VBA Logical Operators – AND, OR, NOT, XOR
FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
Visual Basic for Applications is basically called VBA, which is an event-driven programming language from Microsoft. VBA is used with MS Office applications like MS-Excel. These logical operators are basically used to combine more than one condition. Here, we will discuss the logical operators such as AND, OR, XOR and NOT in VBA.
Developer Options in VBA
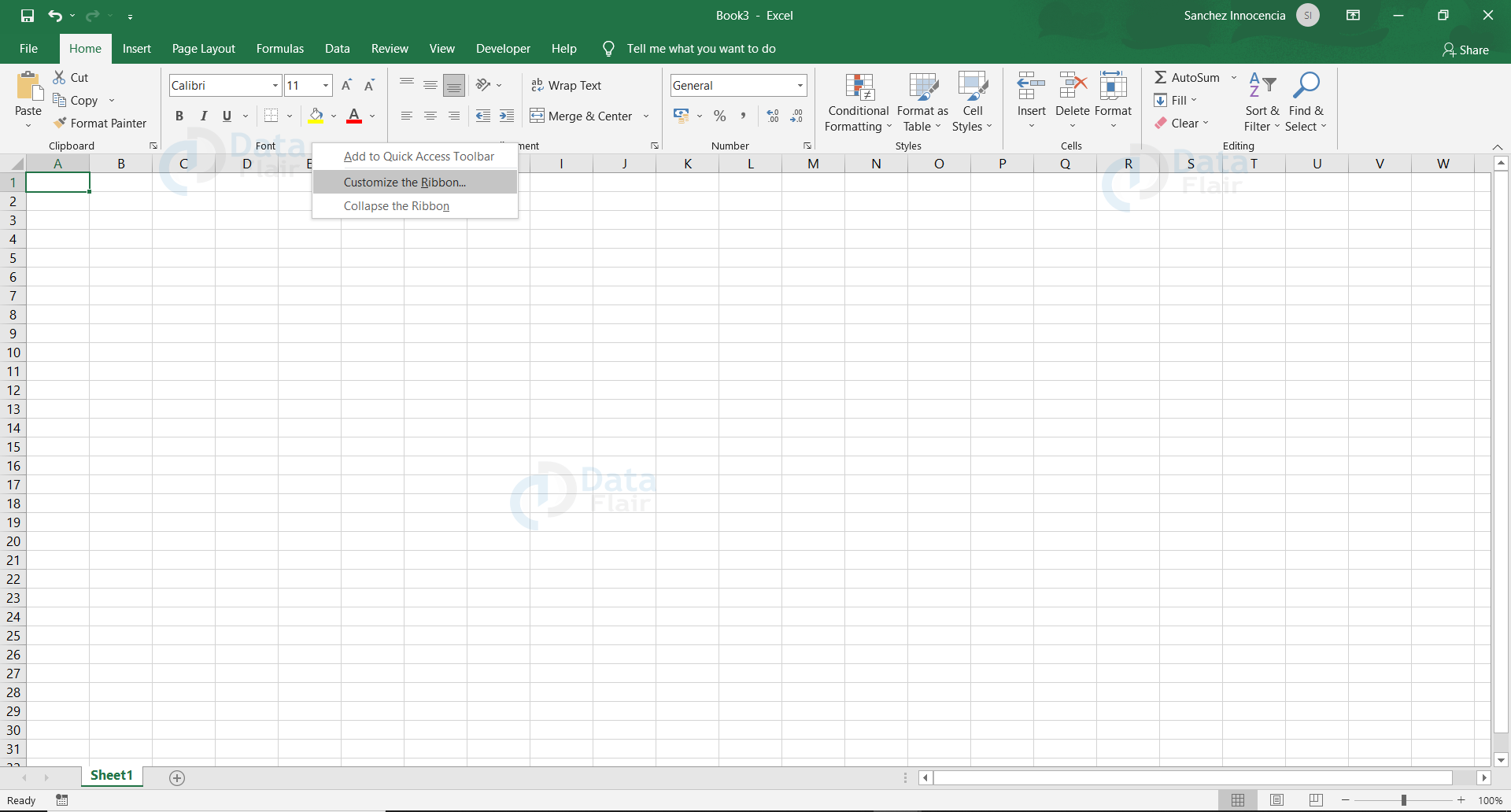
Step 1:
To get the Developer Options tab, first we need to right click on the Home, click on the Customize the Ribbon button and that leads to a Dialog Box.
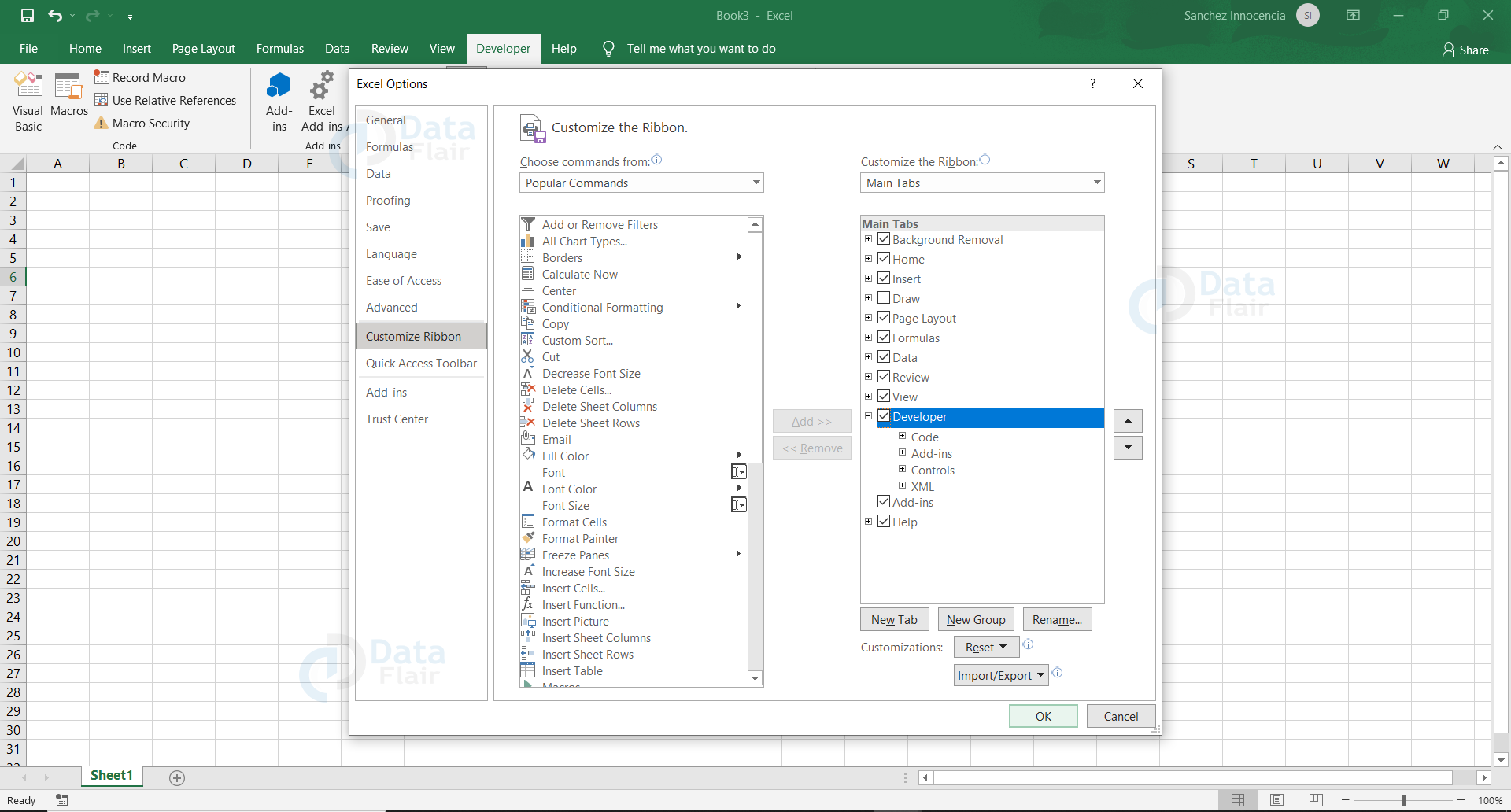
Step 2:
From the Customize the Ribbon tab, check the Developer Options to enable the Developer tab and then click Ok.
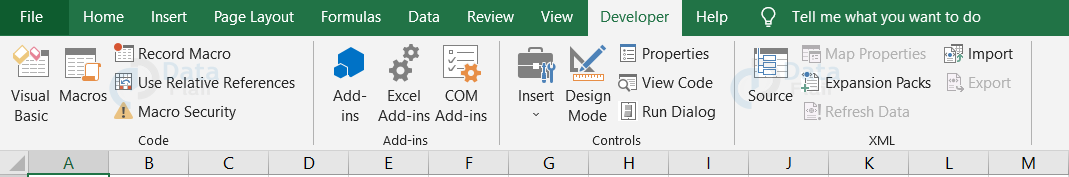
Step 3:
Here, you find the Developer tab being enabled. In the Insert Option in the Developer tab, click the Command Button, so that it gets enabled.
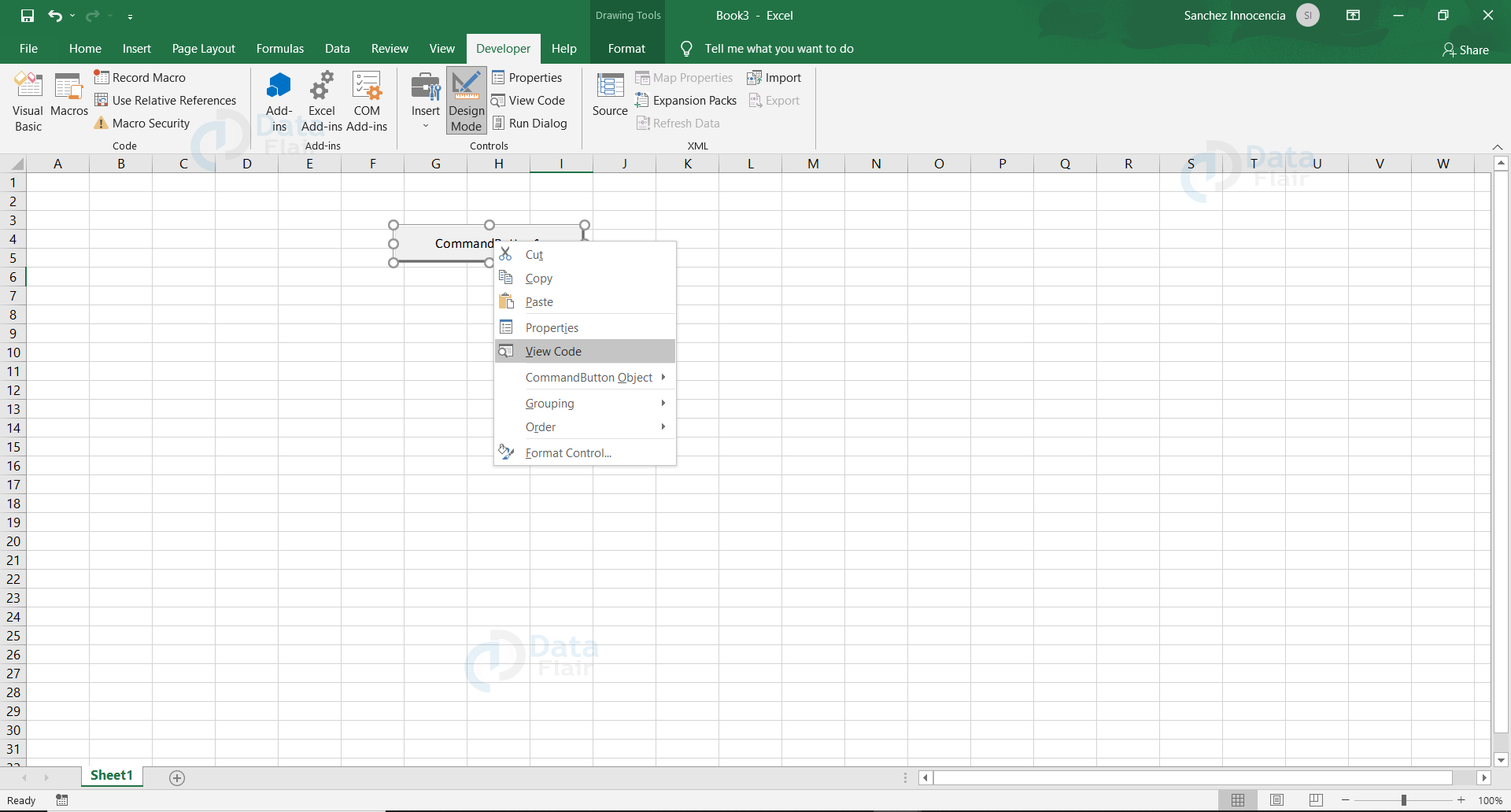
Step 4:
Right-click on the Command Button and click View Code, so that it leads to the coding environment.
Logical AND Operator in VBA
The Logical AND operator condition applies if all the given conditions are True. If it occurs as such, the value will be evaluated to True, else, if any of the given conditions is False, it is False.
Example of VBA Logical AND Operator
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim s1 As Integer, s2 As Integer, result As String
s1 = Range("A1").Value
s2 = Range("B1").Value
If s1 >= 60 And s2 > 1 Then
result = "pass"
Else
result = "fail"
End If
Range("C1").Value = result
End Sub
Code Explanation:
Here, s1, s2 are the variables and now we are going to check whether the s1 variable value is greater than or equal to 60 and the s2 variable value is greater than 1. If these two conditions satisfy then the result outputs as true or even if one condition fails, the output results as false. The output appears in the C1 cell.
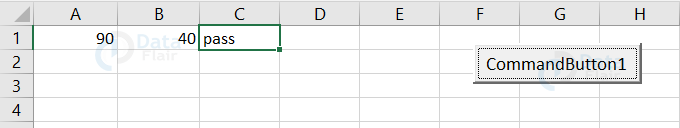
Output:
Since both the conditions satisfy, the result appears as pass.
Logical OR Operator in VBA
The Logical OR operator condition applies if any one of the given conditions is True, then value will be evaluated to True, else, if all of the given conditions is False, then it will be evaluated to False.
Example of VBA Logical OR Operator
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim s1 As Integer, s2 As Integer, result As String
s1 = Range("A1").Value
s2 = Range("B1").Value
If s1 >= 60 Or s2 > 1 Then
result = "pass"
Else
result = "fail"
End If
Range("C1").Value = result
End SubCode Explanation
Here, s1, s2 are the variables and now we are going to check whether the s1 variable value is greater than or equal to 60 or the s2 variable value is greater than 1. If any of these conditions satisfy then the result outputs as true or if both the conditions fail, the output results as false. The output appears in the C1 cell.
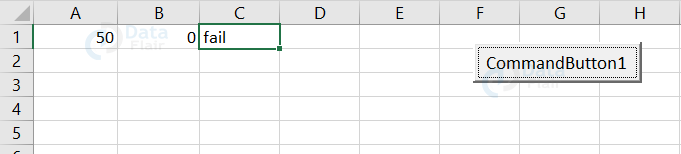
Output:
Since both the conditions are not satisfied, the result appears as fail.
Logical NOT Operator in VBA
The Logical NOT operator condition is one which works as an Inverse Function. If the given condition is True, then it returns False and if the given condition is False, it returns True.
Example of VBA Logical NOT Operator
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim s1 As Integer, s2 As Integer, result As String
s1 = Range("A1").Value
s2 = Range("B1").Value
If s1 >= 60 And Not s2 > 1 Then
result = "pass"
Else
result = "fail"
End If
Range("C1").Value = result
End Sub
Code Explanation:
Here, s1, s2 are the variables and now we are going to check whether the s1 variable value is not greater than or equal to 60 or the s2 variable value is not greater than 1. If any of these conditions satisfy then the result outputs as false or if both the conditions fail, the output results as true. The output appears in the C1 cell.
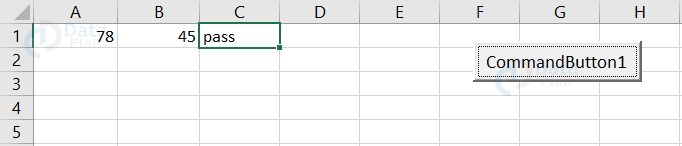
Output:
Since both the conditions fail, the result appears as pass.
Logical XOR Operator in VBA
The Logical XOR operator is the combination of NOT and OR logical operators. It is also called logical exclusion. This operator results true only if one of the conditions evaluates to be true or else it returns false.
Example of VBA Logical XOR Operator
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim s1 As Integer, s2 As Integer, result As String
s1 = 100
s2 = 50
If (s1 <> 0 Xor s2 <> 0) Then
MsgBox ("The test condition passes")
Else
MsgBox ("The test condition fails")
End If
End Sub
Code Explanation
Here, s1, s2 are the integer data type variables and now we are going to check whether the s1 variable value or either the s2 variable value is equal to 0. If any of these conditions satisfy then the result output as “The test condition passes” or else it returns “The test condition fails”. The output appears in the message box.
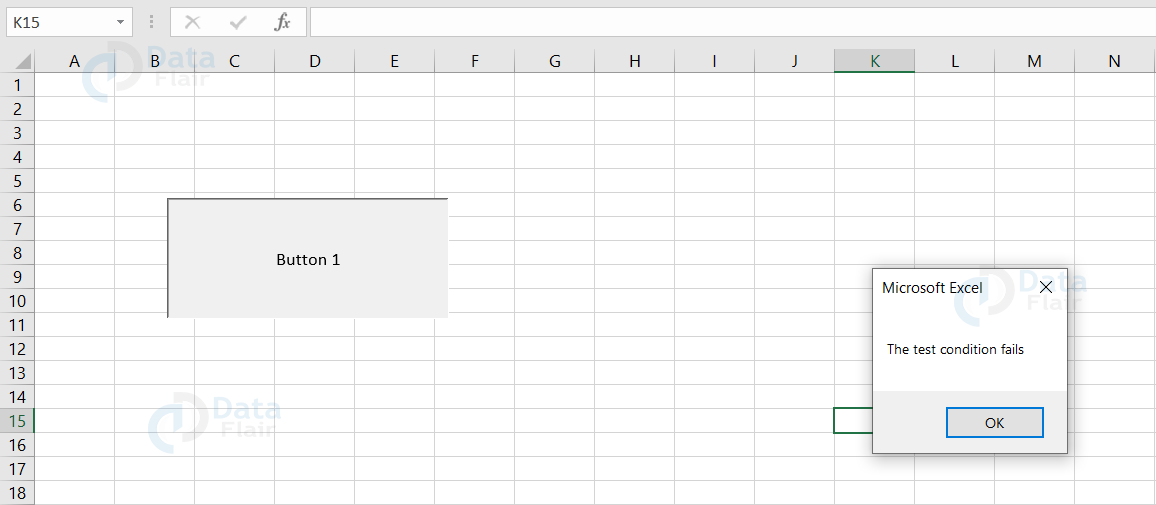
Output
Since both the conditions fail, the result appears as “The test condition fails”.
Summary
From this, we have got to know about the Logical Operators AND, OR, XOR and NOT operators in Visual Basic for Applications(VBA) in MS Excel. The steps for coding in VBA along with the code has been explained.
The initial step is to enable the Developer tab and click on the Command Button, view the Code by right clicking on it and then after coding, we can obtain the final result by clicking on the button in the spreadsheet.
The utilization of logical functions in VBA will help the user to understand and analyze the data. It’s widely used for decision-making purposes.
If you are Happy with DataFlair, do not forget to make us happy with your positive feedback on Google