SAS ODS (Output Delivery Systems) – A Complete Guide
FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
In this article, our major focus will be to understand what is SAS ODS- Output Delivery System and on the creation of various types of output files: Word output and SAS ODS PDF output to files through a step-by-step procedure with examples.
What is SAS ODS (Output Delivery System)?
Traditional SAS output is designed for a traditional line–printer. This type of output has limitations that prevent you from getting the most value from your results.
SAS ODS is designed to overcome the limitations of traditional SAS output. It provides a method of delivering output in a variety of formats and makes the formatted output easy to access.
With ODS, you can create various file types including HTML, Rich Text Format (RTF), PostScript (PS), Portable Document Format (PDF), and SAS data sets.
Through ODS, you can do the following:
- Create HTML, RTF, PostScript, and PDF files.
- Select SAS-supplied styles to enhance reports.
- Create output objects from almost all SAS procedures.
- Create SAS datasets from output objects.
- Provide support for website navigation and management of HTML files.
SAS ODS Syntax-
ODS outputtype PATH path name FILE = Filename and Path STYLE = StyleName ; PROC some proc ; ODS outputtype CLOSE;
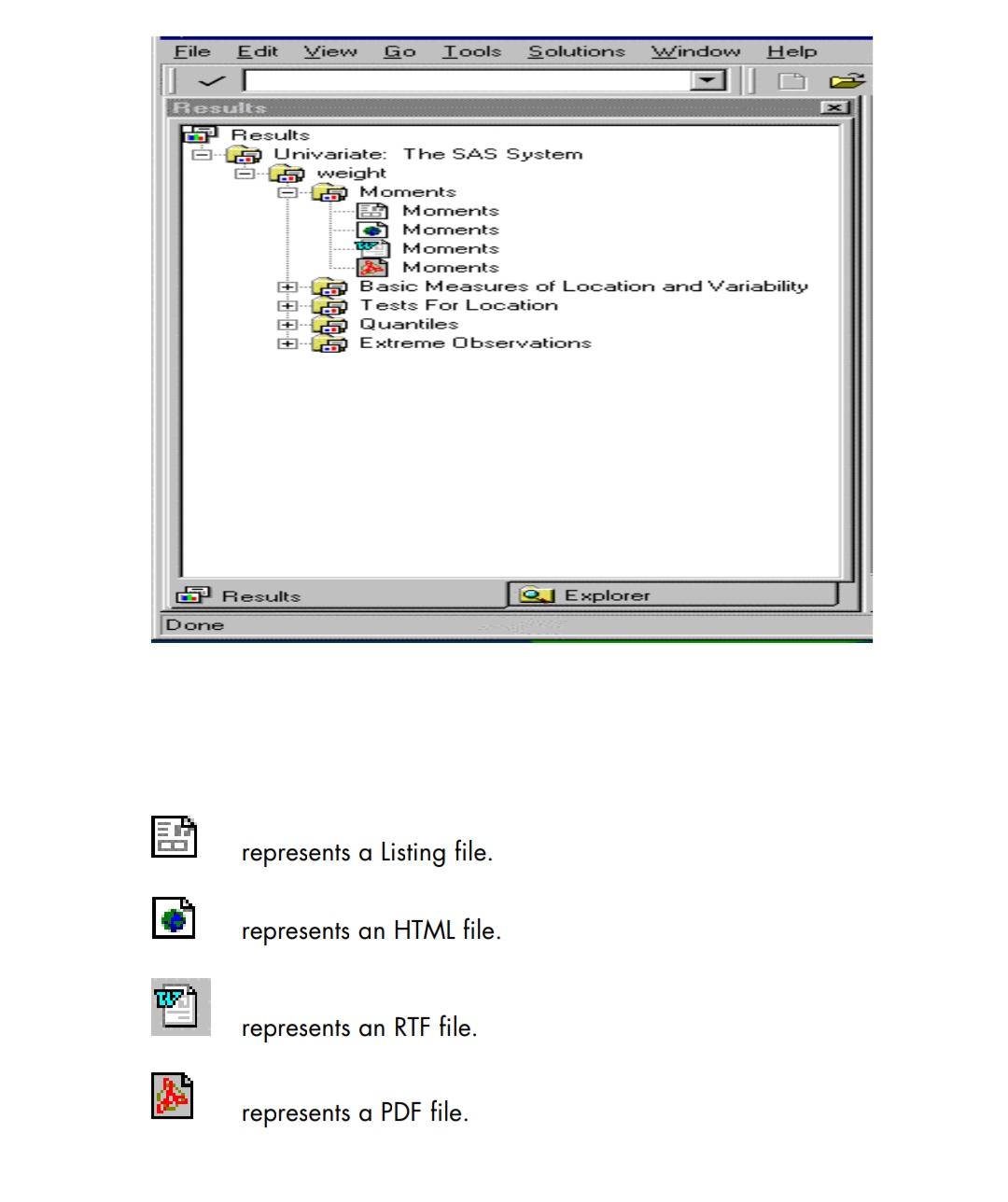
The above image shows a results window with different output delivery options available.
Sending Results to the Web (SAS HTML Output)
Creating web output from SAS is easy. All you have to add is two lines of code:
ODS HTML FILE=’myfilename.html’;
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
After this line of code, you insert the code for your reporting procedure. For example, you could create a table with the TABULATE procedure. Then, after the RUN statement that ends your procedure, you add the following line of code:
ODS HTML CLOSE;
So, the complete code would look like this, with the TABULATE code 2 in the middle of the ODS sandwich.
ODS HTML FILE=’myfilename.html’;
proc tabulate data=census f=dollar8.;
class sex educ;
var income;
table educ='Education',
income='Average Salary'*
mean=' '*
(sex=' ' all);
run;
ODS HTML CLOSE;The SAS ODS HTML result is the output shown below.
| Education | Male | Female | All |
| Not HS Graduate | $ 15,113 | $ 4,449 | $ 13,039 |
| HS Graduate | $ 33,419 | $ 17,539 | $ 28,464 |
| Some College | $ 30,466 | $ 22,730 | $ 27,514 |
| Associates Degree | $ 40,690 | $ 33,988 | $ 38,057 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | $ 46,625 | $ 43,862 | $ 45,821 |
| Post-Graduate Degree | $ 77,195 | $ 45,000 | $60,501 |
If you don’t like this look, you can change it by switching styles. The table above uses the default style, which is called Default. For a different look try:
ODS HTML FILE=’myfilename.html’ STYLE=BarrettsBlue; * the TABULATE code goes here ; ODS HTML CLOSE;
Creating Word Output in SAS
Just as you can use SAS ODS HTML to create output destined for the web, you can use SAS ODS RTF to generate a file in Rich Text Format, which can be opened in Word (or other word processors).
Again, the syntax is to add an ODS statement with a FILE option before your reporting procedure, and an ODS CLOSE statement after the end of your procedure. In this case, both ODS statements specify RTF as the output destination, and the filename has a “.rtf” extension.
Example-
ODS RTF FILE=’myfilename.rtf’; * the REPORT code goes here ; ODS RTF CLOSE;
| Education | Gender | Salary |
| Not HS Graduate | Female | $ 4,449 |
| Male | $ 15,113 | |
| HS Graduate | Female | $ 17,539 |
| Male | $ 33,419 | |
| Some College | Female | $ 22,730 |
| Male | $ 30,466 | |
| Associates Degree | Female | $ 33,988 |
| Male | $ 40,690 | |
| Bachelor’s Degree | Female | $ 43,862 |
| Male | $ 46,625 | |
| Post-Graduate Degree | Female | $ 45,000 |
| Male | $ 77,195 |
The output above shows what your SAS output looks like after it is opened in Word.
Creating PDF Output in SAS
If you need to deliver printable reports via e-mail or the web, you may want to try out the PDF destination. The format can be viewed on many platforms, and its real strength is that your report will print out easily on many different printers, without any problems with margins and page breaks.
The code is quite simple. It’s just like the RTF code, except you call ODS PDF, and the filename gets a “.pdf” extension.
ODS PDF FILE=’myfilename.pdf’; * The REPORT code goes here ; ODS PDF CLOSE;
| Education | Gender | Salary |
| Not HS Graduate | Female | $ 4,449 |
| Male | $ 15,113 | |
| HS Graduate | Female | $ 17,539 |
| Male | $ 33,419 | |
| Some College | Female | $ 22,730 |
| Male | $ 30,466 | |
| Associates Degree | Female | $ 33,988 |
| Male | $ 40,690 | |
| Bachelor’s Degree | Female | $ 43,862 |
| Male | $ 46,625 | |
| Post-Graduate Degree | Female | $ 45,000 |
| Male | $ 77,195 |
You will notice that the output produced by ODS PDF looks a lot like the output produced by ODS RTF. That’s because the two ODS styles used by RTF and PDF are closely related. You can create any look you like in either PDF or RTF by switching to another style or even creating your own custom style.
So, this was all in SAS ODS Tutorial. Hope you like our explanation.
Summary
This was a quick tour of SAS ODS- Output Delivery System. Hopefully, you now have a basic idea of what options are available to you. Since this was only an introduction, as you start to use these techniques, be sure to explore other SAS tutorials.
If you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comment section.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google


For example if the variable x contains the information as 101/24/M/Asian in single line and the ods output should be 101/24/M/
Asian
How can we get the output in this manner