Basics of Computer Network – Evolution, Topologies and Types
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Skills, Zero Cost. Enroll Now!
A network connecting multiple devices to share information and data is a computer network. This network is to share information, access and receive files, and connect external devices like printers and fax to facilitate more options for the user. This interconnection requires certain hardware to set up, they are – Network Cables, Distributors, Router, Repeater, Hub, Switch, Bridge, Modem and Network Card.
The network cable connects computers, the most common one is Category 5 cable RJ-45. The distributor connects the computer to other components like printers, scanners, fax machines, etc. A router is the main component that has ports allowing computers to connect with others using network cables while a modem converts digital signals into analog.
The network repeater generates incoming signals. The network hub joins devices using only one segment to interact. The network switch connects computers to LAN while the network bridge reads the packet description to deliver it correctly. Lastly, the network card that allows the computer to connect to a network.
It is of two types – Internal and External Network Cards. The internal network cards go inside the motherboard slot and they use either Peripheral Component Interconnect or Industry Standard Architecture. While the external network cards may be wireless or USB-based. These were the basics of a computer network. Now let us get into detail about what all it consists of –
Network Topology
The layout arrangement is different in all sorts of networks. The topologies connect computers in a certain manner making them different from the other network. The most common one is ring topology due to the use of ethernet in LAN and WAN. Point to Point topology also exists but it only connects one computer to another. An extension of this more computers in one line leads to a line topology. And the mixture of more than one type of topology creates a hybrid topology. Some main topologies are – Bus, Star, Mesh, Tree, and Ring.
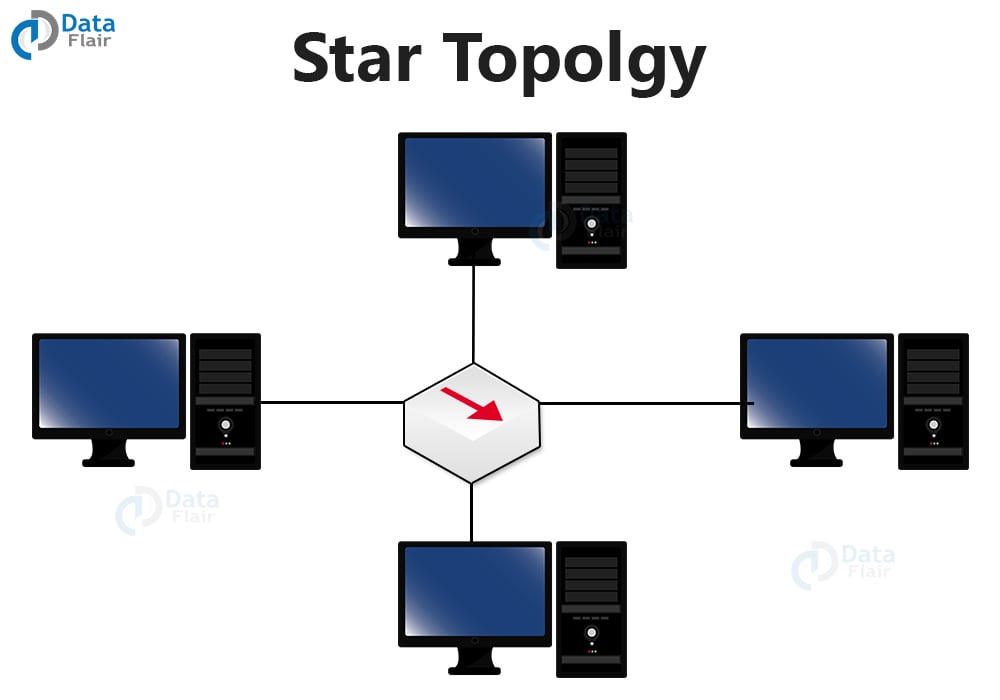
1. Star Topology
This type of network has a central node that connects the computers but at the same time maintains an independent connection with each computer. Thus even if one device disconnects, the functioning of the others remains the same. This requires large rolls of cable to establish a proper connection.
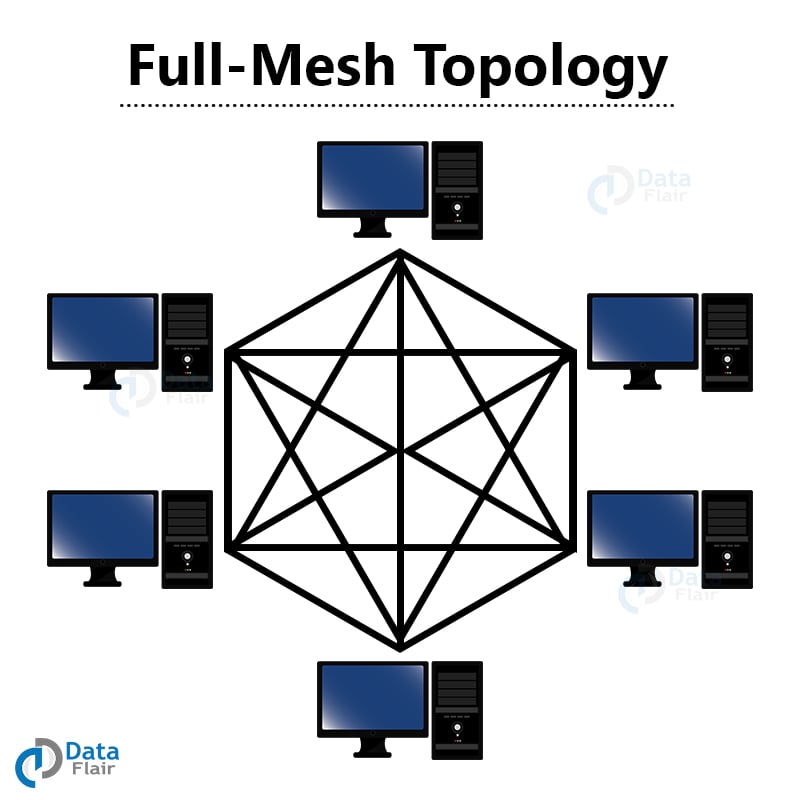
2. Full Mesh Topology
This network has each computer interconnected with one another. This allows for transmissions and distribution even if one connection goes down. It is commonly used in wireless networks. There are many wires in this connection which may lead to confusion.
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
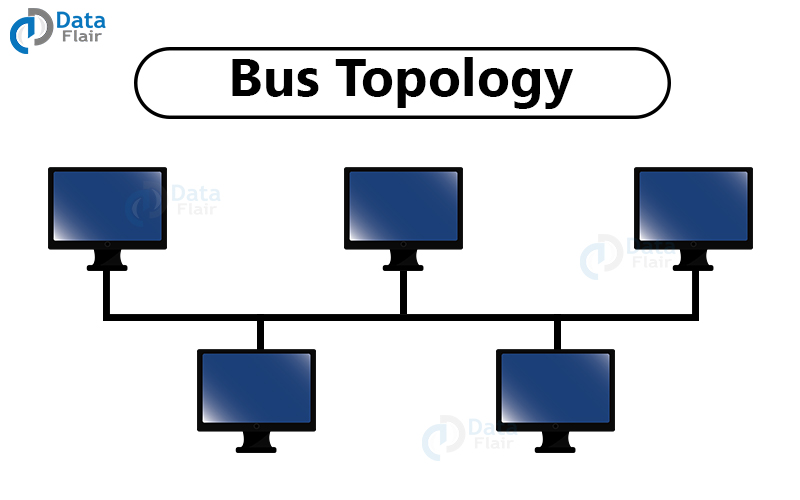
3. Bus Topology
In this type of network, one cable connects all the computers thus every piece of information passes through each computer to reach the end. The cable needed is very less but a single problem in even one computer can break the entire network.
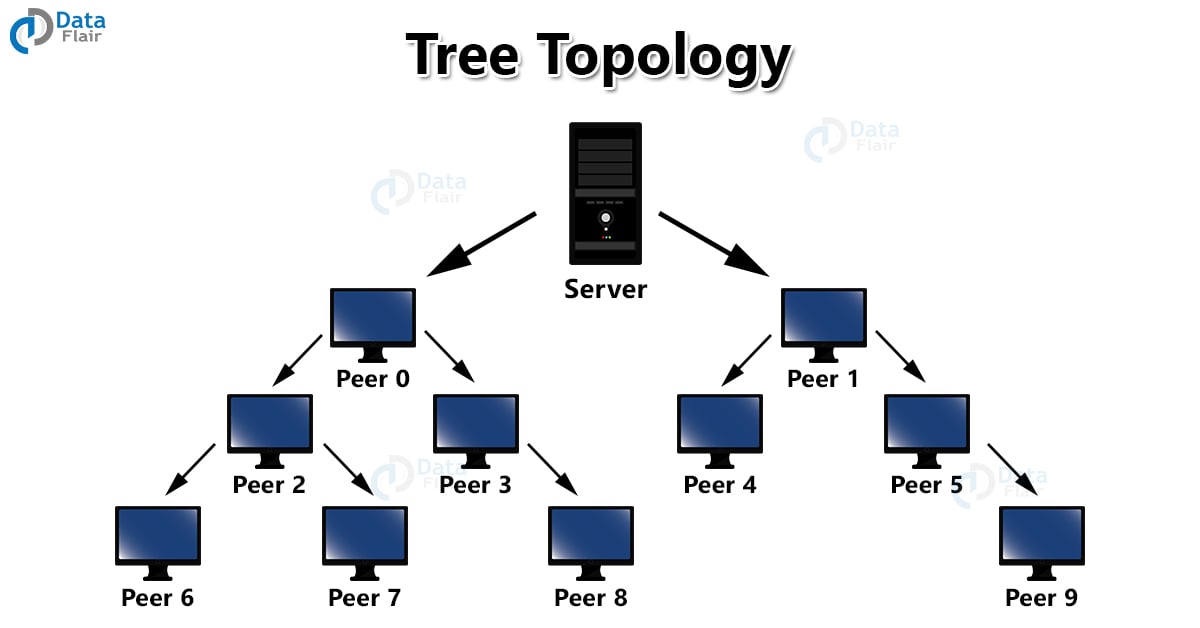
4. Tree Topology
In this type of network, there is a hierarchy of computers connected by one main computer that has a connection to two which goes down connecting to more. Disconnection of one computer will only affect one side and not the entire network. The cable needed is more due to multiple connections.
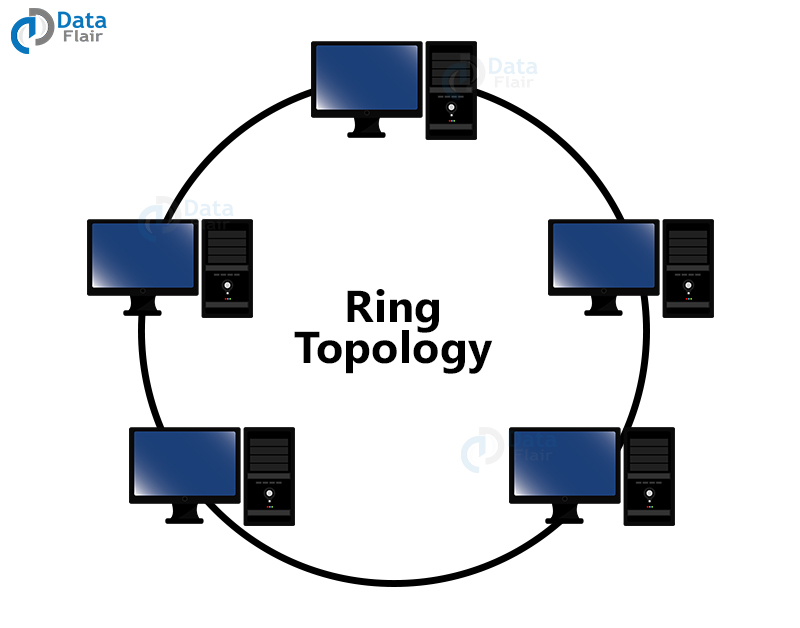
5. Ring Topology
Very similar to the bus topology, it has a single cable but the first computer connects back to the last computer on the network forming a circle. This is a complicated process as the signal may end up taking multiple rounds before reaching the final recipient.
Network Design / Network Types
Like network topology differs, the design of the network also varies. They are either client/server or peer-to-peer networks. Client/server networks have central servers for everything while Peer-to-peer have devices to support the same functions. There are fours most important types of network –
1. Local Area Network
LAN is a local network connecting computers and devices in a very small geographical area like home, school, small offices, etc. Very commonly used for sharing resources like files, games, and other applications. It allows one type of transmission by connecting one computer to another. The number of computers cannot exceed 5000 in this case.
Characteristics of LAN
- Allows full control by the owner as it is a private network.
- It is comparatively fast in speed due to the smaller area.
- Works well for token rings and ethernet.
Advantages of LAN
- Many computer resources can share local area networks reducing hardware purchase costs.
- The licensed software can also work on multiple devices reducing the cost again.
- One hard disk can store the data of all of the computers in the network.
- Transfer of data and information is instant and easier between networked computers.
- Data is secure as it is in one place only.
- One internet connection works for all the networked computers.
Disadvantages of LAN
- The installation charges of the setting cost quite high.
- The admin has access to all the files reducing the privacy of the user.
- An unauthorized person can access all the data in one go.
- It needs daily administration as there are many setup-related issues.
2. Personal Area Network
This kind of network connects computers for solely personal use with 10m of range. The man behind its development is Thomas Zimmerman. Personal devices like laptops, mobile phones, and play stations usually use this network.
Characteristics of PAN
- They are of two types – wired personal area network and wireless personal area network.
- Wireless networks use WiFi, Bluetooth but have a very low range.
- The wired network uses USB.
- Body area networks move with the person like a mobile network.
- An offline network is a home network for connecting printers, tv, etc.
- Small home offices use VPN-based corporate networks.
Advantages of PAN
- They are most secure and safe
- Has a short-range solution becoming faster
- Strictly restricted to limited space
Disadvantages of PAN
- Many device connections may lead to bad or poor speed.
- The distance limits the user space of the network
3. Metropolitan Area Network
It has a computer connection across a larger space like a city, university campus, etc. Unlike LAN it moves beyond a building or site. It can cover approximately several miles of area.
Characteristics of MAN
- Covers towns or cities within 50 km range
- Uses optical fibers or cables as a medium
- The Data rates are comparatively for computing applications.
Advantages of MAN
- High-speed carriers establish a fast connection.
- Support large networks giving access to WAN.
- The data transmission can be multidirectional.
- Includes selected areas or an entire city.
Disadvantages of MAN
- The cable requirement is very high due to the larger space.
- The large setting invites more hackers.
4. Wide Area Network
This network is spread over a large geographical area such as states and countries. It uses telephone lines, fiber optic, or satellite links to establish a connection. The Internet remains the biggest WAN of all time. Government, large businesses, universities, etc uses WAN the most. And mobile broadband, last mile, and private networks of companies are all examples of WAN.
Characteristics Of Wide Area Network
- They have a large capacity and connect many computers together.
- They are inherently scalable.
- Sharing of regional resources is possible for them.
- Have uplinks connecting LANs and MANs to the Internet.
Advantages Of Wide Area Network
- There is a large geographical area allowing many branches to use the same network making the working space more efficient and effective.
- It allows users to store centralized data allowing the admin to not pay for emails, files, or backup servers.
- Due to the presence of live servers, the data gets updated every second.
- The transmission of messages is fastest here as we all can see with today’s messaging applications.
- The users can also share software and hard drives over this network.
- Allows MNCs to do business globally.
- Increase the productivity of an organization due to high bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Wide Area Network:
- There is a security problem due to all technologies coming together.
- Needs expensive antivirus and firewall software to secure sensitive information about the organizations.
- The setup cost is very high due to the large geographic area.
- And due to the same reason, it becomes tougher to troubleshoot problems.
Internetwork
When two or more types of the network come together, they create an internetwork. It is very common in all sorts of sectors using Open System Interconnection. They are of two types – extranet and intranet. Extranet has intent protocols like TCP to share information by users with the login credentials. MAN and WAN fall under this category.
While intranet is a private network using TCP but only accessible to members of a particular organization. The Intranet is more easy and cheap to use for communication like email and meetings. It allows collaboration with authorized users. There is platform independence due to neutral computer architecture. And it is cost-effective as the same devices are accessible to all computers.
Some other important types of networks are –
1. WLAN
This is a wireless local area network for linking devices using wireless communication in a defined space. Users can move around in the area using this connection and it has IEEE 802.11 standards.
2. Storage-Area Network
This type of network allows users to have a combined, restricted data storage mainly used in storage devices like disk array, tape libraries, etc.
3. System-Area Network
System Area Network is a local network offering high-speed connection as it operates on a single system only.
4. Passive Optical Local Area Network
POLAN is a technology allowing the integration of structured cabling to resolve ethernet protocols and network app issues. It uses an optical splitter for separating the signals and then combining them into one.
5. Home Area Network
Interconnection of two or more computers inside a house creates this kind of network. The owner connects multiple counters to share files, data, and other information and connects external devices as well.
6. Enterprise Private Network
This network is for businesses looking for secured locations to use computer resources throughout the network.
7. Campus Area Network
This is an interconnection of LAN in a limited area like a university campus where different departments connect using this network.
8. Backbone Network
It is not an entire network but a part of it connecting pieces and information to create a path for exchange.
9. Virtual Private Network
A private network that uses a public network for connecting sites and users with virtual connections. It is a free/paid service for keeping the browser secure over public wifi hotspots.
Network Protocols
The languages that computers use to communicate are network protocols defining their function and grouping. Each network can have multiple protocols to facilitate the use of different applications. TCP and IP are the most common ones.
Wired and Wireless Networks
The protocols may be wired or wireless though now most people use wireless technology only. Wifi is the most common one for computer networks as many wireless gadgets can stay connected to one other using it. Mobile networking is also an example of this to build a larger network.
Evolution of Computer Networking
The digitisation requires certain transformation for computer networks as well. The architecture of the new age networking is –
Software-defined – SDN
The programming of the softwares has changed and has become more automated. The traffic control of these softwares is in the hands of the central software team allowing them to keep diversifying to meet the dynamic conditions.
Intent-based – IBN
The intent of networking provides agility to the host to achieve certain sets of objectives by automation, deep analysis, problem troubleshooting, security and bringing together all businesses.
Virtualized
The virtuality of the networks also has physical network infrastructure underneath creating a layered network. Each of the layers has specific security or quality roles to meet.
Controller-based
They ensure that the network is secure and safe by using multiple configurations, vigil monitoring, and more to ensure the best performance of the organisation. The controllers make the work of an organisation easy.
Multidomain Integrations
Many organisations have networking domains for different locations interacting with each other using controllers. This interconnection is usually to exchange information and data within an organization by keeping safety in mind.
Service Computer Networks
The cloud and software tech has become very popular due to internet networking. It includes
network segmentation, firewalls for security. Creates a sophisticated network that is secure and safe as well.
Key Networking Terms
- Open System Interconnection – a model for reference setting protocols and functionalities of the network. It has an open and closed system. An open system network connection and communication while the closed system for vice versa.
- Nodes – devices that can send and receive network packets.
- Network packets – the data that the nodes send.
- Network address translation – routers use it to provide internet service to devices in public IPs.
- Dynamic host configuration protocol – gives dynamic IP addresses to every host with an internet service provider
- Internet service providers – companies responsible for providing internet connection
- Hostname – the unique name of the network with a unique device
- Internet Protocol address – address of network on the internet browsers providing it with an identity
- Media Access Control address – a physical address becoming a unique identifier of each host with its network interface card
- Port – a channel to transfer data and information from one end to another
Conclusion
The computer networks consist of multiple details like their topology, tier types, the protocol it follows, the functions it has and much more. All these things are covered in the above article keeping in view the important exams like SBI PO, IBPS, RBI Exams, and RRB as they have computer aptitude as part of their syllabus.
Thus this article is relevant for all the applicants for the above-mentioned exams. All the basic concepts are briefly written to make your exam preparation process simpler.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google


excellent