Stop and Wait Protocol
FREE Online Courses: Transform Your Career – Enroll for Free!
What is the Stop and Wait Protocol?
Stop and wait indicates that whatever data the sender wishes to convey is sent to the recipient. After transferring the data, he comes to a halt and waits for the receiver’s acknowledgment. The stop and wait protocol is classified as a flow control protocol. Flow control is one of the data connection layer’s services.
Stop and wait protocol is a data-link layer protocol that is used for data transmission across noiseless channels. It supports unidirectional data transmission, which means that it can only send or receive data at the same time. It provides a flow-control mechanism but no error-control mechanism. The reason behind using this frame is that after delivering the frame, the sender waits for the acknowledgment before sending the next frame.
Rules of Stop and Wait Protocol:
Sender Side | Receiver Side |
| The sender transfers data packets one at a time. | The data packet is received and then consumed. |
| When the preceding packet’s acknowledgment is received, the sender transmits the next packet. | When a data packet is consumed, the receiver sends an acknowledgment back to the sender. |
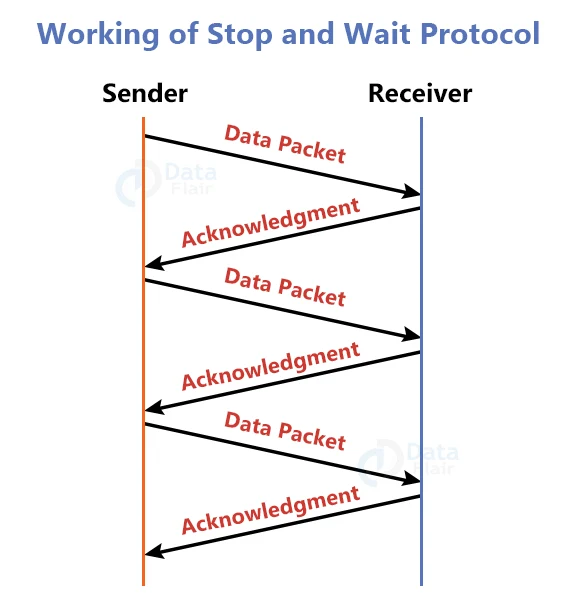
Working of Stop and Wait Protocol:
The stop and wait technique is depicted in the diagram above. If there is a sender and a receiver, the sender sends the packet, which is referred to as a data packet. The sender will not transmit the second packet until the first packet is acknowledged. The acknowledgment for the data packet received is sent by the receiver.
The sender transmits the next packet after receiving the acknowledgment. This method is repeated until all of the packets are not transmitted. This protocol’s major virtue is its simplicity, but it also has significant drawbacks.
Disadvantages of Stop and Wait Protocol:
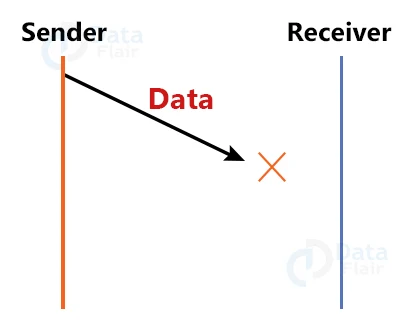
1. Lost Data:
Assume the sender sends the data and it is lost. For a long time, the receiver has been waiting for the data. Because the data is not received by the recipient, no acknowledgment is sent. The sender will not send the following packet since it has not received any acknowledgment. This issue arises as a result of missing data.
This causes 2 problems:
- The sender waits indefinitely for an acknowledgment.
- The receiver waits an indefinite time for data.
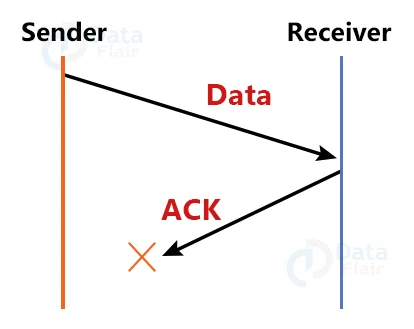
2. Lost Acknowledgement:
Assume the data is sent by the sender and received by the recipient. When the packet is received, the receiver sends an acknowledgment. In this situation, the acknowledgment is lost in a network, and the sender has no possibility of receiving it. There is also no way for the sender to transmit the following packet because in the stop and wait protocol, the next packet cannot be sent until the preceding packet’s acknowledgment is received.
This causes the following problem:
- The sender waits indefinitely for an acknowledgment.
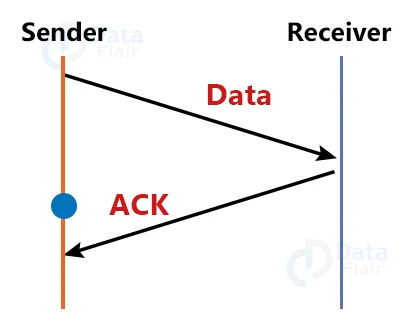
3. Delayed Data or Acknowledgement:
Assume the data is sent by the sender and received by the recipient. The receiver then transmits the acknowledgment, but it is received after the sender’s timeout period has expired. Because the acknowledgment is received late, it may be mistaken for the acknowledgment of another data packet.
Summary:
In this article, we covered the concept of the Stop and Wait Flow Control Protocol. We looked at the mechanism of this protocol, and the various problems that are inherent in this protocol. We also looked at the main rules of this protocol.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder
Please share your happy experience on Google