Syllabus and Strategy for Economics for UPSC Prelims, Mains and Optional
Are you ready for UPSC Exam? Check your preparation with Free UPSC Mock Test
Economics is a field of study which focuses on interactions of economic agents. It studies the behaviour and how the economies work. The UPSC Exam focuses on this academic discipline majorly. Economics is present for UPSC Prelims, UPSC Mains and as an UPSC Mains Optional Subject.
The subject syllabus overlaps in all three stages. The prelims have very basic economic questions while the mains have complex economic questions. And the optional gets to the roots of the economy of India and the World.
The Union Public Service Commission is interested because of its relevance in contemporary society. The future IAS officer must know how to handle economic situations around them. And it is not possible to do that without knowing the subject.
Thus it is mandatory for all the candidates to study this subject for at least prelims and mains. This article will help understand the economics syllabus for prelims, mains and optional with strategy for each of them. Let us take a look at them to understand the subject and exam pattern better.
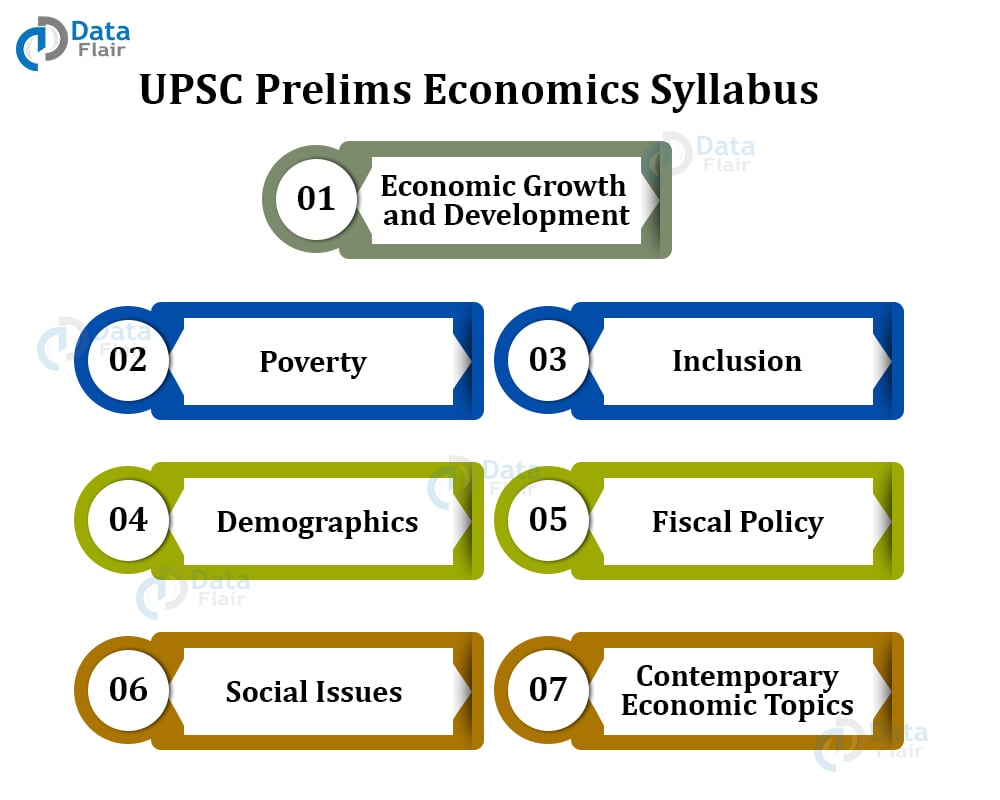
UPSC Prelims Economics Syllabus – Detailed
Economic growth and development
- Basic concept and definition of economics
- Uses and transfer of resources
- Distributive effects
- Macro and micro economic policy
- Micro-macro balance
- Distributive impact of economic policies
- Development versus growth
- Determinant of growth and development
- Concepts such as MPI, HDI, PQLI, GEM, GDI, TAI, Green index
- Sustainable development
- India’s ranking in the various indices
Poverty
- Definitions
- Causes
- Distribution-deprivation
- Income versus calories
- Measurement of poverty
- Status of poverty
- Eradication programmes
- Poverty and resource policy
- Tribal rights and issues
- Livelihood missions
Inclusion
- Definition
- Relevance
- Types
- Financial inclusion
- Recent initiatives
Demographics
- Census data
- Populations by gender and other criterias
- Trends in human development
- Interstate comparison
Fiscal policy
- Definition
- Component
- Receipts
- Revenue and Capital account
- Tax revenue
- Expenditure
- Budget
Social issues
- Financing health policy
- Education policy
- Sanitation
- Drinking water
- Social security
- Infrastructure policy
- International trade issues
- Regional cooperation
Contemporary Economic Topics
- MNERGS
- MSMEs
- Make in India
- Industrial corridors
- NITI Ayog
- Black money
- International treaties and organisations
- India’s policies with neighbours
Study Material for UPSC Prelims Economics
These are some of the reference study material which aspirants can use for general studies paper II of UPSC Prelims
- Indian Economy by Ramesh Singh
- EconomicPolicies in India by Jain & Ohri
- NCERT XI
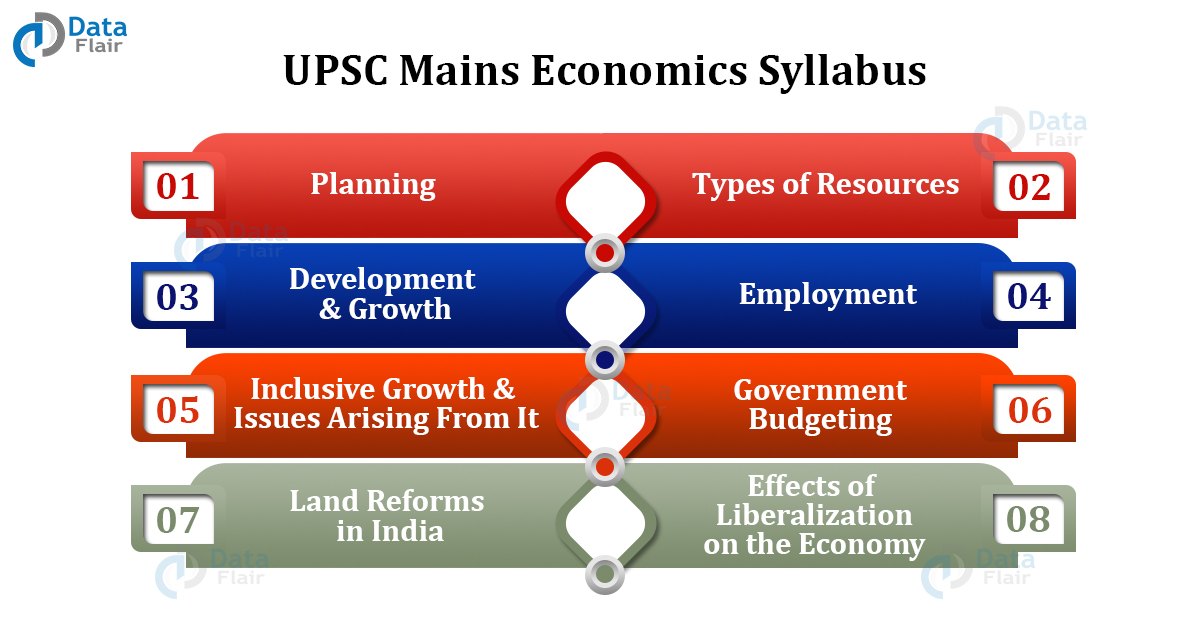
UPSC Mains Economics Syllabus / GS III – Detailed
Planning
- Definition and Need for Planning
- Imperative Vs. Indicative Vs. Structural Planning
- Objectives of Planning
- Indian Planning History
- Techniques of Indian Planning
- Achievements & Failures of Indian Planning
- Shortcomings of Planning in India
- NITI Aayog Vs. Planning Commission
- Mobilisation of Resources
Types of Resources
- Need for Resource Mobilisation
- Role of Savings & Investment
- Government Resources
- Banking Sector & NBFCs
- Capital Market
- External Sources
- Public Borrowing & Management of Public Debt
- Challenges in Mobilising Resources for Development
Development & Growth
- Difference – Development & Growth
- Determinants of Growth & Development
- Importance & Limitations of Economic Growth
- Types of growth
- Dimensions of Development
- Measurement & Indicators of Development
- Approaches to Development
- Challenges to Development & Growth
Employment
- Nature – Rural vs. Urban, Formal Vs. Informal
- Terms Related to Employment
- Sectoral Distribution of Employment
- Quality of Employment
- Causes of Lack of Employment
- Restructuring of Workforce
- Government Initiatives for Employment
Inclusive Growth & Issues Arising From It
- Definition and Elements of Inclusive Growth
- Need for Inclusive Growth
- Indicators of Inclusive Growth
- Challenges in Achieving Inclusive Growth in India
- 12th Fifth Year Plan & Inclusive Growth
Government Budgeting
- Need for Government Budgeting
- Components of the Government Budget
- Changes in Budgetary Process in 2017
- Measures of Government Deficit
- Deficit Reduction
- FRBM Act
- Other Types of Budgets
Land Reforms in India
- Rationale for Land Reforms
- Components of Land Reforms
- Impact of Land Reforms
- Problems in Implementation of Land Reforms
- Success of Land Reforms
- Recent Initiatives
Effects of Liberalization on the Economy
- Phase of Liberalisation
- Impact on Different Sectors of the Economy
Industrial Policy & Effects on Growth
- The Industrial Policy Before 1991
- Industrial Policy After 1991
- Phases of Industrial Growth
- Linkage Between Economic Reforms and Economic Outcomes
- Weaknesses and Failures of Industrial Policies
- National Manufacturing Policy
- SEZs
- Make in India
Infrastructure
- Energy
- Ports
- Roads
- Airports
- Railways
Investment Models
- Need for Investment
- Sources of Investment
- Types of Investment Models
- Investment Models Followed by India
Strategy for UPSC Mains Economics – GS III
These are some of the reference study material which aspirants can use for general studies paper III of UPSC Mains.
- NCERT textbook classes X – XII
- Indian Economy by Ramesh Singh
- Indian Economy by Sanjeev Verma
- Union Ministry Official Websites
- Economic Survey of India
- Different Budgets of India and World
- Administrative Reforms Commissions Reports
- PIB
- Newspapers – Economic Times, The Hindu, The Economist
- Magazines – Economic and Political Weekly, Yojana, Kurukshetra
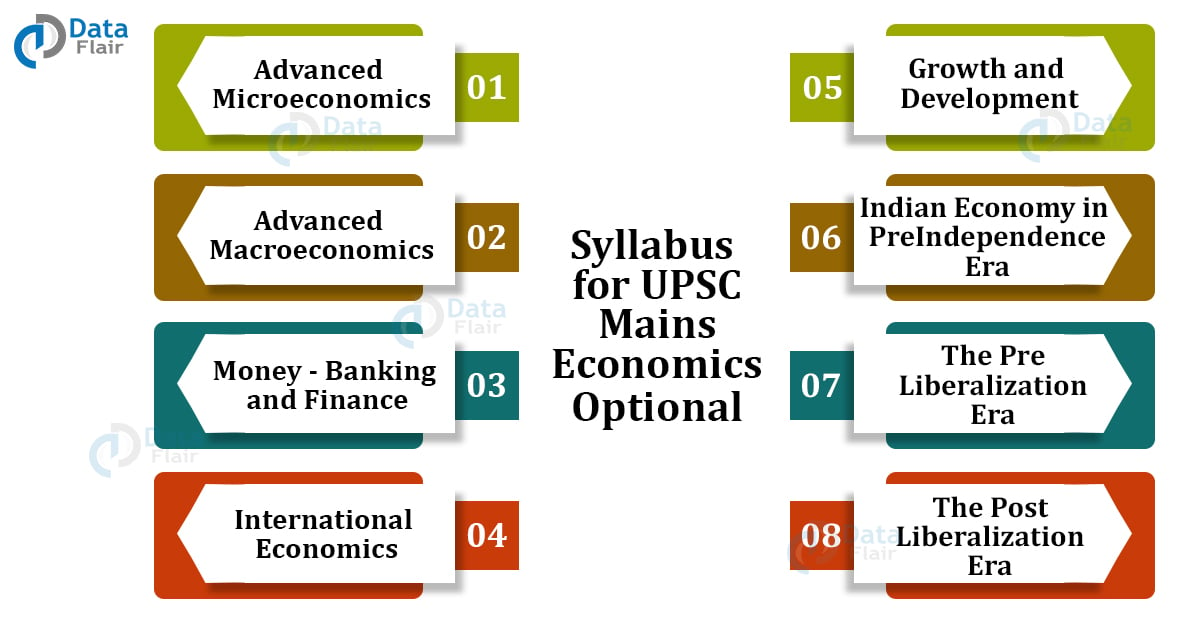
Syllabus for UPSC Mains Economics Optional – Detailed
Advanced Microeconomics
- Marshallian and Walrasiam Approaches to Price determination.
- Alternative Distribution Theories – Ricardo, Kaldor, Kaleeki
- Markets Structure – Monopolistic Competition, Duopoly, Oligopoly
- Modern Welfare Criteria
- Pareto Hicks & Scitovsky
- Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem
- A.K. Sen’s Social Welfare Function
Advanced Macroeconomics
- Approaches to Employment Income
- Interest Rate determination
- Classical, Keynes (IS-LM) curve
- Neo classical synthesis and New classical
- Theories of Interest Rate determination
- Interest Rate Structure
Money – Banking and Finance
- Demand for and Supply of Money
- Money Multiplier Quantity Theory of Money
- Keynes’s Theory on Demand for Money
- Goals and Instruments of Monetary Management
- Relation between the Central Bank and the Treasury
- Proposal for ceiling on growth rate of money
- Public Finance and its Role in Market Economy
- Allocation of resources and in distribution and development
- Sources of Govt. revenue
- Forms of Taxes and Subsidies
- Their incidence and effects
- Limits to taxation, loans and borrowings
- Public Expenditure and its effects
International Economics
- Old and New Theories of International Trade
- Comparative Advantage
- Terms of Trade and Offer Curve
- Product Cycle and Strategic Trade Theories
- Trade in an open economy
- Forms of Protection
- Tariff and quota
- Balance of Payments Adjustment
- Price versus income
- Income adjustments under fixed exchange rates
- Theories of Policy Mix
- Exchange rate adjustments under capital mobility
- Floating Rates and their Implications for Developing Countries
- Trade Policy and Developing Countries
- BOP, adjustments and Policy Coordination
- Speculative attacks
- Trade Blocks and Monetary Unions
- WTO – TRIMS, TRIPS, Domestic Measures
- Different Rounds of WTO talks
Growth and Development
- Theories of growth
- Lewis model of development with surplus labour
- Balanced and Unbalanced growth
- Human Capital and Economic Growth
- Research and Development and Economic Growth
- Process of Economic Development of Less developed countries
- Role of Agriculture in Economic
- Development of less developed countries
- Economic development and International Trade and Investment
- Role of Multinationals
- Planning and Economic Development
- Welfare indicators and measures of growth
- Development and Environmental Sustainability
- Renewable and Non Renewable Resources
- Environmental Degradation
- Intergenerational equity development
Indian Economy in PreIndependence Era
- Land System and its changes
- Commercialization of agriculture
- Drain theory
- Laissez faire theory and critique
- Manufacture and Transport
- Money and Credit
The Pre Liberalization Era
- Contribution of Vakil, Gadgil and V.K.R.V. Rao
- Agriculture – Land Reforms and land tenure system
- Green Revolution
- Capital formation in agriculture
- Industry Trends in composition and growth
- Role of public and private sector
- Small scale and cottage industries
- National and Per capita income
- Broad factors determining National Income and distribution
- Measures of poverty
- Trends in poverty and inequality
The Post Liberalization Era
- Agriculture and WTO
- Food processing
- Subsidies
- Agricultural prices and public distribution system
- Impact of public expenditure on agricultural growth
- New Economic Policy and Industry
- Strategy of industrialization
- Privatization
- Disinvestments
- Role of foreign direct investment and multinationals
- New Economic Policy and Trade
- Intellectual property rights
- Implications of TRIPS, TRIMS, GATS
- New EXIM policy.
- New Exchange Rate Regime
- Partial and full convertibility
- Capital account convertibility
- New Economic Policy and Public Finance
- Fiscal Responsibility Act
- Twelfth Finance Commission
- Fiscal Federalism and Fiscal Consolidation
- New Economic Policy and Monetary system
- Role of RBI under the new regime
- Planning
- From central Planning to indicative planning
- Relation between planning and markets for growth
- New Economic Policy and Employment
- Employment and poverty
- Rural wages
- Employment Generation
- Poverty alleviation schemes
- New Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme
Strategy for UPSC Economics Optional Paper
These are some of the reference study material which aspirants can use for economics optional paper of UPSC Mains.
- Indian Economy by Mishra-Puri and Dutt-Sundaram
- The Economics of Development & Planning by M. L. Jhingan
- International Economics by H.G. Mannur
- NCERT Class XI
- Public Finance by H.L. Bhatia
- Money and Banking by S.B.Gupta
- Macroeconomic Theory by M. L. Jhingan
- Macroeconomics NCERT book
- PIB
- Newspapers
- Modern Banking by R.S. Sayers
- Monetary Theory and Public Policy by Kenneth Kurihara
- National Income Accounting by Neethu
- Outline of Monetary Economics by A.C.I. Day
Tips for UPSC Economics Optional Paper
- Economics works on statistics and numbers. The best idea is to use graphs to justify all your answers.
- The terms of economics are a bit confusing. In case of confusion avoid using proper terminology. It will completely change your answer.
- There are many equations as well. Writing them is a great idea but only if they are correct. Prefer making graphs over them.
- The numbers are important. Try using data and figures to justify your answer and prove your equation.
- Use as many examples as possible. You can pick them up from real life situations as well.
Question Distribution in UPSC Economics Optional
| Topic | Average Number of Questions |
| Indian Economy | 40 – 45 |
| Micro and Macro Economics | 35 – 40 |
| International Economics | 15 – 20 |
| Money, Banking & Public Finance | 10 – 15 |
| Growth and Development | 10 |
| Statistics | 7 – 10 |
Conclusion
This article covered all aspects of economics for the UPSC examination. We saw the syllabus for prelims, mains and optional. In addition to this there are study materials suggested for each of these papers.
And lastly tips for economics optional subject as that is more detail oriented. The idea is to prepare candidates for every part of the paper. This article will help you study a detailed syllabus for economics covering all the topics and sub topics.
And this article is not for just economics students but for all UPSC aspirants. All the candidates must read the article to get a better idea of the subject.
Did you like our efforts? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google