IPv4 vs IPv6
FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
IP is short for Internet Protocol. Each device connected to a network is given an IP address. Each device communicates using an IP address. It also functions as an identifier since the address is used to identify the device on a network. It specifies the packets’ technical format. Both networks, i.e., IP and TCP, are primarily integrated, and as a result, they are referred to as TCP/IP. It establishes a virtual link between the source and the destination.
An IP address may alternatively be defined as a numerical address issued to each device on a network. Each device on a network is given an IP address so that it may be recognized individually. TCP/IP protocol employs a 32-bit logical address known as IPv4 to simplify packet routing (Internet Protocol version 4).
An IP address is made up of two parts, the first of which is a network address and the second of which is a host address.
What is IPv4?
IPv4 basically means – Internet Protocol, version 4. It is the most recent version and the most widely used IP address. It is a 32-bit address composed of four integers separated by a dot (“.”). Each device has its own address.
Example: 66.94.29.13
The IP address in the above example is represented by octets, which is a set of digits separated by periods. Each number in an octet is between 0 and 255. This address may generate 4,294,967,296 distinct addresses.
The IPv4 address is made up of four sets, which are referred to as octets. Each octet’s bits indicate a number.
An octet’s bits can be either 1 or 0. If the bit is 1, the number it represents counts; if the bit is 0, the number it represents does not.
Representation of 8 bit Octet:
For example, the IP address above (66.94.29.13) would be represented as follows:
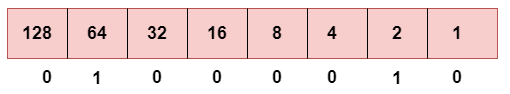
a. First Octet
This is the representation of 66 in binary.
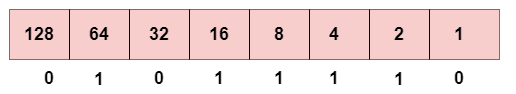
b. Second Octet
This is the representation of 94 in binary.
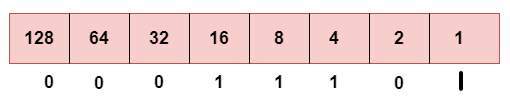
c. Third Octet
This is the representation of 66 in binary.
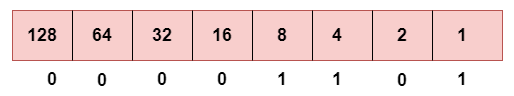
d. Fourth Octet
This is the representation of 13 in binary.
Drawbacks of IPv4:
1. The world’s population is at 7.6 billion people. Every user has many devices linked to the internet, and private businesses rely on it as well.
2. As we all know, IPv4 generates 4 billion addresses, which is insufficient for every device connected to the internet in the world.
3. Although many approaches, including variable-length masking, network address translation, port address translation, classes, and inter-domain translation, have been developed to preserve IP address bandwidth and limit the depletion of IP addresses.
4. These approaches turn a public IP address into a private IP address, allowing a person with a public IP address to access the internet.
IPv6:
IPv4 generates 4 billion addresses, and the developers believe that this number is sufficient, however they are mistaken. IPv6 is the more modern category of Internet Protocol addresses. The primary distinction between IPv4 and IPv6 is the size of IP addresses. IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long, whereas IPv6 addresses are 128 bits in length. IPv6 has a larger address space and a simpler header when compared to IPv4.
It provides the following transition techniques for converting IPv4 to IPv6, which are as follows:
- Dual stacking: It enables us to have both IPv4 and IPv6 versions on the same device.
- Tunneling: In this arrangement, all IPv6 users connect with an IPv4 network in order to reach IPv6.
- Network Address Translation: This facilitates communication between hosts that use various versions of the Internet Protocol (IP).
This hexadecimal address comprises numbers as well as alphabets. IPv6 is capable of providing about 340 undecillion (3.4*1038) addresses due to the use of both digits and alphabets.
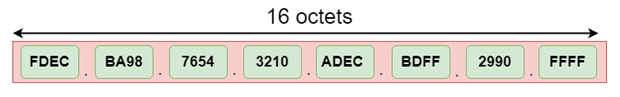
IPv6 is a 128-bit hexadecimal address composed of 8 groups of 16 bits each, separated by a colon. Each hexadecimal character in IPv6 represents four bits. As a result, we must convert four bits at a time to hexadecimal numbers.
Address Format of IPv6:
Comparison of IPv4 vs IPv6:
Parameter | IPv4 | IPv6 |
| Address Length | IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long. | IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long. |
| Fields | IPv4 is a numeric address that consists of four elements separated by a dot (.). | IPv6 is an alphanumeric address made up of eight elements separated by a colon. |
| Classes | IPv4 addresses are classified into five classes: Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class E. | IPv6 does not have IP address classes. |
| No. of IP Addresses | IPv4 addresses are restricted in quantity. | There are a lot of IP addresses in IPv6. |
| Virtual Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) | It is compatible with VLSM (Virtual Length Subnet Mask). VLSM denotes that IPv4 converts IP addresses into subnets of varying sizes. | VLSM is not supported. |
| Address Configuration | It allows for manual and DHCP configuration. | Manual, DHCP, auto-configuration and renumbering are all supported. |
| Address Space | It creates 4 billion distinct addresses. | It creates 340 trillion distinct addresses. |
| End-to-end connection integrity | End-to-end connection integrity is not possible with IPv4. | Here End-to-end connection integrity is possible with IPv6. |
| Security Features | Security in IPv4 is determined by the application. This IP address was not created with the security feature in mind. | IPSEC is a security protocol created for IPv6. |
| Address Representation | The IP address in IPv4 is given in decimal. | The hexadecimal form of an IP address in IPv6. |
| Fragmentation | Senders and forwarding routers are responsible for fragmentation. | Fragmentation is performed solely by senders. |
| Packet Flow Indication | It does not have a technique for identifying packet flows. | It identifies packet flows by using the flow label field in the header. |
| Checksum Field | In IPv4, the checksum field is accessible. | In IPv6, the checksum field is not accessible. |
| Transmission Scheme | Broadcasting. | Multicasting. |
| Encryption and Authentication | It doesn’t support encryption or authentication. | It offers encryption and authentication. |
| No. of octets | It is made up of four octets. | It is made up of 8 fields, each of which includes two octets. As a result, the total amount of octets in IPv6 is 16. |
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the concepts of IPv4 and IPv6. This article covers the structure of the addresses of both IPv4 and IPv6, and lastly, a direct comparison between them.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder
Please share your happy experience on Google