TELNET – Terminal Network
FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
TELNET is an abbreviation for Terminal Network. It is essentially a TCP/IP protocol used for virtual terminal services, and it was primarily proposed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
It is a client/server application software that may be used for a variety of purposes.
This software allows the connection to the distant system to be established in such a way that the local system begins to appear as a terminal at the remote system.
It is a TCP/IP standard that is used for virtual terminal service.
In layman’s terms, TELNET allows the user to connect to a distant computer. After signing in, the user can utilise the remote computer’s services and then transmit the results back to the local computer.
TELNET was primarily created during a period when most operating systems operated in a time-sharing environment. A big computer may also handle numerous users in this sort of setting. Interaction between the computer and the user is often accomplished through the use of a terminal (It is a combination of keyboard, mouse, and monitor).
TELNET makes use of a single TCP/IP connection.
History of TELNET:
Telnet was first implemented using Network Control Program (NCP) protocols. It was eventually dubbed Teletype Over Network Protocol, or TONP. While it has been used unofficially for some time, it was officially established in published documents on March 5, 1973.
Telnet’s early versions employed ASCII characters transmitted over an 8-bit channel to allow remote computers to interact with simple text.
Several Telnet extensions have been developed throughout time. Telnet has been around for several decades as a programming tool. In the 1960s, the first version of Telnet was developed for the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET), the precursor to the modern internet. It was one of the first tools designed to remotely connect computers over long distances. A Telnet protocol was developed by researchers and professionals in 1971 followed by the Telnet system in 1983.
TELNET Modes of Operation:
1. Default Mode:
When no other modes are called, this mode is utilised.
In this mode, the client performs echoing.
In this mode, the user enters a character, and the client repeats it on the screen but does not send it until the entire line is done.
2. Character Mode:
Each character entered in this mode is transmitted to the server by the client.
In this mode, the server typically repeats the character back to the client’s screen.
3. Line Mode:
Line editing, such as echoing and character deleting, is done on the client side.
The entire line will be sent to the server by the client.
Types of TELNET Login:
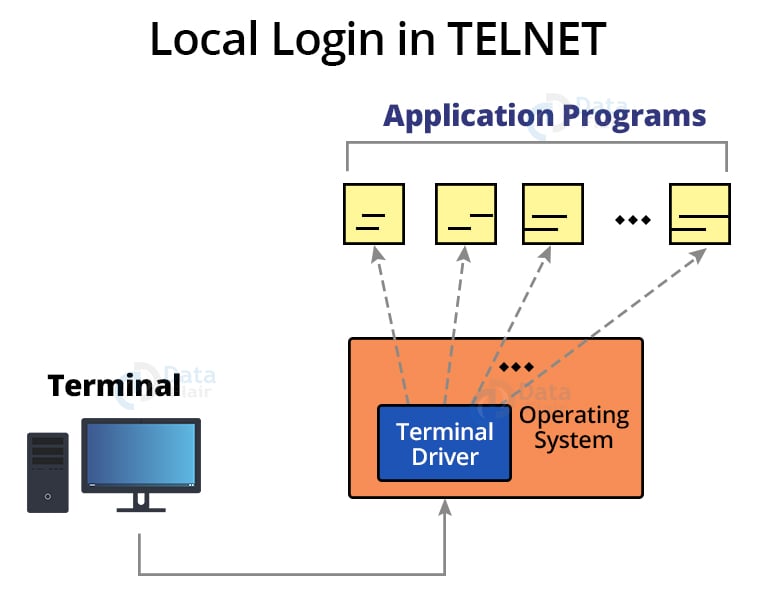
1. Local Login:
Local login occurs when a person logs into a local computer.
The terminal driver accepts keystrokes entered by the user when the workstation is running the terminal emulator. The terminal driver subsequently forwards these characters to the operating system, which ultimately launches the required application software.
The operating system, on the other hand, assigns particular significance to special characters.
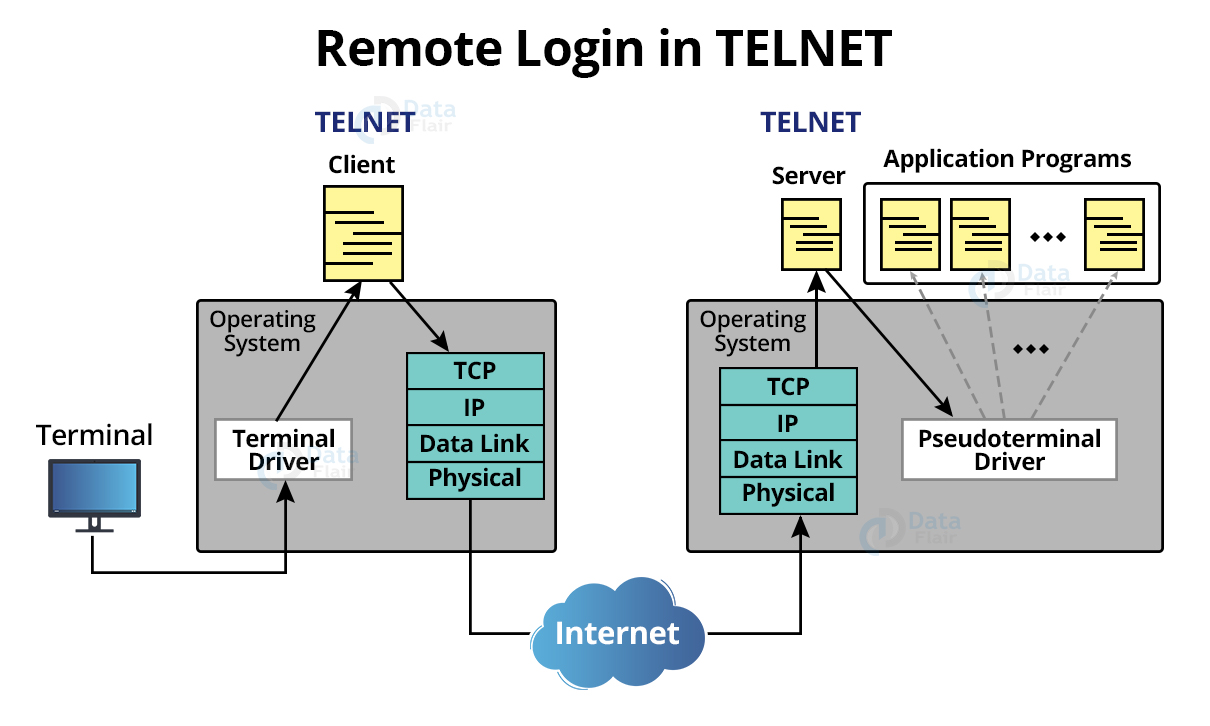
2. Remote Login:
In this case, the user primarily transmits the keystroke to the terminal driver, where the operating system only receives and does not understand the characters.
Then the characters are transferred to the TELNET client, which converts them into characters known as Network Virtual Terminal (NVT) characters.
TELNET client converts them and sends them to the TCP/IP protocol stack. The text in the form of NVT then travels via the internet until it reaches the TCP/IP protocol stack on the distant system. The characters are subsequently transmitted to the operating system, which forwards them to the TELNET Server.
TELNET Server then converts these NVT characters into characters that the Remote machine can understand.
The characters cannot be transmitted directly to the remote computer’s operating system because the operating system is not designed to receive characters from a TELNET server.
It is built in such a way that it can receive characters from the Terminal Driver. A software application called Pseudoterminal driver is introduced and mostly pretends that the characters are coming from the Terminal.
TELNET Commands:
| Character | Decimal | Binary | Meaning |
| WILL | 251 | 11111011 | Offer/accept to enable |
| WON’T | 252 | 11111100 | Accept/Offer to disable |
| DO | 253 | 11111101 | Requesting/Approving enable operation |
| DON’T | 254 | 11111110 | Disapproving enable/request to disable |
TELNET Command Options:
- 0 – Binary Transmission
- 1 – Echo Data
- 3 – Suppress go ahead signal
- 5 – Status of TELNET
- 6 – Timing Mark
- 8 – Line Width
- 9 – Page Size
- 24 – Terminal Type
- 32 – Terminal Size
- 34 – Change to Line Mode
Advantages of TELNET:
1. It provides remote access to another computer system.
2. It employs plain text. As a result, the user has more access with fewer data transfer issues.
3. TELNET saves a significant amount of time.
4. TELNET is a universal protocol that can be used on any computer. Even the oldest system can readily connect to newer computers, even if they have different versions of the operating system.
Disadvantages of TELNET:
1. For novices, it may be quite tough.
2. Because data is delivered in plain text, there is no idea of encryption. As a result, it is not a secure approach.
3. Furthermore, because many capabilities are blocked, remote devices are unaware of the local device’s capabilities.
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the operation and uses of TELNET. We also looked at the modes of operation and the types of login available in TELNET, as well as some commands that are frequently used in TELNET. The advantages and disadvantages of TELNET were also covered.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google