Reproduction in Plants – Sexual Reproduction and Asexual Reproduction
Are you ready for UPSC Exam? Check your preparation with Free UPSC Mock Test
Reproduction is the process of giving birth to another organism from an existing organism. It is an important concept that defines the existence of life on planet earth. This biological idea is applicable to all living organisms in the world.
No matter which kingdom they belong to. It is essential to continue the races of different organisms. This process began with the first living organisms only. The biology of every organism is different.
This is because of their distinctive structure and set of features. These factors define their reproduction method as well.
The plant reproduction is producing an offspring from an existing plant. They can follow either sexual or asexual methods of reproduction. This again depends on the structure and features of the plant we are looking at. The major difference between the methods is the existence of seeds.
The mode of reproduction decided the genetic structure of the plant. Asexual reproduction produces new organisms without seeds while in sexual reproduction, seeds are mandatory. This is just one of the differences.
They have several methods and processes under them. Let’s look at Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Plants in detail.
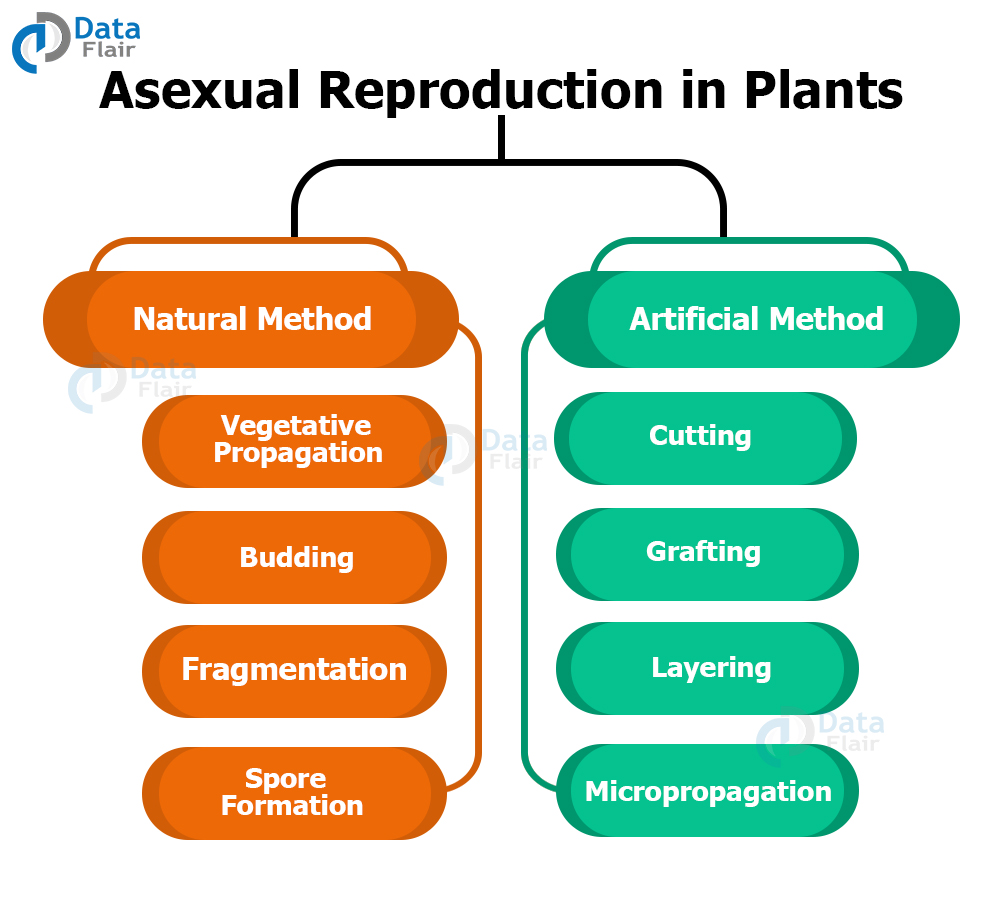
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
The asexual mode of reproduction does not include male and female gametes’ mating and produces genetically identical organisms to their parents. There are two ways to follow this mode of reproduction. They are – natural methods and artificial methods.
The natural method looks at Vegetative Propagation, Budding, Fragmentation, and Spore formation. While the artificial method looks at Cutting, Grafting, Layering, and Micropropagation. Let us take a look at each of them in-depth:
Natural Methods of Asexual Reproduction in Plants
1. Vegetative Propagation in Plants
The vegetative parts of the pants are roots, stems, and leaves. Vegetative Propagation involves the reproduction of new plants from roots, stems, leaves, and buds. Because the process is by the vegetative parts, the term used is vegetative propagation.
Every stem has nodes where buds grow. Mostly these buds grow into a new plant. In the case of roots, a new plant grows from a tuber or modified roots. Sweet Potato is an example of root propagation.
And lastly, the fallen leaves are capable of propagating a new plant. Bryophyllum is an example of leaf propagation. Some other examples are Cacti that detaches from the main to grow into a new plant.
The Vegetative Propagation is faster than pollination and grows the flower faster. The offspring is completely identical to the parent because of single parent involvement.
2. Budding in Plants
This asexual method of reproduction involves the development of a new plant from an outgrowth of the parent plant. This outgrowth is bulb-like in appearance and the term of it is Bud. Cell division at certain places often leads to the creation of buds in plants.
Once it develops a tissue system, it detaches from the parent plant. This is possible in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Yeast and hydra are the two most prominent examples of budding. Hydra follows the process mentioned above.
But yeast divides from the nucleus and that detaches from the main body.
3. Fragmentation in Plants
In this method of asexual reproduction, fragments of the parent plant grow into a new organism. The most common example is algae. In suitable conditions, algae grow simultaneously by the process of fragmentation.
It breaks into pieces and each of the pieces develops into an individual body. In the case of plants, a small part of the plant falls and starts growing. Suitable soil increases the rate of growth. It is a common method at plant nurseries.
4. Spore Formation in Plants
The spore is an asexual reproductive body. They are light in weight and are capable of covering long distances in a short time. The spores have a hard protective layer which helps them survive extreme conditions.
Under suitable conditions, the spore develops into a new organism by germination. Moss and Ferns are examples of this reproductive organism. Fungi also work on the same phenomenon to reproduce.
Artificial Method of Asexual Reproduction in Plants
1. Cutting in Plants
This artificial asexual method involves cutting down of a plant part with nodes. This part is kept in soil and requires regular watering. It leads to the reproduction of a new plant from the soil.
It is one of the cheapest methods of artificial asexual reproduction. This is also termed as artificial vegetative propagation in plants.
2. Grafting in Plants
This asexual method of reproduction involves two plants. The stem of one plant and the roots of another are joined to grow together. The roots plant is stock while the stem plant is graft. This method requires expertise in the field of botany to reproduce.
3. Layering in Plants
This asexual method of reproduction involves bending of the stem in the ground. The stem is lowered in the ground and grows in covered soil.
The stems start to grow roots and still remain attached to the parent plant. Once the roots get mature, the stem detaches and grows as an independent individual or plant.
4. Micropropagation in Plants
This asexual reproduction method takes place in a laboratory. This method is for a large number of plants that have become extinct or endangered. The scientists create suitable conditions for these plants to grow in a short interval of time. This is a very expensive method to practice.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
1. Flowers
The flowers of a plant act as a reproductive organ of the body. These flowers have male reproductive parts as well as female reproductive parts. The flowers having both reproductive parts are bisexual while the flower with only of the part is unisexual.
Stamens are the male reproductive part while the pistil is the female reproductive part. Corn, Papa, Cucumber, etc comes under unisexual flowers.
And rose, mustard, petunia, etc. are bisexual flowers. The unisexual flowers of both genders can be in the same plant or in different plants. Stamen has anther which contains pollen grains or male gametes.
A pistil has stigma, style, and ovary, the ovary consists of ovules. The female gamete lives in the ovule. The male and female gamete fuses to produce zygote under sexual reproduction.
2. Spores
This is the opposite of seeds and is the reproductive cells that form a new individual without fusing with a different cell. They are microscopic in size but have the capability to grow into a multicellular plant under suitable conditions.
They are common in plants like algae, mosses, and ferns and are under the leaves and disperse by wind or water. But unlike seeds, animals cannot eat them but bacteria may consume them.
3. Cones
Conifers have their reproductive organs in their cones. The male cones produce pollen and are smaller than the female cones that produce eggs. The ovule after fertilization develops into a seed. The male and female cones are mostly in the same plant but the female cones are on higher branches.
This is for better cross-fertilization and avoids self one. In most cases, pollen reaches a female of a different plant because of the wind.
Features of Sexual Reproduction in Plants
- Involvement of two parents ie male and female.
- Formation of gamete and fusion between them.
- It is a time taking process.
- The offspring are genetically and physically different from their parents.
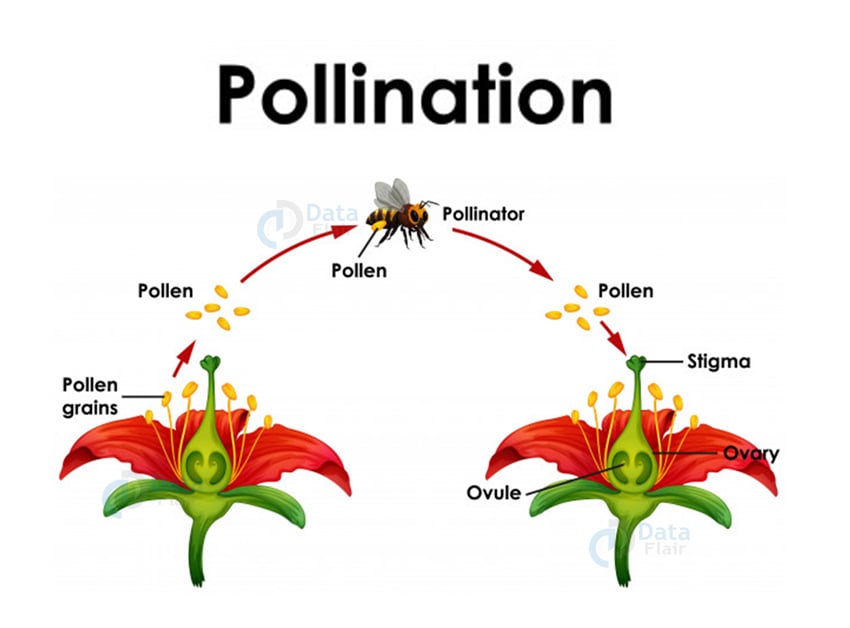
Pollination in Plants
The pollen grains produce the male gametes of the plant. They usually have a hard outer layer to protect them. They are very light in weight making it easy for wind and water to carry them. Some insects carry them too.
Some of this pollen drops on the stigma of the flower and this process of transfer is pollination. If the pollen grains reach the same flower, it becomes self-pollination. And if it reaches another flower, then it becomes cross-pollination. The agents of this process are pollinators.
| Self-Pollination in Plants | Cross-Pollination in Plants |
|
|
Fertilization in Plants
The fusion of male and female gametes in sexual reproduction leads to the formation of zygote. The process of fusion of two gametes is fertilization. The zygote over a period of time develops into an embryo. Fertilization takes place in self-pollination as well as in cross-pollination.
Fruits and Seeds
The development of seed takes place inside the ovary. The seed has an embryo protected with a hard coating. The ovary with time grows into a fruit with the seed still inside. They are embryonic and often contain protein.
The dispersion of seeds is by water, air, animals, and other agents as well. Some pollinators are often animals, especially spiny seed plants. Urena and Xanthium are examples of this. These seeds get dispersed because of sudden jerks in animal movement. Castor and Balsam are examples of this.
This situation is seed dispersal. And in case of fruit formation, once it ripens, the other parts of the flower fall off. Some examples of sexual reproductive plants are mango, apple, almond, and walnut.
Difference – Asexual and Sexual Reproduction | |
Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| Involvement of one parent only | Involvement of male and female parents both |
| Takes place in Unisexual Plant | Takes place in Bisexual Plants |
| Common in lower plants | Common in higher plants |
| No reproductive organs | Developed reproductive organs |
| No zygote formation | Formation of zygote |
| No seeds required | Requires seeds |
| Similar to one parent only | Similar to both parents |
| The parent may die after reproduction | Parents live after reproduction |
Conclusion
The reproduction in plants process is important for the generation continuation of the earth. Be it humans or plants, both are equally important. The reproduction plants increase the greenery in the ecosystem making the lives more comfortable.
This article was about the reproduction methods used by plants. It can be sexual or asexual reproduction method. The mode depends on certain features. All these things are discussed above in detail. This article will guide you step by step by every mode and sub-method with examples.
Competitive exams like UPSC, SSC, RRB, and more ask basic science questions in general studies paper. This topic comes under basic science only. If you are a UPSC aspirant then this article will help you get a clear understanding of this topic.
Your opinion matters
Please write your valuable feedback about DataFlair on Google