Paging vs Segmentation in Operating System
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Your Skills, Zero Cost Attached - Enroll Now!
Paging and segmentation are both storage mechanisms that help store processes. There is a very slight difference between these mechanisms.See paging vs segmentation in OS.
Paging in Operating System
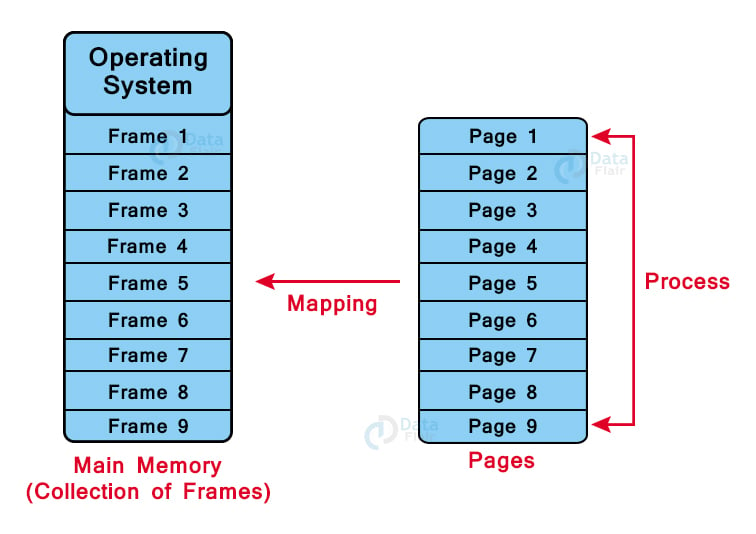
Paging is a logical concept that allows the OS to retrieve processes into the main memory from the secondary storage. It provides faster access to data as processes are stored in the form of pages.
The main system memory is divided into frames i.e., small fixed-size blocks of physical memory where the size of frames is equal to the size of pages. This provides maximum utilization of the main system memory and helps avoid external fragmentation.
Advantages of Paging in OS
Following are the advantages of Paging:
- The memory management algorithm is easy to use.
- External Fragmentation is not required.
- Swapping between equal-sized pages and page frames becomes easier.
Disadvantages of Paging in OS
Following are the disadvantages of paging:
- Internal fragmentation.
- Additional memory consumption by Page tables.
- Memory reference overhead due to multi-level paging.
Segmentation in Operating System
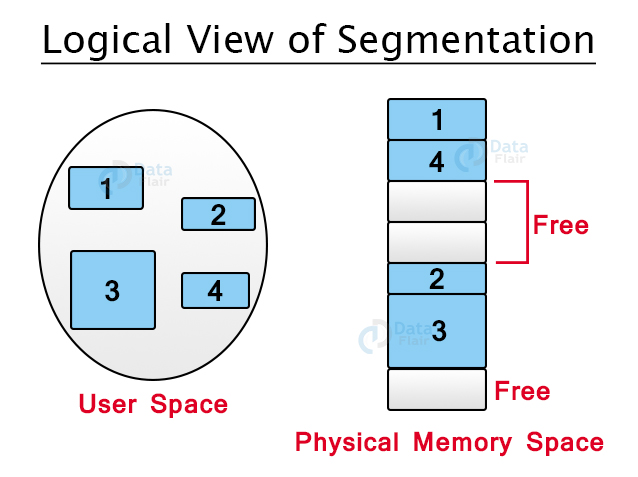
Segmentation is similar to paging, except that the length of segments is variable and pages have a fixed size. The segment of a program comprises the program’s main function, data structures, utility functions, etc.
All this information about processes is maintained in the form of a segment map table by the OS. This table includes a list of segment numbers, free memory blocks, their sizes, and their memory locations in the main memory or virtual memory.
Advantages of segmentation in OS
Following are the advantages of segmentation:
- Provides protection within segments.
- Segments referencing multiple processes can help achieve sharing.
- No internal fragmentation
- As compared to paging, segment tables use lesser memory.
Disadvantages of Segmentation in OS
Following are the disadvantages of segmentation:
- The separation of free memory space into small pieces can cause external fragmentation.
- It is costly.
Paging vs Segmentation in OS
| Paging | Segmentation |
| Fix sized pages | Variable sized segments |
| Internal fragmentation | No internal fragmentation |
| Hardware decides the page size | The user decides the segment size |
| Faster memory access | Memory access is slower as compared to paging |
| Page table stores data | Segmentation table stores data |
| Sharing of procedures is not allowed | Sharing of procedures is allowed |
| Cannot distinguish and secure procedures and data | Can separate and secure procedures and data |
| 1-D address space | Multiple independent address spaces |
| A single integer address is divided into page number and offset by the hardware | The user divides address in segment number and offset |
Summary
Paging and segmentation are both storage mechanisms that help store processes. Paging is a logical concept that allows the OS to retrieve processes into the main memory from the secondary storage. Segmentation is similar to paging, except that the length of segments is variable and pages have a fixed size.
Did you like this article? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google