PGP – Pretty Good Privacy
FREE Online Courses: Enroll Now, Thank us Later!
What is PGP?
PGP is an abbreviation for Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), which was created by Phil Zimmermann. It was meant to offer all four dimensions of security in email transmission, namely privacy, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation.
PGP provides integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation through the use of a digital signature (a mix of hashing and public key encryption). It provides anonymity by combining secret key encryption and public key encryption. As a result, the digital signature employs one hash function, one secret key, and two private-public key pairs.
PGP is an open source and publicly downloadable email security software suite. It uses Digital Signatures to offer authentication. It ensures secrecy by employing symmetric block encryption.
PGP supports ZIP compression as well as EMAIL compatibility through the radix-64 encoding method.
How to Select PGP Software:
The main reason you use PGP is to protect the security of your correspondence. When searching for PGP software, security should be your first priority. Though PGP itself is unbreakable, particular implementations have been hacked in the past. Unless you are an expert developer, detecting these flaws is nearly impossible; thus, the best option is to look for any documented vulnerabilities in the product you are considering.
Aside from that, selecting PGP software is a personal (or commercial) decision. It’s doubtful that you need to encrypt every email you send, so downloading an add-on for your regular email client may be overkill. Consider utilising an online PGP service to transmit sensitive emails instead.
Finally, look for a software supplier that offers dedicated assistance, either through a customer service team or a user community. Learning to use PGP might be frustrating at first as you traverse the system, and you’re likely to require assistance at this time.
What services does PGP provide?
PGP employs public key cryptography, symmetric key cryptography, hashing, and digital signatures. It offers:
- Message Integrity
- Privacy
- Message Integrity
- Non-repudiation
It also offers data compression and key management services in addition to these security services. Rather than creating new cryptographic algorithms, PGP uses existing ones such as RSA, IDEA, MD5, and others.
What are the steps involved in PGP?
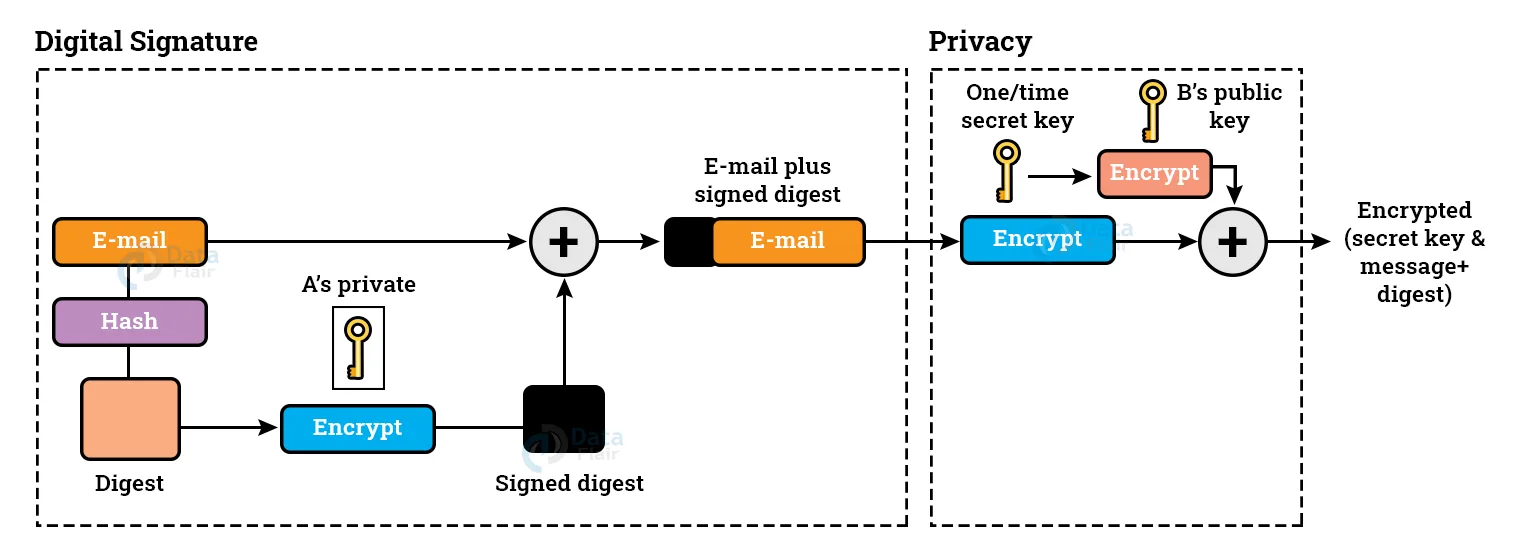
1. PGP at the Sender Side:
To generate a digest, the e-mail message is hashed using a hashing algorithm.
The digest is then encrypted with the sender’s private key to produce a signed digest, and the signed digest is appended to the original email message.
The original message and signed digest are encrypted using the sender’s one-time secret key. Public key of the recipient is used to encrypt the secret key.
The encrypted secret key, as well as the encrypted message and digest combination, are sent simultaneously.
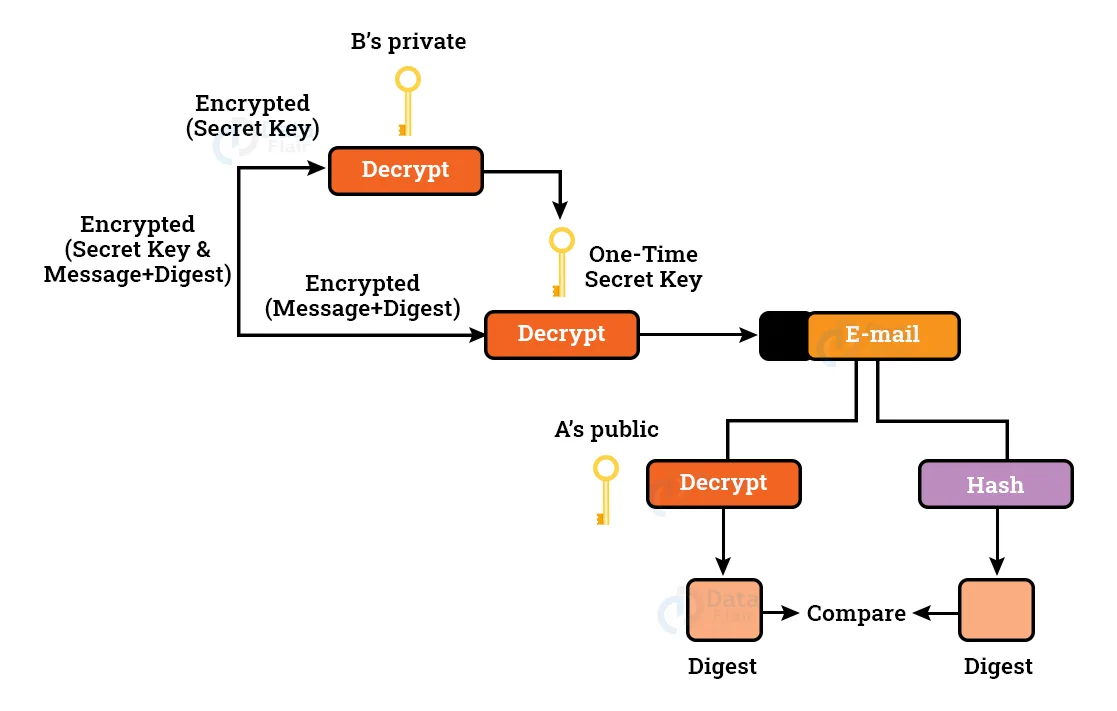
2. PGP at the Receiver Side:
Both the encrypted secret key and message digest are received by the recipient.
To get the one-time secret key, the encrypted secret key is decoded using the receiver’s private key.
The secret key is then used to decode the message and digest combination.
The digest is decrypted using the sender’s public key, and the original message is hashed to generate a digest using a hash function.
Both digests are compared; if they are equal, it implies that all features of security are retained.
PGP Certificate:
A chain of trust is typically used to establish a PGP key certificate. For example, A’s public key is signed with B’s public key, while B’s public key is signed with C’s public key. As the process progresses, a web of trust is formed.
Any user in a PGP environment can function as a certifying authority. Any PGP user can certify the public key of another PGP user. A certificate of this type, however, is only valid to another user provided the user acknowledges the certifier as a trusted introducer.
A certification system like this has a number of flaws. Finding a chain running from a known and trustworthy public key to the required key may be tricky. Furthermore, there may be numerous chains that lead to various keys for the intended user.
PGP may also make use of the PKI infrastructure with a certification authority, and public keys can be certified by a CA (X.509 certificate).
Advantages of PGP:
1. The main advantage of PGP encryption is that it is almost impenetrable. That is why it is still used by journalists and activists and is frequently viewed as the greatest approach to improve cloud security. In summary, it is very difficult for anyone – hacker or NSA – to crack PGP encryption.
2. Though there have been several news reports highlighting security weaknesses in various PGP implementations, such as the Efail vulnerability, it is essential to note that PGP itself is still highly safe.
Disadvantages of PGP:
1. Administration is difficult:
The many versions of PGP complicate administration.
2. Issues with compatibility:
Both the sender and the receiver must use compatible versions of PGP. For example, if you encrypt an email using PGP using one of the encryption techniques, the receiver will have a different version of PGP and will be unable to read the contents.
3. Complexity:
PGP is a difficult technology to master. Other security techniques include symmetric encryption, which employs a single key, or asymmetric encryption, which employs two distinct keys. PGP employs a hybrid method of symmetric encryption using two keys. PGP is more complicated and less well-known than standard symmetric or asymmetric techniques.
4. No Recovery:
Computer administrators must deal with the problem of forgetting their passwords. In such cases, an administrator should recover passwords using a specialised software.
A technician, for example, has physical access to a PC that may be exploited to recover a password. However, PGP does not provide such a specific software for recovery; encryption methods are quite strong, therefore it does not recover forgotten passwords, resulting in lost communications or data.
Summary:
In this article we covered the concept of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) and the services that it provides. We looked at how PGP is implemented on both the sender as well as receiver side. We also took a brief look at PGP Certificates and the disadvantages of PGP.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google