MAC Address
FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
What is a MAC Address?
1. The physical address that uniquely identifies each device on a network is known as the MAC address. We need two addresses to communicate between two networked devices: an IP address and a MAC address. It’s assigned to each device’s NIC (Network Interface Card) that can connect to the internet.
2. Media Access Control, also known as Physical Address, Hardware Address, or BIA, is an acronym for Media Access Control (Burned In Address).
3. It has a globally unique MAC address, which means that no two devices can have the same MAC address. Each device displays it in hexadecimal format.
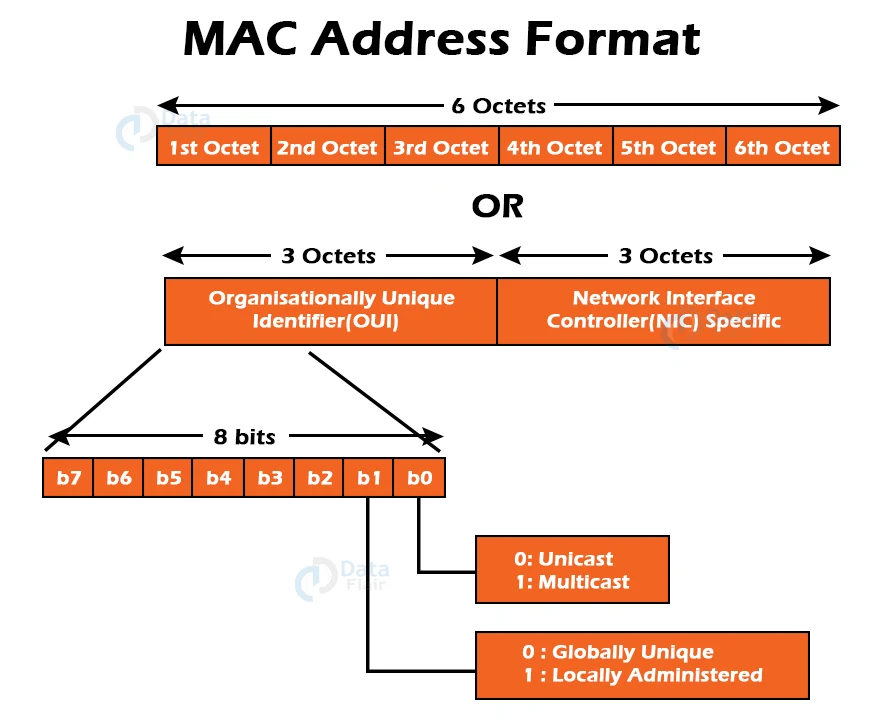
4. It’s 12-digits long and 48 bits long, with the first 24 bits used for OUI (Organization Unique Identifier) and the remaining 24 bits for NIC/vendor-specific information.
5. It operates at the OSI model’s data link layer.
6. It is supplied by the device’s manufacturer at the time of manufacture and is embedded in the device’s NIC, which should not be changed.
7. A logical address is associated with a physical or MAC address using the ARP protocol.
Why do we have both IP and MAC addresses?
Every mac address is assigned to a hardware device’s NIC, which aids in network device identification.
The request to load a page on the internet is responded to and sent to our IP address.
The internet protocol suite operates on different layers for MAC and IP addresses. The MAC address is used at layer 2 to help identify devices that are part of the same broadcast network (such as the router). IP addresses, on the other hand, are used at layer 3 to help identify devices on different networks.
Although we have the IP address to identify the device across networks, we still require a MAC address to locate devices on the same network.
Why are MAC Addresses on a LAN unique?
A LAN network will not function if two or more devices have the same MAC address.
Assume that a switch connects three devices A, B, and C to a network. 11:00:0A:BB:28:FC, 00:00:0A:BB:28:FC, and 00:00:0A:BB:28:FC are the MAC addresses of these devices, respectively. The MAC address of devices B and C’s NICs is the same. If device A sends a data frame to the address 00:00:0A:BB:28:FC, the switch will fail to deliver it to the intended destination because the data frame has two recipients.
MAC Address Format:
It’s a 12-digit or 6-byte hexadecimal number that’s written in colon-hexadecimal notation. It is divided into six octets, each of which has eight bits.
The OUI, or Organisationally Unique Identifier, is made up of the first three octets. The IEEE Registration Authority Committee assigns these MAC prefixes to each organisation or vendor.
Types of MAC Addresses:
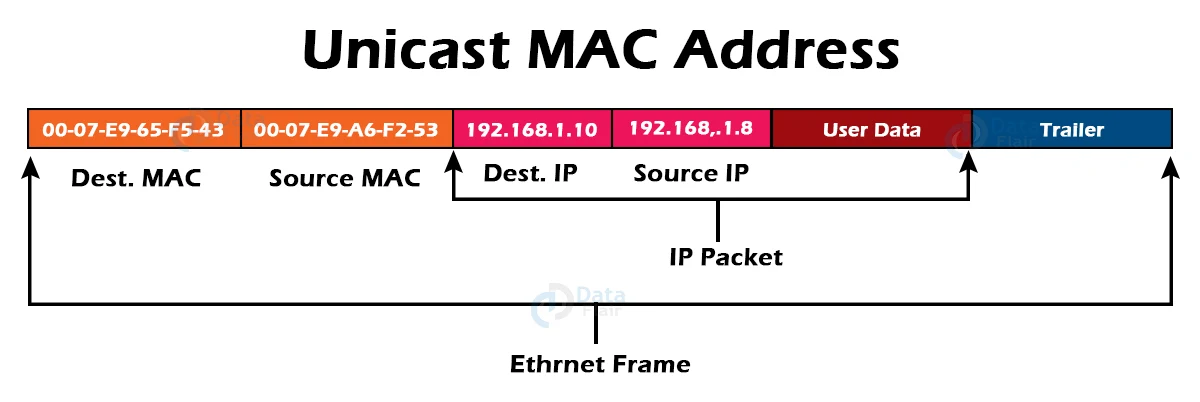
1. Unicast MAC Address:
The Unicast MAC address identifies the network’s specific NIC. A Unicast MAC address frame is only sent out to the interface that is assigned to a single NIC and is thus sent to a single destination device. The frame is intended to reach only one destination NIC if the LSB (least significant bit) of the first octet of an address is set to zero.
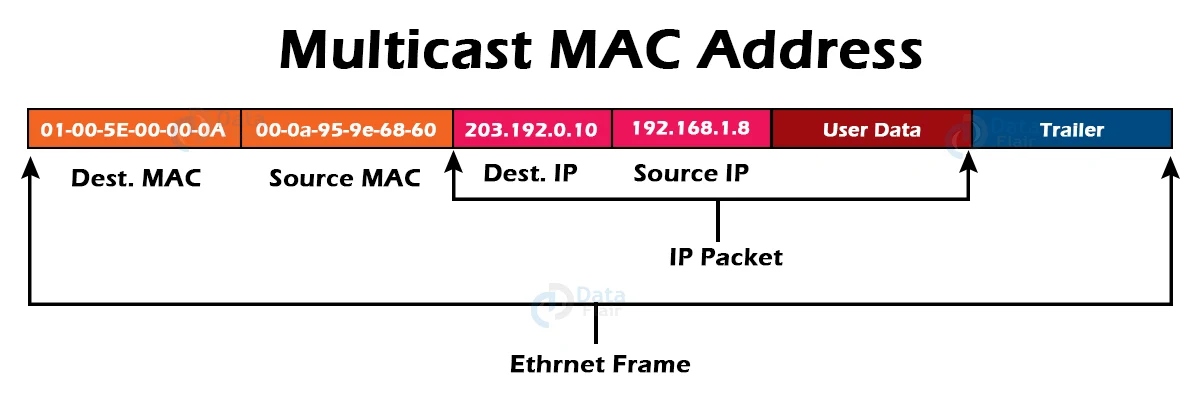
2. Multicast MAC Address:
The source device can send a data frame to multiple devices or NICs using multicast addresses. The LSB (least significant bit) or the first three bytes of the first octet of an address in a Layer-2 (Ethernet) Multicast address is set to one and reserved for multicast addresses. The device that wants to send the data in a group uses the remaining 24 bits. The prefix 01-00-5E is always present in the multicast address.
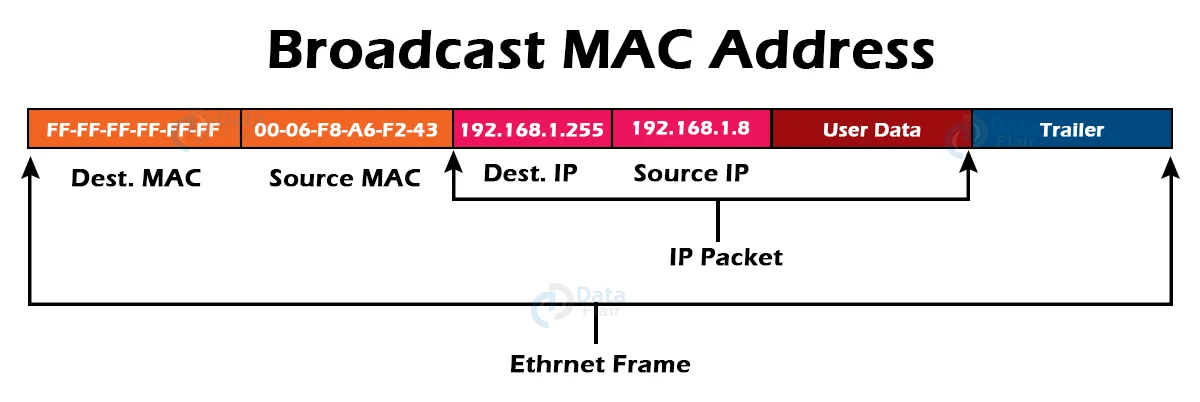
3. Broadcast MAC Address:
It is a representation of all devices in a network. Ethernet frames with ones in all bits of the destination address (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF) are called broadcast addresses. The reserved addresses for the broadcast are all of these bits. Frames with the MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF reach every device on a particular LAN segment. As a result, if a source device wants to send data to all devices on a network, the broadcast address can be used as the destination MAC address.
Finding the MAC Address of a Windows device:
To find the MAC Address of a Windows device, we simply open up the command prompt, and type in the command “ipconfig”.
MAC Address Cloning:
MAC cloning is a method of resolving a device’s ISP connectivity issues. We must set the MAC address of a device’s WAN port to be the same as the MAC address of your PC or another device in this method.
The issue of connectivity arises primarily when we add new MAC addresses to a network, and it can be resolved using MAC cloning.
When installing a service, some ISPs, for example, use the MAC address of your device. The ISP will not recognise the MAC address from the device’s WAN port if we place a router behind the cable modem or DSL modem. In this case, you can either call your ISP provider to register your device’s MAC address, or you can clone the WAN port’s MAC address to match the computer’s MAC address.
Difference between MAC address and IP address:
MAC Address | IP Address |
| MAC is short for Media Access Control. | IP is short for Internet Protocol. |
| It’s the manufacturer’s one-of-a-kind address. | It is the logical address assigned by the Internet Service Provider (ISP). |
| To identify a device within a network, the physical address of the device’s NIC is used. | On the internet, it’s the logical address that identifies a network or device. |
| The data link layer is where it works. | It works at the network layer. |
| It is a hexadecimal address of 6 bytes. | IPv4 addresses are 4 bytes long, while IPv6 addresses are 8 bytes long. |
Summary:
In this article, we explore the concept of MAC Addresses extensively, and we also look at the different types of MAC Address that are currently used. Lastly, we also looked at a direct comparison between MAC Addresses and IP Addresses.e
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google