Network Privacy and its Need
FREE Online Courses: Knowledge Awaits – Click for Free Access!
For thousands of years, the notion of achieving privacy has remained unchanged: communication cannot be encrypted. All unauthorised parties must be kept in the dark about the communication. To some extent, privacy is achieved by the deployment of a suitable encryption/decryption technology. This approach assures that the message’s contents are incomprehensible to the eavesdropper.
Aspects of Network Security:
1. Interruption:
Interruption is a security risk in which the availability of resources is compromised. For example, a user may be unable to access its web-server, or the web-server may have been compromised.
2. Privacy Breach:
A user’s privacy is jeopardised under this danger. Someone who is not permitted is accessing or intercepting data transmitted or received by the authenticated user.
3. Integrity:
Any alteration or modification to the original context of communication is considered a threat of this sort. The attacker intercepts and receives data transmitted by the sender, then alters or creates fake data and transmits it to the recipient. The data is received by the recipient under the assumption that it was delivered by the original Sender.
4. Authenticity:
This hazard happens when an attacker or a security violation impersonates a legitimate user and gains access to resources or communicates with other legitimate users.
What is Encryption and Decryption?
1. Encryption:
Encryption implies that the sender turns the original information into an incomprehensible message and sends it over the network.
2. Decryption:
Decryption is the process of reversing the encryption process in order to return the communication to its original form.
The data that will be encrypted at the sender site is referred to as plaintext, while the encrypted data is referred to as ciphertext. At the receiving location, the data is decrypted.
Types of Encryption/Decryption Techniques:
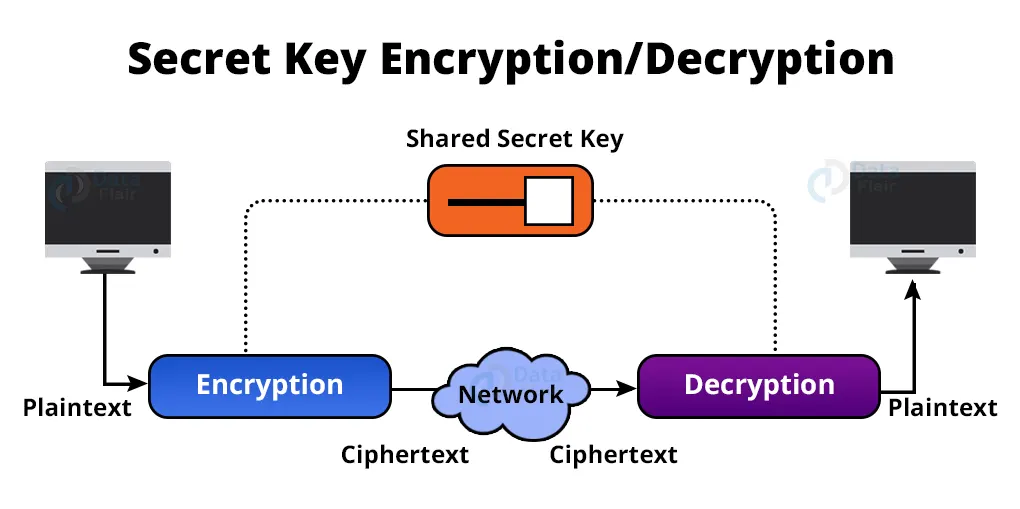
1. Secret Key Encryption/Decryption:
The same key is used by both parties, i.e., the sender and recipient, in the Secret Key Encryption/Decryption process.
The sender encrypts the data using the secret key and encryption algorithm; the receiver decrypts the data using this key and decryption algorithm.
The algorithm used for encryption in Secret Key Encryption/Decryption is the inverse of the method used for decryption. It indicates that if the encryption algorithm employs addition and multiplication, the decryption process employs subtraction and division.
Because the same secret key is used in bidirectional communication, the secret key encryption algorithm is also known as symmetric encryption algorithm.
The secret code is used by the computer to encrypt the information before it is transferred over the network to another computer in the secret key encryption/decryption method.
The secret key necessitates that we know which machines are communicating with one another in order to install the key on each computer.
Data Encryption Standard:
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) was developed by IBM and accepted as the standard encryption technique for nonmilitary and nonclassified usage by the United States government.
The Data Encryption Standard is an encryption standard that is a kind of Secret Key Cryptography.
Advantages of Secret Key Encryption/Decryption:
1. Efficient: Secret key algorithms are more efficient since they require less time to encrypt a message than public key encryption algorithms. The reason for this is that the key is tiny in size. As a result, Secret Key Algorithms are mostly utilised for encryption and decryption.
Disadvantages of Secret Key Encryption/Decryption:
1. For secret key encryption/decryption, each pair of users are required to have a secret key. If N individuals wish to utilise this technique around the globe, then there are N(N-1)/2 secret keys. For example, for every million persons, there are half a billion secret keys.
2. The distribution of keys among several parties may be quite complex. This issue may be overcome by combining the Secret Key Encryption/Decryption algorithm with the Public Key Encryption/Decryption algorithm.
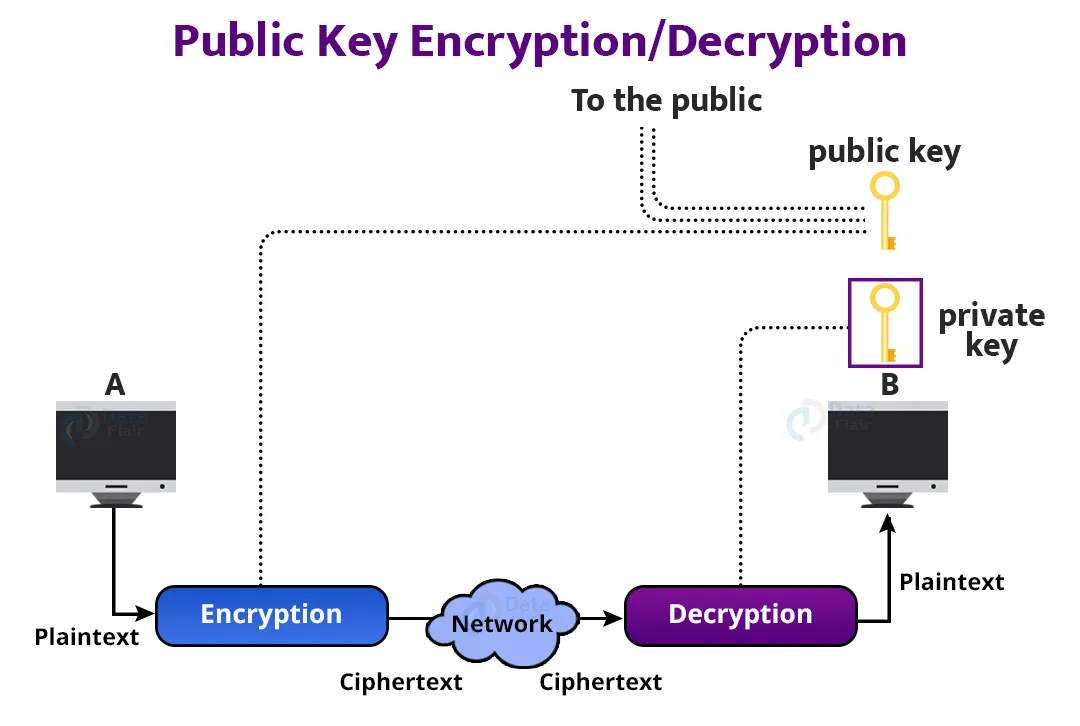
2. Public Key Encryption/Decryption:
In public key encryption, two keys exist – a private key and a public key. The recipient receives the private key, while the public key is made available to the public.
In public key encryption/decryption, the sender’s public key differs from the receiver’s private key. The public key is accessible to the general public, but the private key is held by each individual. RSA is the most commonly used public key algorithm today.
Advantages of Public Key Encryption/Decryption:
The sharing of a secret key is the fundamental limitation of private key encryption. A third party cannot use this key. In public key encryption, each entity generates a pair of keys, one private and one public, and keeps the secret key while distributing the public key.
The number of keys in public key encryption is drastically decreased.
Disadvantages of Public Key Encryption/Decryption:
1. A major drawback of public-key encryption is that it is much slower than secret-key encryption. Secret key encryption uses a single shared key to encrypt and decode the message, which speeds up the procedure, whereas public key encryption uses two keys that are linked by a difficult mathematical process. As a result, with public key encryption, encryption and decryption take longer.
2. Authentication: There is no built-in authentication in public key encryption. Messages can be read or intercepted without the user’s awareness if they are not authenticated.
3. Inefficient: The public key’s major drawback is its complexity. Large numbers are required for the approach to be effective. However, transforming plaintext to ciphertext with large keys takes a long time in public key encryption. As a result, public key encryption techniques are only effective for short communications and not for large ones.
Differences between Secret Key and Public Key Encryption/Decryption:
Parameter | Secret Key | Public Key |
| Definition | Secret Key Encryption is a method that encrypts and decrypts a message using a single shared key. | The approach of using two distinct keys for encryption and decoding is known as public key encryption. |
| Efficiency | It is efficient, and mostly used for large pieces of text. | It is inefficient and mostly used for smaller pieces of text. |
| Also Known As | It is also known as Symmetric Key encryption. | It is also known as Asymmetric Key Encryption. |
| Purpose | The secret key algorithm’s primary function is to transfer bulk data. | The primary goal of the public key algorithm is to safely transfer keys. |
| Speed | It is fast since it employs a single key for encryption and decryption. | Its performance is slow because it employs two distinct keys, each of which is linked to the other via a complex mathematical procedure. |
| Algorithms | DES, 3DES, AES, and RCA are the secret key algorithms. | Diffie-Hellman and RSA are the public key algorithms. |
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the various aspects of network privacy and the two widely used techniques for encryption and decryption. We also looked at the advantages and disadvantages of each technique and the differences between them.
We work very hard to provide you quality material
Could you take 15 seconds and share your happy experience on Google