FREE Online Courses: Knowledge Awaits – Click for Free Access!
We can define a file as a named collection of related information recorded on secondary storage. Some secondary storage devices are magnetic disks, magnetic tapes and optical disks. A file is a combination of bits, bytes, lines or records that are defined by the files creator and user.
| Attributes | Types | Operations |
| Name | Doc | Create |
| Type | Exe | Open |
| Size | Jpg | Read |
| Creation Data | Xis | Write |
| Author | C | Append |
| Last Modified | Java | Truncate |
| Protection | class | Delete |
| File Type | Usual Extension | Function |
| Executable | exe, com, bin | Read to run machine language program |
| Object | obj, o | Compiled, machine language not linked |
| Source Code | C, java, pas, asm, a | Source code in various languages |
| Batch | bat,sh | Commands to the command interpreter |
| Text | txt, doc | Textual data and documents |
| Word Processor | wp, tex, rrf, doc | Various word processor formats |
| Archive | arc, zip, tar | Related files grouped into one compressed file |
| Multimedia | mpeg, mov, rm | For containing audio/video information |
File directories in Operating System
A file directory is a collection of files. It contains information regarding the files like their name, type, address, current and maximum length, last accessed, last updated, owner id, protection information, location, ownership, etc.
The information regarding storage is managed by the OS. A file directory is a file in itself that is accessible through various file management routines. Some operations that we can perform on a directory are: Searching for a file, Creating a file, Deleting a file, Listing a directory, Renaming a file, and Traversing the file system.
Advantages:
- Locating a file becomes quicker.
- Different files can have the same name or the same file can have different names.
- Logical grouping of files is possible.
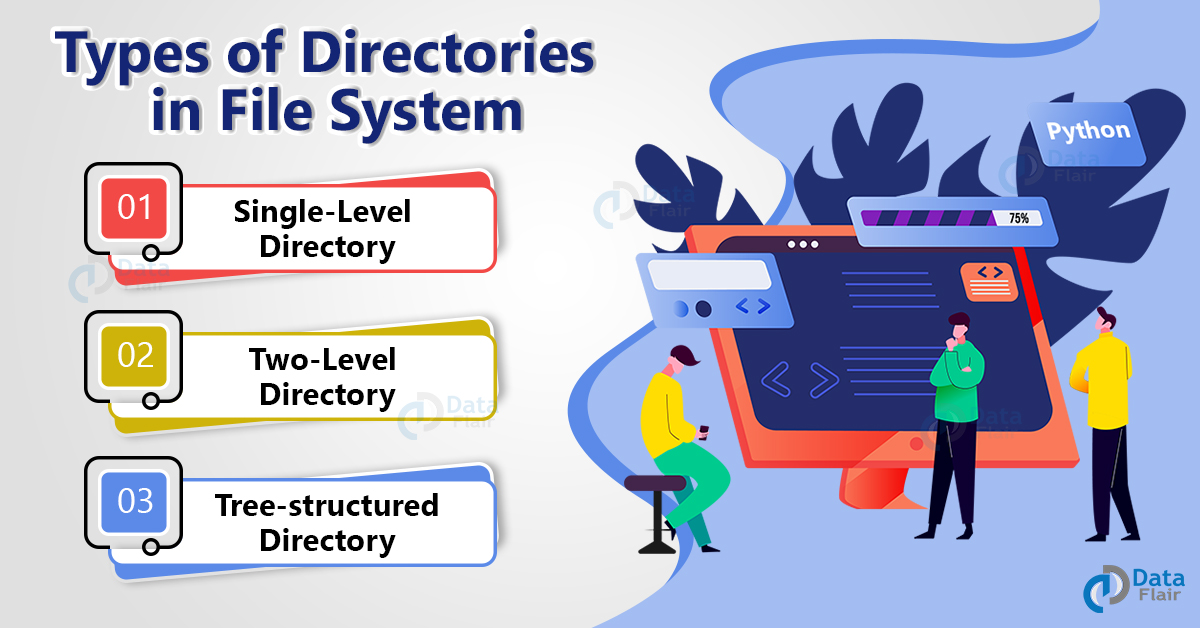
Types of directories in OS
There are three types of directories:
1. Single-level directory: In case of a single-level directory the system maintains one directory for all the users. Two files cannot have the same name in this directory and the users cannot group files according to their needs.
2. Two-level directory: In case of a two-level directory the system maintains a separate directory for each user. There is a pathname for every file in the directory so that the user can locate that file. Different users can have files of the same name and searching becomes efficient.
3. Tree-structured directory: The tree-structured directory is in the form of a tree. It makes searching and grouping efficient. There is an absolute or relative pathname for a file.
File Structure in OS
A File Structure has a proper format that the OS can understand.
- A file should have a defined structure. This structure should be in accordance with its type.
- We can define a text file as a sequence of characters organized into lines.
- We can define a source file as a sequence of functions and procedures.
- Also, we can define an object file as a sequence of bytes organized into blocks. These blocks of bytes are also understandable by the machine.
- When an OS defines file structures, it also has the codes to support these file structures.
File Type in OS
File type is the ability of an OS that helps it to distinguish between different types of files. Some of the commonly found file types are:
1. Ordinary files: Ordinary files contain user information in the form of texts, databases or executable programs. Multiple operations can also be applied by the user on these files like add, modify, or delete.
2. Directory files: Directory files contain file names and information related to these files.
3. Special files: Special files or device files represent physical devices like disks, terminals, networks, etc. These files are further divided into two types:
a. Character special files: This file handles data character by character. We can see this in the case of terminals.
b. Block special files: This file handles data in blocks. We can see this in the case of disks.
File Access Mechanisms in OS
File access mechanism is the way to access the records of a file. These ways to access files are:
1. Sequential access: This is the most primitive form of access where one can access records in a sequence. The processing of information within files takes place in an order, one record after the other.
2. Direct/Random access: This access allows access to records directly. We can directly access these records as every record has a unique address. It is not necessary for the records to be in sequence within the file. Also, they can be in any location on the storage medium.
3. Indexed sequential access: Based on sequential access, this access mechanism creates an index for each file. This index contains pointers to various blocks. We can search this index sequentially where its pointer gives us access to the file.
OS Space Allocation
The OS allocates disk spaces to files. There are three ways to allocate disk space to files.
1. Contiguous Allocation:
- There is a contiguous address space for every file on the disk.
- This assigned address is in linear order.
- It is easy to implement.
- External fragmentation is a major issue.
2. inked Allocation:
- Each file has a list of links to disk blocks.
- The directory contains a link/pointer that points to the first block of a file.
- There is no external fragmentation
- This allocation is effective for sequential access mechanism.
- Direct access mechanism can’t use this allocation.
3. Indexed Allocation
- This solves the problems of the above allocations.
- There is an index block which contains pointers to all the files.
- Each file’s index block stores the file’s disk space addresses.
- The directory stores the addresses of index blocks.
Summary
Collection of related information is known as a file. It is a combination of bits, bytes, lines or records. A file directory is a collection of files. It also contains the file’s attributes. There are three types of directories, namely, single-level, two-level, and tree-structured. There are three file types: ordinary, special, and directory.