Azure Forefront Identity Manager
Free AWS Course for AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C01) Start Now!!
FREE Online Courses: Dive into Knowledge for Free. Learn More!
In today’s article, we will talk about Forefront Identity Manager which is a popular tool. It was used on behalf of Microsoft Identity Manager. So, in this article, we will completely discuss Azure Forefront Identity Manager.
Let us begin.
What is a Forefront Identity Manager in Azure?
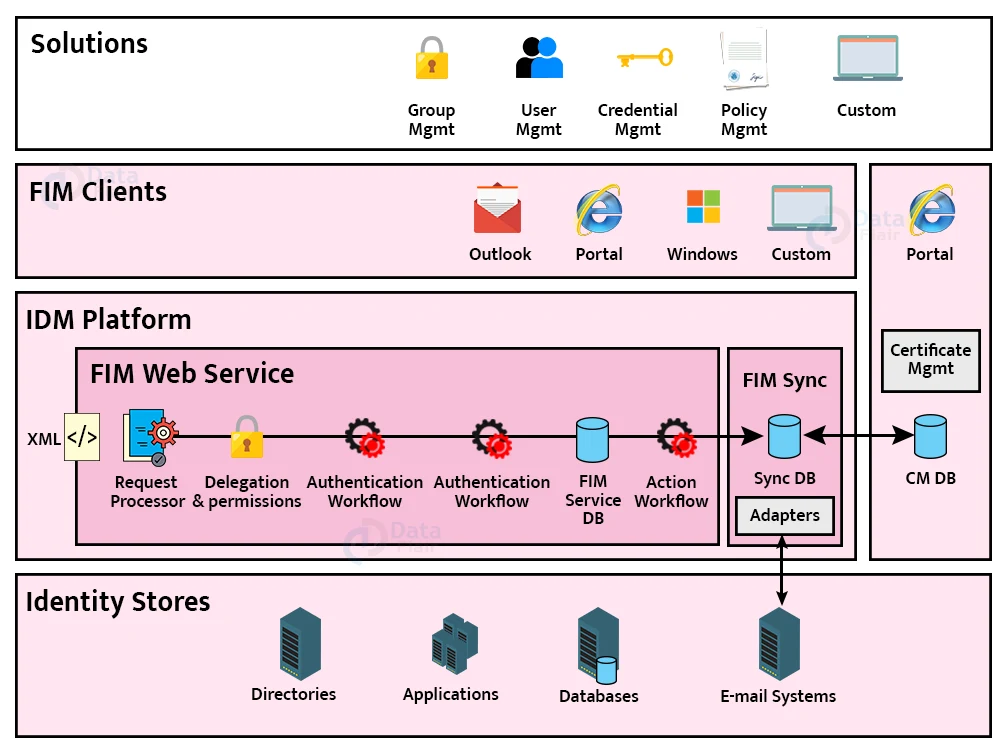
Microsoft ® Forefront Identity Manager 2010 (FIM) provides connectors, delegation, workflow, and a Web service API on a common platform called the Identity Management Platform (IDM Platform).
The IDM Platform enables inventors to integrate stoner operation, credential operation, policy operation, and access operation conditioning. FIM builds on the technology of the synchronization machine that was included in Microsoft ® Identity Lifecycle Manager 2007 (ILM 2007) to attend and meet data among numerous different external databases and systems through an operation agent frame.
The FIM Service builds upon that functionality by furnishing a gate that provides turnkey results for the credential, access, stoner, and policy operation.
The FIM Service also provides Web service APIs, which inventors may use to produce custom guests that interact with FIM. The API also provides extensible conditioning, workflow, and schema.
The components of the IDM Platform and their relationships to external databases and client applications are depicted in the diagram below.
Workflows and Activities in Azure Forefront Identity Manager
Users can design workflows to model business processes and attach them to requests in FIM. By monitoring how FIM workflows are conducted, a user can then audit compliance with business procedures.
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
The Process Designer, a graphical user interface provided by the FIM Portal, is used to model business procedures by creating workflows that contain numerous activities.
In addition, Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) activities and workflows can be used in FIM. Within the Microsoft Visual Studio 2008® development environment, developers who use the Microsoft.NET Framework can create new WF activities.
Following are some examples of activities:
- Approval is a process. An approval activity can be used to obtain permission from one or more people to continue a workflow.
- This is a notification activity. People are notified of a workflow process via a notification activity.
Authentication, authorisation, and action workflows can all include activities that can be mapped to events.
Objects and Request Processing in Forefront Identity Manager
All users, groups, requests, workflows, and other coffers used in FIM are stored as objects in the FIM Service database.
These objects can be modified through Produce, Read, Update, and Cancel ( Smut) requests made to the FIM Service IDM Platform.
For further information, see Web Services Overview. Web service requests are turned into Request objects in the FIM system.
However, authentication, and authorization checks, If a Smut request on the object store passes the rights.
After this step, fresh” Action” workflows (for illustration, announcement conditioning) are run.
These workflows can include conduct performed by the synchronization machine, which manages synchronization of object changes with identity stores external to FIM.
Management Policy, Rights and Events in Forefront Identity Manager
Management Policy Rules (MPRs) are a technique for modeling business processing rules for incoming requests to the FIM Service.
They model the management policy for objects maintained by FIM.
Permissions for requesting operations on FIM objects, as well as the workflows triggered by these requests, can be defined by each Management Policy Rule.
Sets in Forefront Identity Manager
FIM groups items (such as persons and groups) into Sets so those management policies may be applied to the correct resources.
A single object can be part of an infinite number of sets. Sets can be defined either dynamically, based on XPath searches or object attribute values, or statically, as a collection of specified resources. They can also be defined as a mix of all of these characteristics.
Expanding Forefront Identity Manager Functionality
FIM’s functionality can be extended in a number of ways by developers:
- Developers can use web service APIs to build bespoke applications that communicate with FIM and perform CRUD activities on the FIM Service database.
- The Web service APIs allow users to change FIM configuration and behavior because configuration, synchronization, management policy, and the remaining resources are all kept as objects. Using WS-Metadata Exchange, get the FIM Service Schema. End users can see custom objects and attributes if an FIM administrator modifies the portal.
- There is a default object schema available. However, CRUD operations on the FIM Service database can be used to modify and extend the structure.
- Visual Studio can be used to create custom workflows and activities, which are then launched by Windows Workflow Foundation.
- Management agents that communicate with the synchronization engine and external databases and systems can be established. More information is available in the MSDN Library documentation for ILM 2007.
- The Certificate Management Developer Reference for Forefront Identity Manager adds functionality for managing strong credentials like smartcards. Support for third-party certification authorities is included in the FIM 2010 edition.
Forefront Identity Manager 2010 Design Process
This article explains how to plan a Forefront Identity Manager infrastructure. The following fundamental decisions and tasks are addressed in the guide:
Identifying which FIM features will be required, as well as the related data sources and user population in scope, to define the project scope. The features and scope will be mapped into the required FIM server roles.
FIM Synchronization Service, FIM Service, and Certificate Management infrastructure design.
The placement and fault tolerance of the supported SQL Server databases are being planned.
Following the steps in this guide should result in a design that is adequately sized, configured, and located to offer the stated business benefits while also taking into account the system’s performance, capacity, and fault tolerance.
This article provides information about the most common circumstances that someone constructing an FIM infrastructure will face.
Prior to deployment, customers should consider having their architecture assessed by Microsoft Customer Service and Support since that organization is best suited to comment on the supportability of a given design.
This guide covers the following decisions and/or activities that must be made as part of the FIM planning process.
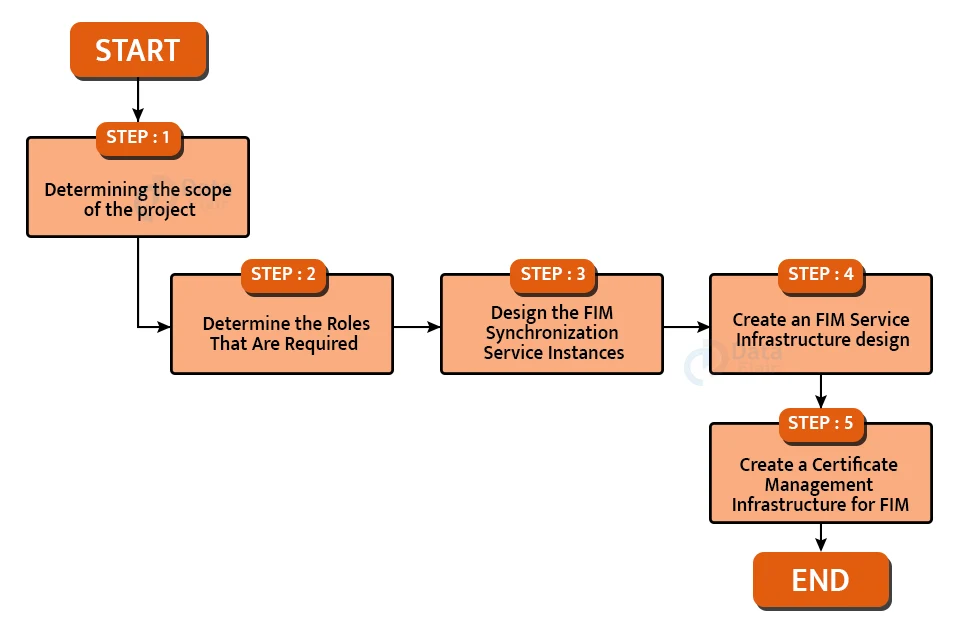
The five steps listed below constitute the most important design components of a well-thought-out FIM:
1: Determining the scope of the project.
2: Determine the Roles That Are Required
3: Design the FIM Synchronization Service Instances
4: Create an FIM Service Infrastructure design
5: Create a Certificate Management Infrastructure for FIM.
Some of the items on this list indicate choices that must be made. If this is the case, a list of commonly used response options will be displayed.
Other things on this list are chores that need to be completed. These issues are addressed because their presence is necessary for the infrastructure design to be completed.
The phases in developing an FIM infrastructure are depicted graphically in Figure 1.
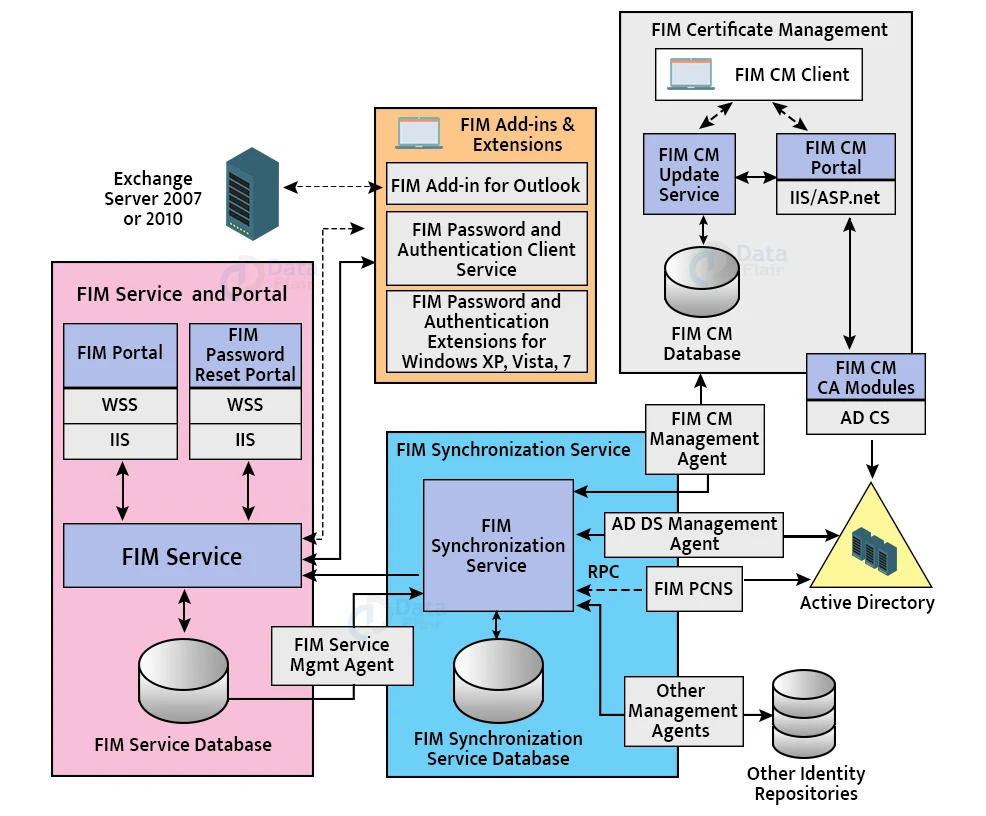
Below image depicts the major components of an FIM architecture.
Scenarios That Apply
- Organizations who want to adopt FIM but don’t have an identity life-cycle management solution.
- Organizations that are planning to switch from another identity life-cycle management system to FIM.
- Also, Organizations that require the Encrypting File System (EFS) Lifecycle Certificate signing service, smart card management, and user administration for applications like encrypted mail.
- Upgrades from Microsoft Identity Lifecycle Manager (ILM) 2007 to Microsoft Identity Lifecycle Manager (FIM) 2010.
Why was the Forefront Identity Manager got Discontinued?
Microsoft’s historical identity management solution is Forefront Identity Manager. Microsoft Identity Manager, an upgraded IAM solution, was released in 2016. Forefront Identity Manager support stopped in October 2017.
Conclusion
Finally, we have reached the last section of today’s article. We hope you liked this article and gained valuable information about Microsoft’s Forefront Identity Manager. In the further articles we will discuss several topics of Azure.
If you are Happy with DataFlair, do not forget to make us happy with your positive feedback on Google