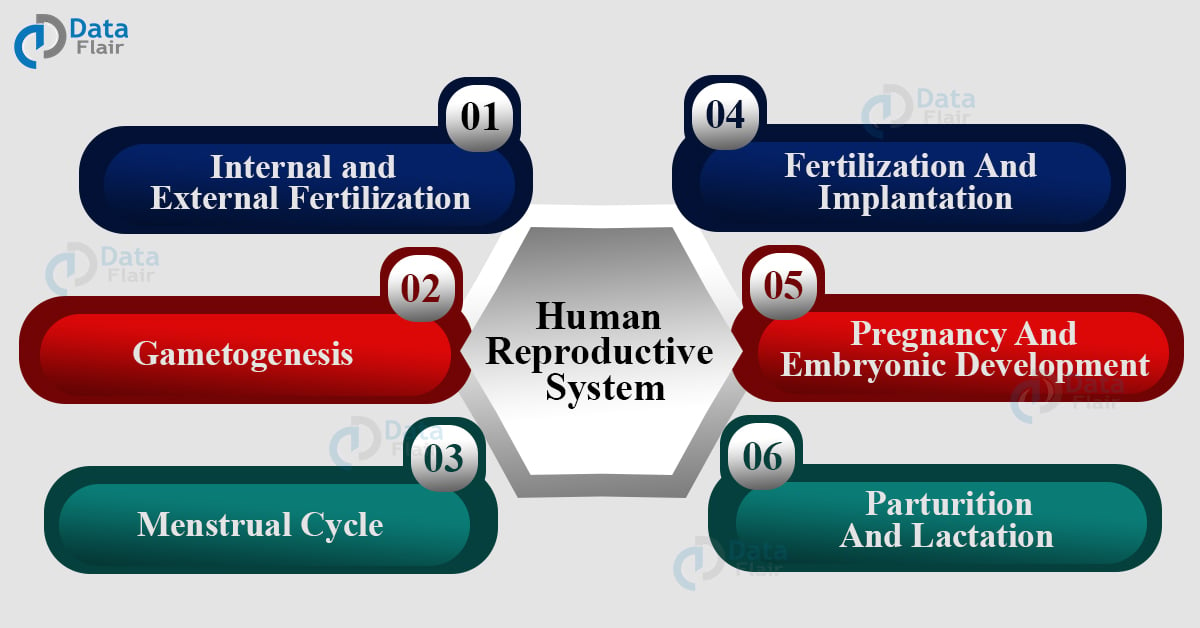
Human Reproductive System – Male and Female
Are you ready for UPSC Exam? Check your preparation with Free UPSC Mock Test
Reproduction is the process of giving birth to another organism from an existing organism. It is an important concept that defines the existence of life on planet earth. This biological idea is applicable to all living organisms in the world.
No matter which kingdom they belong to. It is essential to continue the races of different organisms. This process began with the first living organisms only. The biology of every organism is different.
This is because of their distinctive structure and set of features. These factors define their reproduction method as well.
Human reproduction includes the direct birth of an individual by an existing one. They follow only sexual methods of reproduction. Sexual reproduction includes the fusion of male and female gametes and forms a zygote that develops into a new individual.
The process of zygote formation is fertilization. There is the mating of male sperm and female eggs. The two main parts here are testis and ovaries. In the case of asexual reproduction, only one parent is involved.
Hydra uses this process by a method called budding. The asexual reproduction method used is binary fission in amoeba.
Internal and External Fertilization
Fertilization is the process of fusing eggs and sperms to form a zygote. Internal fertilization is when the baby develops inside the female body. This is common in humans, cows, and dogs. External fertilization includes the fusion of male and female gametes outside the female body.
This is common in aquatic animals like frogs, fishes, and more. The frogs in the rainy season lay large numbers of eggs inflowing streams. The male toads reach and deposit sperm on each egg to fertilize and reproduce. The eggs have a jelly-like outer layer for protection.
Human Reproductive System
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
The reproduction in humans is sexual and thus includes both male and female organs. The mating of male and female gametes is gametogenesis. The transfer of sperm from male to female body is insemination. And the fusion of both the elements to form a zygote is fertilization.
The zygote attachment to the uterus wall is implantation and embryo development in gestation. And the delivery of a baby is parturition.
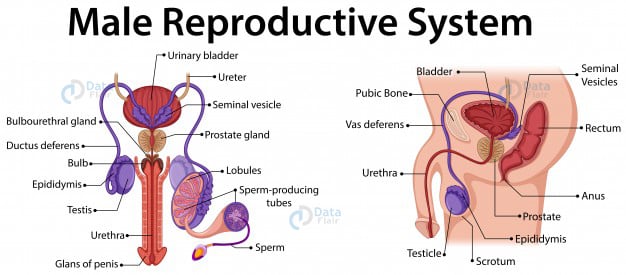
Male Reproductive System
This part of the male human body consists of the testes, scrotum, spermatic ducts, sex glands, and penis. These elements or organs coordinate which leads to the formation of sperms, the male gamete, and semen.
The penis is also a part of the urinary system in a male body. The penis is connected to pelvic bones and lower abdominal glands. Corona is the base of the penis and the urethra is the channel inside the penis.
Penis
It has three erectile tissues in cylindrical spaces. The corpora cavernosa are the larger ones next to each other. And the smaller one is the sinus or corpus spongiosum above the urethra.
The blood filling in this space leads to penis rigidity. The accessory glands are – seminal vesicles, a prostate, and bulbourethral glands.
Scrotum
The sack-like structure that protects the testes is the scrotum. They are responsible for controlling the testes temperature because the sperm needs a slightly lower temperature than the body to survive.
This process of sperm formation is spermatogenesis. The muscles facilitate testes to hang and keep them warm and under protection.
Testes
They are the testosterone-producing part of this organ. They are oval in shape with a length of 1.5 – 3 inches. Testes produce testosterone and sperms. The seminal vesicles are ducts that move through the prostate.
Together they release fluid for sperm nourishment. This gives them maximum volume at the time of ejaculation. There are 250 testicular lobules in each testis.
And each of them has one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules where sperm production takes place. Each tube has 2 cells outside – spermatogonia and Sertoli cells. The meiotic division of male germ cells produces sperms while Sertoli provides its nutrition.
The Leydig cells in seminiferous tubules secrete androgens. The vasa efferentia leads to epididymis which then goes till the urinary bladder. The urethra starts from here and acts as a path for sperms to flow.
Urethra
The tube that connects the urinary bladder and meatus is the urethra. The sperm passage and urine passage is by this tube only. It acts as the transportation channel for the fluid in the male reproductive organs.
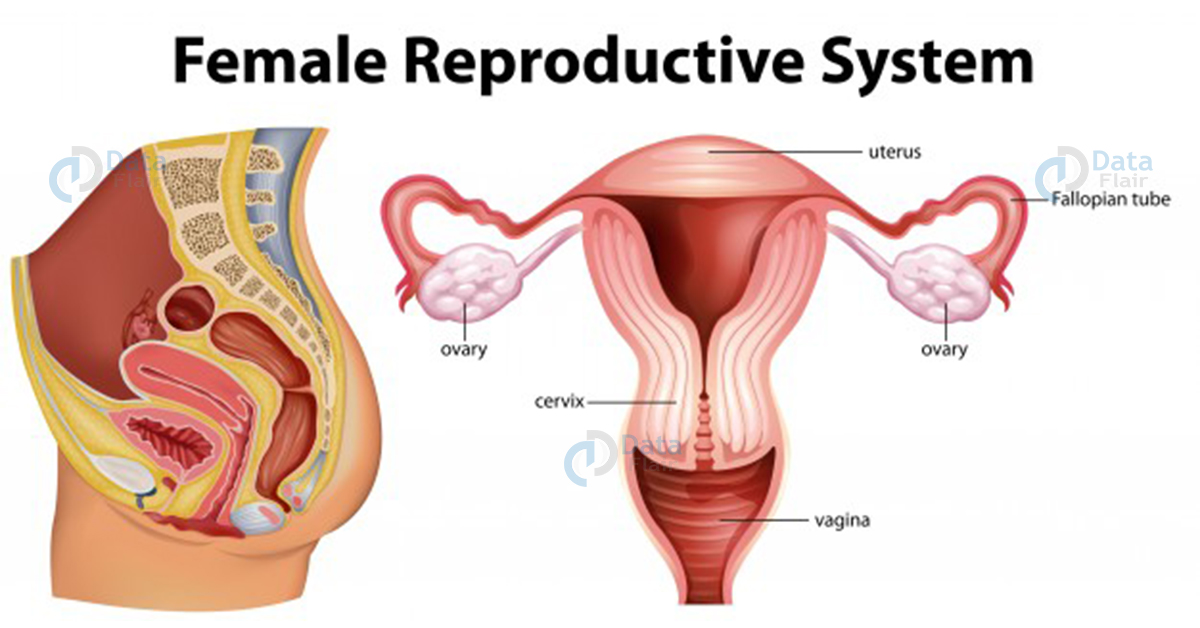
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is made up of ovaries, oviducts, vagina, cervix, uterus, and external genitalia. The mammary glands are also part of the reproducing organs that support the process of ovulation, fertilization, and birth.
Ovaries
These are the mail female organs in the body. They are responsible for producing female gametes and other hormones as well. Their location is near the lower abdomen and is 1-4 cm in length connected to the uterus and pelvic. The epithelium is the thin covering of ovary and ovarian stroma.
The cortex has ovarian follicles for development stages and are the basics of the female reproduction process. There are four regions in the oviduct – ampulla, isthmus, and infundibulum.
Uterus
It is the womb where a child develops. It is a pear-shaped muscular organ with three layers of protection. They are – glandular layer, middle thick layer, and the thin layer. The ligaments on the pelvic wall lead to a narrow cervical opening of the vagina. The vagina and cervix make the birth canal.
Fallopian Tubes
They funnel-shaped muscular tubes starting from uterus corners and connecting to the ovaries. Fimbriae enclose the tubes and wipe at the time of ova release. They drive the ova to the infundibulum for the uterus. Cilia is the covering of these tubes that facilitates this transportation.
Vagina
It is the elastic tube at the end of the cervix and is muscular as well. It is the place penis penetrates at the time of sexual intercourse and transports sperm to fallopian tubes. This is also the birth canal as it expands at the time of fetus delivery.
Pubis, labia majora, labia minora, hymen, and clitoris make up the female external genitalia. The hymen is a thick blood tissue wall inside the vagina. It usually breaks at the time of first sexual intercourse. But in no way or sense, it talks about women’s virginity.
Ovulation
The egg released from the ovaries is ovulation. As the follicle grows fully, the rise in pressure leads to estrogen production in the organ. As the luteinizing hormone reaches its peak, ovulation takes place at stigma. This surge of hormones is essential to create conditions for ovulation.
During this process, the follicle separates from the ovum after releasing follicular fluid. The corona cells separated at a later stage of spermatozoa.
The fimbriae at the end of the oviduct get the ovum and if fertilized, zygote formation takes place for implantation. And if not, the ovum degenerates or breaks in 24 hours.
Gametogenesis
The process of producing gametes by testis and ovaries is gametogenesis. The gametes are sperms and eggs. In testis, spermatogonia are responsible for producing sperms by spermatogenesis when the individual hits puberty.
The spermatogonia under the seminiferous tubules start to multiply and increase by meiotic division. Each of these divisions of spermatogonia has 46 chromosomes.
Some of them are also primary spermatocytes that have only 23 chromosomes each. The secondary spermatocytes generate 4 equal haploid spermatids. The spermiogenesis is the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa.
After this, sperm goes to Sertoli cells and move out by seminiferous tubules. This releasing process is spermiation. The gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion increases at puberty which leads to Spermatogenesis.
This in turn leads to the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The LH is Leydig cells and facilitates androgen secretion. And androgen boosts the process of spermatogenesis.
FSH on the other hand stimulates the secretion of some fluid and supports the Sertoli cells. A sperm is microscopic in size with a head, neck, and tail. The head the nucleus haploid and a cap-like thing acrosome. The acrosome has enzymes that facilitate fertilization.
The middle portion has mitochondria for sperm motility. The human male produces 200-300 million sperms during coitus and 60% of them have a normal shape and 40% have vigorous motility. The accessory ducts assist the sperms from seminiferous tubules.
The epididymis and prostate secretion are important for sperm mobility and maturation. The semen is a part of the seminal plasma as well. And the androgen maintains the testicular hormones.
The oogenesis is the formation of the female gamete in the human body. At the time of embryonic development, the fetal ovary forms the oogonia and ends right there. This process can not take place after birth.
The meiotic division leads to cell division in prophase I and forms primary oogenesis. These oocytes have a granulosa cell layer and are primary follicles. At puberty, many of these degenerates and ovaries are left with only 60,000-80,000 primary follicles.
Another layer gets around these to form the secondary follicles. This follicle becomes the tertiary follicle as the antrum fluid cavity forms. At this stage, the tertiary follicle finishes its first mitotic division. There is an unequal division which leads to a bigger haploid secondary oocyte and a smaller first polar body.
The secondary oocyte gets nutrients from the cytoplasm of the primary oocyte. the tertiary one becomes the Graafian follicle that releases ovum and leads to ovulation.
Menstrual Cycle
Menstruation is a natural phenomenon that begins at puberty in all human females. The menarche is the term of first menses. It is a repetitive cycle every 28 days. The ovum releases in the middle of each menstrual cycle. The menses last for 3-5 days and see the continuous menstrual flow.
The endometrial lining of the uterus breaks during this time and the blood vessels release out of the vagina. This takes place when the ovum doesn’t go under fertilization.
But no menses is not 100% proof of pregnancy, there are other health reasons involved too. The follicular phase starts right after this and sees mature Graafian follicles through proliferation. This is because of the changes in the pituitary and ovarian hormones.
The gonadotropin secretion increases in this phase and reaches highest on the 14th day leading to ovum secretion. The luteal phase after this transforms the Graafian follicle to the corpus luteum.
This releases progesterone in higher quantities which maintains endometrium. The endometrium facilitates the implantation of the ovum. At the time of pregnancy, all menstrual activities stop.
This leads to the disintegration of the endometrium and the formation of a new cycle after pregnancy. Menopause comes around at the age of 50 and a regular menstrual cycle is a sign of a normal reproductive phase.
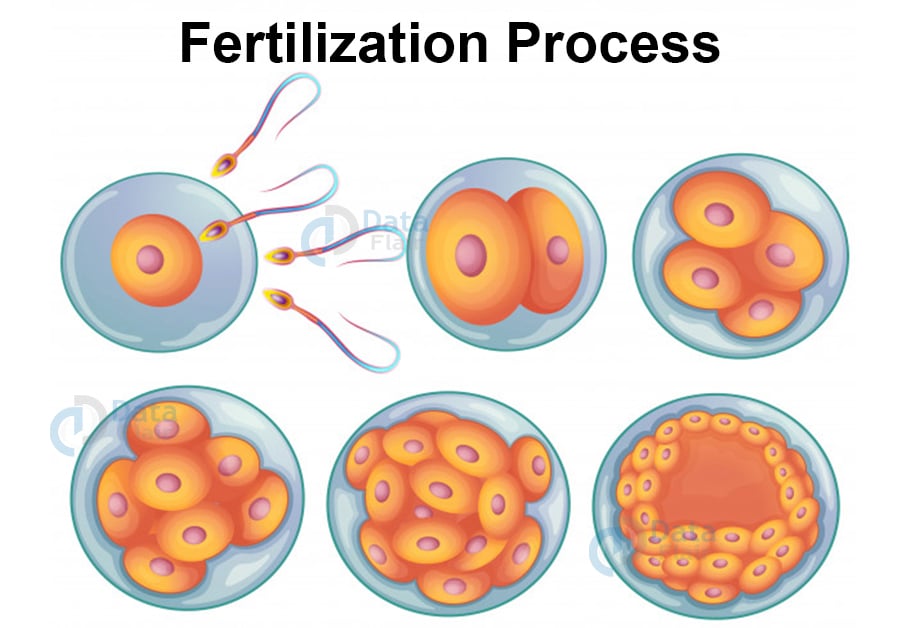
Fertilization And Implantation
The semen when entering the vagina swims till the uterus and then the fallopian tubes. The ovum also reaches the ampullary region where the process of fertilization takes place. This process of transportation must be simultaneous to lead to pregnancy.
The fusion of the gametes is fertilization. Zona pellucida layer of the ovum makes sure that only one sperm enters and fertilizes. The acrosome helps the sperm enter the ovum’s cytoplasm.
Morula is the sperm blast meters and continues to divide after entering the uterus. The blastocyst embeds in the endometrium of the uterus and leads to implantation and pregnancy.
In Vitro Fertilization
There is an oviduct blockage in some female bodies, this blocks the entrance of the sperm for fertilization as well. IVF is a common method for this where fresh male and female gametes are kept together in a tube.
The zygote develops outside the body for weeks and then gets placed in the female’s uterus. The rest of the development takes place inside the female body. These kinds of babies are test-tube babies because of the technique used.
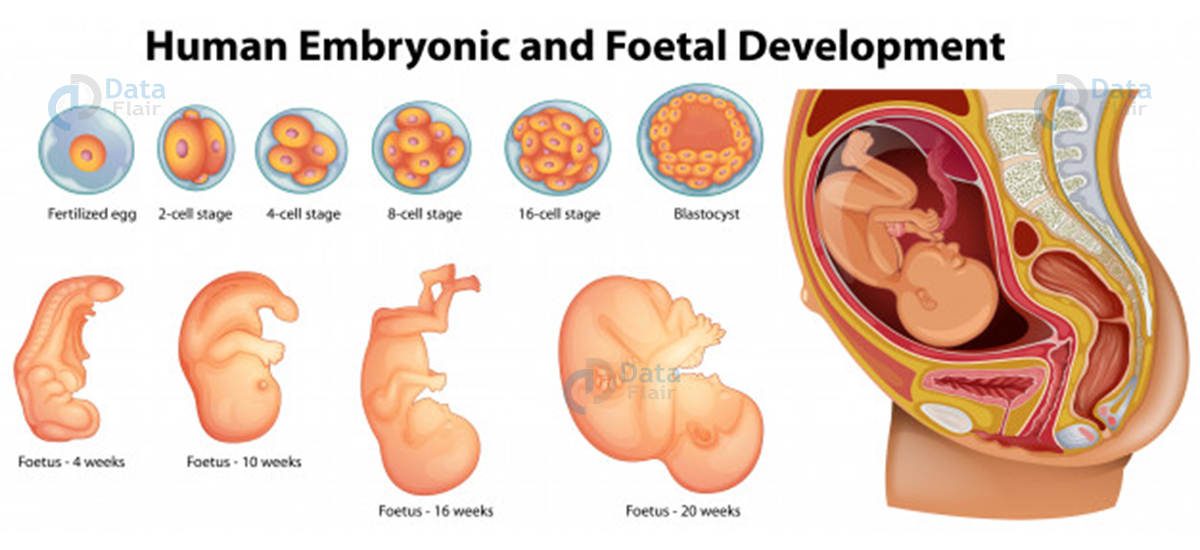
Pregnancy And Embryonic Development
A finger-like projection appears on the trophoblast after implantation. They are chorionic villi that have uterine tissue and maternal blood around it. The uterine joints it and create a unit – placenta for embryo development. It is responsible for oxygen supply and co2 removal by the embryo.
The umbilical cord connects them together for transportation purposes. It also produces chorionic gonadotropin, placental lactogen, estrogens, etc. at the later stage of pregnancy, the ovary releases relaxation hormone as well in addition to estrogens, progestogens, cortisol, and prolactin.
This is important for fetal growth and the mother’s metabolic changes.
The embryo after fertilization differentiates into outer layer endoderm while the ectoderm and mesoderm give rise to tissues in adults. The stem cells are present in the inner cell for tissue generation in the future.
After a month of pregnancy, the embryo’s heart formation completes, and the heart is heard by doctors. The second mother sees the development of limbs and digits. And by the end of 12 weeks, major organs develop.
By the fifth month the head develops and by the 24 months, hair, eyelids, and lashes are visible. And by the end of nine months, the foetus develops into a child completely.
Parturition And Lactation
The human pregnancy lasts for 9 months and this is the gestation period. The contraction of the uterus leads to the delivery of foetus and this process of delivery is parturition. This process follows a neuroendocrine mechanism.
The foetus signals for parturition with mild uterine contractions or foetal ejection reflex. The maternal pituitary releases oxytocin which causes stronger uterine contractions. This results in the expulsion of foetus or baby out of the womb.
The lactation process facilitates the production of milk in mammary glands. The initial milk contains antibodies essential for a newborn and is the colostrum period. It is important for a healthy baby.
Conclusion
This article covered the human reproductive system by the sexual method. It covered all the stages with details of every aspect. This is a biology article for UPSC which aspirants can read to understand the basic idea behind the idea.
It is the most prominent process used to reproduce the human race and research and development. It is easy to understand and even newcomers to the science field can refer to this. If you are planning to appear for the UPSC exam then you must give it a read.
Because it is basic 8th class biology, aspirants can expect this topic in UPSC Prelims as well.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google