Computer Security Tutorial
FREE Online Courses: Dive into Knowledge for Free. Learn More!
The technology evolution has led to endless opportunities for people to grow. They can enjoy all sorts of benefits with just a click. But with this, they have become very vulnerable as well.
All the information about a person or an organization is easily accessible in cyberspace. Many organizations have already encountered cyber threats due to easy access and less cybersecurity.
This is mainly because of three contributing reasons. The first is easy access to hacking tools on the internet. Second, the end-users can use very high-speed technology for processing.
And lastly, the manuals for hacking are also just a click away, leading to curiosity in younger minds. This is why cybersecurity is very important in the modern age.
And this is for everyone and not just large companies with confidential information and sensitive data. Anyone as an individual can also face consequences if proper cybersecurity measures are not taken.
The main components of the computer that needs protection are – hardware, software, and firmware. Now we will see how cybersecurity is relevant to us, what kind of threats we are prone to and how we can overcome it.
What is Computer Security?
Protecting computers from malicious programs, theft and misuse refers to computer security. This process is to prevent and detect these harmful threats to the computer system. All companies have their own computer security protocol.
Potential Losses due to Security Attacks
1. Losing Data
Most of us use computers every day and store our files on them. This may include information about your work and personal life. Hackers can access all this and steal your data for unethical purposes.
2. Computer Resource Corruption
The attackers can also access all the programs and software on the device making them corrupted. The user may end up losing all their work and might struggle to use the same software in the future as well.
3. Reputation loss
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
The users save all their personal information on their devices. This makes it easy for the hackers to know everything about them and then misuse that information to ruin their reputation. Many companies have been a target of such scams where their official account hacking led to falling in their goodwill.
4. Identity theft
Many times hackers may steal personal information to steal the user’s identity. They will act as the users in the public domain misusing their identity for unethical purposes.
Different Elements in Computer Security
1. Confidentiality
The major focus of cybersecurity is on confidentiality. The idea is to protect information from a third party and allow only authorized access. For example – email chats are end-to-end encrypted but a hacker’s access to them compromises confidentiality.
2. Integrity
The trustworthiness of the data and protection from unauthorized users refer to integrity. Data integrity and cryptography are the two main elements of integrity. Origin and authentication of data is data integrity and cryptography is what protects it.
3. Availability
The accessibility of the resources at the time of the need refers to availability. Only users with authority can access it and the rest receive a denial. For example, the bank employees can see the data with proper authentication id preventing hackers to break in.
Why Do Users Get Attacked?
1. Information Theft and Manipulation
Manipulating the confidential information of an organization is a very common threat today. Hackers do it for personal gain or financial gain and many times even sell it in the black market.
2. Damaging the Reputation
In case of personal issues, hackers try to blackmail users by ruining their information in the domain. Cyberbullying is a very common example of this.
3. Business Disruption
The competition in the market often turns unhealthy. If the organization is doing well, many people try to scam and fraud to gain profits in their name. This is mainly to ruin their goodwill and damage it for the long run.
4. Financial Loss
Just like above, hackers also use organization’s data to hinder their profit-making process. They will misuse the information in such a way that the user faces some financial loss.
5. Achieving Military Objectives
In case of rivalry between the nations, hackers try to steal the political information of the country and use it for propaganda against them. This includes secrets and confidential information about the country.
6. Creating Chaos and Disruption
A lot of times hackers break into systems just to hinder the functioning of an organization. Like terrorists, they try to gain control over the government’s data to create problems in the nation by using confidential information.
7. Demanding Ransom
Hackers also try to get ransom by exploiting users, this is either through their personal information or blocking their access to servers.
8. Propagating Religious Beliefs
Using confidential information to increase prejudice in the country is also very common. Hurting religious sentiments to fuel political agendas is also something hackers do via the internet.
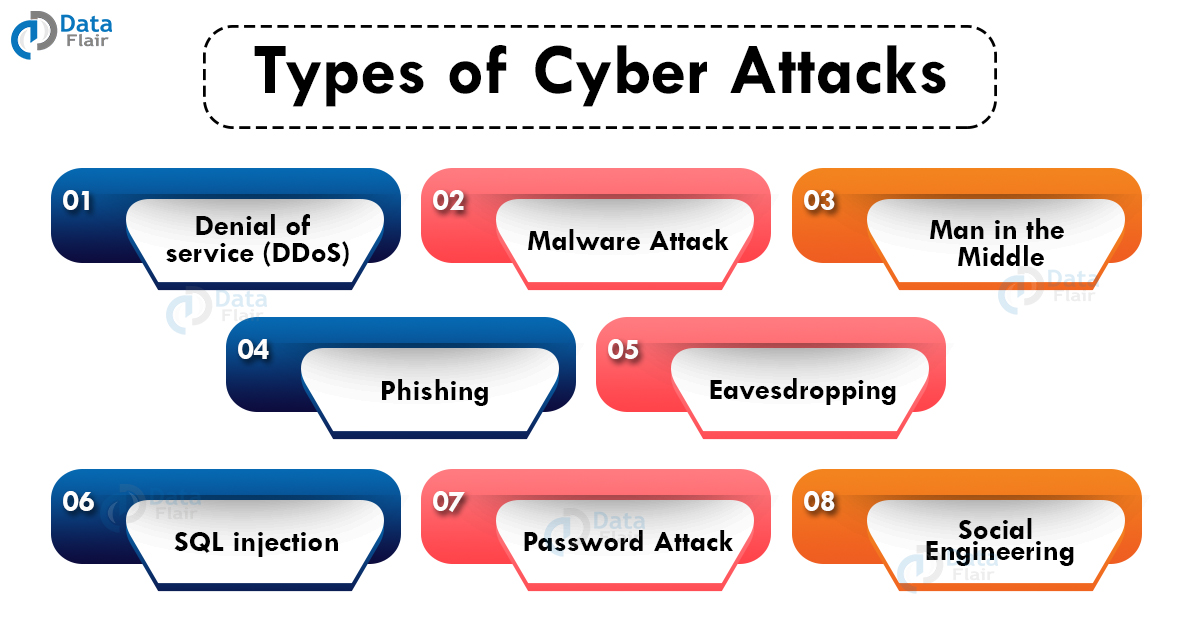
Types of Cyberattacks
The threats by cyber-security have three folds –
1.Targeting systems for financial gain or disruption
2.Political action to gather information
3. Cyberterrorism to cause panic and fear
The main types of cyberattacks are –
1. Denial of service (DDoS)
This kind of attack restricts access by the user to a system or a server. The hackers usually fill up the server with meaningless traffic leaving the users in a problem.
The resources are accessed together by the hacker leading to a jammed server. In this case, even the administrator cannot access the resources.
2. Malware Attack
a. Trojan horse – A code that takes over the system to steal and damage everything on the system.
b. Virus – A malicious code that gets into the computer program by replicating to change its functioning. Melisa virus is a common one that spread itself in the system without acknowledging the user. Some people also refer to it as rootkit.
c. Keylogger – They work by recording the movement on the keyboards and are mostly to steal passwords and accounts details.
d. Worms – An independent program that infects the computer system through network devices like W32.Alcra.F. T.
e. Adware – An advertising software to spread malware.
f. Botnets – A malware network to infect computers without users’ acknowledgment.
g. Spyware – A secret program that tracks all the movements of the user secretly and then uses that information against them.
h. Ransomware – This malware locks the files and data on the system and threatens to delete them if not paid the ransom.
3. Man in the middle
This type of attack includes intercepting communication between the people and then stealing data from their conversation. Open wifi networks are the most common place where this kind of attack takes place.
4. Phishing
This works on the idea of setting a bait to scam people. This may be to get money or any other personal information.
Lottery scams, job scams, etc . are few common examples of phishing. Platforms like emails, text messages, social media, and more are where these messages come from.
5. Eavesdropping
This is like spying as hackers will monitor the system traffic and all the movements of the user on the system. This can be by – Email monitoring, website monitoring, and seeing your download history.
6. SQL injection
This is when an attacker injects an unauthorized input into the SQL statement. But this is only possible on websites where hackers can access the database using your id and password.
7. Password attack
Many hackers try to get your password by –
- Dictionary attack where they try different possible passwords from the dictionary.
- A brute force where they do trial and error to decode the password but is time-consuming.
- Keylogger is again tracking movements on the keyboard to get passwords.
- Shoulder surfing is a physical observation that people do by looking over the user’s shoulder.
- The Rainbow table has precomputed hash values to find passwords.
8. Social engineering
Creating a social situation to get information from the user refers to social engineering. Like getting a call from the mobile company saying your device is in danger. You blindly trust and give out all the information without any verification.
How to secure your computer?
1. Two-way authentication
This follows the layering of security for the authentication process. The users have to go through two steps to verify themselves and then get access to the file.
An example would be a google password followed by a security email on the phone to verify the account. This leads to account protection even if the password is accessible by anyone.
2. Secure passwords
Creating strong passwords is very important so that hackers can’t guess them easily. A few things to keep in mind –
- Have at least 15 characters
- Use capital letters, special characters and numbers
- Be unpredictable
- Try having different passwords for different accounts
- Don’t share a password with just anyone
3. Regular updates
Try to keep updating your software as they have a better defense system. This includes the operating system as well to get protection against the threats.
4. Antivirus
Always have antivirus software in your computer system. Their design prevents, detects, and removes any type of malware. This ensures the protection of the system all the time. Example – McAfee.
5. Firewalls
Ensure that your system has proper firewalls to prevent unauthorized access by anyone. Many hackers try to get in using private networks but firewalls don’t let them enter.
6. Anti-Phishing Tactics
In case you get an unexpected suspicious-looking text, follow this –
- Do not click on the attached link
- Don’t share personal details
- Do not open the attached files
7. Encryption
Converting readable language into an unreadable one only accessible by the receiver refers to encryption. Applications like banking, computer password, and e-commerce transactions use this to secure the users. Users should always ensure that they are using encrypted servers and websites.
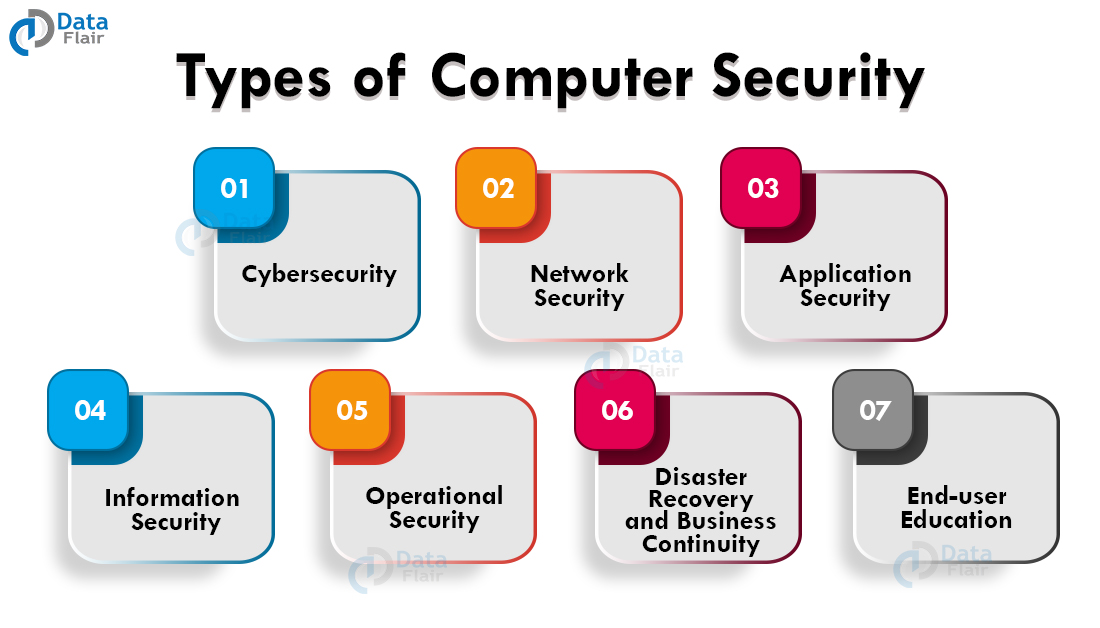
Types of Computer Security
- Cybersecurity is defending all technological devices from online threats. Many categories like mobile computing and business use this term frequently.
- Network security is securing a computer network from any type of cyber attack.
- Application security is protecting software and programs and is usually inbuilt in the applications.
- Information security is responsible for protecting the integrity and privacy of data everywhere.
- Operational security involves protecting the data assets by deciding their storage and accessing procedures.
- Disaster recovery and business continuity is the response of the cybersecurity accident leading to loss of data. The recovery policies define the procedure to continue operations in the organization. Business is the plan by which this operation takes place.
- End-user education refers to the measures that the user takes on a personal level to protect themselves from these threats.
End-user protection
The most important aspect is the way users protect themselves in cyberspace. Cybersecurity helps them by –
- Following cryptographic protocols to encrypt all the messages and data. This protects the information during transmission and reduces the chances of theft.
- Security software also scans computers for malware and codes. They identify them and remove them immediately protecting all the data. This even save the user from the Master Boot Record where data is encrypted and vanishes automatically.
- They also work on real-time malware detection using heuristic and behavioral analysis to monitor. Any change or disturbance in the system functioning alerts them and they immediately start with the inspection.
Computer Security Terminology
- Unauthorized access – Gaining access to data, server, etc. without having the permission of the administrator.
- Hacker – A person who exploits people by breaking into their device.
- Threat – An action that may lead to a breach in cybersecurity.
- Vulnerability – A problem or an error that leads to undesirable events in cybersecurity.
- Attack – An assault by someone on cybersecurity.
- Antivirus or Antimalware – program to protect devices from malicious software.
- Social Engineering – A technique to steal data using psychological manipulation and social scenes.
- Virus – A malicious software that downloads on its own on the computer for unethical purposes.
- Firewall – A filter to manage network traffic rules.
Conclusion
As highlighted many times, the users are the ones responsible to take all the measures of cybersecurity. Antivirus programs are still evolving and are getting better at combating all the threats. This is why cybersecurity knowledge is very important to protect yourself.
Competitive exams test the basic computer knowledge of the candidates to see if they can handle the tasks or not. Also, protecting data is something that will be useful in every job. Thus, this article is to help all the applicants in the long run.
You give me 15 seconds I promise you best tutorials
Please share your happy experience on Google