Switching in Computer Network
We offer you a brighter future with FREE online courses - Start Now!!
Switching is the process of forwarding packets from one port to another that leads to the destination. When data enters a port, it is referred to as ingress, and when data exits a port, it is referred to as egress.
A switch, in its most basic form, is a device that allows us to join links to build a bigger network. A switch is a device with many inputs and outputs that transmits packets from one input to one or more outputs.
In the above image, all the devices denoted by alphabets are the end devices of the network, while the devices denoted by numerals are switches. Each switch is linked to multiple other devices/switches.
Characteristics of Switching:
- Messages are sent across the network of transmission media when a user connects to the internet or another computer network that is not in their local vicinity.
- Switching refers to the process of moving information from one computer network to another.
- Switches are used to perform switching in a computer network.
- A switch is a tiny piece of technology that connects numerous computers to a single local area network (LAN).
- In the OSI model, network switches function at layer 2 (Data link layer).
- Switching is invisible to the user and requires no setup in the home network.
- Switches are used to route packets depending on their MAC addresses.
- A switch is used to send data solely to the device that has been specified. It checks the destination address to ensure that the packet is routed correctly.
- It works in full duplex mode.
- Packet collision is minimal since it communicates directly between the source and destination.
- Because of limited bandwidth, the broadcast of messages does not happen.
Categories of Switching:
1. Connection-less:
- Data is transmitted on behalf of forwarding tables in a connectionless manner.
- There is no need for prior handshaking, and acknowledgments are optional.
2. Connection-oriented:
- Prior to switching the data to be transmitted to the destination, a circuit must be made along the path between both ends. The data is then sent through that circuit.
- Circuits can be preserved for future use or switched off immediately when the transfer is complete.
Advantages of Switching:
- The network’s bandwidth is increased through switching.
- It minimizes the strain on individual PCs by sending data to only the device that has been targeted.
- It improves network overall performance by decreasing network traffic.
- As the switch establishes a collision domain for each connection, there will be fewer frame collisions.
Disadvantages of Switching:
- A switch costs more than a network bridge.
- A switch cannot readily identify network connection difficulties.
- To handle multicast packets, the switch must be properly designed and configured.
Why is Switching Required?
Switching was created for the following reasons:
1. Bandwidth:
- Bandwidth is the cable’s maximum transfer rate. It is an important and costly resource.
- As a result, switching strategies are employed to make the most of a network’s capacity.
2. Collision:
- Collision is the effect that happens when several devices send the same message over the same physical medium and clash with each other.
- To address this issue, switching technology is used to ensure that packets do not clash with one another.
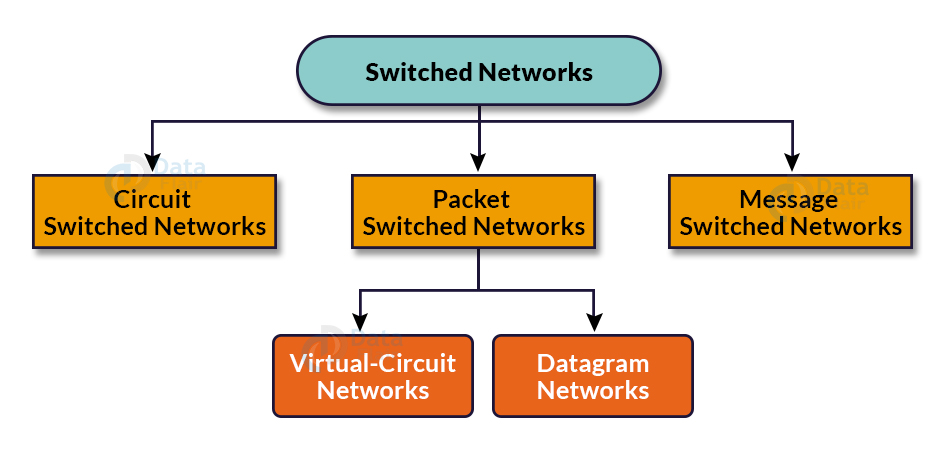
Methods of Switching:
There are 3 main methods to implement switching:
1. Circuit Switching
2. Packet Switching
3. Message Switching
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the concept of switching in Computer Networks. We explored its different types and categories, and also its advantages and disadvantages. We also had a brief look at the need for switching in Computer Networks.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google