Microsoft Windows Tutorial – History, Versions, Features, Applications
FREE Online Courses: Enroll Now, Thank us Later!
Bill Gates and Paul Allen are the founders of Microsoft that came into existence in 1975. They took inspiration from the Altair 8800 that Allen saw in Popular Electronics. They got in touch with Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems to manufacture Altair BASIC. This led to both men moving to Albuquerque. The registration of the company took place in 1976 with only thirteen employees.
The Microsoft Windows came out in November 1985 as a personal computing system. Today it is available in 138 languages.
The windows operating system uses several graphical user interfaces to function. It enables users to use the internet, store data, share and communicate with others, etc. The idea was to move beyond the regular operating systems and give users more innovation.
Before Windows, Microsoft users were resorting to the MS-DOS operating system. The term windows came in as this operating system allows users to do multiple tasks simultaneously.
Another reason was no trademark was available for such commonly used terms like windows. There are many versions of this operating system that came and went.
Let us understand them –
History of Microsoft Windows
1. Windows 1.0
Microsoft began with their Interface Manager” in 1983, but the first version of the windows came out in November 1985. The system had a pure operating environment with a friendly graphical user interface.
The graphics were very simple but were a new thing for the users. This version allowed limited multi-tasking but there was a lot of scope for improvement.
2. Windows 2.0
The second version of the windows came out in December 1987. This had an operating environment of a 16-bit graphical user interface.
Control panel was first seen in this version and so were MS Word and Excel. The users were able to overlap applications and multitask more.
This was the last version to function without a hard disk and thus relied on hardware devices.
3. Windows 3.0
This version of Windows came out in 1990 with 8086 microprocessors inside. This was better for multitasking and storage facilities. It had a feature of conventional and expandable memory for which it was critically appreciated.
4. Window 95
This was the first complete operating system by Microsoft that came out in August 1995. This was a combination of MS-DOS and Windows products. It had a 16 to 32 bit GUI with a taskbar and start menu.
Some additional features were – plug and play feature, saving long files name, and the first version of internet explorer.
5. Windows 98
This version of Windows came out in May 1998 with a 32-bit product base. This was mainly a modification of Windows 95 as most of the features were the same.
Internet Explorer 4.01 came out with this version. But it did not support USB printers and large storage devices.
6. Windows 2000
This version came out in February 2000 with sector-wise targeting – server, professional, advanced, and datacenter server. This was very secure and came in with a local disk manager. It also had a multilingual user interface allowing the use of different languages.
7. Windows XP
The launch of this Windows took place in August 2001 as an advanced portable PC support operating system. It had an automatic wireless connection and a fast start-up. There was a better interface with a help and support center.
8. Windows Vista
The first operating system with DVD ROM installation was this version of windows. With a launch in January 2007, it had a better interface as an additional benefit.
9. Windows 7
A version with many new features like libraries, redesigned windows shell, better taskbar, and upgraded windows line. The launch of this version was in October 2009 with extended hardware support.
10. Windows 8
A 2012 windows version with touch-based optimization suitable for laptops, mobiles, and tablets. It had an in-built cloud service and a windows store for software download. There were new security features and an option to download applications directly.
11. Windows 10
The latest Windows version came out in 2015 as a virtual desktop system. It allows using windows store within the desktop without full-screen mode. It had new icons and an option to compress files automatically.
Important Editions of Windows
1. Windows Home
The basic window edition with very fundamental functions. This includes – internet connection, web browsing, office software, watching videos, etc. It was comparatively cheap and was inbuilt in most new computers.
2. Windows Professional
The windows pro is an advanced edition of windows useful for small and medium organizations. It has all features of windows home followed by –
a. Group policy management
This feature allows the admin to specify the policies of a group to manage all the users. This feature is only for versions with at least 128 GB of RAM. It has a flexible update schedule and can postpone it for around 34 days.
b. Trusted Boot
It has encryption on the boot loader to prevent rootkits from entering the computer system.
c. Bitlocker
The Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm allows encryption by the users to protect their data. The computer can only start with the bit locker password. But users cannot retrieve this password in case they forget it. Only Windows 7 and Windows Vista have this feature.
d. Windows Sandbox
This feature allows users to change and test computer security on the network or internet without disturbing the computer system.
e. Remote Desktop
It allows users to create a remote desktop connection allowing device sharing like mouse, keyboard, and display. The help port 3389 allows access to this feature with the help of the team viewer application.
f. Hyper-V
The hypervisor is for virtualizing the x86-64 servers by machines or third-party software.
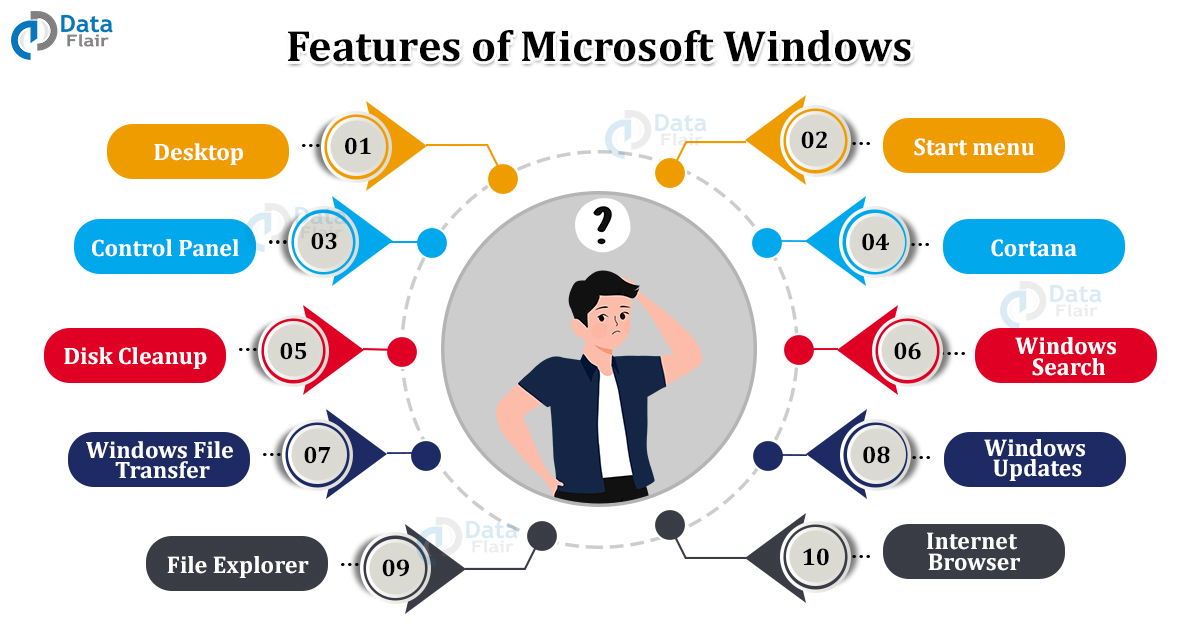
Features of Windows
1. Desktop
The first screen that users see when the computer starts. My computer, documents, The start menu and recycle bin are on the screen by default. The taskbar is at the bottom of the screen where all the applications are visible.
2. Start menu
On the left of the taskbar, it displays installations on the computer. There is a start button on the keyboard to open it.
3. Control Panel
The Control Panel has tools to manage the resources on the computer like change audio, printer, or account setting.
4. Cortana
A feature in Windows 10 that accepts voice commands and then performs those tasks. This can be setting reminders, search, etc. It is similar to Siri and Google Alexa, becoming a support for the system. Windows key + S is the way to activate it.
5. Disk Cleanup
This is to clean up space on the computer by deleting useless files. This boosts up the performance of the computer and its programs. Windows+E is the shortcut to open it or users can right-click on the file and scroll to see the disk clean option in properties.
6. Windows Search
It allows users to search the exact file on the computer without knowing its location at all.
7. Windows File Transfer
Users can transfer files from one location to another or from one device to another. Cables, USB, Bluetooth, etc. are some ways to do it.
8. Windows Updates
The windows can update automatically to keep all the features and functions up to date.
9. File Explorer
The Windows Explorer is for displaying files and folders on the computer. The users can browse data on the drive, copy, delete, transfer, etc. using the file explorer.
10. Internet browser
It is preinstalled in the windows computer allowing users to surf the internet. This may be for searching anything, online shopping, social media, etc. Windows 10 now has Edge as a browser replacing Internet Explorer.
11. Microsoft Paint
Again an inbuilt program since 1985 allowing users to create, view, and edit an image. There are many tools like crop, resize, and saving in different file extensions.
12. Taskbar
This is for displaying currently opened programs allowing users to switch between them. There is also an option to get the notification, time, network, battery, etc on the right side.
13. Task Manager
This is for providing the details about running applications on the computer and to check the storage of each of them.
14. My Computer
This feature takes you to all your files and drives allowing navigation between them. Here you can edit, manage, move, etc.
15. Recycle Bin
All the files after deleting go here for a temporary period. Users can retrieve the file from here in case they need it back but in a particular time frame only. After deleting the bin, the files are gone forever.
16. Remote Desktop Connection
The users can connect their device to another system and work remotely together.
Main Components of Windows
- Configuration and maintenance
- User interface
- Applications and utilities
- Windows Server components
- File systems
- Core components
- Services
- DirectX
- Networking
- Scripting and command-line
- Kernel
- NET Framework
- Security
- Deprecated components and apps
- APIs
Applications in Windows
- Web Browsers
- Adobe Photoshop
- Adobe Reader
- Messenger
- Media Players
- Games
- Audio/ Video Chatting Apps
- Maps & Calendar
- And many more
Difference between Windows and Linux
| Windows | Linux |
| Users can use the command line by going to the Run dialog box and type CMD and then enter. | The command line is more useful for the administration not for end-users. |
| Less reliable as compared to Linux. | More reliable because of system security, process management, and up-time. |
| A simpler interface makes it easy to use but installation time is more. | Easy for completing complex tasks but complicated installation. |
| Secure but due to a large user base attracts more threats. | More secure as attackers find it difficult to breach. |
| Helps users online with information books for all skill levels. | Offers a large set of books to understand the functions. |
| Many update alerts and odd timing with more time consumption. | Users control the updates completely at their ease. The time to update the computer is less comparatively. |
| The license doesn’t allow software modification and needs a Windows key to install anything. | The license has reusability and the users can modify the software as well. |
Microsoft Windows Help Pages
- Windows 10 help
- Windows 8 and 8.1 help
- Windows 7 help
- Windows Vista help
- Windows XP help
- Windows 2000 help
- Windows NT help
- Windows ME help
- Windows 98 help
- Windows 95 help
- Windows 3.1 and 3.11 help
Important Windows Commands
- Cd – change directory
- help – command help
- cls – clear window
- notepad – windows text editor
- dir – List of the current directory
- type – Text file content
- assoc – display/modify file extensions
- attrib – displays/ change file attributes
- call – calls program file from another location
- color – Text and background color settings
- comp – comparison between two files
- copy – copy files to another location
- date – displays date
- del – delete files
- edit – Run MS-DOS text editor
- exit – close MS-DOS window
- find – search for a word in a file
- move – move files to another location
Advantages of Windows
- The operating system is computer and tablet friendly.
- Switching between programs is possible.
- Users with less technical knowledge can also use it.
- It has the major market share due to Microsoft.
- There is a lot of community support and a wide range of applications.
- This is more useful for organizational functioning as a whole.
- There are more gaming options.
Disadvantages of Windows
- There are a few privacy and security issues.
- The cost of an upgrade is high.
- Many viruses and malware attack windows due to easy access.
- Touch-friendliness is still an issue.
Conclusion
The chances are that you are also using a Windows computer right now. Well, that is the range of Microsoft and we all are aware of it. Thus we don’t know everything about it. Most organizations use Microsoft as the default system and thus everyone should know how to use it properly.
RRB, Insurance exam, Bank Exams, etc. also asks questions from this topic in their mains paper. Some even have practical exams for these concepts. Thus all the applicants should make use of their time and study all the topics carefully.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder
Please share your happy experience on Google