Protectionism Types, Advantages and Limitations
Are you ready for UPSC Exam? Check your preparation with Free UPSC Mock Test
Protectionism is a practice of following the trade policies that protect the nation. Protectionist trade policy is the one that allows the Government to promote the domestic producers. Hence, it boosts the domestic production of goods and services.
The production of these goods is encouraged by imposing the tariffs and also limiting the foreign goods and services in the marketplace.
Further, it also helps the government in protecting the developing domestic industries from other established foreign competitors.
Types of Protectionism
Several policies help in implementing the idea of Protectionism. Some of them are:
Tariff
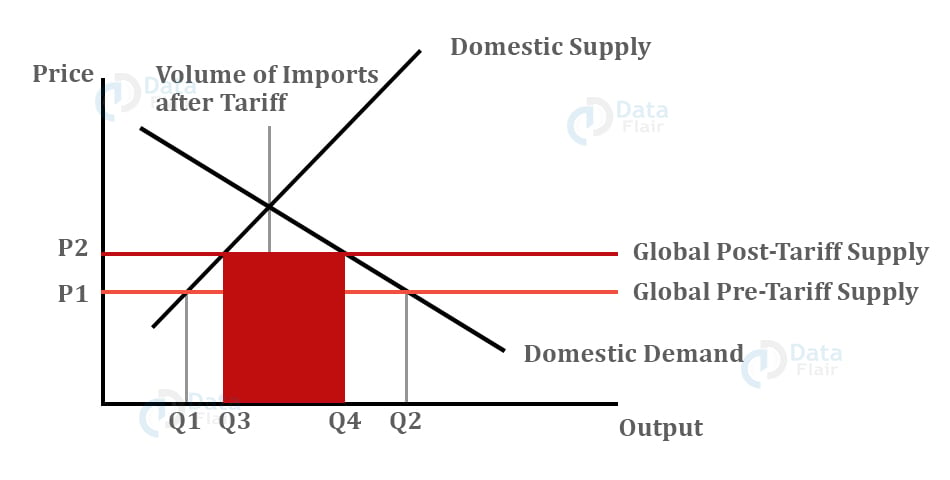
Tariffs are the taxes or the duties that impose on the imports of goods and services. With an increase in tax, the price of the goods also increases, which further leads to a fall in the purchasing power of the customers. This reduces the demand for imported goods and services.
Quota
The restrictions on the volume of the import of the goods and services over a particular time known as Quotas. They are also known as the non-tariff trade barriers. The restrictions lead to an increase in the price of the goods which further leads to a fall in the demand for the respective goods.
They are slightly more effective than tariffs because they completely restrict goods entering the country. Where, tariffs still allow goods to enter, only at a higher price. At the same time, quotas allow goods to come in at a cheaper price than under a tariff, although in limited quantities.
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
This means most protectionist nations will employ both a quota and a tariff to offset the drawbacks of the other nations.
Subsidy
These are the tax credits that are granted to the domestic producer by the government of the country. This causes a difference in the price of the product that is faced by the producer and the one that is faced by the consumers.
Export subsidies oppose domestic subsidies in the fact that it looks to shift the consumption abroad. Yet at the same time, the goal is still to shield the domestic firm.
Standardization
These are the policies and the guidelines that a government enlists, which shall be followed during the import of foreign goods and services.
For example, the Coca-Cola Company uses global standardization in marketing by keeping the appearance of the product relatively constant between different markets and countries.
Exchange Controls
The government can limit the amount of foreign currency that is available for payment of imports. However, Exchange Controls are not allowed amongst member states of the European Union. But, they have become difficult to sustain in a world of highly mobile capital.
There are several ways by which nations implement these controls. One of the examples is dumping and printing currency onto the foreign exchange market. In turn, it increases the supply in the market, by reducing its value.
Voluntary Export Restraints
Voluntary Export restraints are the quotas that are voluntarily agreed between countries. This has happened a significant number of times with the Japanese firms during the 1990s. Over 200 Voluntary Export Restraints were in force in the early 1990s.
Often the firms felt it would help avoid more punitive restrictions, but sometimes it was in their interests. Where the Japanese firms had a significant cost advantage over the domestic producers, the voluntary quotas meant that they could charge a significantly higher price.
With this, the profitability was either maintained or improved.
Import Licensing
This means that the licenses of the importers which are issued to them by the government can be restricted in lieu of the policies of the government regarding international trade.
Murky or Hidden Protectionism
This is a type of protectionism wherein, the policies are not directly but indirectly stated. An example of this could be when the government decides to pay subsidy only over the domestically produced goods.
Another example could be the deliberate interventions of the government into the currency markets.
Restrictions on FDI
Some governments also decide to impose restrictions on the FDI in order to prevent foreign nations from entering their market. But, there are few industries, wherein, FDI is strictly prohibited, this includes, real estate agricultural markets, and more.
Other Protectionist Measures
Some of the other measures that the countries can adopt are Administrative obstacles, Health and safety standards, and environmental standards.
Countries can set administrative hurdles. For example, importers may require significant levels of paperwork to deal with these processes, slowly making it challenging for importers to compete on a level playing field with the other firms.
Countries can also set ominously huge health and safety standards for imported goods, making life difficult for importers. Countries can also set high environmental standards that they feel only domestic firms will be able to achieve.
Need of Protectionism
Protectionist policies are to encourage domestic investment in a specific industry. For example, tariffs on the foreign import of clothes would encourage domestic producers to invest more resources.
In addition, budding domestic cloth producers will not be at risk from established foreign cloth producers. As a result of protectionist policies, domestic producers are fitter off, domestic consumers are worse off, as they may have to pay higher prices for inferior goods or services.
Therefore, protectionist policies serve to be very popular with the businesses and very unpopular with the consumers.
Advantages of Protectionism
There are several advantages to the concept of Protectionism. Some of them are-
a. Escalates Growth
It helps to increase the growth and opportunities of the smaller or the domestic industries in the country. Because of the restrictions that are imposed over the import of foreign goods, it gives a chance to the domestic industries to bloom and take over the market that previously demanded imported goods.
b. Fall in Imports
Due to an increase in the prices of imported goods, it leads to a fall in the demand, hence, a further fall in imports. The prices of imported goods increase because of the tools of protectionism that are used by the government.
c. Employment Opportunities
By enabling and encouraging the domestic industries, it helps in providing and fostering the job opportunities for the public of the country.
Growth in employment opportunities will induce a higher standard of living for the people of the country, which will further lead to satisfaction amongst the employees, hence, better work.
d. Higher Gross Domestic Product
The growth of the domestic industries helps to shoot the Gross Domestic Product of the country as a whole. The Gross Domestic Product will help the country to further broaden its reach and produce higher than before, making a mark in the international market.
Disadvantages of Protectionism
With advantages, this policy also comes up with several disadvantages which are as follows –
a. Stagnating Technological Advantages
Due to a fall in the competition in the market, the local industries lose the strive to produce high-end quality goods. They no longer need to compete with foreign brands and this causes technological stagnation.
b. Limited Choices for the Consumers
A fall in the import of foreign goods leads to lesser choices for the customers in the market. Where previously they had ten different varieties of goods, now, due to a fall in the import of foreign goods, they are left with lesser variety.
This can further lead to a situation where the producers will start to exploit the consumers by charging higher prices for the goods.
c. Higher Prices
Due to a lack of competition in the market, the producers tend to exploit the consumers by charging high prices for the goods without an upgrade in the quality.
This will be done because now, the domestic producers start to feel that the consumers have no other choice, and to fulfill their needs, they will eventually have to purchase the domestically produced, and comparatively lower quality goods.
d. Economic Isolation
Protectionism often leads to political and cultural isolation which further leads to an increase in economic isolation. This happens because the policies of protectionism do not only affect one country but more than it.
For example, If India puts a policy of protectionism over Chinese goods, it will affect both the markets of India and China. This can also lead to the backing off from the side of China in the case of other treaties that are yet to be signed between the two countries.
Conclusion
It is important to acknowledge the advantages and the positive effects on the economy, but due to its access usage, it might also end up draining the economy and its relations with foreign countries.
It can also lead to unsatisfied consumers in society, which will either ultimately discourage the production of the particular good or the society will end up settling for less, either of which is harmful to economic growth.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google