FREE Online Courses: Your Passport to Excellence - Start Now
When dealing with a large network or a very long-distance data transmission, we need the assistance of external hardware. As a result, we need a specific path for our data packets to follow. Because there are so many options for which road to pursue, we must choose one. Switching refers to the process of determining the path via which our data packets will be sent. Let us learn switching
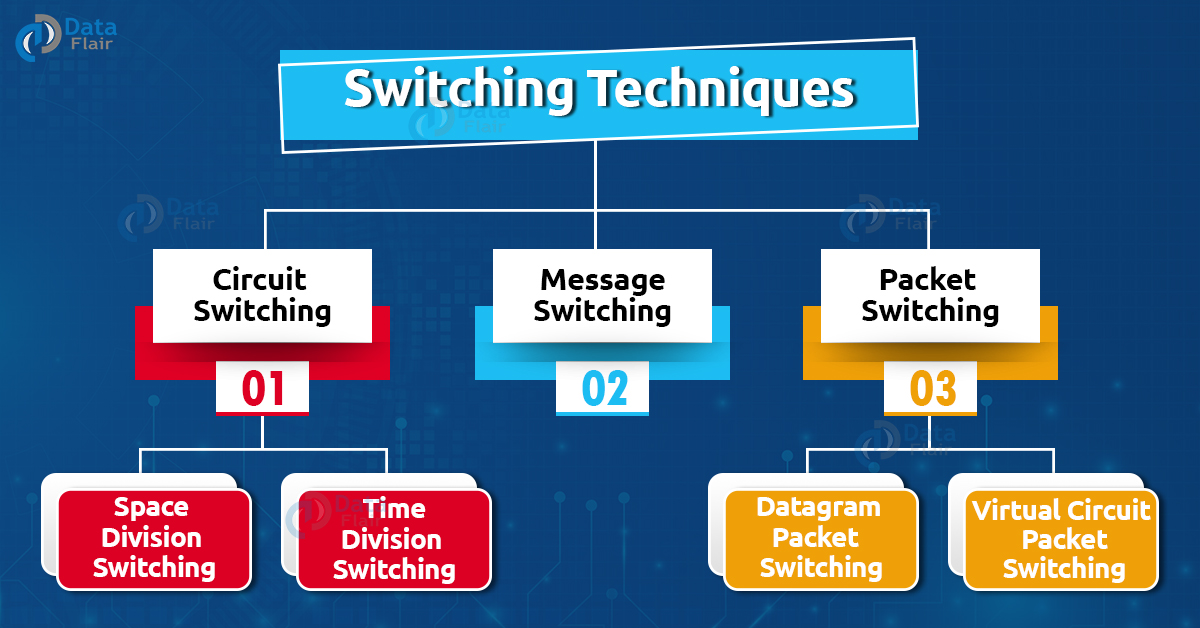
Types of Switching Techniques:
1. Circuit Switching:
Circuit switching is a switching method that creates a dedicated channel between the transmitter and the receiver.
Once the link is created via the Circuit Switching Technique, the dedicated path will exist until the connection is cancelled.
Circuit switching in a network works in the same manner that the telephone does.
Before communication takes place, a complete end-to-end route must exist.
When a user wishes to transfer data, audio, or video using the circuit switching approach, a request signal is sent to the receiver, and the receiver responds with an acknowledgment to guarantee the availability of the dedicated path for message transmission. After obtaining acknowledgment, the data is sent through a designated route.
In a public telephone network, circuit switching is used. It is used to transmit voice. In the circuit switching technology, fixed data may be transmitted at the same time.
a. Space Division Switching:
Space Division Switching is a circuit switching method that uses a physically distinct set of crosspoints to achieve a single transmission route in a switch. Switches in Space Division Switching are fast, robust, and nonblocking.
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
Two types of switches are used in Space Division Switching:
i. Crossbar Switch:
The Crossbar switch is a two-way switch with n input and n output lines. The crossbar switch has n2 crosspoints, which are intersection points.
ii. Multistage Switch:
The multistage switch is created by dividing the crossbar switch into smaller parts and then connecting them. It cuts down on the number of crosspoints. If one path fails, another path becomes available.
b. Time Division Switching:
Time Division Switching refers to the process of receiving and re-transmitting incoming and outgoing messages in a separate time slot. The digitized message/data is divided into time periods or slots.
Advantages of Circuit Switching:
- The communication channel is dedicated and exclusive in the case of the Circuit Switching method.
- It has a fixed bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Circuit Switching:
- The only delay in data transfer happens once the dedicated channel is created.
- It takes around 10 seconds to establish a connection, during which no data may be sent.
- This is more costly than other switching approaches since each connection requires a dedicated route.
- It is inefficient to utilize since the capacity of the path is squandered after the path is built and no data is transmitted.
- In this situation, the connection is devoted, thus even if the channel is free, no additional data may be sent.
2. Message Switching:
Message switching is a switching mechanism that transfers a message as a full and complete unit and routes it through intermediate nodes which store and forward the message. There is no specific path between the sender and recipient in the Message Switching method.
The message’s destination address is added. Message Switching enables and facilitates dynamic routing by routing the message through intermediary nodes based on the information and data included in the message.
Message switches are configured in such a way that they give the most efficient routes. Every node saves the full message before forwarding it to the next node. This is referred to as a store and forward network.
Message switching handles each message as though it were a separate entity.
Advantages of Message Switching:
- Data channels are shared across connecting devices, which improves the efficiency with which available bandwidth is used.
- Because the message is briefly held in the nodes, traffic congestion can be minimised.
- The network may be managed using message priority.
- The size of the message transmitted across the network can be altered. As a result, it can handle data of any scale.
Disadvantages of Message Switching:
- The message switches must have enough storage to hold the messages until they are forwarded.
- Long delays can arise as a result of the message switching technique’s storing and forwarding capabilities.
3. Packet Switching:
Packet switching is a switching technique in which the message is split into smaller bits and delivered separately rather than all at once.
The message is broken down into smaller bits known as packets, and each packet is assigned a unique number to indicate its sequence at the receiving end.
The headers of each packet contain information such as the source address, destination address, and sequence number. Packets will go across the network in the quickest possible way. At the receiving end, all packets are reassembled in the right order.
If any packet is missing or corrupted, the message will be resent. If the packets are received in the right order, the acknowledgment message is delivered.
There are two methods to achieve Packet Switching:
a. Datagram Packet Switching:
It is a packet switching approach that treats each packet, known as a datagram, as a distinct entity. Each packet contains information about the destination, which the switch utilises to route the packet to the right location. At the receiving end, the packets are reassembled in the right order.
The route is not set in the Datagram Packet Switching method. To forward packets, intermediate nodes have to make important routing decisions. It is also known as connection-less switching.
b. Virtual Circuit Packet Switching:
Another name for virtual circuit switching is connection-oriented switching. Before messages are transmitted, a preplanned path is established in the case of virtual circuit switching.
The call request and call accept packets are used to connect the sender and recipient. The route is fixed in this situation for the duration of a logical link.
Difference between Datagram and Virtual Circuit Packet Switching:
| Datagram Packet Switching | Virtual Circuit Packet Switching |
| To forward packets, the node makes routing decisions. | There is no routing decision made by the nodes. |
| Congestion cannot develop since all packets go in opposite directions. | Congestion occurs when a node is overburdened and does not allow other packets to flow through. |
| It is more adaptable since each packet is considered as an individual entity. | It is not particularly adaptable. |
Advantages of Packet Switching:
- Because packet switching devices do not require huge secondary storage to hold packets, costs are reduced to some extent. As a result, we can claim that the packet switching approach is cost-effective.
- If any of the nodes are busy, packets can be redirected. This guarantees that the Packet Switching method delivers consistent communication.
- Packet switching is a time-saving method. It does not require any established path prior to transmission, and several users can utilise the same communication channel at the same time, making effective use of available bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Packet Switching:
- Packet Switching cannot be used in applications that need low latency and high-quality services.
- The protocols used in packet-switching are quite complicated and have a significant implementation cost.
- If the network is overcrowded or damaged, lost packets must be retransmitted. It can also result in the loss of crucial data if mistakes are not recovered.
Summary
This article covers the concepts of the switching techniques that are used in computer networking. We looked at the different kinds of message switching techniques that are in use today, and also at the advantages and disadvantages of each. We also looked at the two subtypes of Packet Switching, namely Datagram and Virtual Circuit and also the differences between them.