Macros in C Programming – Don’t Consider it as an Outdated Feature
Today, macros in C is considered as outdated in modern programming practices, it still finds applications in C by making things easier for the programmer. We will help you to develop a clear understanding of macros by covering even the minute concepts.
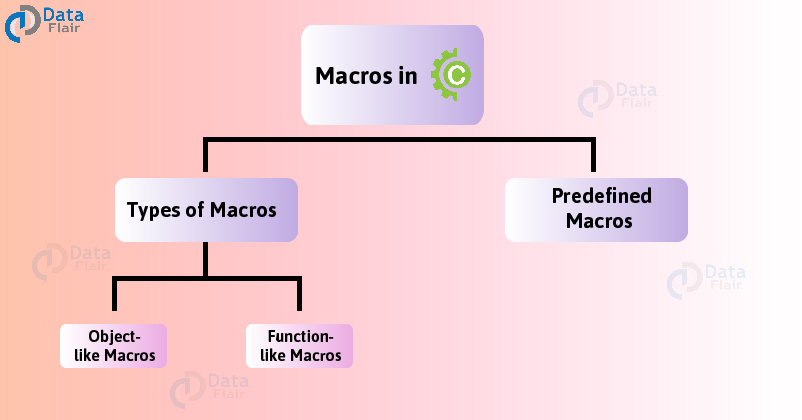
In this tutorial, we will discuss:
- Macros in C Programming
- Types of macros
- Different predefined macros
1. Macros in C Programming
Macros are nothing but a piece of code based on the #define preprocessor. In the C programming language, a macro would generally look like:
#define MACRO macro_value
Key takeaway: It is important to note that the macros are not terminated by a semicolon (;)
For a better understanding of Macros, it is important to understand preprocessors in C.
2. Types of Macros in C Programming
In C, Macros are broadly classified into two distinct types. They are namely:
2.1 Object-like Macros
It appears to be a symbolic constant. It can be termed as an alternative way to define an identifier used to represent constant expressions. The simplest example would be:
#define PI 3.14
2.2 Function-like Macros
It is an expression, used to perform a particular operation. It is an alternative way to define a function. A simple example would be:
#define RECTANGLE(l,b) l*b
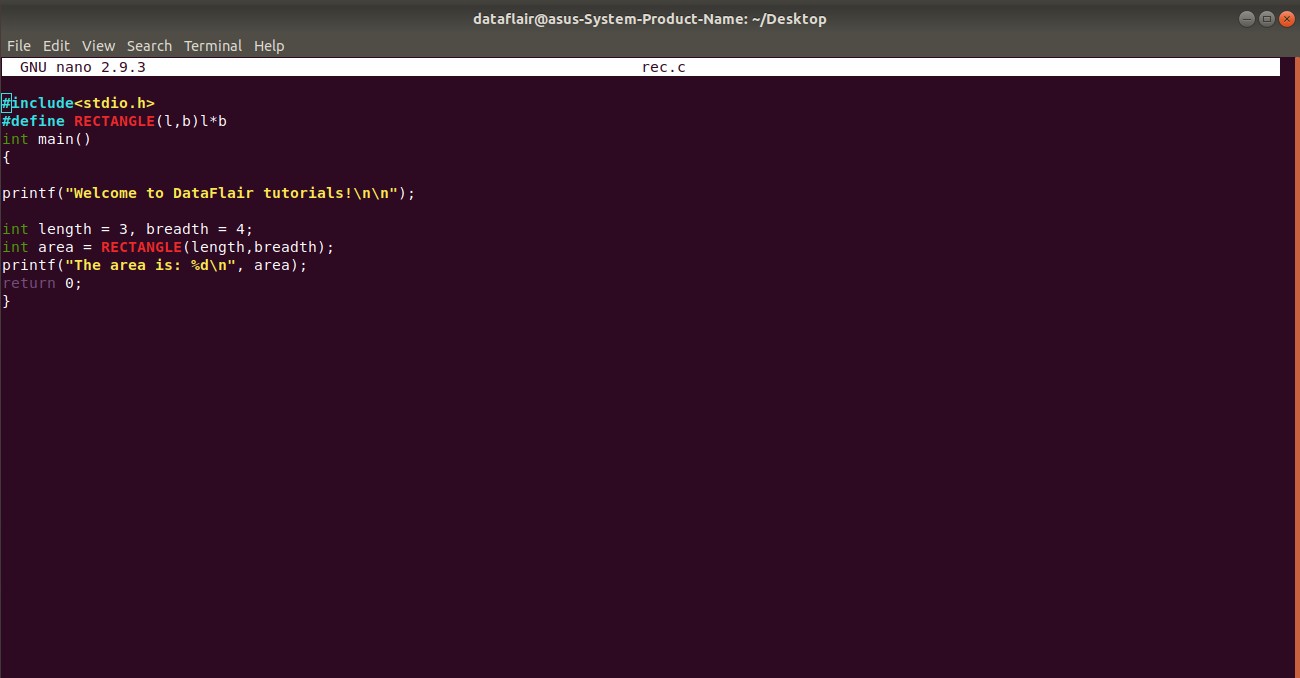
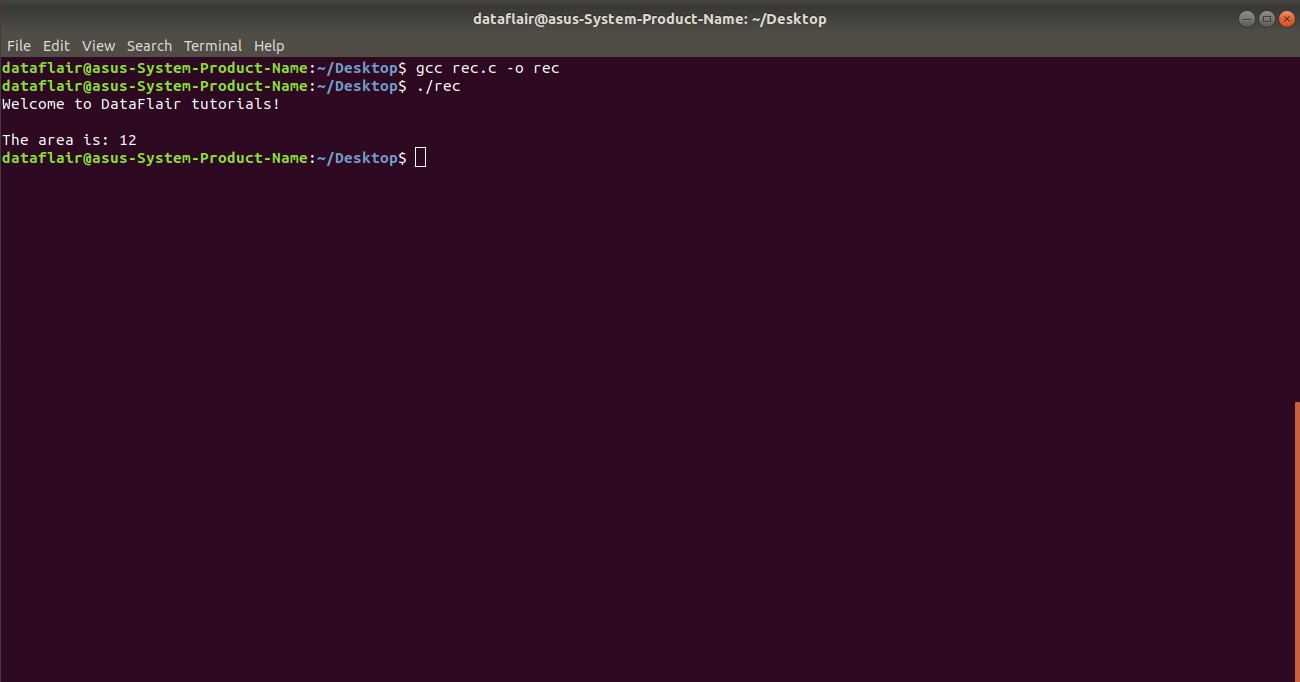
Here is a code in C that illustrates the use of macros to find the area of a rectangle:
#include<stdio.h>
#define RECTANGLE(l,b)l*b
int main()
{
printf("Welcome to DataFlair tutorials!\n\n");
int length = 3, breadth = 4;
int area = RECTANGLE(length,breadth);
printf("The area is: %d\n", area);
return 0;
}Having problems in understanding the above program? Check this out Basic Syntax Rules – Learn the ABC’s of CProgramming
Code on Screen-
Output-
Types of Predefined Macros in C
Here is a table that summarizes some of the basic macros used in the C programming language:
- _DATE_ – Used to represent the current date in MM DD YYYY format.
- _STDC_ – Used to indicate when the compiler compiles the code successfully by returning the value 1.
- _TIME_ – Represent the current time in HH:MM:SS.
- _LINE_ – Represent the current line number.
- _FILE_ – Represent the current file name.
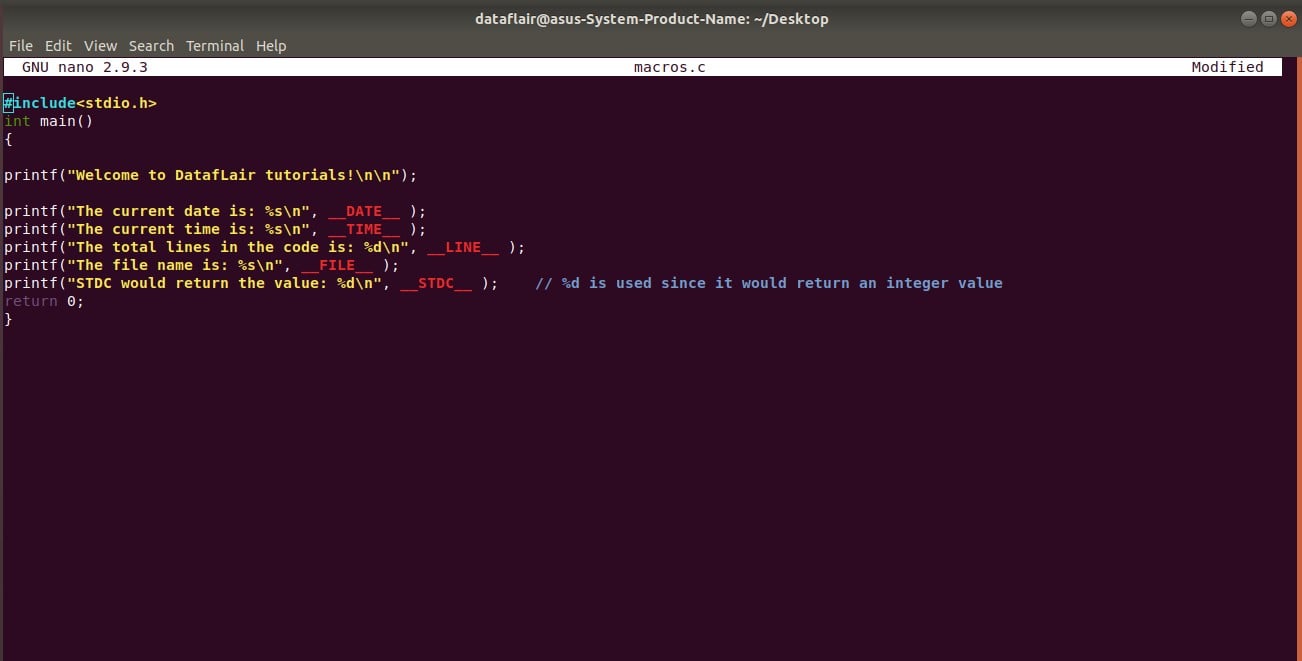
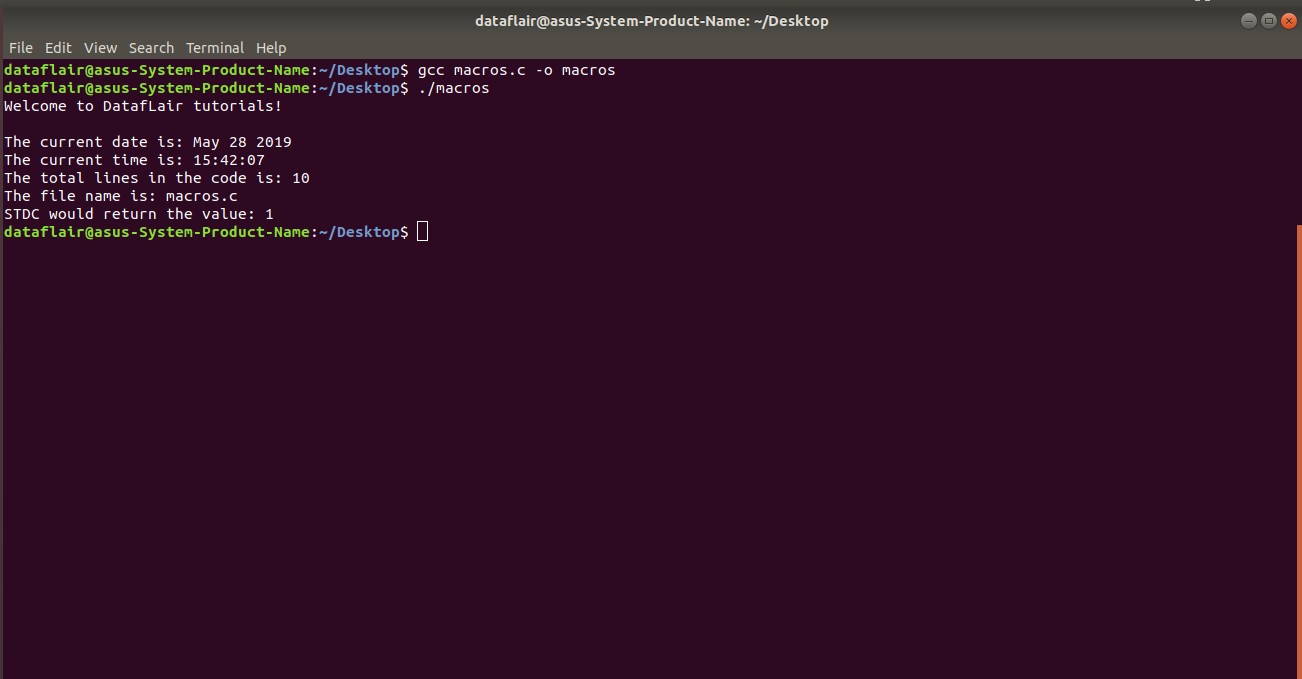
Here is a code in C that illustrates the use of macros:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Welcome to DatafLair tutorials!\n\n");
printf("The current date is: %s\n", __DATE__ );
printf("The current time is: %s\n", __TIME__ );
printf("The total lines in the code is: %d\n", __LINE__ );
printf("The file name is: %s\n", __FILE__ );
printf("STDC would return the value: %d\n", __STDC__ ); // %d is used since it would return an integer value
return 0;
}Code on Screen-
Output-
Quiz on Macros in C
Summary
In this tutorial, we discussed the basic meaning of macros, its 2 basic types with appropriate examples. We further carried our discussion on the various types of predefined macros available in the C programming with the help of a program.
It’s the right time to explore Typecasting and Type Conversion in C
We hope you liked the article. Don’t forget to share your experience.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google


Sir,’check’ option not working ….how do i check answer which one is right or wrong…..