Proxy Server And Its Working
FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
Every computer connected to the internet has an IP (Internet Protocol) address that uniquely identifies it. A proxy server, on the other hand, is a network computer with its own IP address. However, there are times when we need to access restricted websites or servers and do not want to reveal our identity (IP address). The proxy server is activated in such a situation. Using a proxy server, we can achieve the same result. It offers various levels of functionality, security, and privacy, depending on the use case, company needs, or policies.
What is a Proxy Server:
The proxy server is a computer connected to the internet that accepts client requests and forwards them to the destination server. It functions as a link between the user and the internet. It has its own Internet Protocol (IP) address. This isolates the client and web server from the rest of the network.
To put it another way, the proxy server enables us to access any website using a different IP address. It acts as a link between users and the websites or servers that are being targeted. It gathers and distributes data in response to user requests. A proxy server’s most important feature is that it does not encrypt traffic.
The two main purposes of proxy server are:
1. To keep the original system hidden.
2. Caching is a technique for speeding up access to a resource.
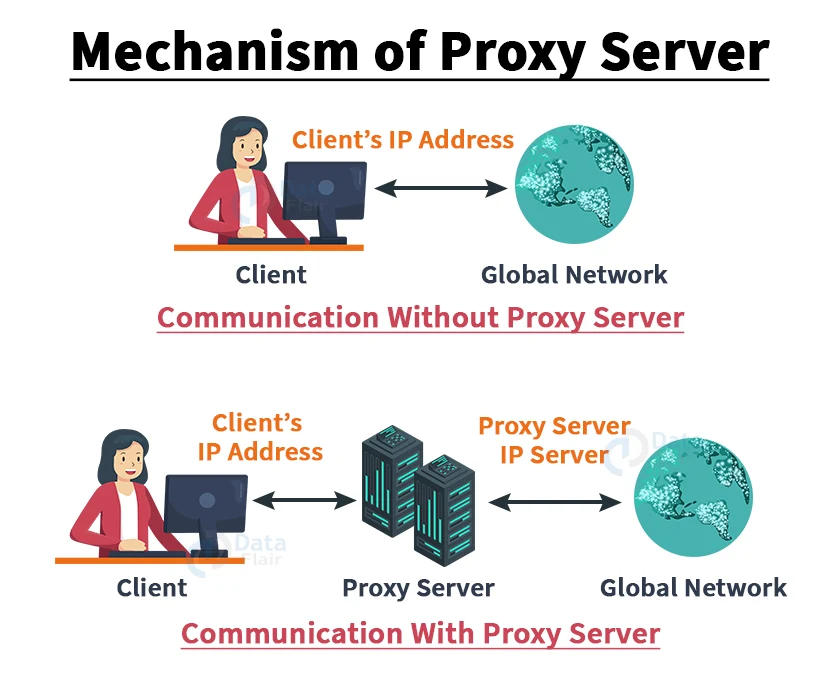
Mechanism of Proxy Servers:
The proxy server accepts the client’s request and responds according to the following criteria:
1. If the requested data or page is already in the proxy server’s local cache, the proxy server provides it.
2. The proxy server forwards the request to the destination server if the requested data or page does not exist in the local cache.
3. The responses are transferred to the client and cached by the proxy servers.
As a result, the proxy server can be described as both a client and a server.
Types of Proxy Servers:
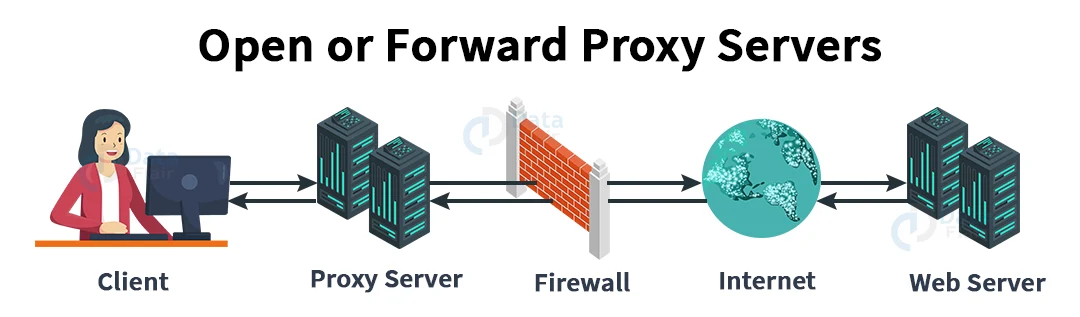
1. Open or Forward Proxy Servers:
It is the most well-known type of intermediary worker that the customer encounters. An open or forward proxy server is a type of intermediary that receives requests from web clients and then browses destinations to gather the requested data. After collecting data from websites, it sends the information directly to internet users. It gets around the authorities’ firewall.
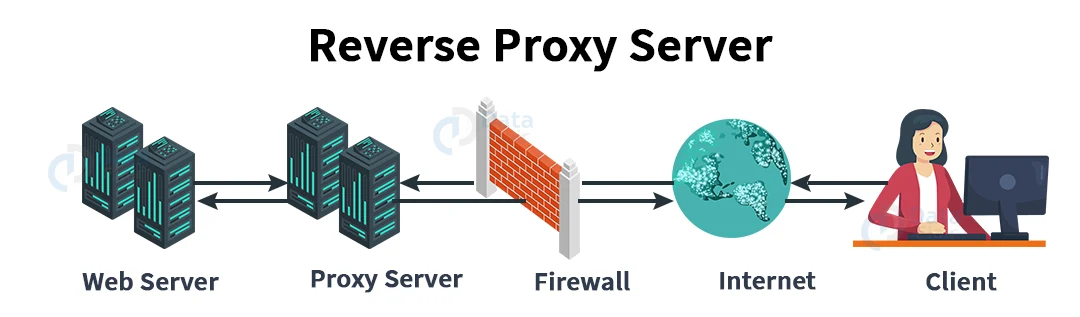
2. Reverse Proxy Server:
It’s a proxy server that’s installed in close proximity to a number of other internal resources. It validated and processed a transaction without requiring direct communication between the clients. Varnish and Squid are the most popular reverse proxies.
3. Split Proxy Server:
It consists of two programs that are installed on two different computers.
4. Transparent Proxy:
It’s a proxy server that only modifies requests and responses to the extent necessary for proxy authentication and identification. It connects to the internet via port 80.
5. Non-Transparent Proxy:
It’s a middleman who modifies the client’s response to the solicitation in order to provide additional services. Web requests are sent directly from the intermediary, regardless of the worker from whom they originated.
6. Hostile Proxy:
It’s used to listen in on data traffic between the client machine and the web server.
7. Intercepting Proxy Server:
It combines a proxy server and a gateway in one package. It is commonly used in businesses to prevent employees from circumventing acceptable use policies and to make administration easier.
8. Forced Proxy Server:
It’s a mix of interception and non-interception policies.
9. Caching Proxy Server:
Client requests are serviced using previously saved contents from previous requests, rather than communicating with the specified server.
10. Web Proxy Server:
A web proxy server is a proxy server that is dedicated to the internet.
11. Anonymous Proxy:
The server makes an attempt to anonymize web browsing.
12. Socks Proxy:
It’s a standard developed by the ITEF (Internet Engineering Task Force). It’s similar to a proxy system that allows proxy-aware applications to run. It prevents external network components from collecting information about the client who initiated the request. It is made up of the following elements:
- A client library for the SOCK protocol.
- FTP, telnet, or an internet browser or other such client programmes.
- A SOCK server for the operating system specified.
13. High Anonymity Proxy:
In a request header, the proxy server does not include the proxy server type and the client IP address. Clients who use the proxy are untraceable.
14. Rotating Proxy:
Each client connected to it is assigned a unique IP address. It’s ideal for users who do a lot of web scraping on a regular basis. It enables us to return to the same website on a regular basis. As a result, using the rotating proxy necessitates greater attention.
15. SSL Proxy Server:
The data between the client and the server is decrypted. It means that data is encrypted both ways. Because proxy hides the fact that it exists from both the client and the server. It is best suited for organisations that want to improve their threat protection. The encrypted content is not cached in SSL proxy.
16. Shared Proxy:
A shared proxy server is one that is used by multiple users at the same time. It assigns the client an IP address that can be shared with other clients. It also allows users to choose the location from which they want to conduct their search. It’s perfect for people who don’t want to spend a lot of money on a fast internet connection. It has the benefit of being inexpensive. The disadvantage is that a user may be held responsible for the misdeeds of others. As a result, the user may be barred from the site.
17. Public Proxy:
There is no charge for using a public proxy. It’s ideal for users who are concerned about cost but not about security or speed. It moves at a slow pace most of the time. Using a public proxy puts the user at risk because information on the internet can be accessed by others.
18. Residential Proxy:
It gives a specific device an IP address. All of the client’s requests were routed through that device. It’s perfect for users who want to double-check ads that appear on their websites. We can block unwanted and suspicious ads from competitors using the residential proxy server. The residential proxy server is more dependable than other proxy servers.
19. Distorting Proxy:
It differs from others in that it identifies itself as a website proxy while concealing its own identity. By providing an incorrect IP address, the actual IP address is changed. It’s ideal for customers who don’t want to reveal their location while surfing.
20. Data Center Proxy:
It’s a unique type of proxy that isn’t connected to an ISP. Other corporations provide it through a data centre. Physical data centres are where these servers can be found. It’s ideal for clients who need answers quickly. It does not offer complete anonymity. As a result, it poses a significant risk to client information.
21. HTTP Proxy:
HTTP proxies are proxy servers that save cache files from websites that are visited. Because cached files are stored in local memory, it saves time and improves performance. If the user wants to access the same file again, the proxy provides it without the user having to browse the pages.
Advantages of Proxy Servers:
1. It makes the user’s security and privacy more secure.
2. It conceals the user’s identity (IP address).
3. This regulates traffic and prevents collisions.
4. By caching files and compressing incoming traffic, it also saves bandwidth.
5. Defend our network from malicious software.
6. Access to the restricted content is granted.
Need for Proxy Servers:
1. It lowers the risk of data breaches.
2. It adds an extra layer of security between the server and the outside world.
3. This also safeguards against cyber-attacks.
4. It does so by filtering the requests.
Proxy Server vs VPN:
Basis of Comparison | Proxy Server | VPN |
| Encryption | The traffic is not encrypted. | It encrypts the data transmission. |
| Software | It doesn’t have any software of its own. | This has its own operating system. |
| Speed | It’s a lot faster than using a VPN. | In comparison to the proxy server, it is slower. |
| Cache | It makes use of cache. | It does not make use of a cache. |
| IP Address | The IP address is hidden, but the proxy owner can see the IP address of the client. | The IP address is hidden completely. |
| Connection | It’s in a state of flux. | It’s completely seamless. |
| Pricing | The majority of it is free. | This has a fee attached to it. |
| Reliability | Its connection is becoming increasingly erratic. | It has a more stable connection. |
| Level of Working | It works at the level of the application. | This works at the level of the operating system. |
| Security | It’s not as safe. | It gives you more security. |
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the functioning of proxy servers and the various types that are currently in use. Lastly, we also looked at a direct comparison between proxy servers and VPNs.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google


Hello,can you add my company’s website to this article,how much does it cost?