Node.js MySQL Tutorial
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Your Skills, Zero Cost Attached - Enroll Now!
In this article, we will see how we can use the sql database with node.js. We will look at how to create a database, connect databases, create a table and other sql methods with code and examples.
What is MySQL?
Mysql is a relational database management system. It is an open source and most popular relational database written in C and C++.
Why connect MySQL with nodejs?
- MySQL is a free database.
- It supports most of the operating system.
- It can be used with almost all the languages.
- Fast even when it has large data.
How to Install MySQL:
Npm has a mysql module which we will use in this article. To install it run the below command.
Npm install mysql
To utilize it use the require function:
Let mysql=require(‘mysql’)
Connect to MySQL:
Replace the username and password in the below code with your mysql credentials.
Code for creating connection:
let mysql = require('mysql');
let con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "yourusername",
password: "yourpassword"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Connected!");
});
Output:
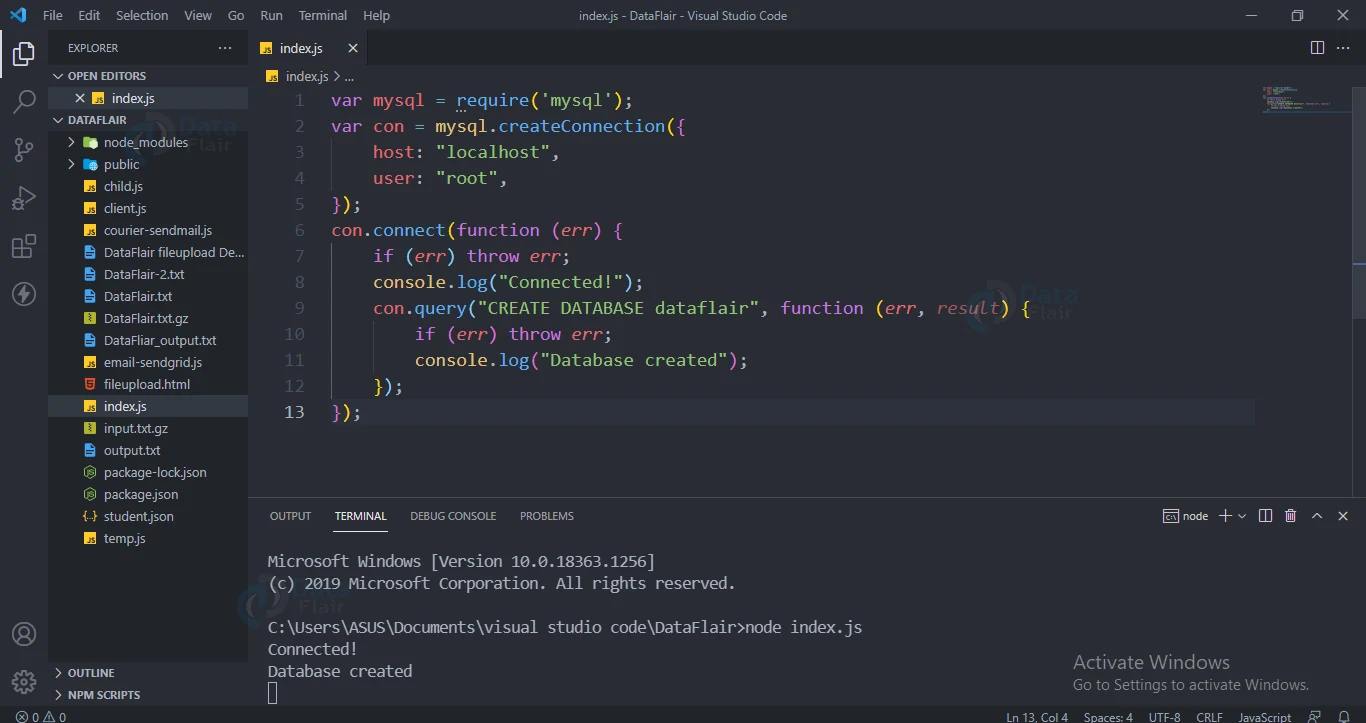
Query for Creating a database:
Use CREATE DATABASE to create a database in MySQL.
Code for creating a database:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Connected!");
con.query("CREATE DATABASE dataflair", function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Database created");
});
});
Output:
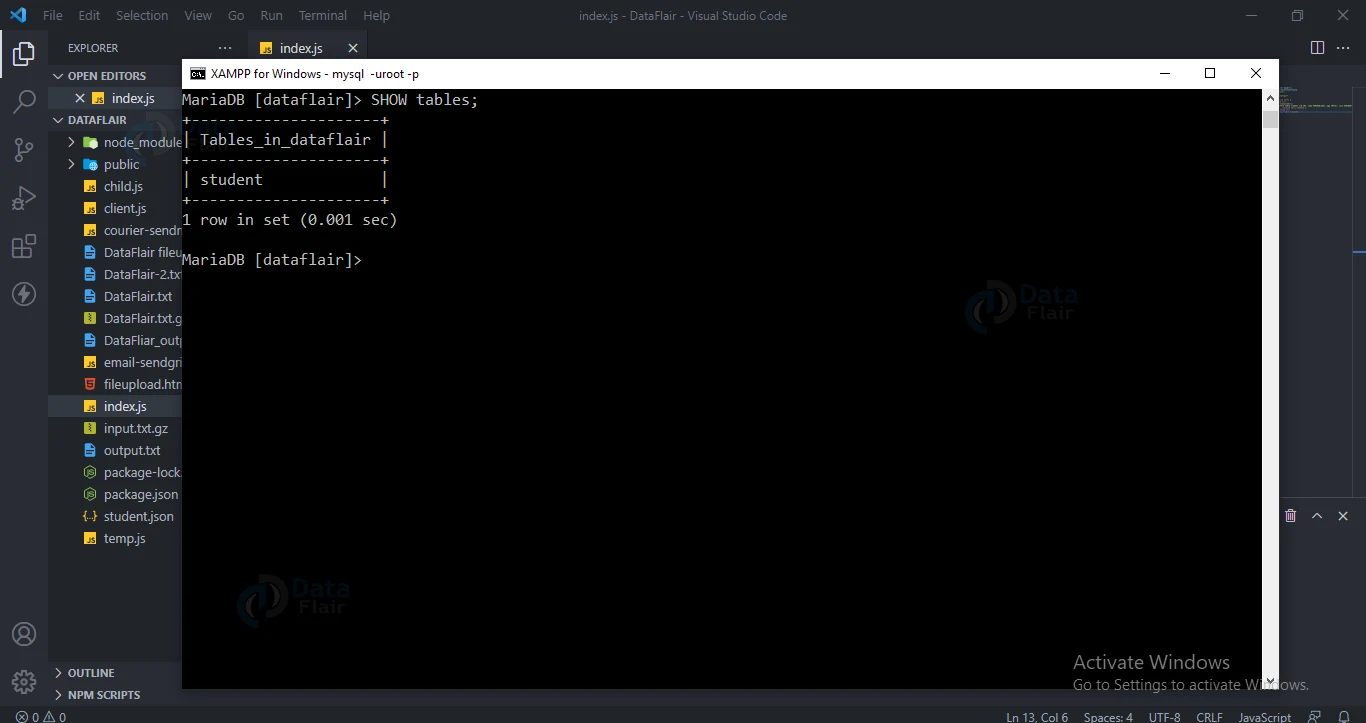
Creating Table in MySQL:
Use CREATE TABLE to create a table in MySQL database.
Code for creating a table:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Connected!");
var sql = "CREATE TABLE student (id INT, name VARCHAR(255), age INT(3), city VARCHAR(255))";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Table created");
});
})
Output
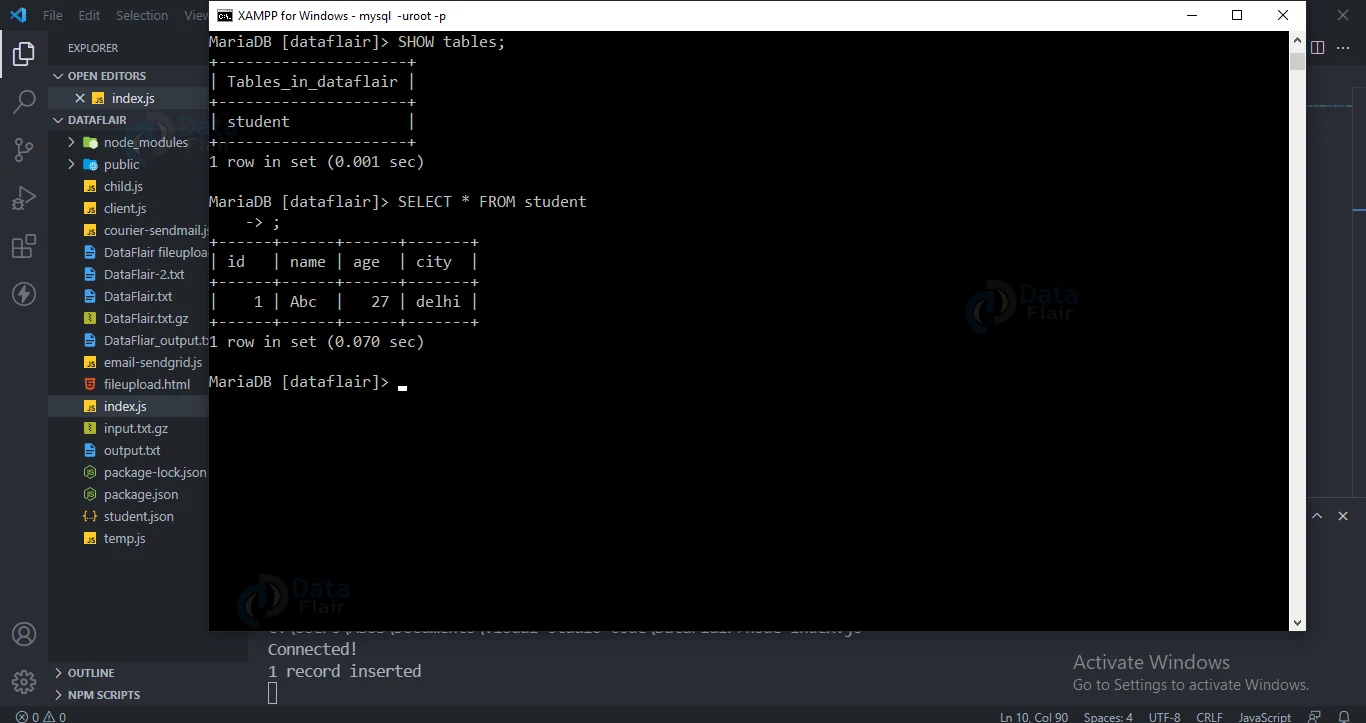
Insert into Table:
Use INSERT INTO to insert a row in the MySQL database table.
Code for inserting into table:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Connected!");
var sql = "INSERT INTO student (id, name, age, city) VALUES ('1', 'Abc', '27', 'delhi')";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("1 record inserted");
});
});
Output:
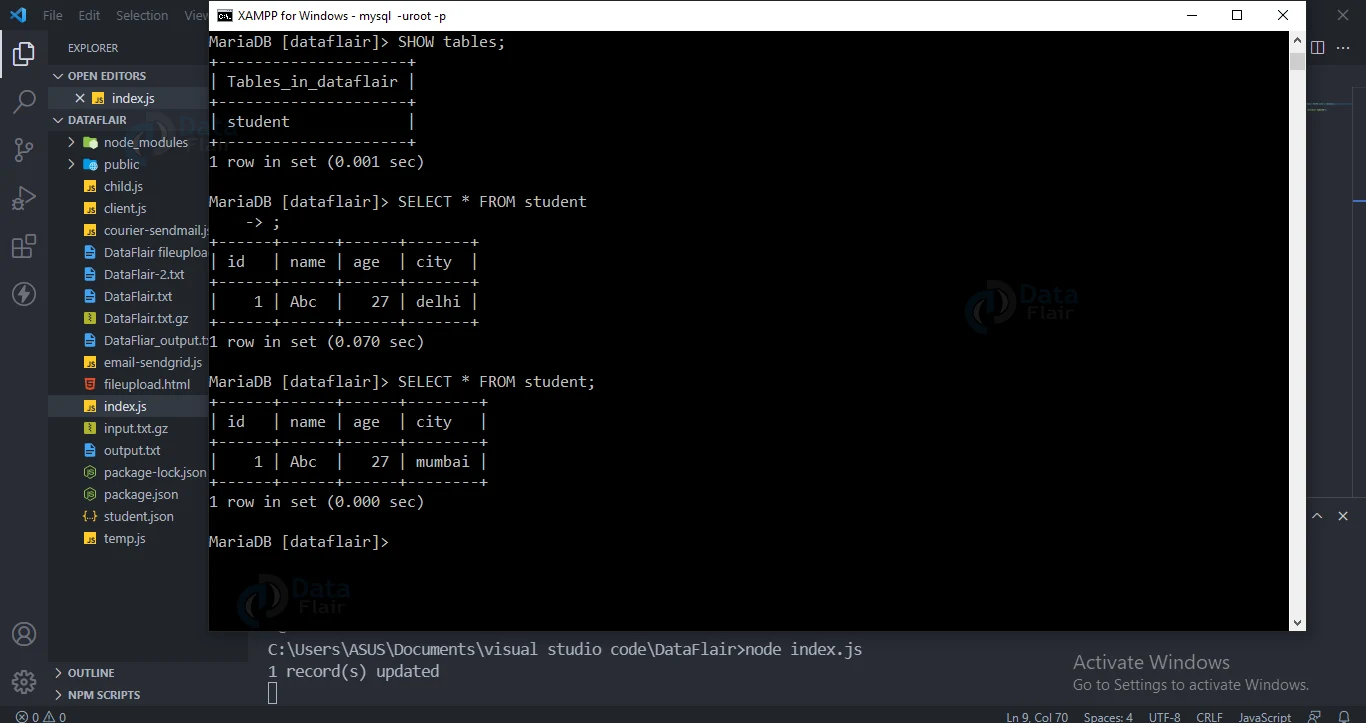
Update records:
Use UPDATE to update a row in the MySQL database table.
Code for updating a record:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
var sql = "UPDATE student SET city = 'mumbai' WHERE city = 'delhi'";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result.affectedRows + " record(s) updated");
});
});
Output:
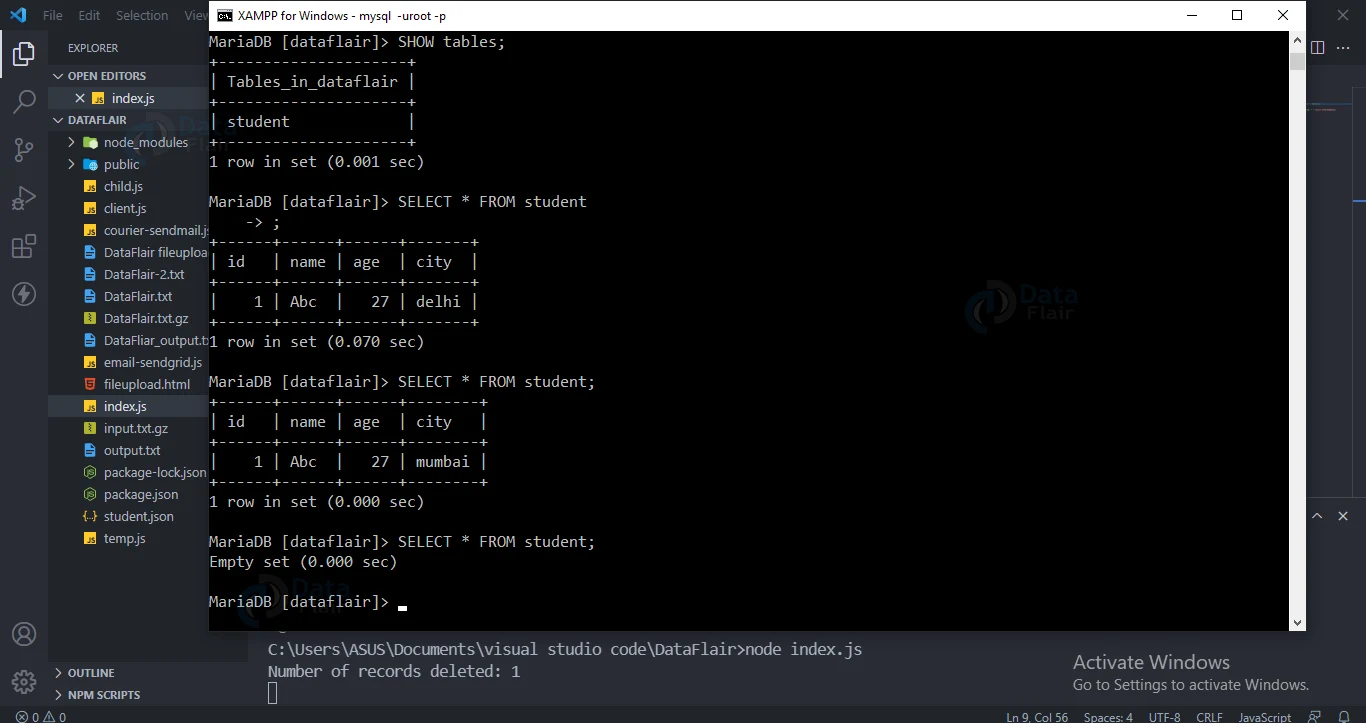
Delete records:
Use DELETE FROM to delete a row in the MySQL database table.
Code for deleting a record:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
var sql = "DELETE FROM student WHERE city = 'mumbai'";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Number of records deleted: " + result.affectedRows);
});
});
Output:
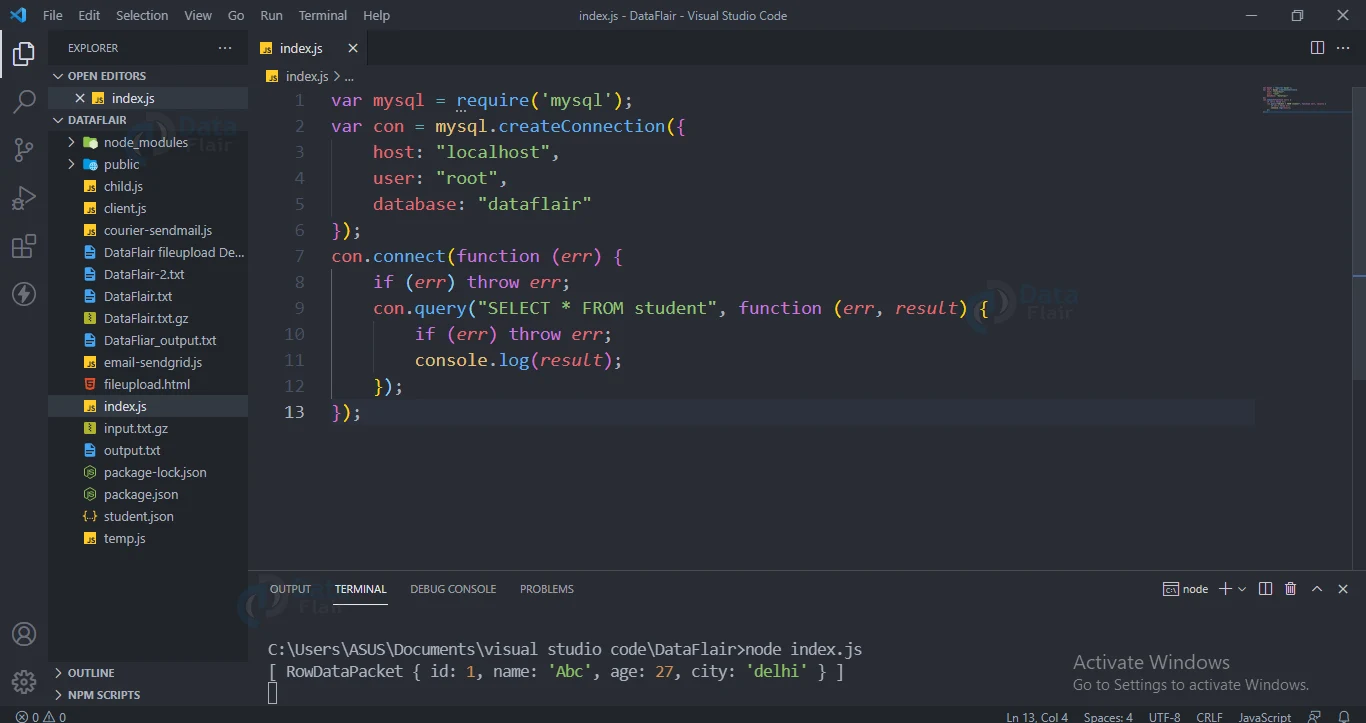
SELECT records:
Use SELECT to see a row in the MySQL database table.
Code for using select statement :
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
con.query("SELECT * FROM student", function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result);
});
});
Output:
Mysql Where:
If we want to select a specific row based on some criteria we use where.
Code for mysql where:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
con.query("SELECT * FROM student WHERE city = 'delhi'", function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result);
});
});
Output:
Mysql order by:
You can use order by to sort the data.
Code for Mysql order by
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
con.query("SELECT * FROM student ORDER BY name", function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result);
});
})
Output:
{id:2,name:’XYZ’,age:28,city:’delhi’}
Mysql LIMIT:
In order to get only a few rows from the table we use a limit.
Code for mysql limit:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
var sql = "SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 1";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result);
});
});
Output:
Mysql JOIN:
In order to join two tables we use the mysql JOIN
Code for mysql join:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
var sql = "SELECT student.name AS name, school.name AS school FROM student JOIN school ON student.school = school.id";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result);
});
});
Output:
{name:’XYZ’,school:’school2’}
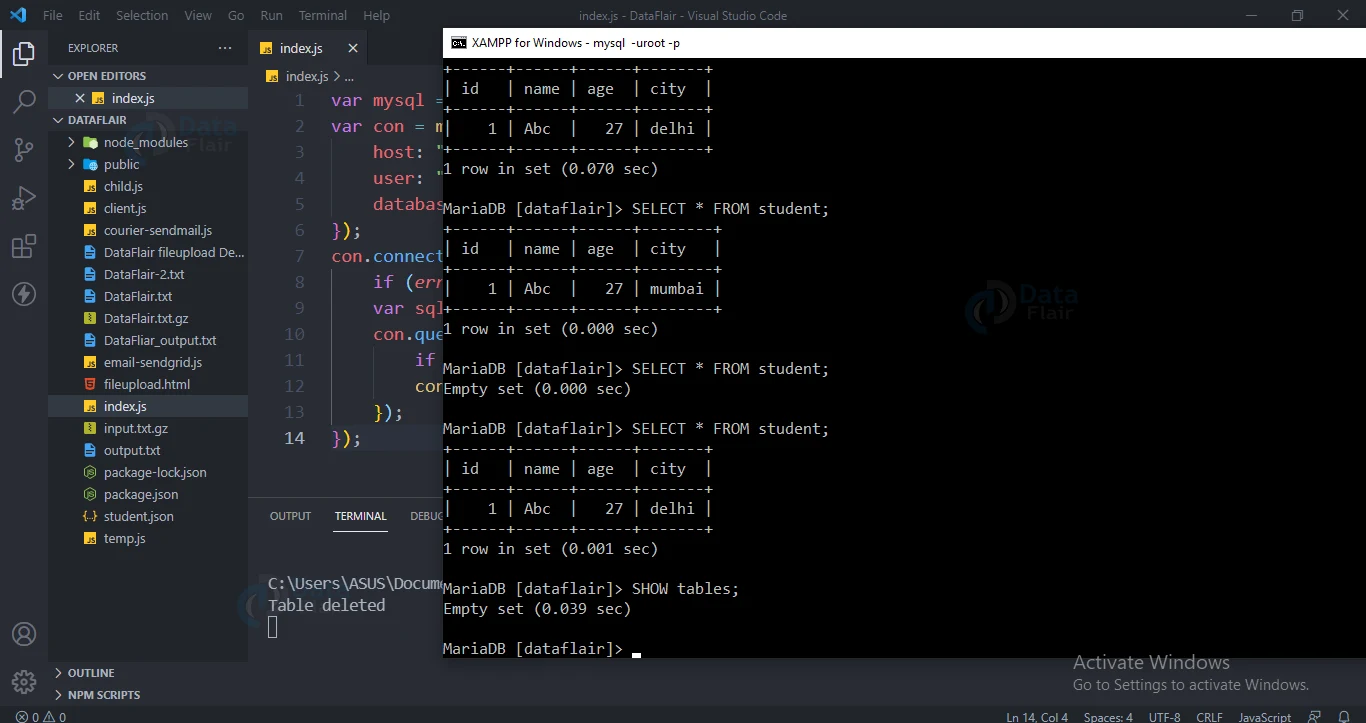
DROP Table:
Use DROP TABLE to drop a MySQL database table.
Code for dropping table:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "root",
database: "dataflair"
});
con.connect(function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
var sql = "DROP TABLE student";
con.query(sql, function (err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Table deleted");
});
});
Output:
Calling MySql stored procedure:
You can call stored procedures and use it for query;
Code for stored procedure:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `selectAll`()
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM student;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
function call(sp) {
let spQuery = 'CALL ??';
let query = mysql.format(spQuery,[spName]);
pool.query(query,(err, result) => {
if(err) {
console.error(err);
return;
}
});
}
Output:
{id:2,name:’XYZ’,age:28,city:’delhi’}
Conclusion:
We hope you were able to learn using Mysql with node js. Do check the DataFlair website for other amazing articles.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google