions which include:
- Transfer Of Funds: This occurs from one bank branch to the other or during any transactions.
- Periodic Accumulation: Gathering remunerations, wages, pensions, etc on behalf of their associates.
- Periodic Payments: Payment of rent and various other bills and expenditures on behalf of their client.
- Cheque Collection: Accumulation of deposits from exchange bills via the clearing section of its members.
- Portfolio Management: Buying and selling of associate shares or debt instruments and hence portfolio debiting or crediting.
- Other Functions: These include basic roles such as trustee, administrator, advisors, etc.
2. Utility Functions of Bank
These include the following:
- Managing project reports and details.
- Deciding and venturing into foreign exchanges by handling Demat accounts.
- Issuing credit letters, cheques, etc.
- Organizing and participating in social welfare programs.
- Securing important documents, valuables, and assets any provision of lockers.
- Underwriting of shares and promise pay such as debentures.
- Providing guarantee on its visitor’s behalf.
Conclusion
This article improves knowledge of the functions and responsibilities of a bank. It also helps in preparing well for various competitive exams. This increases public awareness and encourages them to invest in the various schemes of the bank.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google