Types Of Computer Networks
FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
A computer network is a group of computers connected by a shared communication route. These computers work together to transfer resources from one computer to another, which are provided by or located on the network nodes.
The following are some examples of computer network applications:
- Email, video, instant messaging, and other forms of communication.
- Printers, scanners, and other devices can be shared.
- File sharing.
- Remotely sharing software and operating systems.
- Enabling network users to conveniently access and retain data
Types of Computer Networks
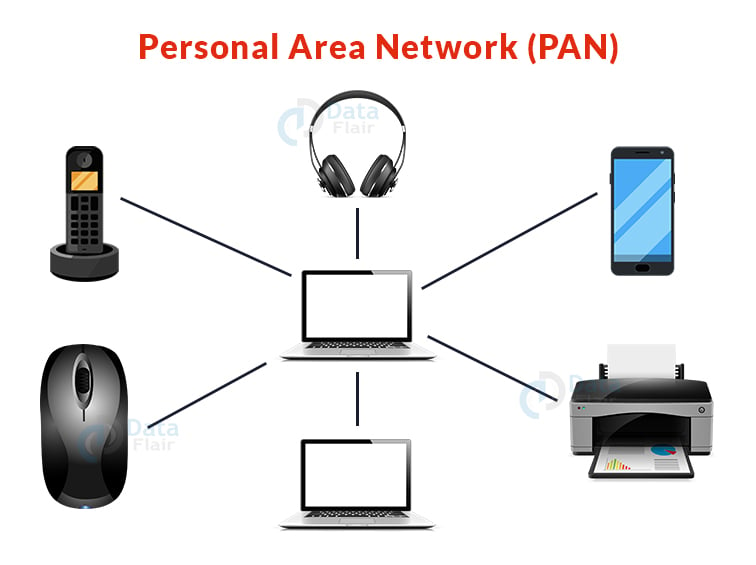
1. Personal Area Network (PAN):
- The most basic form of computer network is a PAN. This network is limited to a single person, which means that communication between computer devices is limited to an individual’s work environment.
- PAN provides a network range of 10 metres from a person to the communication equipment.
- Example: Bluetooth communication.
Advantages of PAN:
- PAN networks are reasonably safe and secure.
- It only provides a short-range solution of up to 10 metres.
- Strictly confined to a small specific area
Disadvantages of PAN:
- It may make a poor connection to other networks using the same radio frequencies.
- There are distance restrictions.
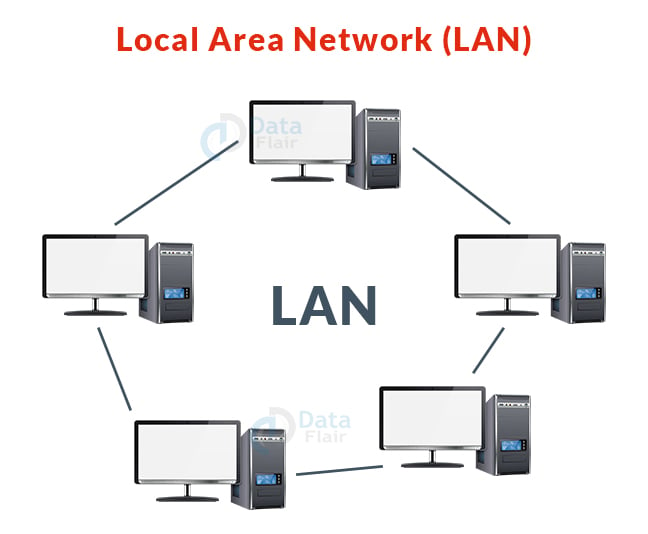
2. Local Area Network (LAN):
- The most common network is the LAN.
- A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that brings computers together via a shared communication route that is contained inside a small area, i.e., locally.
- A LAN is made up of two or more computers that are linked via a server.
- Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most significant technologies in this network.
- Example: Networking in a school, home, library etc.
Advantages of LAN:
- Local area networks can be used to share computer resources such as hard drives, DVD-ROMs, and printers. This greatly decreases the cost of purchasing hardware.
- Instead of acquiring licenced software for each client in the network, you may use the same program over the network.
- Data from all network users can be kept on the server computer’s single hard disk.
- Data and messages may be readily transferred across networked computers.
- It will be easier to handle data in a single location, making it more secure.
- The Local Area Network allows all LAN users to share a single internet connection.
Disadvantages of LAN:
- Although LANs save money due to pooled computer resources, the initial cost of building Local Area Networks is fairly expensive.
- Because the LAN administrator has access to every LAN user’s personal files, it does not provide enough privacy.
- Unauthorized users can gain access to an organization’s important data if the LAN administrator is unable to safeguard the centralized data repository.
- As there are difficulties with software configuration and hardware failures, local area networks require continuous LAN management.
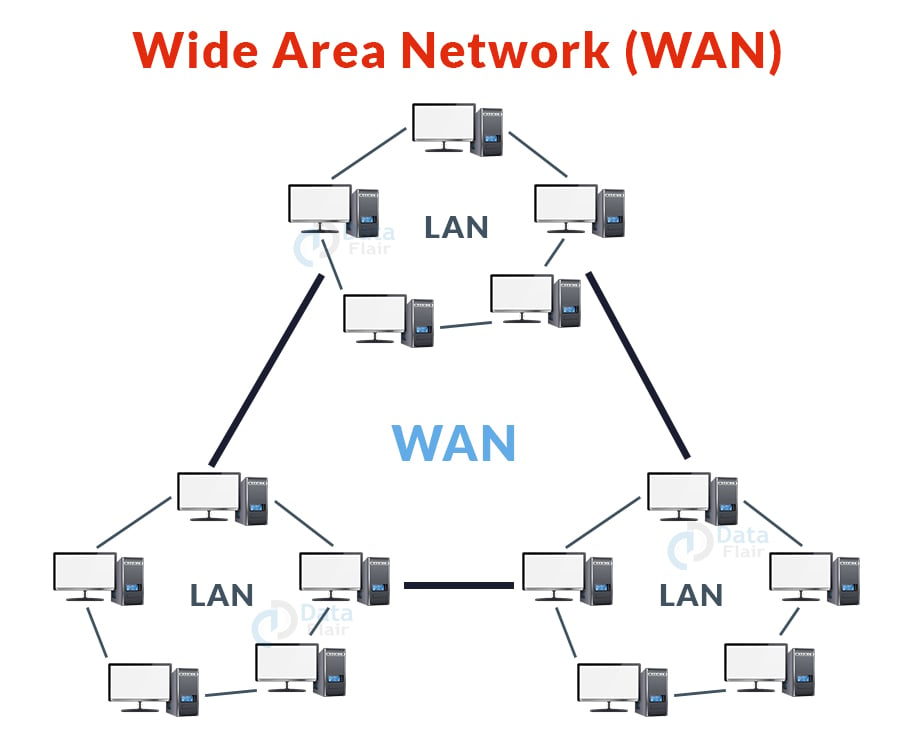
3. Wide Area Network (WAN):
- A wide-area network (WAN) is a form of computer network that links computers across long distances via a common communication channel.
- It is not limited to a single site, but rather spreads across several.
- A WAN is also defined as a collection of local area networks that communicate with one another.
- Example: The internet.
Advantages of WAN:
- Geographic coverage: A Wide Region Network covers a vast geographic area. If our office has a branch in a distant city, we can communicate with them over WAN. We can link to another branch over the internet, which provides a leased line.
- Data is centralized: In the case of a WAN network, data is centralised. As a result, we do not need to purchase emails, data, or backup servers.
- Automatic File Updates: Software firms operate on a live server. As a result, the programmers receive the revised files in seconds.
- Message exchange: Messages are transferred quickly in a WAN network. You may interact with peers via web applications such as Facebook, Whatsapp, and Skype.
- Software and resource sharing: In a WAN network, we may exchange software and other resources such as a hard drive and RAM.
- Worldwide business: We may do global commerce over the internet.
- High bandwidth: When we utilise leased lines for our business, we get a lot of bandwidth. The high bandwidth enhances the data transmission rate, which increases our company’s production.
Disadvantages of WAN:
- Security issue: A WAN network has more security concerns than a LAN or MAN network since all of the technologies are integrated, which causes a security challenge.
- Firewall and antivirus software is required: Because data is sent over the internet and can be altered or hacked by hackers, a firewall is required. Because some people can insert viruses into our systems, antivirus software is required to safeguard us from such threats.
- High Setup Cost: The establishment of a WAN network is expensive since it necessitates the purchase of routers and switches.
- Troubleshooting issues: Because it spans a vast region, resolving any issue is tough.
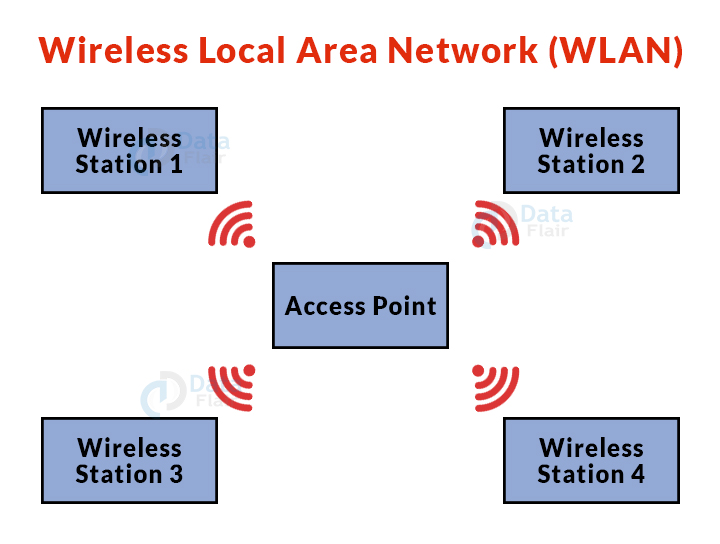
4. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN):
- WLAN is a form of computer network that functions similarly to a local area network but uses wireless network technologies such as Wi-Fi.
- This network, unlike LAN, lets devices connect wirelessly rather than through physical wires.
- Example: Wi-Fi.
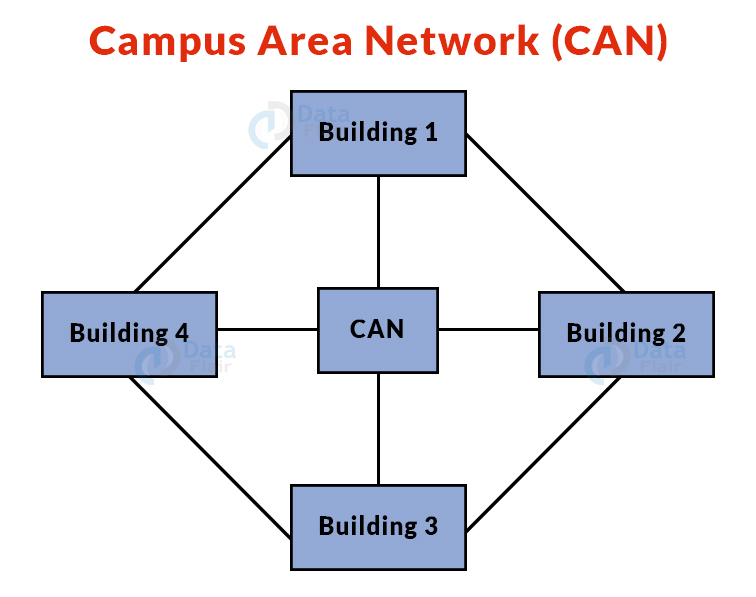
5. Campus Area Network (CAN):
- A CAN network is larger than a LAN but smaller than a MAN network.
- This is a sort of computer network that is commonly seen in locations such as a school or college.
- This network has a limited geographical coverage, since it is dispersed among various buildings on campus.
- Example: Networks that cover schools, colleges, buildings, etc.
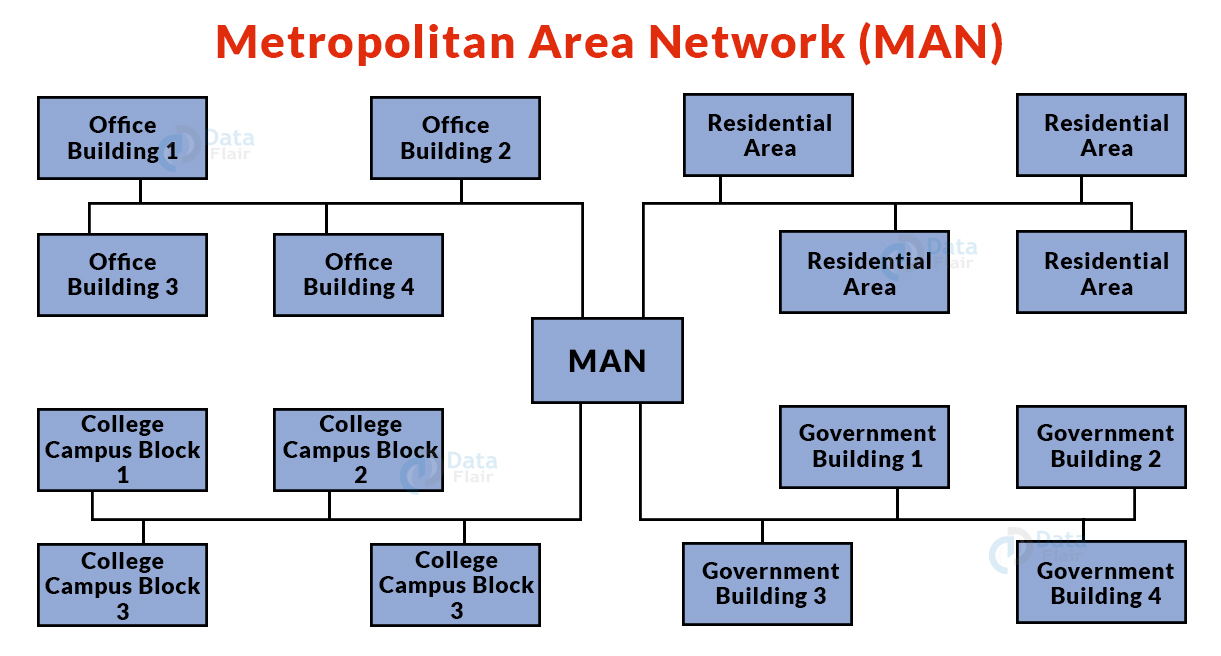
6. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
- A MAN is a network that is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
- This is a sort of computer network that connects computers separated by geographical distances via a common communication channel across a city, town, or metropolitan region.
- Example: Networking in towns, cities, a single large city etc.
Advantages of MAN:
- It enables rapid communication by utilising high-speed carriers such as fibre optic cables.
- It offers good support for a large network and increased access to WANs.
- The dual bus in a MAN network allows data to be sent in both directions at the same time.
- A MAN network often comprises portions of a city or a whole city.
Disadvantages of MAN:
- More cable is required to make a MAN connection from one location to another.
- It is difficult to safeguard a MAN network against hackers.
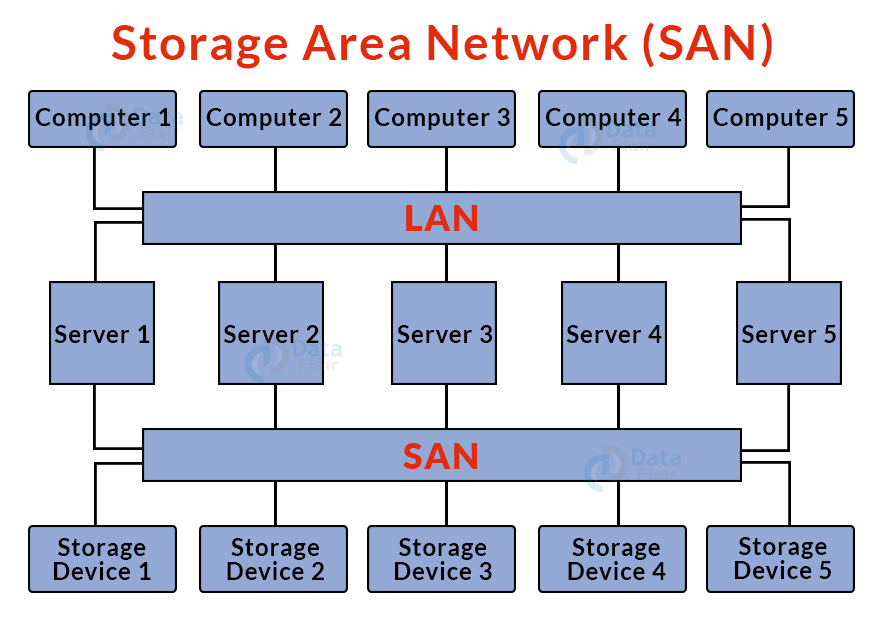
7. Storage Area Network (SAN):
- A storage area network (SAN) is a high-speed computer network that links groups of storage devices to several servers.
- This network is not reliant on LAN or WAN. A SAN, on the other hand, transfers storage resources from the network to its own high-powered network.
- A SAN allows you to access block-level data storage.
- Example: Servers that access a network of disks.
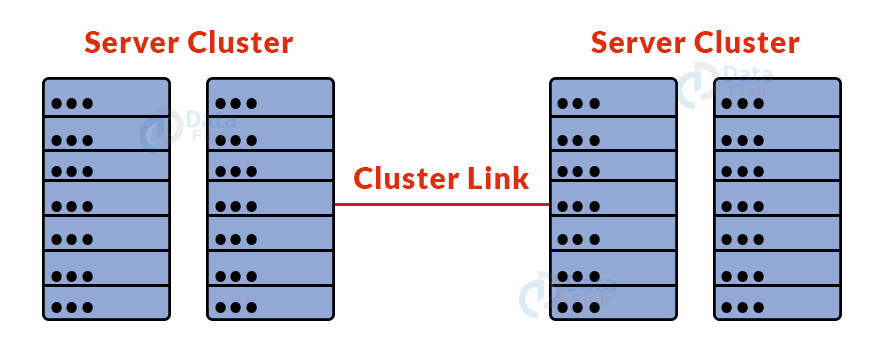
8. System-Area Network (SAN):
- A system area network (SAN) is a sort of computer network that connects a group of high-performance machines.
- It is a network with a high bandwidth and a focus on connections.
- A SAN is a sort of LAN that can handle enormous volumes of data in big requests.
- This network is ideal for processing applications that need a high level of network performance.
- Example: Microsoft SQL Server 2005 using virtual interface adapter.
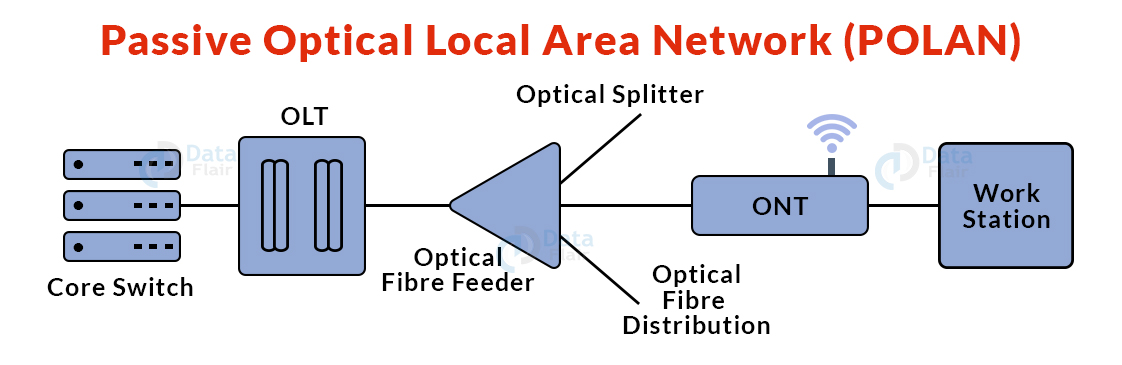
9. Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN):
- A POLAN is a sort of computer network that functions similarly to a LAN.
- POLAN distributes signals among users and devices by splitting an optical signal from a single strand of single mode optical fibre into numerous streams using optical splitters.
- POLAN is a point-to-multipoint LAN design.
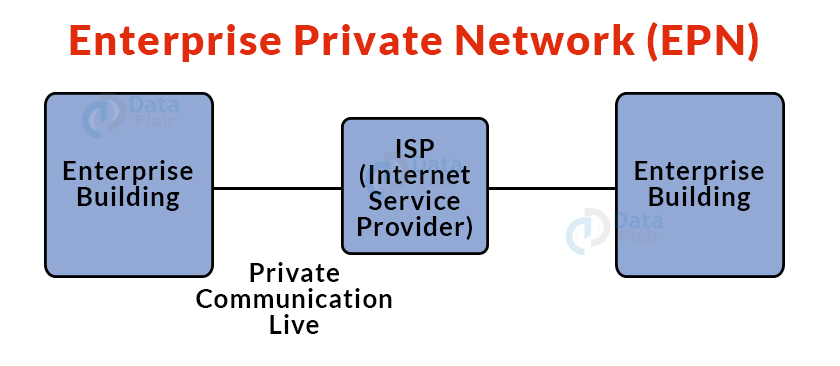
10. Enterprise Private Network (EPN):
- EPN is a sort of computer network that is commonly used by organisations that require a secure connection across several locations in order to share computer resources.
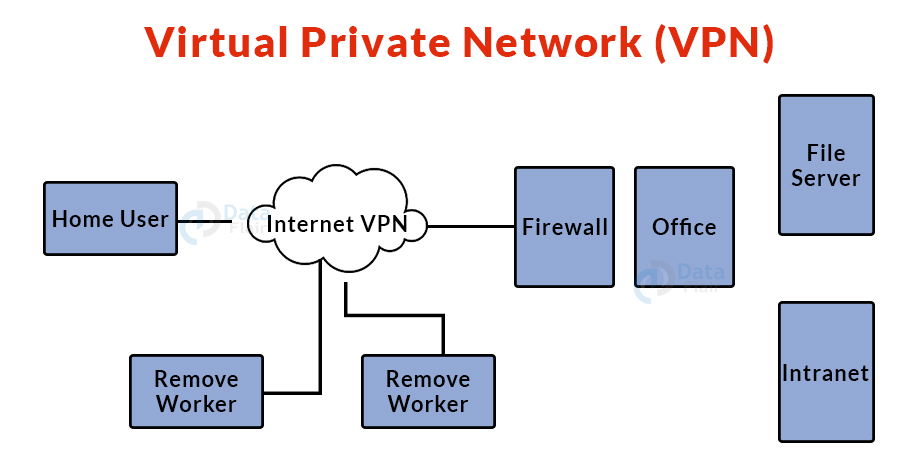
11. Virtual Private Network (VPN):
- A virtual private network (VPN) is a form of computer network that extends a private network across the internet and allows users to transmit and receive data as if connected to a private network.
- Users can connect to a private network remotely via a virtual point-to-point connection.
- VPN shields you from harmful sources by acting as an intermediary that provides you with a secure network connection.
12. Internetwork:
- An internetwork is described as two or more computer network LANs, WANs, or computer network segments that are linked using devices and configured using a local addressing system. This is referred to as internetworking.
- The internet protocol is used in internetworking.
- The Open System Interconnection reference model is used for internetworking (OSI).
Types of Internetwork:
a. Extranet:
- An extranet is a communication network that uses internet protocols such as the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP). It is used to share information.
- Only those users who have login credentials have access to the extranet.
- An extranet is the most basic kind of internetworking.
- It can be classified as a MAN, WAN, or other type of computer network.
b. Intranet:
- An intranet is a private network that uses internet protocols such as the Transmission Control Protocol and the Internet Protocol.
- An intranet is a network that belongs to a company and is only available to employees or members of that company.
- The main goal of the intranet is to exchange information and resources among the employees of the company.
Advantages of Intranet:
- Communication: It enables inexpensive and simple communication. An organisation employee can contact another employee via email or chat.
- Time-saving: Because information on the intranet is disseminated in real time, it saves time.
- Collaboration: One of the most significant advantages of the intranet is collaboration. The information is dispersed among the organization’s workers and may only be viewed by the authorised user.
- Platform independence: It is a neutral architecture in the sense that the computer can be linked to another device with a different architecture.
- Cost-effective: People may see the data and documents via the browser, and duplicate copies are distributed over the intranet. As a result, the cost is reduced.
Summary
This article looks at and covers all the different types of networks that currently exist. This may range from small networks such as Personal Area Networks (PANs) all the way to larger networks such as Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs), and we take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of some of these networks. We also learn that combining larger networks gives us the concept of Internetworking, and we briefly cover the different types of internetworks.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google