FREE Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
An unguided transmission sends electromagnetic waves without the need of a physical medium. As a result, it is sometimes referred to as wireless transmission.
Air is the medium through which electromagnetic energy can freely travel in unguided transmission.
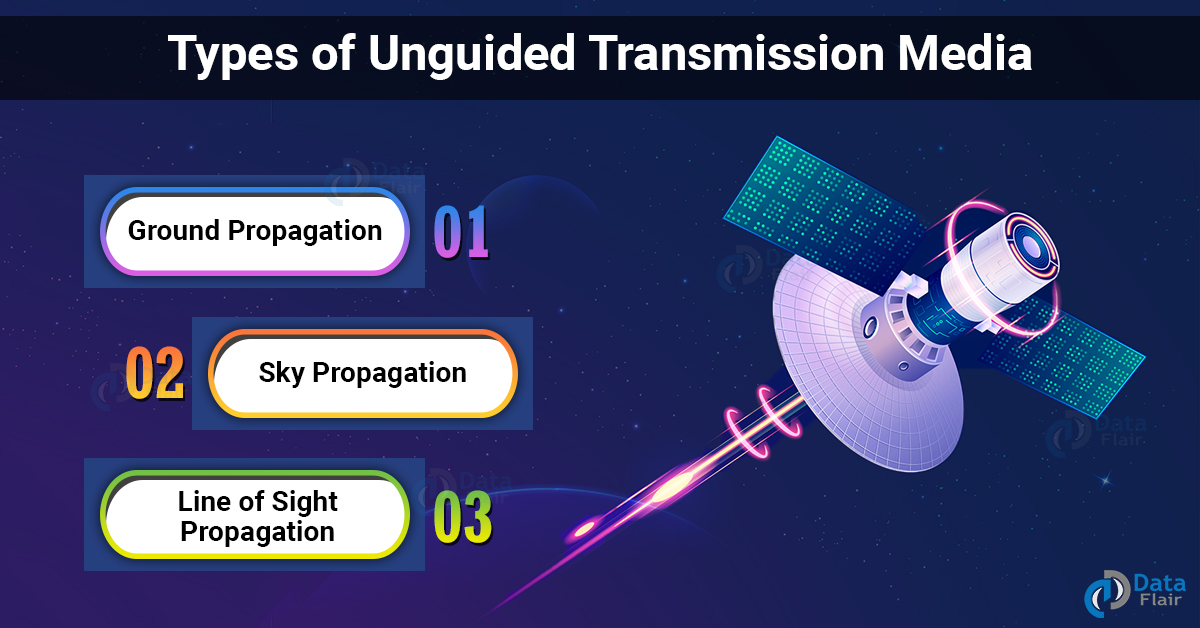
Types of Unguided Transmission:
Unguided Transmission can be achieved in one of three ways:
1. Ground Propagation:
Radio waves in this case go through the lowest part of the atmosphere, touching the Earth. These low-frequency waves radiate from the transmitting antenna in all directions, following the curvature of the globe.
2. Sky Propagation:
Higher-frequency radio waves are sent into the ionosphere and reflected back to Earth in this process. This form of transmission permits transmitting across longer distances while using less power.
3. Line of Sight Propagation:
Very high-frequency transmissions are delivered in straight lines from antenna to antenna in this type.
Classification of Waves used for Unguided Transmission:
1. Radio Waves:
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
- These are electromagnetic waves that may be transmitted in all directions in free space.
- Radio waves are omnidirectional, which means that signals travel in all directions.
- Radio waves have frequencies ranging from 3 Khz to 1 Khz.
- In the case of radio waves, the sending and receiving antennas are not aligned, thus the wave sent by the sending antenna can be received by any receiving antenna.
- FM radio is one example of a radio wave.
Applications of Radio Waves:
- When there is only one transmitter and numerous recipients, a radio wave is helpful for multicasting.
- Radio waves are used by FM radio, television, and cordless phones.
Advantages of Radio Waves:
- Radio transmission is mostly utilised for wide area networks and mobile phones.
- Radio waves may penetrate barriers and cover a vast area.
- A greater transmission rate is provided through radio transmission.
2. Microwaves:
Properties of Microwaves:
- Frequency Range:
- The frequency range of terrestrial microwaves ranges from 4-6 GHz to 21-23 GHz.
- Bandwidth:
- It offers bandwidths ranging from 1 to 10 Mbps.
- Short distance:
- It is a low-cost option for short distance travel.
- Long distance:
- It is costly since a taller tower is required for a longer distance.
- Attenuation:
- The loss of a signal is referred to as attenuation. It is influenced by ambient factors as well as antenna size.
Advantages of Microwave Transmission:
- Microwave transmission is less expensive than cable transmission.
- It does not need the acquisition of land since the installation of cables does not involve the acquisition of land.
- Because installing cable in terrain is a challenging operation, microwave transmission allows for convenient communication.
- Microwave transmission can be used to communicate across oceans.
Disadvantages of Microwave Transmission:
- Eavesdropping:
- Eavesdropping makes communication unsafe. Any unauthorized user with his own antenna can capture the signal in the air.
- Out of phase signal:
- Using microwave transmission, a signal can be shifted out of phase.
- Weather condition:
- A microwave transmission is vulnerable to weather conditions. This implies that any environmental disturbance, such as rain or wind, might cause the signal to be distorted.
- Bandwidth allocation:
- In the case of microwave transmission, bandwidth allocation is limited.
Types of microwaves:
a. Terrestrial Transmission:
- Terrestrial microwave transmission is a method of transmitting a concentrated and focused beam of a radio signal from one ground-based microwave transmission antenna to another.
- Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from 1GHz to 1000GHz.
- Microwaves are unidirectional because the transmitting and receiving antennas must be aligned, resulting in narrowly focused waves produced by the sending antenna.
- Antennas are installed on towers in this example to deliver a beam to another antenna located kilometres distant.
- It is based on line-of-sight transmission, which means that the antennas installed on the towers are in direct sight of each other.
b. Satellite Transmission:
- A satellite is a physical entity that orbits the Earth at a fixed altitude.
- Satellite communication is more dependable nowadays since it is more adaptable than cable and fibre optic technologies.
- Using satellite communication, we can connect with any location on the planet.
Advantages of Satellite Microwave Transmission:
- A satellite microwave has a larger coverage area than a terrestrial microwave.
- The satellite’s transmission cost is independent of the distance from the centre of the coverage region.
- In mobile and wireless communication applications, satellite communication is employed.
- It is simple to set up.
- It is utilised in many different applications, including weather forecasting, radio/TV signal transmission, mobile communication, and so on.
Disadvantages of Satellite Microwave Transmission:
- Satellite design and development need more time and money.
- The satellite must be monitored and operated on a regular basis in order to remain in orbit.
- The satellite has a lifespan of 12-15 years. As a result, another launch of the satellite is required before it becomes inoperable.
3. Infrared Waves:
- Infrared transmission is a wireless technique used for short-range communication.
- The frequency range for infrared wave transmission varies from 300 GHz to 400 THz.
- It is used for short-range communication, such as data transmission between two cell phones, TV remote control operation, and data transfer between a computer and a mobile phone that are both in the same confined area.
Characteristics of Infrared Transmission:
- It has a large bandwidth, therefore the data rate will be quite high.
- Infrared waves are unable to permeate the walls. As a result, infrared communication in one room cannot be disturbed by infrared signals from nearby rooms.
- Infrared communication gives greater security while causing the least amount of disturbance.
- Outside the building, infrared communication is unreliable because the sun’s rays interfere with the infrared signals.
Summary:
In this article, we covered the topic of Unguided Transmission Media. We looked at the classification of unguided transmission based on the method of transmission. We also looked at the various types of electromagnetic waves used for unguided transmission, and also the various characteristics of each wave.