FREE Online Courses: Dive into Knowledge for Free. Learn More!
Now after learning about data extraction, data designing, and modeling in SAP HANA, we will further move on to learn about reporting in SAP HANA.
It means how the data models and information views are used by the end-users and analysts to analyze data and create reports. We have provided a comprehensive tutorial on how reporting is done in SAP HANA.
Introduction to SAP HANA Reporting
SAP HANA is an efficient in-memory database technology which provides its users with platforms to model and design data as per their business requirements.
As an extension to the data extraction and modeling capabilities, SAP HANA reporting tools serve as an essential platform to present the information in proper ways.
The reports created by the reporting tools using processed data from SAP HANA are used by business analysts, business managers, sales managers, and senior managers.
The report enables the people in authority to draw meaningful insights and identify market trends to make strategies and bolster their business in the present as well as for the future.
SAP HANA enables different kinds of reporting tools such as SAP Lumira, Design Studio, Analysis Office, Crystal Reports, Dashboards, Explorer, Web intelligence and even third-party apps like MS Excel. Users can use both historical as well as real-time data to create reports.
Connecting to the Reporting Sources
SAP HANA users or the users at the reporting end of the setup can establish a connection to the other end in two ways:
- First is the direct way where reporting tools can connect directly to the SAP HANA database. This direct connection is an OLAP type connection. The tools which connect directly to the SAP HANA system are Design Studio, SAP Lumira, Business Explorer, Analysis of MS Office, Crystal Reports, etc.
- The second way is an indirect way of connection. It is a relational connection that establishes by creating a universe using the Information Design Tool (IDT). The tools using this method of connection to connect to the SAP HANA database are Web intelligence tools, SAP Dashboards, Crystal reports for the enterprise.
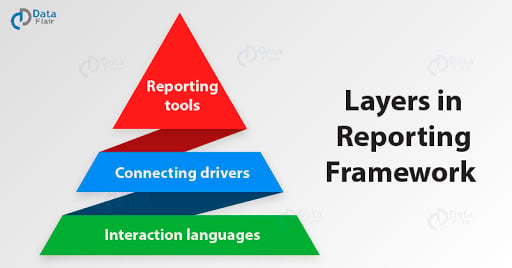
Layers in Reporting Framework
The reporting framework is easy to understand when we divide it into three primary layers;
- Interaction languages
- Connecting drivers
- Reporting tools
At the base of these three layers is the core SAP HANA system database. From there, users can fetch data to use it in the reporting tools. Let us learn about reporting architecture by understanding each layer in detail.
1. Interaction Languages
This layer consists of all the query languages which are used in querying database tables and objects from the reporting tools during report execution. The languages used for this purpose in SAP HANA reporting are MDX, SQL, and SQL ODBC.
- MDX: MDX language is used to access multi-dimensional data objects instead of relational objects from the SAP HANA database. MDX stands for MultiDimensional Expressions. This language is used to query data from MS Excel in SAP HANA reporting. It is the only language that enables hierarchy accessing from SAP HANA system.
- SQL: SQL is a standard database language for accessing data from all kinds of platforms. In SAP HANA reporting, all the reporting tools, which connect data through ODBC and JDBC connections use SQL as the query language.
- SQL ODBC: The SQL ODBC connection accesses data from the reporting tools that connect to the SAP HANA system using a BICS connection. BICS stands for Business Intelligence Consumer Services.
2. Connecting Drivers
The connecting drivers act as a mediator between the SAP HANA database layer and the reporting tools. The drivers transport the language queries from the reporting tool to the database and take back the data.
Every reporting tool connects to the database through a specific connecting driver. SAP HANA uses four main types of drivers as discussed below:
- ODBO (OLE DB for OLAP): The ODBO driver is a driver by Microsoft for connecting MS Excel to the SAP HANA database. This driver is specifically for multi-dimensional reporting (multi-dimensional data stores), and it communicates through MDX language.
- ODBC: The ODBC driver establishes relational database connections between reporting tools and SAP HANA database. Reporting tools like CR Report and Universe layer (IDE) use ODBC driver that communicates via SQL. ODBC stands for Open DataBase Connectivity.
- JDBC: JDBC stands for Java DataBase Connectivity. JDBC driver is a Java-based connection service. We also use it for relational reporting by tools like Explorer, UNIX using IDT, CR Report. JDBC drivers communicate with the database through SQL queries.
- BICS: The BICS driver is SAP propriety connecting driver, which is used by those reporting tools that use SQLDB language as the interaction language with SAP database.
3. Reporting Tools
The topmost layer is the layer of reporting tools. It is the SAP Business Objects BI (4.0/4.2/4.3) reporting platform which serves several reporting applications. The business users analyze data and create reports to generate meaningful insights using these applications.
The SAP BO platform consists of reporting applications such as SAP Lumira, Web Intelligence, SAP BO Explorer, SAP BO Dashboards, Crystal Reports, and SAP BO Universe.
Summary
This tutorial focuses on the basics of reporting and the reporting architecture in SAP HANA. In the upcoming tutorial, we will talk about the different reporting tools which are a part of the SAP Business Object BI client tools.
So, are you clear with the concept of SAP HANA Reporting? If you have any queries, feel free to enter in the comment section.