SAS Functions – Learn the 4 Major Types of Functions with Examples
FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
Through this SAS function cheat sheet, you will be learning different types of functions in SAS. You will also understand how SAS functions can be used to make our program less lengthy and easy to read with the help of examples.
Let’s quickly start the tutorial.
SAS Functions
Functions are applied to a single variable or to a set of variables for analyzing and processing data. There are hundreds of built-in functions in SAS, we will be looking at the most frequently used and important ones.
SAS Functions syntax:
FUNCTIONNAME(argument1, argument2….argumentn)
Types of Functions in SAS
SAS Functions can be divided into different types depending on their usage and the task they perform. Below are the different types of functions in SAS:
1. SAS Arithmetic Functions
These functions are also called SAS Numeric functions. It performs mathematical operations on an argument or a set of arguments.
| ABS(argument) | returns absolute value |
| MAX(argument,argument, …) | returns the largest value of the numeric arguments |
| MIN(argument,argument, …) | returns the smallest value of the numeric arguments |
| MOD(argument-1, argument-2) | returns the remainder |
| SIGN(argument) | returns the sign of a value or 0 |
| SQRT(argument) | returns the square root |
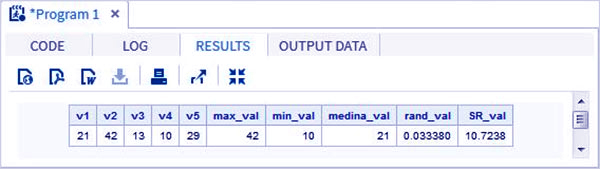
Example-
data Math_functions; v1=21; v2=42; v3=13; v4=10; v5=29; /* Get Maximum value */ max_val = MAX(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5); /* Get Minimum value */ min_val = MIN (v1,v2,v3,v4,v5); /* Get Median value */ med_val = MEDIAN (v1,v2,v3,v4,v5); /* Get a random number */ rand_val = RANUNI(0); /* Get Square root of sum of the values */ SR_val= SQRT(sum(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5)); proc print data = Math_functions noobs; run;
Output-
2. SAS Character (String) Functions
The most frequently used string functions have been explained in detail in our SAS String tutorial.
3. SAS Date and Time Functions
These SAS functions are used to perform operations on date and time values.
| DATE() | returns the current date as a SAS date value |
| DATETIME() | returns the current date and time of day |
| DAY(date) | returns the day of the month from a SAS date value |
| INTCK(‘interval’,from,to) | returns the number of time intervals in a given time span |
| MONTH(date) | returns the month from a SAS date value |
| QTR(date) | returns the quarter of the year from a SAS date value |
| TIME() | returns the current time of day |
| TODAY() | returns the current date as a SAS date value |
| WEEKDAY(date) | returns the day of the week from a SAS date value |
| YEAR(date) | returns the year from a SAS date value |
| YRDIF(sdate,edate,basis) | returns the difference in years between two dates |
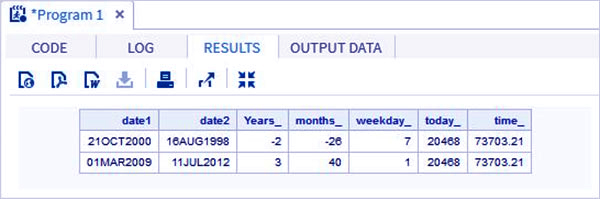
Example-
data date_functions;
INPUT @1 date1 date9. @11 date2 date9.;
format date1 date9. date2 date9.;
/* Get the interval between the dates in years*/
Years_ = INTCK('YEAR',date1,date2);
/* Get the interval between the dates in months*/
months_ = INTCK('MONTH',date1,date2);
/* Get the week day from the date*/
weekday_ = WEEKDAY(date1);
/* Get Today's date in SAS date format */
today_ = TODAY();
/* Get current time in SAS time format */
time_ = time();
DATALINES;
21OCT2000 16AUG1998
01MAR2009 11JUL2012;
proc print data = date_functions noobs;
run;Output-
4. SAS Truncation Functions
These SAS functions return integer values by rounding up the data values.
| CEIL(argument) | returns the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the argument |
| FLOOR(argument) | returns the largest integer that is less than or equal to the argument |
| FUZZ(argument) | returns the nearest integer if the argument is within 1E-12 |
| INT(argument) | returns the integer value |
| ROUND(argument,round-off-unit) | rounds to the nearest round-off unit |
| TRUNC(number, length) | truncates a numeric value to a specified length |
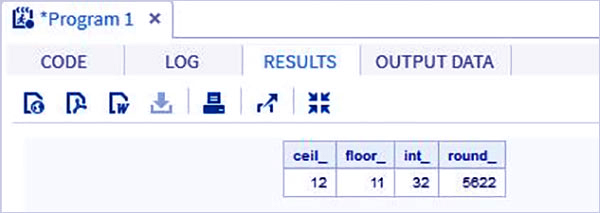
Example-
data trunc_functions; /* Nearest greatest integer */ ceil_ = CEIL(11.85); /* Nearest greatest integer */ floor_ = FLOOR(11.85); /* Integer portion of a number*/ int_ = INT(32.41); /* Round off to nearest value */ round_ = ROUND(5621.78); run; proc print data = trunc_functions noobs; run;
Output-
Summary
We discussed some of the frequently used SAS functions:
- Numeric Functions
- Date Functions
- Time Functions
- Truncation Functions
- Character functions
These functions can be applied to any set of arguments to make our analysis and search easier.
Any feedback or queries? Enter in the comments section. We will be glad to hear from you.
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google


I am having retail banking experience of 7 yrs plus 5 yrs retail mortgage experience, how can SAS help me in advance my career.